Qualitative analysis of chemical components in Lianhua Qingwen capsule by HPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS coupled with GC-MS
2022-01-19ShuiFuRongrongChengZixinDengTingngLiu
Shui Fu,Rongrong Cheng,Zixin Deng,b,Tingng Liu,*
a Key Laboratory of Combinatorial Biosynthesis and Drug Discovery,Ministry of Education and School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Wuhan University,Wuhan,430071,China
b State Key Laboratory of Microbial Metabolism,Joint International Research Laboratory of Metabolic and Developmental Sciences,School of Life Sciences and Biotechnology,Shanghai Jiao Tong University,Shanghai,200030,China
Keywords:
Lianhua Qingwen capsule
HPLC-Q exactive-orbitrap-MS
GC-MS
Chemical components
Peer review under responsibility of Xi’an Jiaotong University.
A B S T R A C T
The Lianhua Qingwen(LHQW)capsule is a popular traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of viral respiratory diseases.In particular,it has been recently prescribed to treat infections caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2(SARS-CoV-2).However,due to its complex composition,little attention has been directed toward the analysis of chemical constituents present in the LHQW capsule.This study presents a reliable and comprehensive approach to characterizing the chemical constituents present in LHQW by high-performance liquid chromatography-Q Exactive-Orbitrap mass spectrometry(HPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS)coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC-MS).An automated library alignment method with a high mass accuracy(within 5 ppm)was used for the rapid identification of compounds.A total of 104 compounds,consisting of alkaloids,flavonoids,phenols,phenolic acids,phenylpropanoids,quinones,terpenoids,and other phytochemicals,were successfully characterized.In addition,the fragmentation pathways and characteristic fragments of some representative compounds were elucidated.GC-MS analysis was conducted to characterize the volatile compounds present in LHQW.In total,17 compounds were putatively characterized by comparing the acquired data with that from the NIST library.The major constituent was menthol,and all the other compounds were terpenoids.This is the first comprehensive report on the identification of the major chemical constituents present in the LHQW capsule by HPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS,coupled with GCMS,and the results of this study can be used for the quality control and standardization of LHQW capsules.
1.Introduction
Lianhua Qingwen capsule(LHQW),produced by Yiling Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.(Shijiazhuang,China),is a patented traditional Chinese medicine(TCM).It was developed to treat patients infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1(SARS-CoV-1)in China.LHQW is based on two TCM formulas,i.e.,Maxing-Shigan-Tang and Yinqiao-San,which were originally mentioned in the classical Chinese books ShangHanLun and WenBingTiaoBian,respectively[1].Both Maxing-Shigan-Tang and Yinqiao-San are prescribed to treat fever,inflammation,and seasonal influenza[2,3].LHQW is composed of 11 herbs[4]:Forsythiae Fructus,Lonicerae Japonicae Flos,Ephedrae Herba,Armeniacae Semen Amarum,Isatidis Radix,Dryopteridis Crassirhizomatis Rhizoma,Houttuyniae Herba,Pogostemonis Herba,Rhei Radix Et Rhizoma,Rhodiolae Crenulatae Radix Et Rhizoma and Glycyrrhizae Radix Et Rhizoma.In addition,it contains Gypsum Fibrosum,a mineral and menthol,extracted from Menthae Haplocalycis Herba.
In China,LHQW has been widely used to treat the symptoms of respiratory diseases.Various reports have established the good anti-influenza activity of LHQW against H7N9[1]and H1N1[5]viruses.In particular,a randomized,double-blind,and positive clinical trial indicated that effectiveness of LHQW against the H1N1 virus is similar to that of Oseltamivir[5].Another recent study has reported that LHQW is also effective against the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2(SARS-CoV-2)[6],the pathogen that causes the coronavirus disease(COVID-19).Thus,LHQW has been included as a representative TCM prescription in the Guideline for the Diagnosis and Treatment of COVID-19 Pneumonia issued by the National Heath Commission of the People's Republic of China[7].However,the use of LHQW is limited to China.For LHQW to be globally accepted,its chemical composition and mechanism of action must be well understood.Thus,it is essential to determine the chemical composition of LHQW,which can further enable its quality control and standardization.
Several analytical methods have been developed for the quality control of LHQW.For example,Zhang et al.[8]and Chen et al.[9]developed ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC)fingerprinting methods for the quality control of LHQW.Qiao et al.[10]and Jia et al.[11]developed methods based on gas chromatography with flame-ionization detection and headspace solidphase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to analyze the volatile constituents and raw materials of an LHQW capsule,respectively.Jia et al.[12]developed a method based on a combination of UPLC with a diode-array detector and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry to determine the major chemical constituents of an LHQW capsule.Nevertheless,a detailed analysis of the chemical composition of an LHQW capsule has not yet been reported.
