Dexmedetomidine:chaperone of anesthesia
2022-01-13JunHuangChengYunHuFeiBiaoDaiJiaWuWangMingShengBaoChaoLiangTang
Jun Huang ,Cheng-Yun Hu ,Fei-Biao Dai ,Jia-Wu Wang ,Ming-Sheng Bao ,Chao-Liang Tang
1Department of Anesthesiology,The People’s Hospital of Chizhou,Chizhou 247000,China.2Department of Anesthesiology,Anhui Provincial Hospital,Wannan Medical College,Hefei 230001,China.3Department of Anesthesiology,The First Affiliated Hospital of USTC,Division of Life Sciences and Medicine,University of Science and Technology of China,Hefei 230001,China.
Abstract:Aim:In this review,it will mainly focus on clarifying the pharmacology of dexmedetomidine and discussing the past,present and future clinical applications of dexmedetomidine as an adjunct in anesthesia.Method:We have searched and reviewed the articles about the use of dexmedetomidine in clinical anesthesia,intensive care unit (ICU),painless gastroenteroscopy and painless labor over the past two decades.Recent findings:Dexmedetomidine,a highly selective agonist of alpha2-adrenergic receptors (alpha2-AR),was primarily approved by the U.S.Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for sedation in ICU due to its pharmacological characteristics with sedative,analgesic and sympatholytic effects.These properties make up the limitations of anesthetics,and it produces a“dexmedetomidine assisted”anesthesia mode as an adjuvant combining with other anesthesia methods,which are all termed as“DEX+”.These new methods can reduce the anesthetics requirement but prolong the action period and alleviate the adverse reactions of anesthetics,thus improving the anesthesia more effectively and safely.Summary:Dexmedetomidine possesses the unique properties exerting synergistic effects and alleviating the side effects as an adjuvant in anesthesia through different administration routes.It is beneficial for the patients’ long-term outcome and will be bound to be the leading innovator of anesthesia in future.
Keywords:dexmedetomidine;alpha2-adrenergic receptor;anesthesia;analgesia;sedation
Background
Early in the year of 1968,Miller demonstrated a study in dogs showing that administration with methyldopa and reserpine dose-dependently reduced the minimal alveolar concentration (MAC)of inhalation anesthetics by decreasing the levels of both central and peripheral norepinephrine [1].Later,the researchers proposed that alpha2-AR agonists had the effect of sedation,and found that oral administration of clonidine decreased the anesthetics requirements[2].These agents were usually used by veterinary for its sedative and analgesic effects,they were often given in combination with ketamine,which could reduce sympathetic responses and provide smooth induction of anesthesia and analgesia [3].Despite the extensive use of these agents as adjuvants to veterinary anesthesia,their anesthetic properties were relatively unknown to many practitioners in human anesthesia[4].
However,it was not concerned or approved by FDA,due to lacking the related alpha2-AR agonists in China,for the sedation in the patients who were to undergo general anesthesia and mechanical ventilation until 2009.The sedative and analgesic effects of alpha2-AR agonists have been recognized for 5 decades,although dexmedetomidine was not the first concerned alpha2-AR agonist,its highly selectiveness of alpha2-AR determines its more powerful adjuvant effect [5].
Dexmedetomidine is a highly selective drug of alpha2-AR and imidazoline receptor agonist,not only have the effects of analgesia,sedation and no respiratory inhibition,but also can inhibit sympathetic nerve excitability,enhance vagus nerve excitability and stabilize hemodynamics.With the deepening of clinical understanding of dexmedetomidine,it has become a common drug in the course of clinical perioperative procedure[6].
