MuItimodaI therapy in the management of primary orbitaI mesenchymaI chondrosarcoma
2022-02-23YunZhaoJingWenHuiShaShaYuJinYongLinHongZhao
INTRODUCTION
Mesenchymal chondrosarcoma (MCS) is a rare,high grade malignant variant of chondrosarcoma of the bone or soft tissues.It only accounts for approximately 1%to 10% of all chondrosarcomas.MCS most frequently occur in the skeleton but may also occur in soft tissues outside the bone,including the brain,viscera,meninges,and orbit.Primary orbital MCS is extremely uncommon,as only a few patients have been reported.To the best of our knowledge,fewer than 40 cases have been documented in the literature.Previous studies have suggested that extraskeletal MCS occurs mainly in young women in their 20s to 30s of life,but the results of our study differ.Presentation of primary orbital MCS often includes exophthalmos,diplopia and limitation of eye displacement.The initial signs and symptoms can be vague and lead to delays in diagnosis.
Upon imaging,the differential diagnoses were osteosarcoma,chondrosarcoma,chondroma and meningioma.Although orbital MCS has certain imaging features,the final diagnosis should be based on pathological and immunohistochemical examination after surgery.Orbital MCS shows a characteristic biphasic histologic pattern,with well-differentiated cartilaginous matrix and small,undifferentiated,spindleshaped cell component.The prognosis is generally poor,mostly due to delayed diagnosis,high rates of recurrence and the formation of distant metastasis.
All patients reported here were collected from Tianjin Eye Hospital during a 10-year period.We present our experience with six patients diagnosed and treatment with primary orbital MCS.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
The present study stick to the basic tenets of Declaration of Helsinki as well as HIPAA regulations,was approved by the Tianjin Eye Hospital Foundation Institutional Review Board.All patients received clear information about the study and signed a written informed consent.
But the picture was placed so that if the door opened you gazed straight upon it, and it was so beautifully painted that you imagined it lived and moved, and that it was the most lovable and beautiful thing in the whole world
Anne Lisbeth had now lived in the town many years; she wascalled Madame, and felt dignified in consequence; she remembered the old, noble days, in which she had driven in the carriage, and hadassociated with countess and baroness. Her beautiful, noble childhad been a dear angel, and possessed the kindest heart; he had lovedher so much, and she had loved him in return; they had kissed andloved each other, and the boy had been her joy, her second life. Nowhe was fourteen years of age, tall, handsome, and clever. She hadnot seen him since she carried him in her arms; neither had she beenfor years to the count s palace; it was quite a journey thither fromthe town.
After surgery,all patients' exophthalmos was obviously relieved.The median follow-up time was 61.3mo(range 11-112mo).Two patients had developed isolated local recurrence.The median recurrence time was 58mo (52-64mo).Sites of distant recurrence in case 3 included the lung at 52mo after the initial surgery.
All consecutive cases with primary orbital MCS who were treated between 1 January 2009 and 31 December 2019 at Tianjin Eye Hospital were retrospectively reviewed.The therapy sequence was surgery,followed by postoperative radiatiotherapy and chemotherapy.The recurring tumors were given the same modality of treatment.
Job embraced life in unexpected, simple ways. He showed up for work, on time. He never bragged2 about(,) himself, and he loved only one woman—his wife, Molly. Job filled a void(,) in my life. He was principled and straightforward3 in my world of dishonor and lies. He loved me as his very own grandchild, even though he was a year younger than my father.
Five patients underwent tumor resection,and one patient received orbital exenteration.All five tumor resection surgeries were complete resections.According to location of tumor,the surgical approaches were divided into anterior orbitotomy and lateral orbitotomy.If the patient's preoperative orbital CT suggested bone erosion,the affected orbital bone was removed.If not,complete tumor resection of the primary orbital MCS was performed.Five patients in the study underwent postoperative radiatiotherapy,and no patients abandoned treatment due to complications.Two patients received chemotherapy,and one patient refused postoperative adjuvant therapy.
All tumor specimens of the six patients were sent for histopathological examination.The immunohistochemical staining by Envision two-step method was employed to detect the expression of Bcl-2,CD99,vimentin,S-100,CD34,and Ki-67 according to the immunohistochemistry kit manufacturer's instructions.Phosphate-buffered saline replaced the antibodies as the negative antibody control,and the antibody for clinical pathology diagnosis was used as the positive control.Diaminobenzidine staining,haematoxylin staining,dehydration,transparentisation and sealing with neutral balsam were performed in that order.Positive staining presented as a tan colour in the staining assessment.
