Clinical analysis of laparoscopic lateral peritoneal suspension in the treatment of severe pelvic organ prolapse
2022-01-13YanHongZhangChongDeWangWenMingCaoKeShuiZhou
Yan-Hong Zhang ,Chong-De Wang ,Wen-Ming Cao ,Ke-Shui Zhou*
1Maternal and Child Health Hospital of Huantai County,Shandong,China.2Shenzhen Longhua District Ping an Hospital,Shenzhen,China.
Abstract:Objective: To investigate the clinical effects of laparoscopic lateral peritoneal suspension for severe pelvic organ prolapse (POP).Methods: Thirty-eight patients who underwent laparoscopic lateral peritoneal suspension for pelvic organ prolapse in the gynecology department of our hospital from January 2019 to January 2020 were selected for retrospective analysis.Postoperative outcomes were recorded for patients at 3,6,and 12 months postoperatively.Results: All 38 patients completed the surgery safely,and the duration of surgery was 85-190 min,with a mean of (138±40.75) min;surgical bleeding was 30-80 ml,with a mean of (57±35.4) ml;the duration of postoperative catheterization was 4-6 days,with a mean of (5±0.73) days;postoperative hospitalization was 6-12 days,with a mean of(8.49±2.18) days.2.18) days.At 3,6,and 12 months after the end of surgery,all follow-up patients had their uterus and anterior vaginal wall restored to normal position without prolapse.The pelvic floor rehabilitation of the patients after surgery was good and their sexual life was significantly improved in all cases.Conclusion: Laparoscopic lateral peritoneal suspension for severe pelvic organ prolapse is safe,efficacious,minimally traumatic,less painful,with short hospital stay,fast postoperative recovery,greater choice of uterine de-positioning,with the advantages of permanence and good pelvic floor anatomical recovery,and this procedure can maintain a certain vaginal length with 100% efficiency,which is worthy of clinical promotion.
Keywords:laparoscopic lateral peritoneal suspension;uterine prolapse;anterior vaginal wall prolapse,mesh,uterosacral ligament,round ligament
Introduction
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is an abnormal position and dysfunction of the pelvic organs caused by the descent of the pelvic organs due to abnormalities in the muscles and fascial tissues of the pelvic floor,with prolapse of the vaginal mass,ulceration of the prolapse,and difficulty in sexual life as the main manifestations [1].According to statistics,the lifetime probability of adult women suffering from POP is 12.6%,and its risk increases with age[2].
Pelvic organ prolapse,seriously affects the health and quality of life of women.It is expected that the number of POP cases in China will increase by about 50% by 2050.Taking traditional vaginal wall repair surgery can solve part of the problem,but the recurrence rate after surgery is as high as 30%-40%.In recent years,54 patients with pelvic organ prolapse were treated by laparoscopic lateral peritoneal suspension in our hospital,and satisfactory clinical results were achieved.This procedure is worthy of clinical promotion because of its advantages of minimally invasive,less bleeding,quick recovery,good anatomical effect and high surgical satisfaction.It is reported as follows.
Subjects
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is an abnormal position and dysfunction of the pelvic organs caused by the descent of the pelvic organs due to abnormalities in the muscles and fascial tissues of the pelvic floor,with prolapse of the vaginal mass,ulceration of the prolapse,and difficulty in sexual life as the main manifestations [1].According to statistics,the lifetime probability of adult women suffering from POP is 12.6%,and its risk increases with age[2].Thirty-eight patients with uterine prolapse and anterior and posterior vaginal wall prolapse who underwent surgical treatment in our gynecology department from January 2019 to January 2020 were selected.The patients were between 39 and 74 years old and were all menstruating mothers,including 8 patients who had one child and 30 patients who had two or more children.All patients were quantified according to the pelvic organ prolapse quantification scale (POP-Q) and were in POP-Q stage II-IV.All patients had varying degrees of vaginal obstruction,dyspareunia and lower abdominal cramping or lumbosacral pain.
Quantitative staging of pelvic organ prolapse was performed by POP-Q,and all patients were POP-Q II-IV.Exclusion criteria:(1) acute inflammation of genitourinary system.(2) Severe internal and surgical diseases cannot tolerate surgery.(3) Contraindications of laparoscopic surgery.(4)complicated with uterine body lesions and cervical lesions.(5) Patients with malignant tumors.