Pharmacology of dexmedetomidine
Mechanism of action
Alpha2-AR,a member of the G protein-coupled family,defined to have three iso-receptors including alpha2-AR A,alpha2-AR B,alpha2-AR C,usually express in the presynaptic and postsynaptic membrane of central and peripheral nerve system and also in other tissue including liver,pancreas,kidneys,eyes and platelets (Table 1)[7,8],which,when activated,shows up to inhibit the adenylate cyclase and reduce the formation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate(cAMP),thereby resulting in improving the intracellular anabolism,also,the calcium-stimulated potassium channel of nerve terminal allows the efflux of potassium to increase from neurons and reduce the influx of calcium ion,which results in the membrane hyperpolarization and the postsynaptic inhibition.On the other hand,the decrease of the calcium ion influx into the presynaptic membrane suppresses the release of norepinephrine from presynaptic membrane(Figure 1) [9].Equally,dexmedetomidine exhibits the same effects on every organ in human as other alpha2-AR agonists do[9,10].
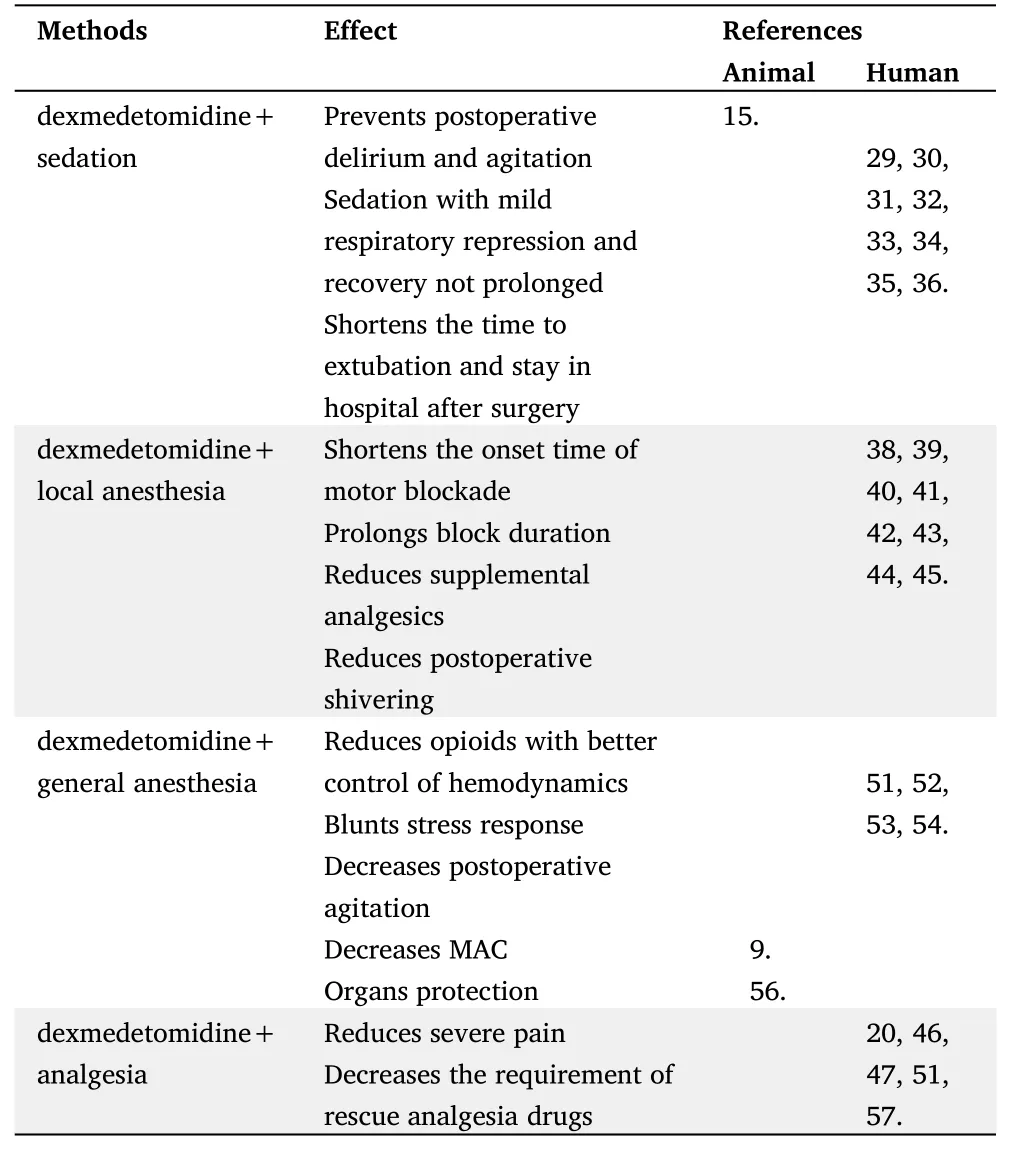
Table 2 “Dexmedetomidine+”anesthesia in conjunction with other methods.