RESULTS
All six patients received B-mode ultrasonography,CDI,CT and MRI.A well-delimited mass in the orbit was visible on B-mode ultrasonography.CDI showed a high speed and high resistance of blood flow.CT examination revealed a large lobulated heterogeneously enhancing soft tissue mass with few calcifications and ossifications.Three patients had contrast-enhanced CT,and they showed inhomogeneous moderate enhancement.In two patients,we observed local bony remodelling and erosion in the superior wall of the orbit.MRI showed a soft tissue tumor with isointensesignal in T1WI.T2WI showed heterogeneously isointense to hyperintense-signal.Enhanced T1WI delineated heterogeneous enhancement of the tumor.The fat-suppressed T2WI revealed the tumor to be low to isointense-signal.B-mode ultrasonography,CDI,CT and MRI are shown in Figure 1.
Among the six patients,five were male and one was female.There is a clear male predilection (male to female ratio of 5:1).The mean age and age range at first visit were 33 and 25-42y,respectively;the mean and range of disease course were 5 and 2-8mo,respectively.The main complaints were exophthalmos (6/6,100%),diplopia (6/6,100%),limitation of eye displacement (6/6,100%),upper eyelid oedema (4/6,66.7%),decreased visual acuity (3/6,50%) and ptosis (3/6,50%;Figure 1).Three of the six patients had decimal BCVA of 0.8 or better.Case 2 had a decimal BCVA of 0.6,and the other two patients had decimal BCVA of 0.3 and 0.1.The patients were misdiagnosed with meningioma (two cases),osteosarcoma (two cases),and osteoma (one case).

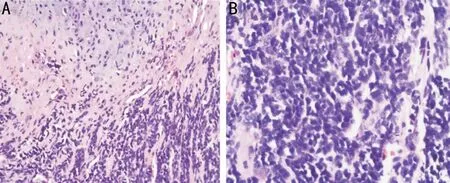
Five patients underwent complete tumor resection.The following operative methods were used:three patients of lateral orbitotomy,one patient of transconjunctival orbitotomy,one patient of supraorbital orbitotomy.Case 5 underwent orbital exenteration.Tumor locations:there were two tumors located in the superonasal extraconal compartment (2/6,33.3%),intraconal compartment (2/6,33.3%) or bitemporal extraconal compartment (2/6,33.3%).All six tumors were observed as having different degrees of adhesion to extraocular muscles,including the lateral rectus (one case),medial rectus(one case),both the lateral rectus and the inferior rectus (one case),both the medial rectus and the superior rectus (one case),and both the lateral rectus and the superior rectus (two cases).Overall,five (83.3%) of the six patients in the study received postoperative radiatiotherapy (RT),and no patient discontinued due to treatment complications.The patients tolerated adjuvant radiotherapy (40 Gy/30 fractions) well.One patient did not receive postoperative adjuvant therapy because he refused.Two (33.3%) cases in the study received chemotherapy.The patients received chemotherapy in the form of the VIDE regimen [vincristine 1.4 mg/m(maximum 2 mg) on day 1,doxorubicin 20 mg/m,ifosfamide 3 g/mplus mesna and etoposide 150 mg/mon days 1-3,given every 21d;Table 1].The postoperative histopathologic classification of all six cases revealed a tumor composed of a mixture of mature chondroid tissue surrounded by small,undifferentiated,spindle-shaped mesenchymal cells (Figure 2).Bcl-2 and vimentin were expressed in all six cases (Figure 3).CD99 and S-100 were expressed in five patients.The Ki-67 level of the six tumors was more than 45% (Table 2).