Preoperative evaluation:Basic pelvic and urinary fluid dynamics examination,cervical fluid based cytology,high-risk HPV-DNA,and staged curettage were performed for patients with abnormal vaginal bleeding to ensure no organ or tissue lesions.Exclusion criteria:(1)acute inflammation of genitourinary system.(2) Severe internal and surgical diseases cannot tolerate surgery.(3) Contraindications of laparoscopic surgery.(4) complicated with uterine body lesions and cervical lesions.(5) Patients with malignant tumors.
Surgical Procedures
A cystoscopic bilateral ureteral indwelling catheter was placed,a urinary catheter was left in place,and a uterine lifter was placed.Four perforation holes in the abdominal wall were made,namely,an incision about 1.0 cm long at the superior border of the umbilical port,an incision about 1.0 cm long at the point of Mai,an incision 0.5 cm long in the left lower abdomen,and an incision 0.5 cm long in the abdominal midline.Preservation or removal of the uterus depends mainly on the patient's age,needs,and preservation of the uterus mainly for anterior pelvic prolapse.
(1) If the uterus is preserved:the mesh is prepared and cut into a"long T" shape,the transverse arm is 18 cm long on one side,the longitudinal arm is 6 cm long and 4.5 cm wide,and placed into the abdominal cavity,the mesh is placed transversely and the longitudinal arm of the mesh is placed on the cervix with 3-0 absorbable sutures forfixation.A 0.5 cm incision was made at 4 cm on the left anterior superior iliac spine and 3 cm outside,and the caudal end of the left transverse arm of the mesh was drawn through the retroperitoneum;the uterus and anterior vaginal wall were successfully suspended and lifted by transvaginal examination.
(2) If the uterus is removed:cut the round ligament of the uterus,pelvic funnel ligament,electrocoagulation cut the parametrial tissue to the vascular area of the uterus;open the bladder uterine peritoneal reflex and push down the bladder to the level of the external cervical opening,continue to separate the bladder vaginal gap downward for about 4.0 cm,ultrasonic knife open the rectovaginal gap,push down the rectum for about 3.0 cm;cut the main ligament and sacral ligament in turn close to the cervix;use electrocoagulation hook to circumferentially cut through the The vaginal vault is removed and the uterus and both adnexa are removed transvaginally;the vaginal stump is sutured and sutured to the bilateral round ligament severed ends in suspension.The mesh is prepared,cut and sutured into a long"cross" shape,the horizontal arm is 18 cm long on one side,the longitudinal arm is 4 cm long anteriorly,and the longitudinal arm is 6 cm long and 4 cm wide posteriorly,the mesh is placed horizontally and the longitudinal arm is placed on the anterior and posterior vaginal walls with interrupted 3-0 absorbable sutures for fixation.A 0.5 cm incision was made at 4 cm above and 3 cm outside the left anterior superior iliac spine,and the left side of the vaginal stump was pierced along the retroperitoneum,and the tail end of the left transverse arm of the mesh was pulled through the retroperitoneum,and the right side was treated in the same way,and the excess mesh was cut off;the vagina was filled with one roll of sterile oil gauze.
Perioperative management
Preoperative vaginal flushing three times or more,such as combined vaginitis,vaginal medicine symptomatic treatment.Fasted for 6 hours postoperatively and cefazolin 2.0 was routinely administered 30 minutes before surgery to prevent infection.If the vaginal posterior wall detachment II or more patients can be repaired after surgery.The posterior wall of the vagina was repaired by traditional hand.
Observation indicators and efficacy evaluation
General Indicators.Operation situation,operation time,blood loss during operation,intraoperative and postoperative complications,postoperative catheter indwelling time,postoperative residual urine volume and length of hospital stay.