Figure 1 The possible mechanism is coupled to the alpha2-AR through a G protein. (far left) the alpha2-AR,when activated via binding with alpha2-AR agonist (dexmedetomidine),inhibits the adenylate cyclase (AC),subsequently decreases the accumulation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP).(far right) the activated alpha2-AR inhibits the Ca2+ entry into the nerve terminal through the voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channel which is also coupled to the alpha2-AR through a G protein.This suppression blocks the fusion of norepinephrine (NE)-containing vesicles with the presynaptic membrane.In addition,the activation of the alpha2-AR is also involved in the opening of G protein-coupled outwardly K+-directed channel,which hyperpolarizes the postsynaptic membrane and suppresses the neural secretion.
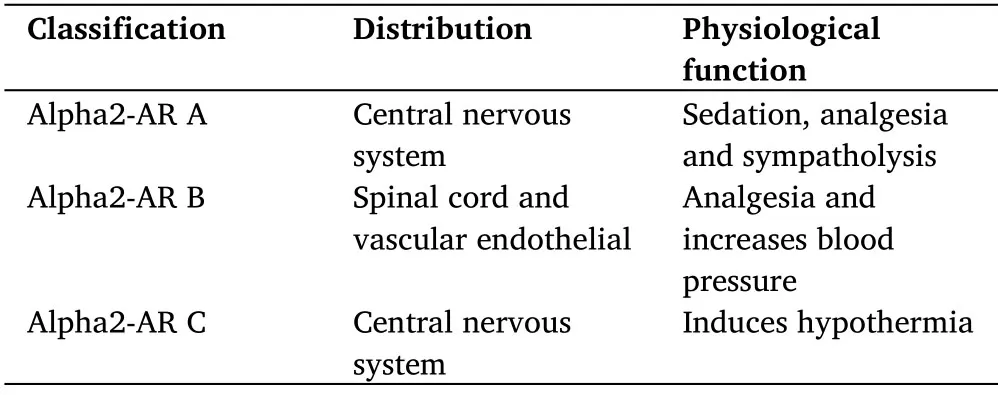
Table 1 Classification,distribution and physiological function of alpha2-AR
The clonidine,a selective agonist at the alpha2-AR with a ratio of 200:1 (α2:α1),has been shown to decrease the release of central and peripheral catecholamine,however,its use is limited at greater doses by the ceiling effect and alpha1 actions such as vasoconstriction,while dexmedetomidine has a higher affinity for the alpha2-AR about eight times that of clonidine (α2:α1=1600:1),with only 6 min of distribution half-life and 2h of elimination half-life,moreover,dexmedetomidine can reduce MAC significantly [11].In clinical studies,dexmedetomidine is also found to be an effective auxiliary drug for inhalation anesthetics [12].
Sedation
Dexmedetomidine,a highly selective alpha2-AR agonist,has been introduced into the practice of anesthesia for its sedative property via central mechanism in the brainstem-relayed Locus coeruleus (LC)which contains pathways involved in the maintenance of vigilance and a high prevalence of alpha2-AR.Dexmedetomidine stimulates the presynaptic membrane receptors,then negatively regulates to reduce the norepinephrine release from presynaptic membrane and blocks the activation of the norepinephrine signaling pathways from LC upward to subcortex [13].Further,the decrease of noradrenergic release from the LC disinhibits the release of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and galanin from the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO).This disinhibition is believed to suppress the neurons in the LC and tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN) which is the only source of arousal-promoting histamine,and thought to be responsible,at least in part,for loss of wakefulness,thereby attenuating the histamine receptors stimulation in the subcortex and inducing a sedative response that exhibits properties similar to natural sleep (Figure 2)[14,15].