Orbitrap mass spectrometry(MS)has become a powerful tool to characterize the chemical components in TCMs because of its high sensitivity,high mass resolution,and high mass accuracy[13,14].This method also helps analyze MSnfragments,thus facilitating the structural elucidation of a compound.Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry(GC-MS)has been widely applied for the detection of volatile components in a TCM[15].In this paper,we present the unprecedented comprehensive analysis of the major chemical components in an LHQW capsule by high-performance liquid chromatography(HPLC)-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS coupled with GCMS.In total,104 compounds including 6 alkaloids,33 flavonoids,7 phenols,9 phenolic acids,16 phenylpropanoids,7 quinones,12 terpenoids and 14 other phytochemicals,were putatively identified via HPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS.In addition,17 volatile compounds were putatively identified via GC-MS.Thus,a total of 120 compounds were successfully extracted and characterized.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Chemicals and materials
LHQW capsules(Lot No.B2001158)were obtained from Yiling Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.(Shijiazhuang,China).Acetonitrile(ACN,HPLC grade)and methanol(HPLC grade)were obtained from Merck KGaA(Darmstadt,Germany).Watsons-distilled water was purchased from Jingdong Mall(Beijing,China).Formic acid(FA),acetone(HPLC grade),and hexane(HPLC grade)were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific(Waltham,MA,USA).Ethyl acetate was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich(St.Louis,MO,USA).
2.2.Sample preparation
For the HPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS analysis,the raw material(brown powder;0.4 g)of the LHQW capsule was accurately weighed,dissolved in 60% methanol(V/V;20 mL),and sonicated for 30 min.The solution was centrifuged at 12,000 r/min and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.22μm membrane.
For GC-MS analysis,three different extraction solvents were used:hexane,acetone,and ethylacetate.The raw material(1 g)was accurately weighed,dissolved in the extracted solvent(10 mL),and sonicated for 20 min.The resulting extracts were centrifuged at 12,000 r/min and the supernatants were analyzed.
2.3.HPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS analysis
An HPLC-high resolution mass spectrometer(HPLC-HRMS;Ultimate 3000 HPLC system,Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA)equipped with a reversed-phase Hypersil Gold aQ C18column(2.1 mm×150 mm,3μm;Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA)was used to determine the chemical constituents present in the LHQW sample.The column temperature was maintained at 40°C.The mobile phases included 0.1% FA in ACN(A)and 0.1% FA in H2O(B).A constant flow rate was maintained(0.2 mL/min).The elution gradient was maintained at 5% A for 1 min,increased to 95% A over 41 min,and maintained at this phase for 4.9 min.The column was then re-equilibrated at 5% A for 3 min.The samples were maintained at room temperature and the injection volume was 5μL.
The Q Exactive mass spectrometer(Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA)equipped with a heated electrospray ionization interface was operated under both electrospray ionization(ESI)negative and ESI positive modes.The instrument was calibrated with the calibration solutions provided by the manufacturer.Data were acquired using Xcalibur 4.1 software(Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA),and all obtained data were processed by the Compound Discoverer(CD)3.0(Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA)and Xcalibur 4.1 software packages.The source parameters were optimized with a spray voltage of 3.5 kV(+)/3.2 kV(-).The other parameters were set as follows:capillary temperature,320°C;auxiliary gas heater temperature,350°C;sheath gas pressure,40 arb;auxiliary gas pressure,15 arb;sweep gas pressure,0 arb;S-lens RF level,50 V.
The Q Exactive detector was operated in full scan and datadependent MS2(dd MS2)modes.In full scan mode,the resolution was set at 70,000.The automatic gain control(AGC)target and maximum injection time(IT)were 1×106ions capacity and 100 ms,respectively.For the dd MS2mode,the acquisition parameters were:resolution,17,500;AGC target,2×105ions capacity;maximum IT,50 ms;scan range,100-1500 m/z;loop count,3;normalized collision energy(stepped),20%,40%,60%;isolation window,1.2 Da;apex trigger,5-15 s;dynamic exclusion,5 s.The Top N(N=number of top abundant ions for fragmentation)was set to 5.
2.4.GC-MS analysis
The GC-MS analysis was conducted on a Trace GC Ultra system equipped with an AS 3000 auto-sampler,a split/splitless injector,and TSQ Quantum XLS MS detector with triple quadrupole(Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA).The TR-5 MS capillary column(30 m × 0.25 mm,0.25μm film thickness)was purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific(Waltham,MA,USA).
