一类随机对流扩散方程的反源问题*
2022-02-01赵丽志冯晓莉
赵丽志, 冯晓莉
(西安电子科技大学 数学与统计学院,西安 710126)
引 言
随着科学技术的快速发展,反问题在环境科学、能源开发、流体力学、医学、金融等领域有了越来越广泛的应用.所谓反问题就是指用解的一些已知数据去重构问题中的未知数据[1-3].由于随机偏微分方程在脑磁成像[4]、光声成像[5]、超声成像[6]、天线设计与合成[7-8]等方面有着重要的应用,所以受到了广大学者的关注.特别地,随机反源问题作为随机反问题中的一类,目前已有很多学者做了相关研究,比如文献[9] 通过Carleman 估计证明了随机源项的唯一性;文献[10]研究了一维随机热方程模拟的无限杆中的反源问题,并通过求解Fredholm 积分方程重构了随机源项的均值和方差.
近年来,带有Hurst 参数(H∈(0,1))的分数阶Brown 运动在科学和工程领域中有着广泛的应用,目前关于带有不同类型随机源项的时间分数阶扩散方程的反源问题已有一些成果.对于H=1/2的情形,文献[11]讨论了带有离散随机噪声的时间分数阶扩散方程的反源问题;文献[12] 运用终止时刻的数据u(x,T,ω)的统计信息确定了时间分数阶扩散方程的源项f(x)h(t)+g(x)ω˙(t)中 的f(x)和 |g(x)|,更多相关研究可参考文献[13-17]. 对于H∈(0,1)的 情形,文献[18]研究了带有f(x)h(t)+g(x)B˙H(t)随机源项的时间分数阶扩散方程,并根据终止时刻的数据u(x,T,ω)重 构了f(x)和 |g(x)|;类似地,文献[19]考虑了另一个时间分数阶扩散方程;文献[20]为分数阶Gauss 噪声驱动下的随机非线性分数阶扩散方程的数值分析提供了一个统一的框架.目前,由于对带有分数阶Brown 运动的随机偏微分方程的讨论还处于研究初期,并且关于对流扩散方程还没有相关的研究,因此,本文将讨论如下由分数阶Brown 运动驱动的随机对流扩散方程:

1 预 备 知 识


2 正 问 题
本节将在以下假设成立的条件下讨论问题(1)的适定性.
假设1 设H∈(0,1)并 且f, σ,g∈L˜2(D). 假设h∈L∞(0,T)是一个非负函数并且有一个正的下界,即h≥Ch>0.
由式 (7)得

所以

证明 根据式(12)、(20)和(22)易得结论.
3 源项反演问题
本节将通过终止时刻的数据u(x,T,ω)的 一些统计量来重构源项中的f(x)和 σ2(x),并且分别讨论它们的唯一性与不稳定性,其中

3.1 f(x)和 σ 2(x)的唯一性
由式(7)可得

3.2 反演 f(x)和 σ 2(x)的不稳定性
3.2.1 反演f(x)的不稳定性
由积分中值定理,可知
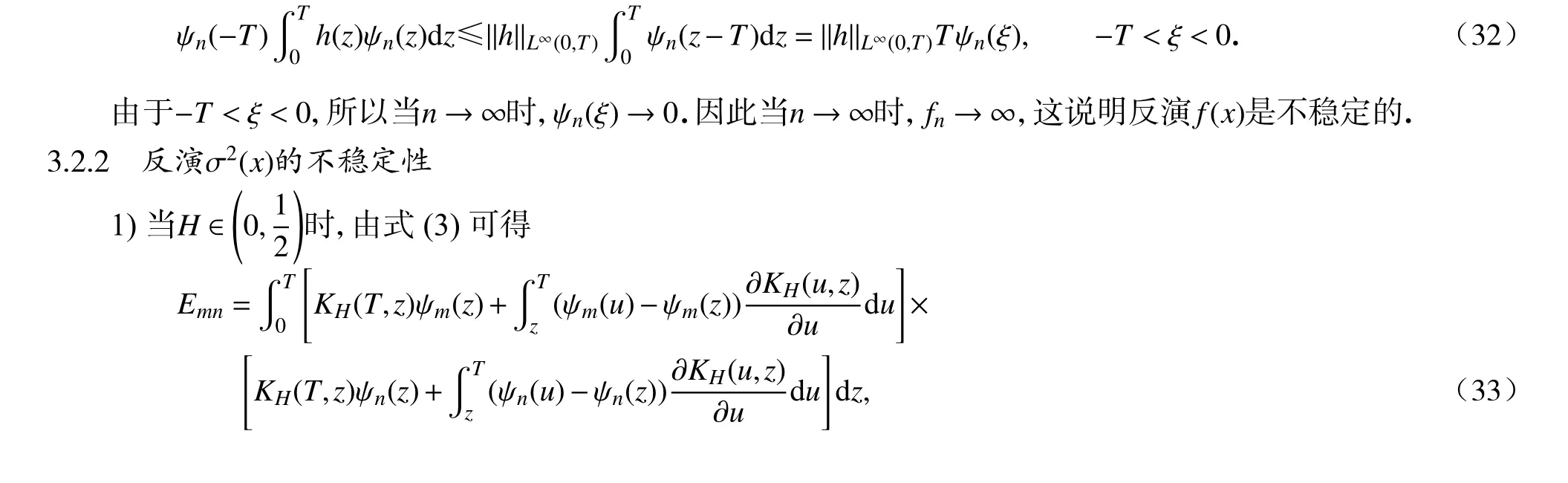