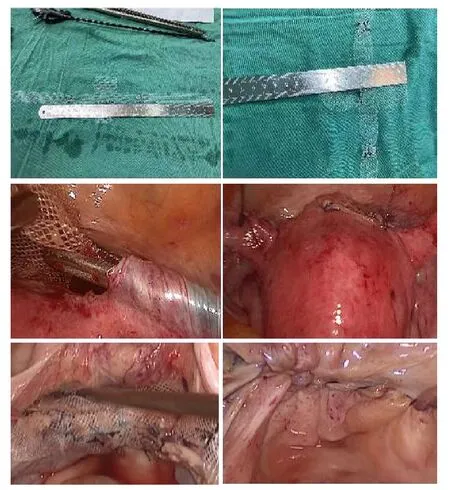
Figure 2 Laparoscopic peritoneal suspension mesh clipping
Objective efficacy evaluation.Postoperative outcomes were recorded at 3,6,and 12 months after surgery,with 8 patients completing 12-month follow-up records,16 patients completing 6-month follow-up records,and 38 patients completing 3-month follow-up records.At 3,6,and 12 months postoperatively,the positions of the POP-Q indicator points (Aa,Ba,C,D,Ap,Bp,gh,pb,and TVL) were measured (see Table 2 for the description of each indicator point).Among them,point C correlates most strongly with the choice of procedure and surgical outcome for mid-pelvic defects,and point B represents defects in the deep luminal surface of the vaginal wall,which overlap with point A in the absence of POP[5].
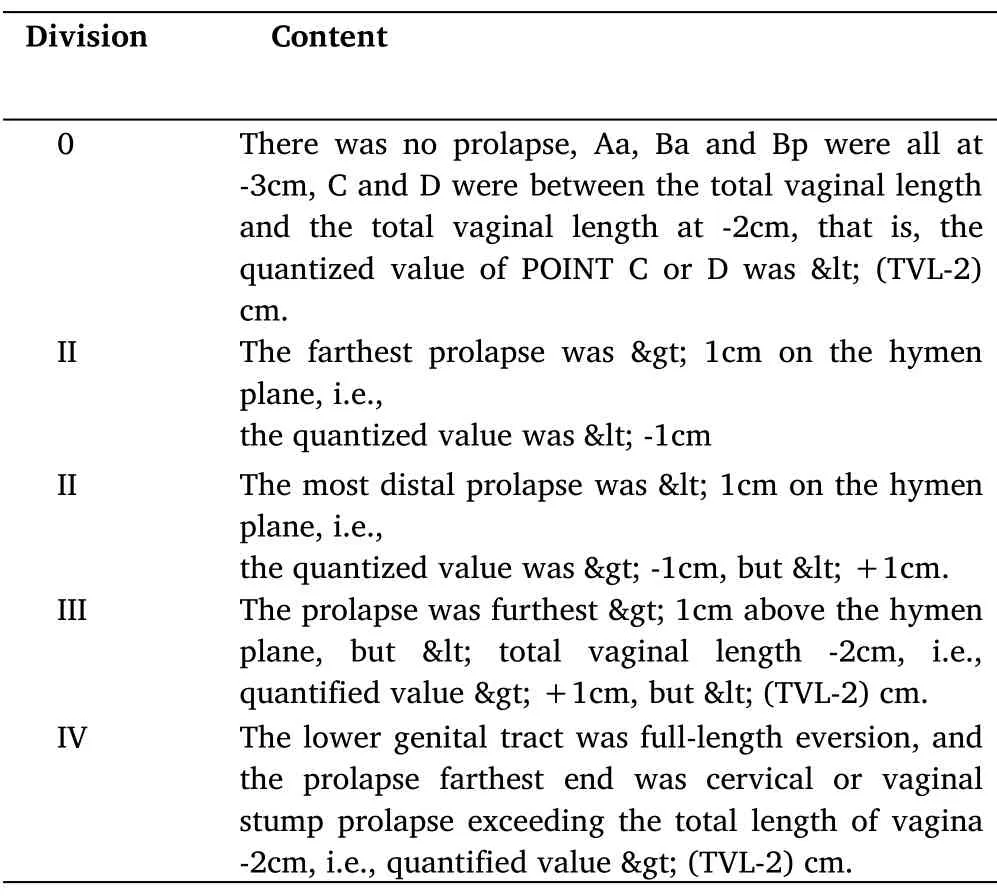
Table 1 Staging of pelvic organ prolapse(POP-Q staging)
Subjective efficacy evaluation.Subjective cure:No POP symptoms such as lumbar or vulvar cramps,normal defecation,urination and vaginal discharge after surgery.Objective cure:Cured by POP-Q points and pelvic floor image evaluation,POP-Q ≤stage I.Recurrence:Point C is displaced down to or beyond 1/3 of the full length of the vagina,or either point A or B reaches the hymenal plane or lower,or with prolapse symptoms[6].Recurrence of prolapse with POP-Q score assessment ≥II during follow-up.