The injection temperature and ion source temperature were 250°C.The oven temperature program was maintained at 50°C for 1 min,increased to200°C(rate:8°C/min),maintained at 200°C for 5 min,increased to 280°C(rate:10°C/min),and maintained for 5 min.Helium was used as the carrier gas(flow rate:1 mL/min).Sample injection volume and split ratio were 1μL and 50:1,respectively.The ionizing energy was 70 eV.The chromatograms were obtained by collecting the total ion currents in the scan range of m/z 50-550.Data were acquired using the Xcalibur 2.2 software.
2.5.Data processing and compound identification
The raw data acquired from the HPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS analysis were processed by the CD 3.0 software.The data matrices of the molecular masses,retention time,fragments,and peak areas from both ESI positive and negative modes were extracted and aligned to the mzVault library,which was integrated in the CD software.The mzVault spectral library(Thermo Fisher Scientific,Waltham,MA,USA)contained the retention time,precise mass ions,and MS2fragments of 1200 commercial reference standards, which were analyzed by Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS.The CD software equipped with the mzVault library identified peaks with a high mass accuracy(<5ppm)and an isotope pattern variation within 85%.The molecular compositions adhered to the hydrogen to carbon ratio rules,and were matched to potential compounds using rings and double-bonds equivalents.The MS2spectra were compared with the reference spectra from the mzVault library.Compound identification was accepted only when the matching score was greater than 85(total score=100).In addition,the accuracy of the compound identification was improved by comparing the obtained data and possible fragmentation patterns with those reported in the literature.
3.Results and discussion
3.1.HPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS analysis
The base peak chromatograms of the LHQW capsule in positive and negative ion modes are depicted in Fig.1.In total,104 compounds,including alkaloids,flavonoids,phenols,phenolic acids,phenylpropanoids,quinones,terpenoids,and other phytochemicals,were putatively identified(as listed in Table 1[16-44])using the library alignment method.According to previous studies[16-44],the identified compounds are present in the herbs used in the LHQW formulation.No phytochemical was identified from Dryopteridis Crassirhizomatis Rhizoma.The compound identification of several specific compounds is presented below.
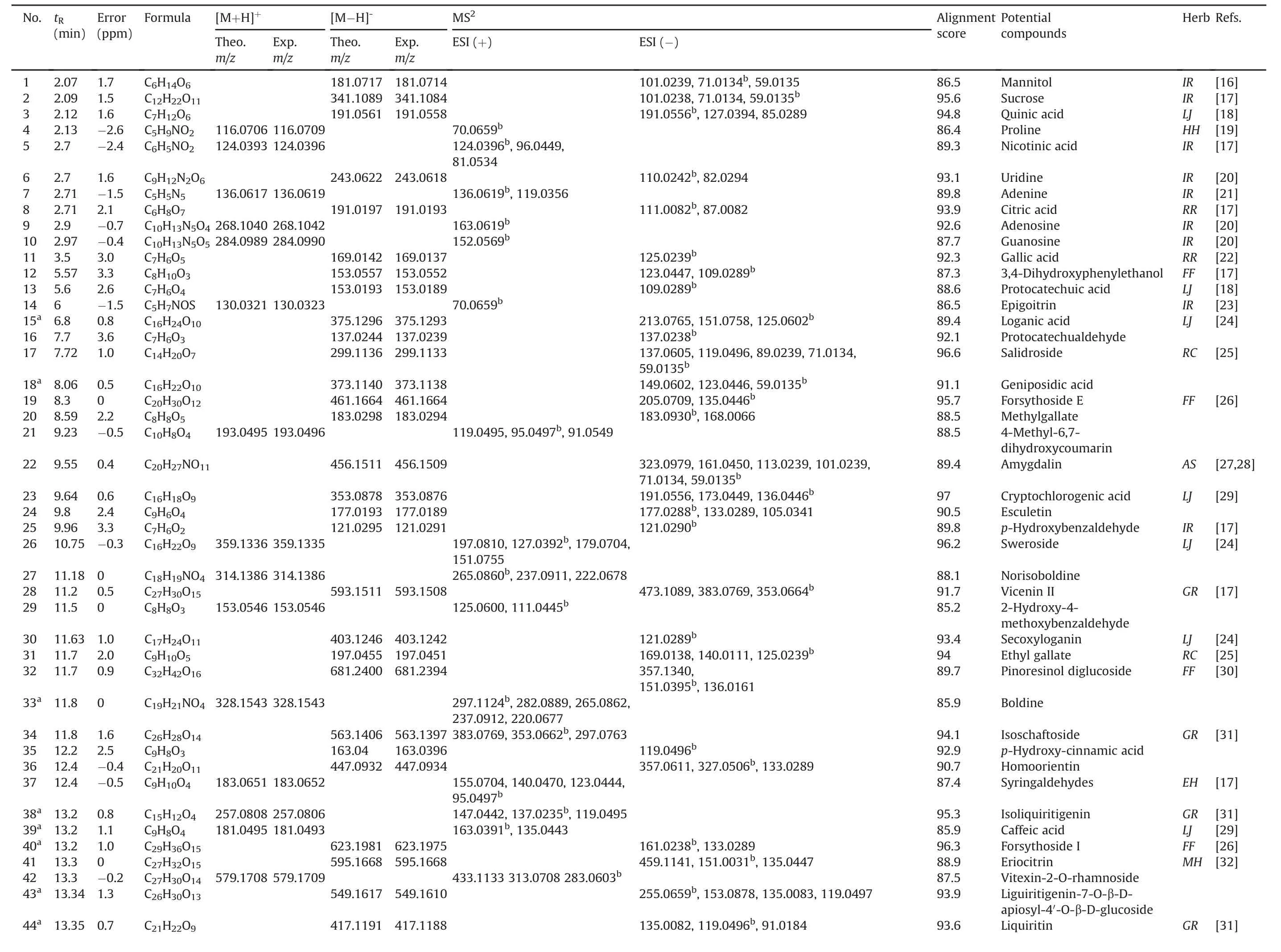
Table 1Identification of the chemical constituents in the LHQW capsule using HPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS.