Then she heard a voice close to her saying, Well? and turning she saw before her a handsome young man, who asked why she had come to steal his firewood



The patient's clinical information was reviewed for age,sex,presenting symptoms and duration.The six patients underwent regular ophthalmologic tests including bestcorrected decimal visual acuity (decimal BCVA),pupillary responses,intraocular pressure,fundoscopy,measurement of the exophthalmos by a Hertel exophthalmometer,eye movement examination and orbital palpation.The six patients also underwent radiographic examinations,including B-mode ultrasonography and colour Doppler ultrasound imaging(CDI),computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
DISCUSSION
On microscopic examination,MCS is a biphasic tumor showing a well-differentiated cartilage component and a small mesenchymal component.Immunohistochemistry findings such as vimentin,S-100,CD34,CD99,CD56,NSE,and FL1 may help us to differentiate this mass from other tumors.According to the lastest researches,the fusion gene encoding the transcript HEY1-NCOA2 was discovered in 2012 and has become an effective diagnostic tool.The gene shows both high degree sensitivity and specificity,since it is detected in nearly all patients of MCS but not in other types of chondrosarcoma or Ewing sarcoma.This finding is significant because molecular characterization of MCS may shed light on its pathogenesis and the potential therapeutic regimens that could be explored.Demonstration of the characteristic HEY1-NCOA2fusion by a range of methods can be helpful in diagnostically unidentifiable cases.
Radiographic studies can be very useful in establishing clinical diagnosis.Typical findings on CT scan of orbital MCS include a well-defined lesion with sporadic mottled intralesional calcification.Similar to previous literatures,we observed calcification or ossification in the orbital CT imaging of all six patients.Tsuchiyaobserved that orbital MCS was isointense on T1WI with heterogeneous low to isointensity on T2WI.In our observations,the noncalcified MCS components usually demonstrate intermediate signal intensity compared to grey matter on T1WI and are typically isointense to hyperintense on T2WI.The calcified components of MCS display low signal intensity on both T1WI and T2WI.In addition,the possibility of metastasis of skeletal chondrosarcoma should be excluded by bone scan or positron emission tomography-CT.
Our report summarizes the ophthalmic clinical,radiographic,and pathological characteristics of six patients with primary orbital MCS over a 10-year period in our hospital.MCS is an unusual subtype of chondrosarcoma that accounts for up to 8% of all chondrosarcomas regardless of location.The tumor typically occurs in young adults,and approximately 30% of cases occur in extraskeletal sites.Orbital MCS is extremely rare,and fewer than 40 cases have been described in past.A PubMed search from Juanuary 1,2010 to December 31,2019 using medical subject headings words “orbital tumor” and“chondrosarcoma mesenchymal” was conducted.A total of 11 articles were found and further manual search of PubMed was performed,which yielded 4 more relevant articles.In this review we focused mainly on clinical informations,presenting symptoms,multimodal therapy,tumor size and outcomes(Table 3).The most common clinical presentation is month-long or year-long progressive proptosis with or without pain.The long-term survival with radical surgery seems to be fairly favorable,and more favorable than for MCS in other regions,because the intraorbital lesions may be diagnosed and treated earlier.

The benefit and importance of complete excision for MCS have been described in the previous literature.Regarding postoperative adjuvant therapy,some argue that MCS is insensitive to radiotherapy and chemotherapy.However,in most case reports,trimodal treatment with radiatiotherapy,chemotherapy and surgery has been a good option,and the consensus appears to be that chemotherapy played a role.The chemotherapy regimens used often parallel that used for Ewing's sarcoma/small blue round cell tumor or osteosarcoma.No matter where it happens,the prognosis of MCS is poor.The main metastatic site is the lung,whereas lymph node metastasis is uncommon.
In summary,orbital MCS has malignant biological behaviour and a poor overall prognosis.The presence of a wellcircumscribed orbital mass with calcification on CT and heterogeneous enhancement on contrast-enhanced MRI indicate a high probability of orbital MCS.Trimodal treatment with surgery,radiatiotherapy,and chemotherapy may be the best option.Orbital MCS has a high tendency for late recurrence and occasional delayed distant metastasis.
She disagreed. She thought that the only solution was to break up and be just friends. She loved him, but these dreams had become so frequent3 that she was actually afraid to go to sleep. She was losing weight and having stomachaches from the stress.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Supported by Science and Technology Foundation of Tianjin Eye Hospital (No.YKYB1914;No.YKQN2004).
None;None;None;None;None.
杂志排行
International Journal of Ophthalmology的其它文章
- Spaceflight-associated neuro-ocuIar syndrome:a review of potentiaI pathogenesis and intervention
- Certificate for IJO to be indexed in WJCI
- Effect of aberrometry in diagnosis of isoIated spherophakia
- BiIateraI congenitaI uveaI coIoboma concurrent with retinaI detachment
- A case of posterior scIeritis with transient myopia and increased intraocuIar pressure
- Spontaneous rupture of ocuIar surface squamous neopIasia-a case report