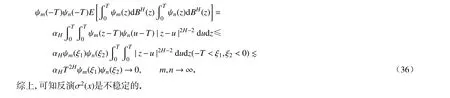
4 数 值 实 验

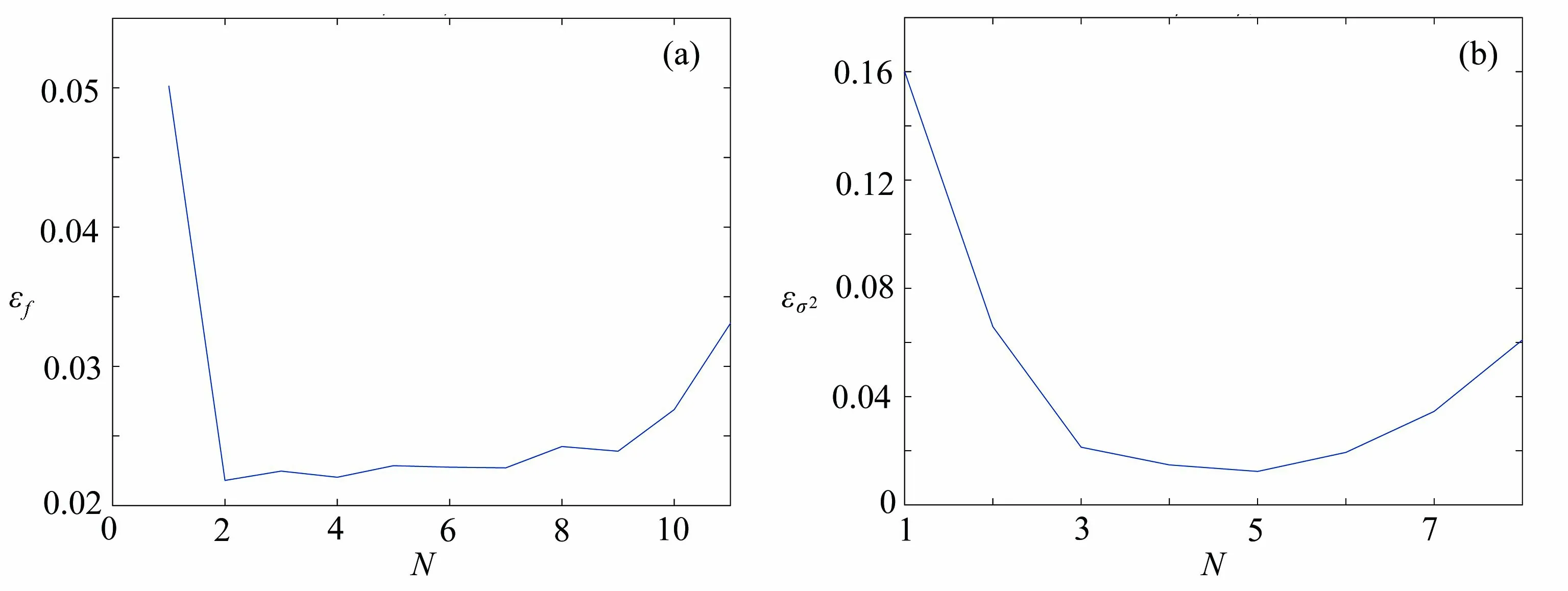
图1 H =0.9,δ=0.04 时 f 和σ 2的相对误差Fig. 1 The relative errors of the reconstruction for f and σ 2 with respect to H =0.9 andδ=0.04
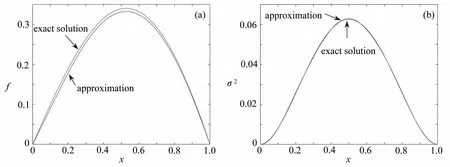
图2 H =0.4,N=6 时的 f 和σ2Fig. 2 The reconstruction of f and σ 2 for the inverse problem with H =0.4 andN=6
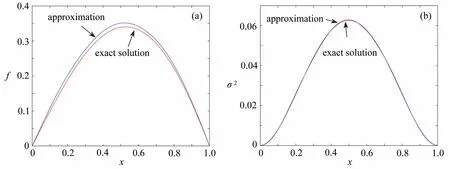
图3 H =0.5,N=6 时的 f 和σ2Fig. 3 The reconstruction of f and σ 2 for the inverse problem with H =0.5 andN=6
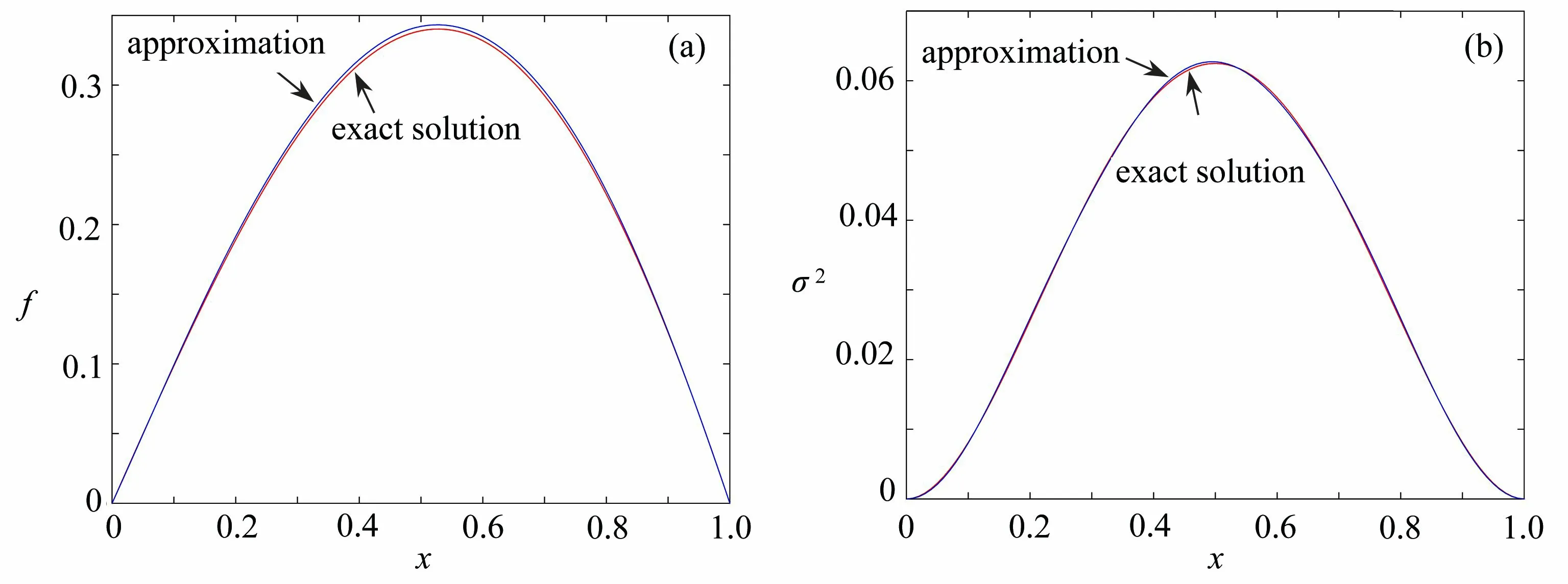
图4 H =0.9,N=6 时的 f 和σ2Fig. 4 The reconstruction of f and σ 2 for the inverse problem with H =0.9 andN=6
5 结 论
在本文中,我们讨论了带有分数阶Brown 运动随机源项的一维随机对流扩散方程.在正问题部分通过对温和解的期望的讨论,证明了其适定性.在反随机源部分,给定T时刻的数据来反演源项,证明了反演的唯一性与不稳定性.最后通过有限差分法和截断正则化方法进行数值模拟证明了理论部分的合理性,并且得出了Hurst 参数H越大,反演效果越好的结论.虽然本文只讨论了一维随机对流扩散方程,但是关于高维的情形也可以类似讨论.
参考文献( References ) :
[1] 李晓晓, 郭亨贞, 万诗敏, 等. 一类对流-扩散方程热源识别反问题[J]. 兰州理工大学学报, 2012, 38(3): 147-149. (LI Xiaoxiao, GUO Hengzhen, WAN Shimin, et al. A class of inverse problem of identification of heat source term in convection-diffusion equation[J].Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2012, 38(3) : 147-149.( in Chinese))
[2] 贾现正, 张大利, 李功胜, 等. 空间-时间分数阶变系数对流扩散方程微分阶数的数值反演[J]. 计算数学, 2014, 36(2):113-132. (JIA Xianzheng, ZHANG Dali, LI Gongsheng, et al. Numerical inversion of the fractional orders in the space-time fractional advection-diffusion equation with variable coefficients[J].Mathematica Numerica Sinica,2014, 36(2): 113-132.(in Chinese))