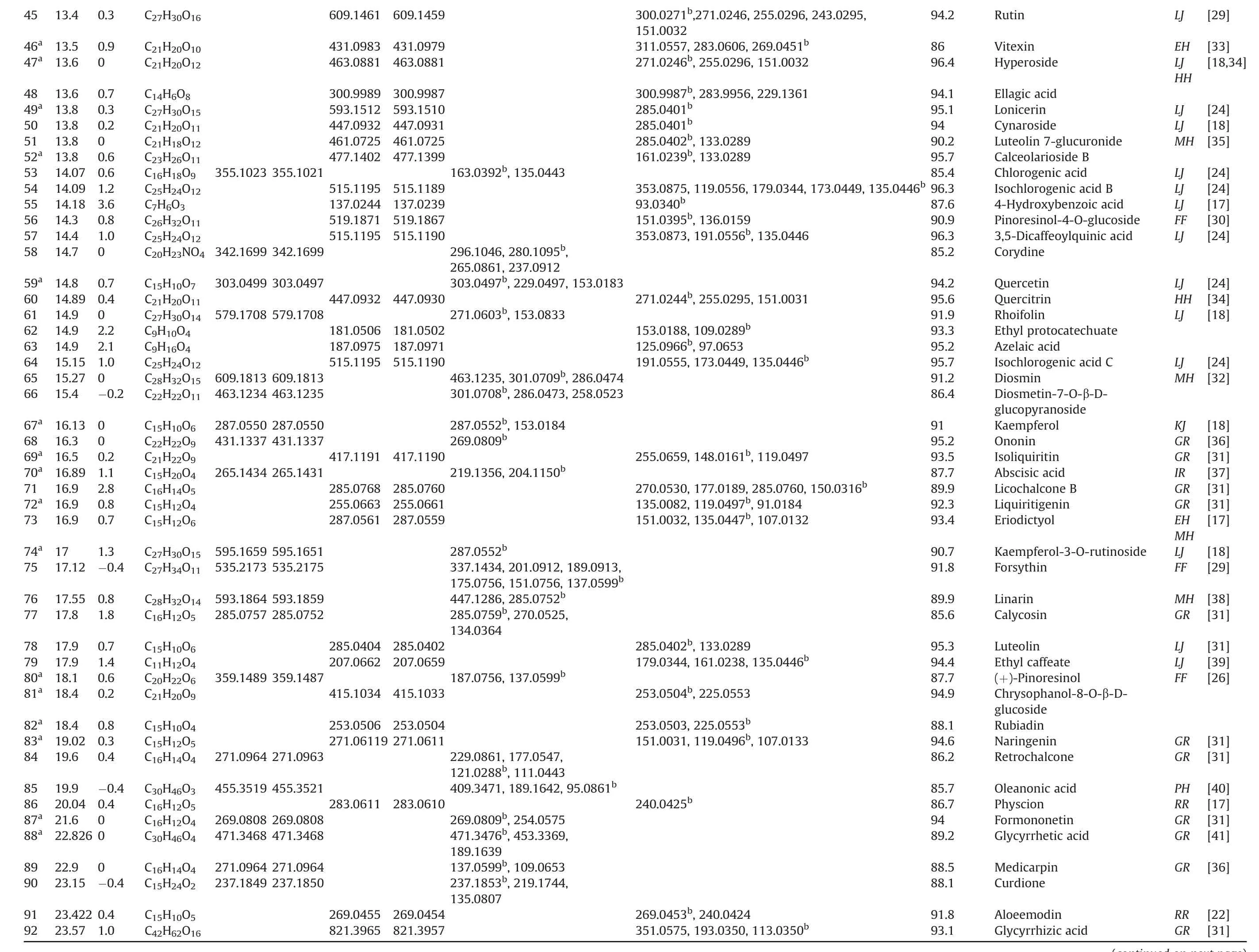
(continued on next page)
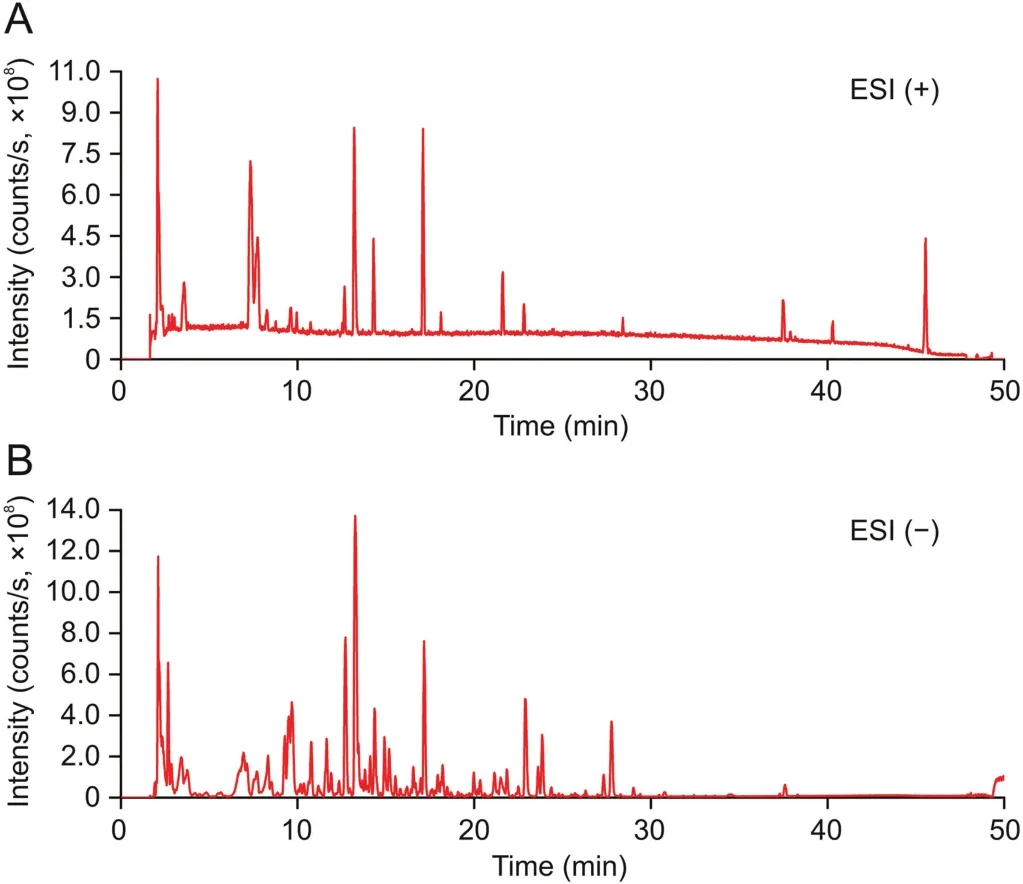
Fig.1.Base peak chromatogram of the Lianhua Qingwen(LHQW)capsule analyzed using HPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS analysis in(A)electrospray ionization(ESI)positive mode and(B)ESI negative mode.
3.1.1.Flavonoids
The molecular formula of compound 71 was C16H14O5,as established by the[M-H]-peak at m/z 285.0760.The MS2spectrum was similar to that previously reported[31]for licochalcone B.The MS2spectrum and the possible fragmentation pathway are shown in Fig.S1A.The peak at m/z 270.0530 indicates the formation of[M-H-CH3]-.The base peak at m/z 150.0316 is attributed to the fragment generated by the cleavage of groups around the carbonyl carbon,followed by loss of CH3unit.The fragment responsible for the peak at m/z 177.0189 is shown in Fig.S1A.The mzVault library alignment results(Fig.S1B;score:89.9)revealed that the compound was licochalcone B,which is a phytochemical present in Glycyrrhizae Radix Et Rhizoma.