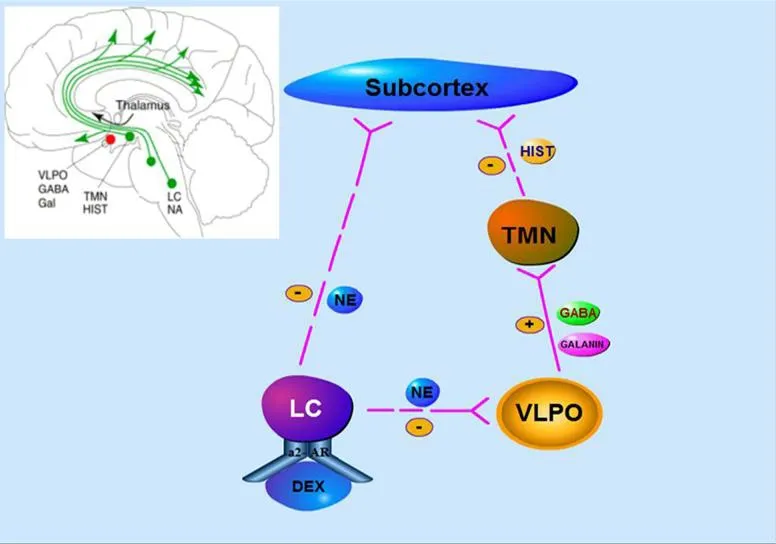
Figure 2 Simplified nonrapid eye movement (NREM)sleep-promoting pathway induced by dexmedetomidine. A dexmedetomidine-mediated inhibition of noradrenergic neurons firing in the locus coeruleus (LC) which is the site of initiation of alpha2-adrenergic anesthesia,releases a tonic noradrenergic inhibition of the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus (VLPO).The activated VLPO is believed to release γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and galanin into the tuberomammillary nucleus (TMN),subsequently inhibits its release of arousal-promoting histamine (HIST) into the cortex to induce loss of consciousness.
Dexmedetomidine is used to induce states of sedation which is described as homologous to nonrapid eye-movement (NREM) sleep with less delirium or agitation [16,17].However,recent studies showed that dexmedetomidine-induced sedation was characterized by behavioral,electrographic,and immune histochemical phenotypes which were distinctly different from normal sleep in the SD rats [18].
Analgesia
Dexmedetomidine has been employed in anesthesia not only for its sedation,but also for its analgesic properties via activation of the alpha2-AR.It acts on the presynaptic membrane and reduces the release of norepinephrine,which in turn leads to the hyperpolarization of neuronal membranes and inhibits the transmission of pain signals [8].However,use of these agents for analgesia in humans is limited by unwanted side effects.
Studies described alpha2-AR A and alpha2-AR C subtypes in rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG),alpha2-AR B and alpha2-AR C account for more than 95% of total alpha2-AR predominately in human DRG at all spinal cord levels.These findings provide an additional step in unraveling exact action site or sites of alpha2-AR agonists to exert analgesia [19].In the opiates addiction study,investigators demonstrated that activation of alpha2-AR in LC,an important conducting site of the nociceptive sensory neurons,reduced the physiologic and psychologic signs in opiates-dependent patients withdrawing from opiates,which revealed the alpha2-AR in LC may be the analgesia site out of spinal cord[20,21].
In rat models,dexmedetomidine was also found to have enhanced analgesic potency in the peripheral nervous system.Studies have shown that intrathecal dexmedetomidine may inhibit the expression of protein kinase C (PKC) in the spinal dorsal horn,thereby improving the behavioral ability and reducing the pain level of rats with chronic neuropathic pain [22].Further,the addition of dexmedetomidine during bupivacaine spinal anesthesia increases the pain threshold and prolongs block duration [23].