For sexual function:The POP/incontinence sexual life questionnaire(PISQ-12) was used to assess the sexual life of the patients,and the scale included physical factors,emotional factors and sexual partner factors dimensions,with a total score of 48,with higher scores indicating a higher quality of sexual life.See Table 3.
For quality of life:The Pelvic Dysfunction Impact Questionnaire(PFDI-20) and the Pelvic Disease Quality of Life Impact Questionnaire Short Form (PFDI-7) were used.The PFDI-20 consists of 3 main subscales:POP Distress Scale (POPDI-6),Defecation Dysfunction Scale(CRADI-8) Urinary Dysfunction Scale (UDI-6),which focuses on bladder,bowel and pelvic symptoms.The PFDI-7 consists of three subscales that describe the impact of prolapse symptoms on daily life,social relationships,and emotional well-being.higher scores on the PFDI-20 and PFDI-7 scales indicate a greater impact of prolapse symptoms on quality of life.
The visual analogue scale (VAS) was used to assess patients'subjective satisfaction on a scale of 0-10,with the higher the score,the higher the satisfaction.
Statistical methods
SPSS 22.0 software was used for statistical analysis.The count data were expressed as percentage (%) and χ2 test was used.Measurement data were expressed as mean±standard deviation (X±S),and P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Surgical results
All 38 patients completed the surgery safely,and the time spent in surgery was 85-190 min,with a mean of (138±40.75) min;the surgical bleeding volume was 30-80 ml,with a mean of(57±35.4)ml;the patients were on catheters for 4-6 days after surgery,with a mean of (5±0.73) days;the postoperative hospital stay was 6-12 days,with a mean of (8.49±2.18) days.
Anatomical efficacy
All patients had their uterus and vaginal wall returned to normal position without prolapse at 3-12 months after the end of surgery.The differences were statistically significant (P<0.05) between the preoperative and postoperative POP-Q measurements at 3,6,and 12 months;see Table 2,and Table 3.The patients had good pelvic floor recovery after surgery,and all of them had significant improvement in sexual life,and the difficulty in urination,urinary frequency and vaginal obstruction disappeared.
Functional efficacy
At 3,6,and 12 months after surgery,all patients'subjective symptoms such as lumbar and abdominal cramps,vulvar foreign body or painful sensation,and abnormal discharge disappeared,and urination and defecation returned to normal,and 94.74% (36/38) of patients had a subjective satisfaction VAS score ≥ 8.At 3,6 and 12 months after surgery,the PFIQ-7 and PFDI-20 scores decreased compared with those before surgery,and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).See Table 3.
Postoperative pelvic floor dysfunctional disease symptom questionnaire short form (PFDI-20),POP Distress Scale (POPDI-6),and Urinary Dysfunction Inventory (UDI-6) scores were significantly lower than before surgery,with statistically significant differences (P< 0.05).POP/Incontinence Sexual Life Questionnaire (PISQ-12)scores were significantly higher than before surgery,with statistically significant differences (P<0.05).See Table 3.