3.1.2.Terpenoids
The molecular formula of compound 26 was C16H22O9,as indicated by the molecular ion peak([M+H]+)at m/z 359.1335.Fragmentation occurred via the loss of a neutral glucose(Glc)molecule(m/z 197.0810;[M+H-Glc]+),and the resulting ion was further fragmented to generate[M+H-Glc-H2O]+(m/z 179.0704)and[M+H-Glc-H2O-CO]+(m/z 151.0755).The base peak at m/z 127.0392 is attributed to the fragment that was generated by the retro-Diels-Alder fragmentation,as shown in Fig.S2A.The library alignment(Fig.S2B;score:96.2)and comparison with literature data[24]revealed that compound 26 was sweroside,a phytochemical present in Lonicerae Japonicae Flos.
3.1.3.Quinones
The molecular formula of compound 97 was C15H10O5,as established by the[M-H]-peak at m/z 269.0454.Peaks at m/z 241.0502,225.0553,and 197.0603 can be attributed to[M-H-CO]-,[M-H-CO-O]-,and[M-H-CO-O-CO]-fragments,respectively(Fig.S3A).Library alignment(Fig.S3B;score:96.8)and comparison with literature data[42]revealed that the compound was emodin,a constituent of Rhei Radix Et Rhizoma.
3.1.4.Phenolic acids
Compound 31 had a molecular formula of C9H10O5,as evaluated from the molecular ion peak at m/z 197.0451([M-H]-)in the MS2spectrum(Fig.S4A).The characteristic fragments were[M-H-C2H4]-(m/z 169.0138)and[M-H-C2H4-CO2]-(m/z 125.0239).Comparison with literature data[25]and library alignment(Fig.S4B;score:94)revealed that compound 31 was ethyl gallate,a component of Rhodiolae Crenulatae Radix Et Rhizoma.
3.1.5.Phenylpropanoids
The peak at m/z 579.2079 in the MS spectrum of compound 75 is attributed to the[M+HCOO]-adduct,while the peak at m/z 533.2019 corresponds to[M-H]-.Characteristic peaks were m/z 371.1490,356.1250,and 121.0288 in the MS2spectrum.Library alignment(Fig.S5B)and a comparison with literature data[29]revealed that compound 75 was forsythin,a phytochemical present in Forsythiae Fructus.The possible fragmentation pathways and the characteristic fragments are shown in Fig.S5A.
3.1.6.Phenols
The peak at m/z 299.1133in the MS2spectrum of compound 17 is attributed to the[M-H]-ion.Some characteristic peaks and the corresponding fragments were at m/z 137.0605([M-H-Glc]-)and m/z 119.0496([M-H-Glc-H2O]-),and the data are in accordance with that of previous studies[25].The possible fragmentation pathway is shown in Fig.S6A.Library alignment(Fig.S6B;score:96.6)identified the compound as salidroside,a compound derived from Rhodiolae Crenulatae Radix Et Rhizoma.
3.1.7.Alkaloids
The molecular formula of compound 7 was C5H5N5.There were only two characteristic peaks in the MS2spectrum(Fig.S7A):m/z136.0619([M+H]+)and m/z 119.0356([M+H-NH3]+).Comparison with literature data[21]and the library alignment results(Fig.S7B)revealed that compound 7 was adenine,an alkaloid present in Isatidis Radix.
3.1.8.Miscellaneous
Compound 22 had a molecular formula of C20H27NO11,as indicated by the peaks at m/z 458.1675([M+H]+)and m/z 475.1922([M+NH4]+).The peak atm/z296.1129 is attributed to[M+NH4-Glc]+,and the other characteristic fragments,along with the possible fragmentation pathway are shown in Fig.S8A.Comparison of the possible fragmentation pathway with reference data[27,28],along with the library alignment(Fig.S8B)of the retention time in ESI(-)mode indicated that compound 22 was amygdalin,a chemical constituent present in Armeniacae Semen Amarum.
3.2.GC-MS analysis
The volatile constituents in the LHQW capsule were extracted in three different solvents,i.e.,hexane,acetone,and ethyl acetate,and then detected using GC-MS.The total ion chromatograms(TICs;Fig.S9)of all three extracts were similar.The TIC of the LHQW capsule extracted in ethyl acetate is shown in Fig.2.In total,17 volatile compounds(Table 2)[43,45-48]were putatively identified by comparing the obtained data with that from the NIST mass spectra library and previously reported literature[11].The results showed that the major constituent was levomenthol with a relative percentage of 97.89%,as calculated by the peak area normalization method.The other most abundant components were patchouli alcohol(0.47%),β-pathchoulene(0.33%),α-guaiene(0.22%),andα-bulnesene(0.20%).Patchouli alcohol has anti-virus and anti-inflammatory activities reported by Kiyohara et al.[49].Most of the components were terpenoids derived from Menthae Haplocalycis Herba and Pogostemonis Herba.