Cardiovascular system
Alpha2-AR agonist compounds were first found to be useful as anti-hypertensive agents.The known cardiovascular properties of these compounds include a biphasic response.In clinical practice,dexmedetomidine,when given by intravenous administration in humans,exerts the biphasic effects on blood pressure as initial transient hypertension,presumably mediated by alpha2-AR B-induced vasoconstrictive response in the peripheral vasculature and is related to elevated blood pressure and bradycardia mediated by baroreceptors,then followed by a longer lasting decrease,largely due to the activation of centrally located alpha2-AR,the reduction of the circulating catecholamine and the sympathetic tone.Also,it reduces the heart rate (HR) through the resetting of the baroreceptor system and an enhanced parasympathetic outflow [24].In addition,previous hypertension history has been found to be the only independent risk factor for hypertension or tachycardia after dexmedetomidine withdrawal [25].
Respiratory system
The dexmedetomidine is a new class of alpha2-AR agonist that is being investigated for use in ICU,with some properties additionally benefiting critically ill patients who require sedation,causing marked sedation with only mild respiratory depression in resting ventilation.Most animal experiments have shown that dexmedetomidine can only cause mild respiratory depression [26],and it is clinically confirmed that even higher doses of dexmedetomidine will not cause respiratory acidosis [27].However,recent studies have found that dexmedetomidine can reduce the regulation of hypoxia and hypercapnia on respiration when the sedation degree of dexmedetomidine is similar to that of propofol,which indicates the necessity of continuous respiratory monitoring during sedation with dexmedetomidine[28].
Other effects
In recent years,dexmedetomidine has been used as an adjuvant to anesthesia induction.Researchers show that effects of dexmedetomidine premedication in lowering intraocular pressure and the pressor response to intubation and laryngoscopy,reducing cerebral blood flow,cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) in cerebral surgeries.And the anti-postoperative shivering property has also been studied,which is due to the stimulation of the alpha2-AR B located in the temperature regulation center of the hypothalamus[29].In addition,dexmedetomidine was shown to have a good neuroprotective effect in vivo and in vitro experiments [30,31].
“Dexmedetomidine assisted”combined anesthesia (DEX+)
Dexmedetomidine was primarily introduced into the use in ICU,which provides analgesic,sedative and anxiolytic effects,and was widely extended into the clinical practice of anesthesia afterwards due to its properties above.It produces a“dexmedetomidine assisted”anesthesia mode as an adjuvant combining with other anesthesia methods (Figure 3).
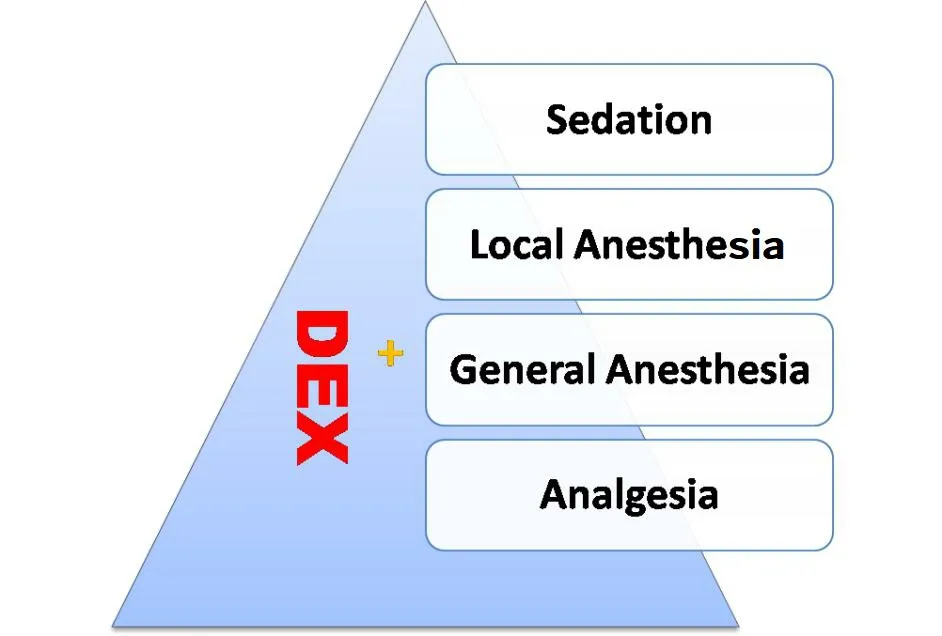
Figure 3 “Dexmedetomidine+”anesthesia in conjunction with other methods.