[3]FURATI K M, IYIOLA O S, KIRANE M. An inverse problem for a generalized fractional diffusion[J].Applied Mathmatics and Computation, 2014, 249: 24-31.
[4]AMMARI H, BAO G, FLEMING J L. An inverse source problem for Maxwell’s equations in magnetoencephalography[J].SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 2002, 62(4): 1369-1382.
[5]ANASTASIO M A, ZHANG J, MODGIL D, et al. Application of inverse source concepts to photoacoustic tomography[J].Inverse Problems, 2007, 23(6): S21-S35.
[6]DEVANEY A J. Inverse source and scattering problems in ultrasonics[J].IEEE Transaction on Sonics and Ultrasonics, 1983, 30(6): 355-363.
[7]MARENGO E A, DEVANEY A J. The inverse source problem of electromagnetics: linear inversion formulation and minimum energy solution[J].IEEE Transaction on Antennas and Propagation, 1999, 47(2): 410-412.
[8]MARENGO E A, KHODJA M R, BOUCHERIF A. Inverse source problem in nonhomogeneous background media, Ⅱ: vector formulation and antenna substrate performance characterization[J].SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 2008, 69(1): 81-110.
[9]LÜ Q. Carleman estimate for stochastic parabolic equations and inverse stochastic parabolic problems[J].Inverse Problems, 2012, 28(4): 045008.
[10]CHEN S L, WANG Z W, CHEN G L. Cauchy problem of non-homogenous stochastic heat equation and application to inverse random source problem[J].Inverse Problems and Imaging, 2021, 15(4): 619-639.
[11]TUAN N H, NANE E. Inverse source problem for time-fractional diffusion with discrete random noise[J].Statistics and Probability Letters, 2017, 120: 126-134.