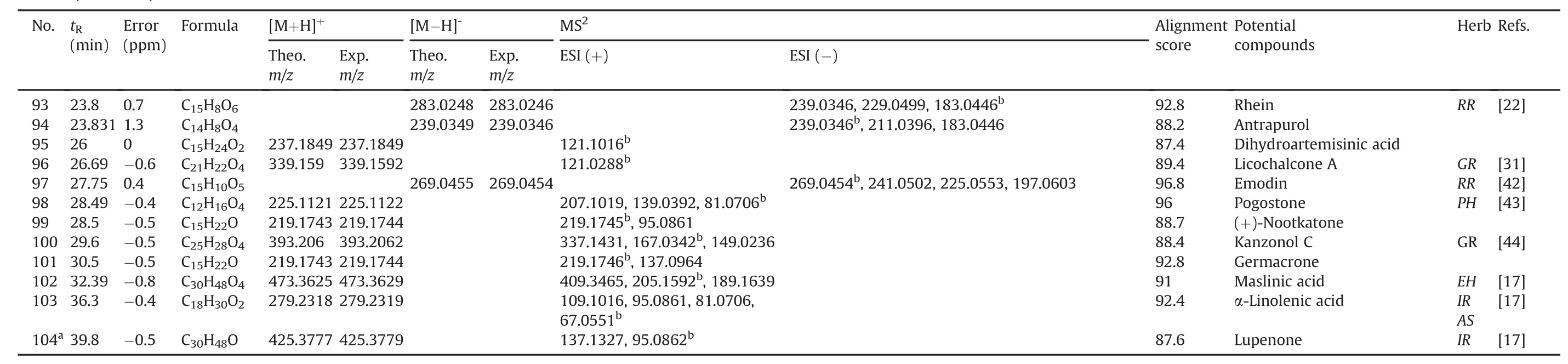
Table 1 (continued )
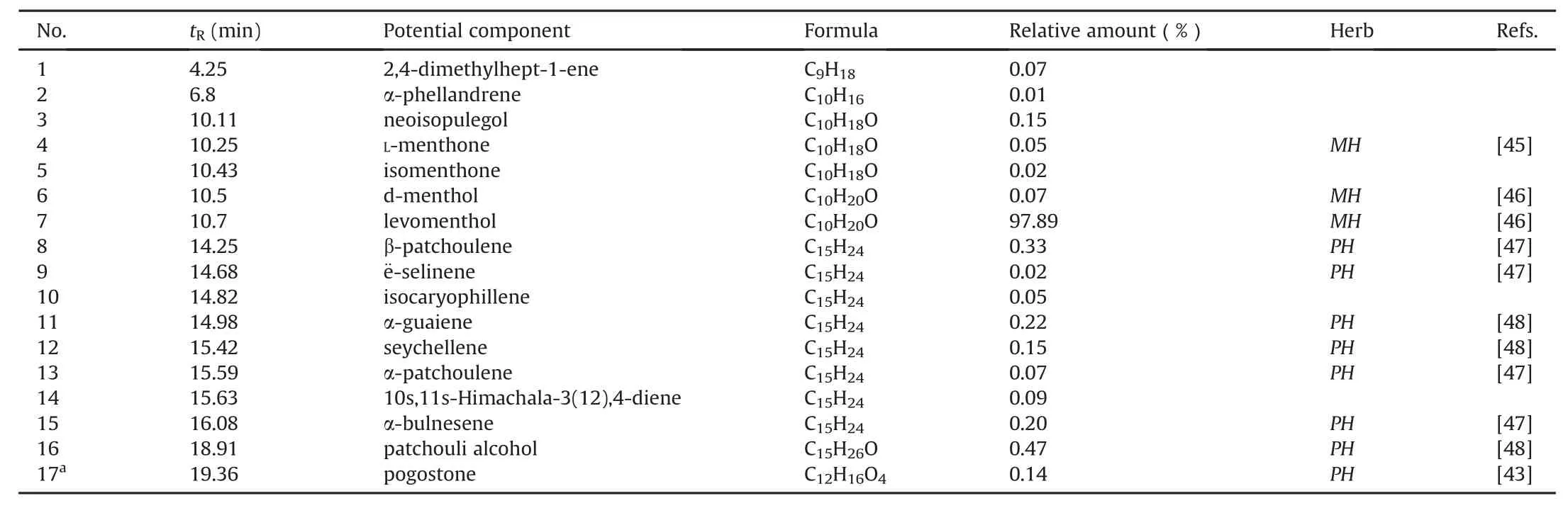
Table 2Identification of the volatile components in the LHQW capsule(extracted in ethyl acetate)using GC-MS.