DEX+sedation
Agitated delirium was particularly problematic among the patients receiving mechanical ventilation in ICU setting,and dexmedetomidine was primarily identified to be able to shorten this established delirium and the time to extubation with rare adverse events.Subsequently,it was approved by the FDA to be used for sedation in the non-intubation patients,which was further confirmed by several multi-center studies.The investigators suggested that dexmedetomidine was safer,more effective and less delirium in sedation of patients undergoing mechanical ventilation in ICU after cardiovascular surgery,and had good hemodynamic stability with compared to the patients receiving propofol [32-35].However,which of note was that some studies were of dexmedetomidine as a sedative agent rather than as a therapy for delirium.
Interestingly,a lately randomized,double-blind,placebo-controlled trial showed that the incidence of post-operative delirium was reduced from 44% to 18% when dexmedetomidine was given to patients aged≥60 years undergoing cardiac and non-cardiac surgery during perioperative period [36].
Dexmedetomidine is a highly selective agonist of alpha2-AR which provides conscious sedation with adequate analgesia and no respiratory depression.It has been widely employed not only in the operation room but also during other procedures such as upper gastrointestinal system endoscopy,local or intraspinal anesthesia,awake procedures and for performing children’s examination procedure,which attenuates stress responses to procedures with better patients tolerance and hemodynamic stability,in addition,the patients recover rapidly after use [37-39].
Dexmedetomidine is considered,at present,the most commonly used alternative to propofol,a player in anesthesia,to deliver conscious sedation with greater safety in terms of hemodynamic stability and less respiratory depression as well as reduced number of adverse events,thus,as some perspectives of researchers go that the dexmedetomidine is most likely to replace the propofol to be a leader player in anesthesia as a sedation agent [40].
DEX+regional anesthesia
The peripheral nerve block may be used for surgical anesthesia alone or combining with general anesthesia for improving the analgesia in patients.Some adjuvants,such as opiates,midazolam,have been mixed into local anesthetics attempting to enhance the blockade and postoperative analgesia,but with some risks of adverse effects.
Clinical trials have confirmed the efficacy of alpha2-AR agonists in regional blockade anesthesia techniques.The addition of dexmedetomidine,a highly selective alpha2-AR agonist,to local anesthetics decreased the onset time of motor and sensory block,prolonged the duration of block significantly,as well as postoperative analgesia,and reduced the requirement for analgesic [41-44].Furthermore,no matter intravenous injection or subarachnoid or epidural administration of dexmedetomidine,the incidence of postoperative shivering can be reduced to varying degrees [45,46].A controlled trial indicated that both perineural and intravenous administration of dexmedetomidine in conjunction with local anesthetic generate a similar blockade effect without prolonging the duration of motor blockade [47].
In addition to the use of dexmedetomidine in regional anesthesia,infusion of the dexmedetomidine in conjunction with local anesthetic improves the analgesia and the sensory blockade effect significantly with shortened onset time of the motor blockade,which can be safely used in cesarean [41,48].Moreover,the intra-articular and the intranasal administrations of the dexmedetomidine also work [49,50].
Local anesthetics are inherently toxic to neurons via disruption of signal transmission and cell membrane as well as subcellular proteins.Fortunately,safety data showed that both intrathecal and peripheral administration of dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant were found to improve block duration without neurotoxic properties through blockade of the hyperpolarization-activated cation current and synaptic transmission,and actually decrease perineural inflammation compared with local anesthetic alone due in part to reducing the binding activity of nuclear factor kappa-B[51].