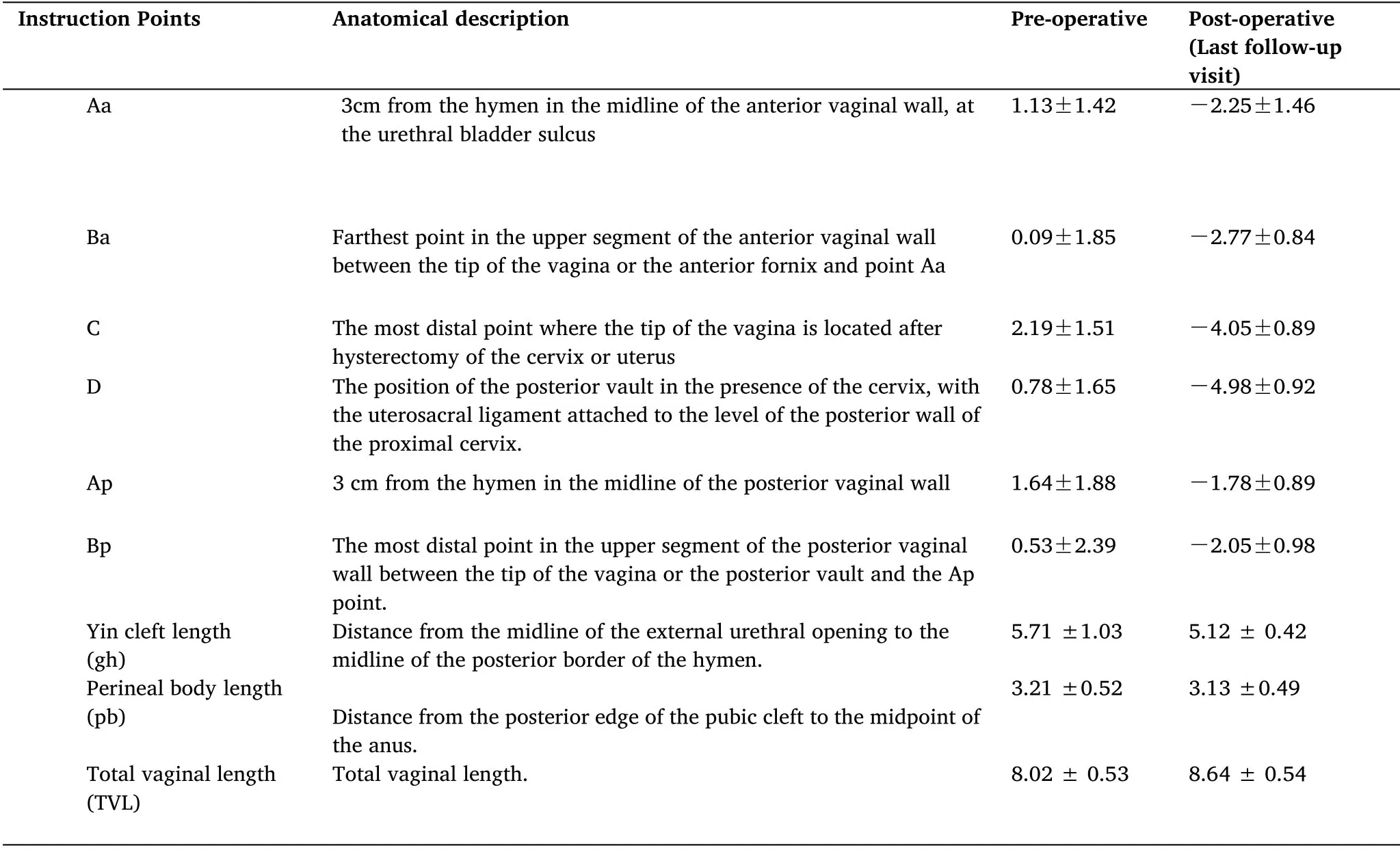
Table 2 Change in the position of each indicator point of POP-Q at the last follow-up preoperative and postoperative visits (cm)x±s
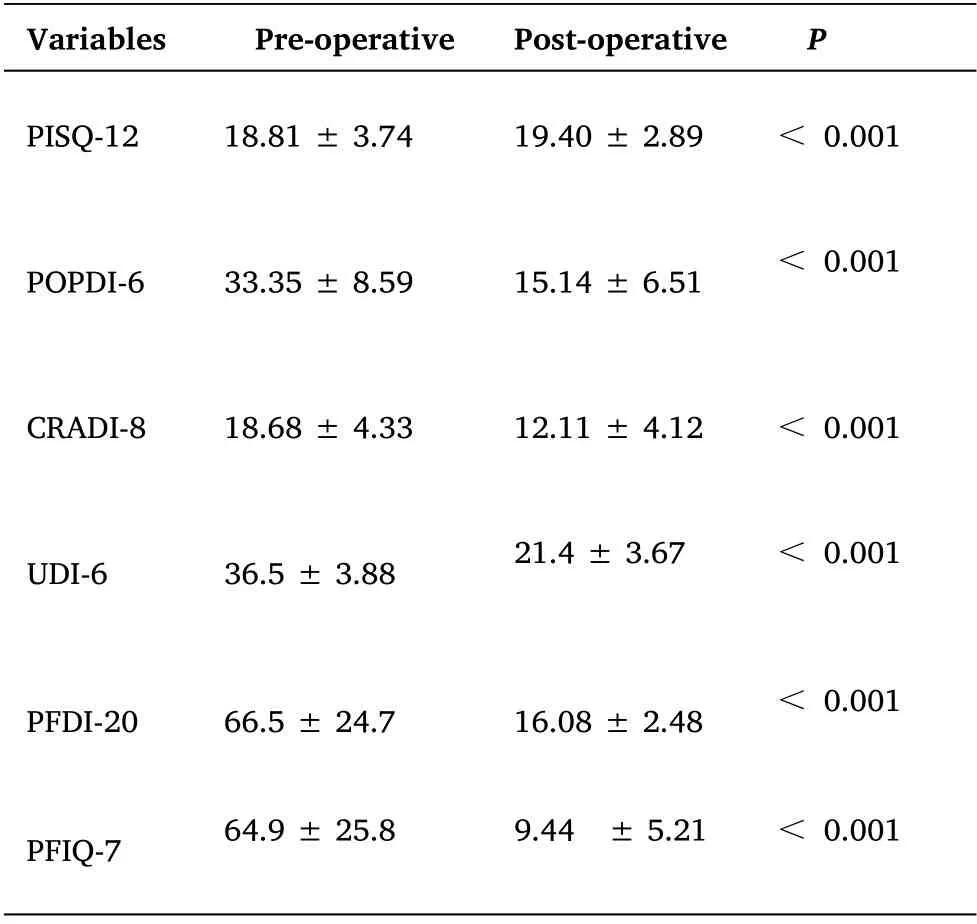
Table 3 .Comparison of quality of life of patients at the last follow-up preoperatively and postoperatively (x ± s,points)
Complications
No organ damage,infection,or hemorrhage occurred in any of the 38 patients.The lower abdominal pain disappeared and returned to normal within 1 month in all cases.The vaginal length and elasticity of the patients were at normal levels.
Discussion
Pelvic organ prolapse(POP) refers to the prolapse of the pelvic organs inside or outside the vagina and was proposed by the National Institutes of Health in 2001:POP means that the anterior edge of any vaginal segment reaches or exceeds the hymenal edge by more than 1 cm and can occur alone,but in most cases in combination.The causes are mainly related to pregnancy and childbirth,aging,estrogen deficiency,abdominal obesity,chronic colony,pneumoperitoneum,continuous weight bearing,constipation,history of pelvic surgery,etc.Some scholars even call it "social cancer",which seriously affects women's physical and mental health and quality of life.
There are various surgical approaches for pelvic organ prolapse(POP),including traditional anterior and posterior vaginal wall repair,mid-pelvic suspension (sacrospinous ligament fixation,uterine or vaginal sacral fixation,high sacral ligament suspension,etc.),pelvic floor reconstruction surgery with transvaginal mesh,and vaginal closure.The choice of