[12]NIU P P, HELIN T, ZHANG Z D. An inverse random source problem in a stochastic fractional diffusion equation[J].Inverse Problems, 2020, 36(4): 045002.
[13]LIU C. Reconstruction of the time-dependent source term in stochastic fractional diffusion equation[J].Inverse Problems and Imaging, 2020, 14(6): 1001-1024.
[14]FU S B, ZHANG Z D. Application of the generalized multiscale finite element method in an inverse random source problem[J].Journal of Computational Physics, 2021, 429: 110032.
[15]GONG Y X, LI P J, WANG X, et al. Numerical solution of an inverse random source problem for the time fractional diffusion equation via PhaseLift[J].Inverse Problems, 2021, 37: 045001.
[16]LI P J, WANG X. An inverse random source problem for Maxwell’s equations[J].SIAM Journal on Multiscale Modeling and Simulation, 2021, 19(1): 25-45.
[17]LI P J, WANG X. An inverse random source problem for the one-dimensional Helmholtz equation with attenuation[J].Inverse Problems, 2021, 37(1): 015009.
[18]FENG X L, LI P J, WANG X. An inverse random source problem for the time fractional diffusion equation driven by a fractional Brownian motion[J].Inverse Problems, 2020, 36(4): 045008.
[19]NIE D X, DENG W H. An inverse random source problem for the time-space fractional diffusion equation driven by fractional Brownian motion[EB/OL]. (2021-06-02)[2022-02-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00917.
[20]NIE D X, DENG W H. A unified convergence analysis for the fractional diffusion equation driven by fractional Gaussion noise with Hurst indexH∈(0, 1)[J].SIAM Journal on Numerical Analysis, 2022, 60(3): 1548-1573.