DEX+general anesthesia
In clinical practice,combining epidural with general anesthesia may benefit patients undergoing major thoracic,and abdominal surgery,epidural anesthesia can suppress sympathetic hyperactivity and block the stress response to surgery,spare the use of opioids.However,epidural catheter placement is of risks and contraindications,including technical failure,back pain,and local anesthetic toxicity and neurologic complications.
In view of the extensive use of opioids in perioperative period,Song et al.conducted a prospective study on opioid-free anesthesia(OFA),which will provide a scientific basis for the efficacy of OFA [52].However,recent studies have shown that balanced OFA with dexmedetomidine will lead to more serious adverse events,such as bradycardia,hypoxemia and prolonged extubation time during post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) [53].Also,dexmedetomidine,with the properties of analgesia,sedation and anti-sympathetic tone,inhibits the stress responses to intubation and surgeries,reduces postoperative opioid consumption,the patients recover rapidly from anesthesia with less postoperative agitation and delirium,which compensates for shortcomings of current general anesthetics [54-57].In addition,dexmedetomidine has been found to exert organ protection both in animal experiments and in clinic[58,59].
DEX+analgesia
Dexmedetomidine is the most selected alpha2-AR agonist clinically available with a short terminal half-life (around 2 h) and produces anti-nociception.A meta-analysis showed an evidence that dexmedetomidine administration leads to less postoperative pain,reduced consumption of opioid,with the recovery time not prolonged,and a lower risk of opioid-related adverse events [21,54].
Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) by intravenous opioids allows the individualization of pain management,which is a safe and effective strategy to obtain a satisfactory postoperative pain relief.However,opioid-related side effects such as nausea,vomiting,pruritus,and constipation are a major concern.The dexmedetomidine-opioids combination greatly attenuates those adverse events and improves the quality of analgesia without respiratory depression and bradycardia [21,60].
Conclusion
The alpha2-AR agonists have been employed to treat hypertension and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder for decades.In more recent years,dexmedetomidine,a class of alpha2-AR agonist,has been introduced into use as adjuvants to exert synergistic effects.It delivers conscious sedation with mild respiratory depression,reduces the general anesthetics requirements with greater hemodynamic stability and early extubation,in addition,the patients rouse with less agitation as well as postoperative shivering.Moreover,it enhances the efficacy of the local anesthetics in regional block.An increasing number of basic researches and clinical trials on dexmedetomidine have been carried out in the past decades,we still need large sample,multi-center and high-quality clinical researches in clinical practice to further confirm the indications except the instructions.
Contributions to the literature on applications of dexmedetomidine in paediatric have increased over recent years.Some studies have suggested the dexmedetomidine to be neuroprotective,inhibiting apoptosis in animals and humans.However,currently,there is no established approval for administration of dexmedetomidine to the paediatric population worldwide.Thus,a comprehensive understanding of the pharmacological,pharmacokinetic,and pharmacodynamic effects of dexmedetomidine is crucial to maximize its safe,efficacious,and efficient use in paediatric anesthesia.What’s more,we are still exploring the application of dexmedetomidine to replace the general anesthetics or opioids.
In general,the dexmedetomidine,as mentioned above,produces a“dexmedetomidine assisted”(DEX +) anesthesia in combination with other anesthesia methods,which,as the“internet +”changes the world and bring us more convenience,will inevitably play the leading role in the anesthesia innovation in future to escort for patients’ safety and comfort.
杂志排行
Clinical Research Communications的其它文章
- Clinical analysis of laparoscopic lateral peritoneal suspension in the treatment of severe pelvic organ prolapse
- Clinical efficacy of integrated Chinese and western medicine in the treatment of the corona virus disease 2019(COVID-19):A meta-analysis
- Study on the pharmacological mechanism of chaihu shugan powder in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- The application research progress of intelligent robot in orthopedics