surgical approach requires a comprehensive assessment of the patient's own condition and personal tendencies,whether there is a combination of bladder and bowel symptoms,the site of anatomical defects,and whether there are lesions in the uterusand adnexa,etc.Individualized surgical approaches are adopted for different patients,and although anatomical recovery is closely related to functional recovery,functional recovery is often the result of a combination of mechanisms.
Surgery for pelvic organ prolapse is traditionally mostly transvaginal hysterectomy+anterior and posterior vaginal wall repair,but local tissue suture repair has a high recurrence rate in the distant future,with up to one-third of patients requiring reoperation[7].Traditional hysterectomy for uterine prolapse requires removal of the uterus,and hysterectomy can result in varying degrees of shallow vaginal length,vaginal scarring,and high rates of vaginal granulation,combined with diminished ovarian function,vaginal dryness and discomfort,and scarring can reduce its elasticity and affect the quality of sexual life [8].Therefore,patients with uterine prolapse have an increasing desire to preserve the uterus.During hysterectomy,many doctors emphasize the role of suturing the main sacral ligament.However,simply suturing the main sacral ligament correspondingly may also fail to prevent vault prolapse after hysterectomy.Instead,preserving the uterus is equivalent to preserving the intact pericervical ring,which is important for maintaining the stability of the pelvic floor structure if it is then reasonably suspended [9].