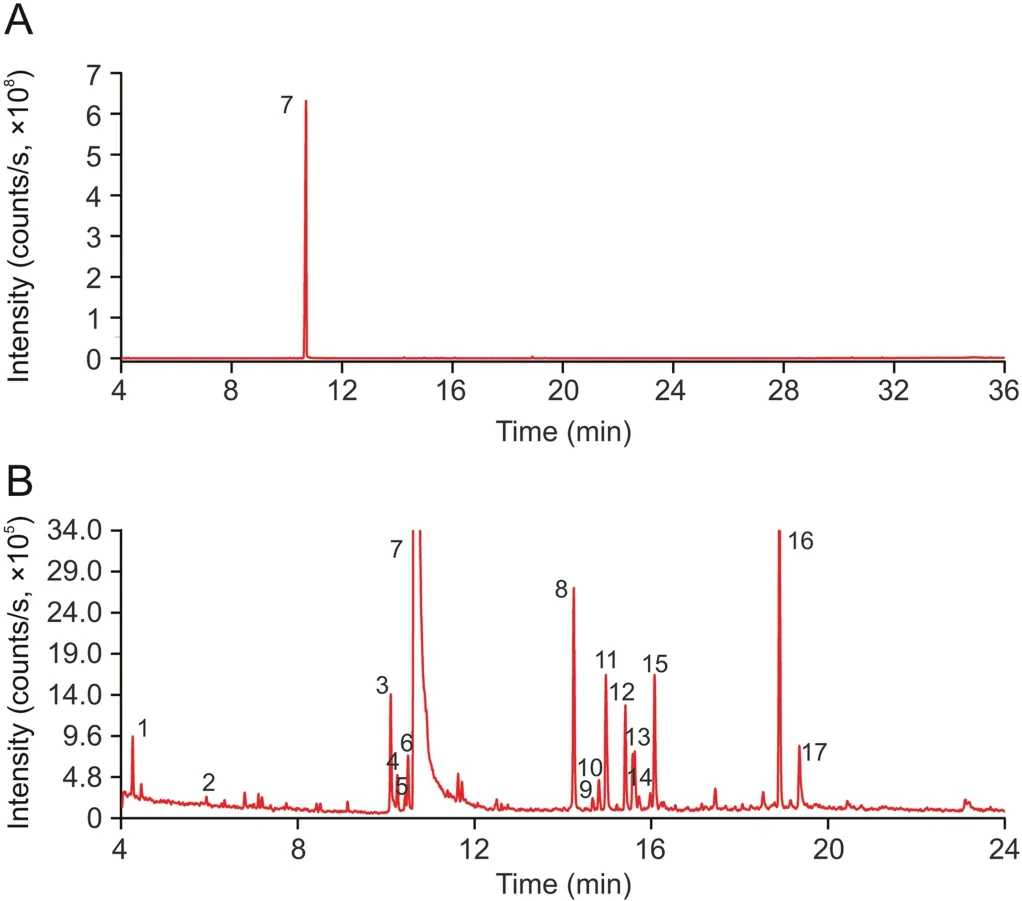
Fig.2.(A)Total ion chromatogram(TIC)of the LHQW capsule(extracted in ethyl acetate)analyzed by GC-MS.(B)Enlarged image of the TIC from 4 to 24 min.
4.Conclusion
In this study,HPLC-Q Exactive-Orbitrap-MS coupled with GCMS method was used for the first time to identify the chemical constituents in the LHQW capsule,a popular TCM prescribed to treat the symptoms of SARS-CoV-2 infections.In addition,the MS and MS2spectrum library alignment method was found to be a convenient approach to rapidly identifying the components of a complex mixture.A total of 120 constituents,including alkaloids,flavonoids,phenols,phenolic acids,phenylpropanoids,quinones,terpenoids,and other phytochemicals,were successfully detected and putatively identified in this study.The findings of our study can contribute to future investigations on the active chemical constituents and the mechanism of action of the LHQW capsule.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work is financially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(Grant No.:2042020kf1003).
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2021.01.004.
杂志排行
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis的其它文章
- Effect of Shengmai Yin on the DNA methylation status of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell and its radioresistant strains
- Spectroscopic studies of the interaction between phosphorus heterocycles and cytochrome P450
- Impaired tricarboxylic acid cycle flux and mitochondrial aerobic respiration during isoproterenol induced myocardial ischemia is rescued by bilobalide
- Evaluation of the gastrointestinal anti-motility effect of Anacardium occidentale stem bark extract:A mechanistic study of antidiarrheal activity
- Synergistic effects of methyl 2-cyano-3,11-dioxo-18beta-olean-1,-12-dien-30-oate and erlotinib on erlotinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells
- A living cell-based fluorescent reporter for high-throughput screening of anti-tumor drugs