Recent basic anatomical findings suggest that there are three main levels of pelvic floor support structures for the uterus and vagina:the main ligament and the uterosacral ligament complex are the main support structures;the paravaginal support structures are the cervical and rectal fascia of the bladder;and the peripheral soft tissue support.The etiology of pelvic organ bulges such as uterine prolapse is due to damage to the connective tissue on both sides of the parametrium and above the vagina,loss of integrity of the main ligament and the uterosacral ligament complex and weakness of the pelvic septum resulting in a downward shift in the position of the uterus and the position of the vaginal vault [10].Therefore,hysterectomy has no significance for pelvic floor repair in bulging genital tract disease,a novel concept that has been widely accepted abroad [11].The integrity of the cervicovaginal complex is crucial for maintaining normal pelvic floor structure and function,and preserving the uterus is equivalent to preserving the intact pericervical ring,which is important for maintaining the stability of the pelvic floor structure[12].
The laparoscopic lateral peritoneal suspensions performed in our hospital all have the following four advantages:
(1) good safety:no need to suture the mesh to the sacrum compared to sacral fixation,avoiding injury in this region;no more foreign bodies in the periosteum,avoiding osteochondritis;avoiding postoperative back pain;avoiding injury to the sacral region:iliac vessels,aorta,vena cava and ureter;avoiding the risk of irritation and injury to the infra-abdominal plexus;reducing mesh intestinal adhesions The risk of mesh intestinal adhesions is reduced;the risk of mesh erosion is reduced by lateral peritoneal suspension with preservation of the uterus.
(2) High success rate of anatomical repositioning and significant improvement of symptoms.Tension-free suspension without immobilization;high success rate of 93.6 % [13],reduced difficulty in intercourse;helps to improve constipation.
(3) Simple and quick,short learning curve and reduced suture use.
(4) Simple,standardized procedure with reduced peritoneal injury,simple crossing of the peritoneum,no need for fixation in any ligamentous structures,no involvement of the sacral promontory or other ligamentous connections,separate,tension-free lateral adjustment,mesh bimanual fixation outside the peritoneum.
Conclusion
Modern principles of pelvic floor reconstructive surgery include the restoration of anatomical structures and functional reconstruction.With the trend of surgery gradually becoming individualized and minimally invasive,the doctor-patient relationship model has also changed from pure biomedicine to a humanistic care medicine model,with more emphasis on individual subjective satisfaction with the medical disposition [14].Gynecological pelvic floor science widely believes that restoration of normal pelvic floor anatomy can achieve restoration of pelvic floor function [15].The modified uterine suspension implemented in our hospital,which uses its own tissue for pelvic floor reconstruction,has fewer complications and lower costs compared with mesh treatment for pelvic floor reconstruction,simple and easy to learn operation,less intraoperative bleeding,shorter operation time,less postoperative complications while preserving the uterus reduces the potential complications of hysterectomy,and preserving the uterus increases sexual satisfaction in patients psychologically and physiologically;postoperative vaginal anatomy restoration is more physiological The postoperative vaginal anatomy is more physiological.However,we still need to accumulate a lot of clinical data to further investigate whether the mesh has any disadvantages such as erosion and rejection.
In conclusion,comparing the advantages and disadvantages of various surgical procedures,laparoscopic lateral peritoneal suspension is a better surgical procedure for patients with POP,especially for those who wish to preserve the uterus,to restore the pelvic floor anatomy and improve the function of the pelvic floor,and to improve the quality of life of patients.The surgical procedure is safe,simple to learn,precise in efficacy,less traumatic,less postoperative pain,shorter hospital stay,faster recovery,and better preservation of vaginal function,which is worth promoting.
杂志排行
Clinical Research Communications的其它文章
- Dexmedetomidine:chaperone of anesthesia
- Clinical efficacy of integrated Chinese and western medicine in the treatment of the corona virus disease 2019(COVID-19):A meta-analysis
- Study on the pharmacological mechanism of chaihu shugan powder in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- The application research progress of intelligent robot in orthopedics
