基于区域划分的农村有源配电网动态重构方法
2021-12-30刘志虹盛万兴杜松怀
刘志虹,盛万兴,杜松怀,苏 娟,夏 越
基于区域划分的农村有源配电网动态重构方法
刘志虹,盛万兴,杜松怀,苏 娟※,夏 越
(中国农业大学信息与电气工程学院,北京 100083)
分布式电源和电动汽车的大规模接入,使得农村配电网的“源-荷”侧呈现显著不确定性。传统农村配电网的拓扑结构无法应对“源-荷”双重不确定性所带来的冲击和影响,急需研究新的农村有源配电网动态重构方法。该研究考虑“源-荷”时变特性,提出了一种基于区域划分的农村有源配电网动态重构方法。首先,对配电网络结构进行区域初始划分,确定主干线区域和分支线区域;然后,以促进区域间分布式电源的协同应用为目标,基于图论算法对区域初始划分结果进行动态优化;其次,对网络重构方案进行网络拓扑约束的检验与修正;最后,采用快速非支配排序策略确定最优方案。通过IEEE 33节点和PG&E 69节点算例验证了所提方法的可行性与有效性。算例结果表明,所提方法能够有效促进分布式电源消纳、降低线损和改善电压分布。尤其是在69节点算例中所提算法的优化效果更显著,提升了系统日DG平均消纳利用率16.09个百分点,日线损降低了55.32%,研究可为农村有源配电网重构提供参考。。
能源;算法;农村有源配电网;区域划分;网络动态重构
0 引 言
传统农村配电网多采用辐射式单向供电的方式,以开环形式运行[1-2]。与城市配电网相比,农村配电网的供电模式较为单一,优化运行的调控能力有限。近年来,大量的光伏、风电等分布式电源(Distributed Generation,DG)接入农村配电网。当前农村配电网的网络结构、DG并网的位置与容量、线路传输容量等系统条件,它们与不断增加的农村电力需求产生了冲突。此外,电动汽车(Electric Vehicle,EV)等柔性负荷的并网加剧了负荷侧的波动。传统农村配电网的网络结构无法灵活、高效地应对DG与负荷双重不确定性给配电网运行带来的影响,容易产生弃电、网损增加、电压越限等问题[3-7]。因此,需要一种智能优化控制技术可以灵活、高效地应对DG与负荷的双重不确定性,来增强农村配电网安全可靠经济运行能力。
配电网重构(Distribution Network Reconfiguration,DNR)是配电网优化运行控制的重要手段[8]。DNR是通过改变线路中联络开关与分段开关的开/合状态来寻求拓扑结构,使配电网以更可靠、更经济的方式运行[9]。DNR可分为静态重构与动态重构两类[10]。与静态重构相比,动态重构可以充分考虑DG与负荷的时变特性,根据农村配电网的运行工况对研究周期内的网络结构进行动态优化,从而更具灵活性与实用性。
目前国内外学者对配电网动态重构的研究已有一些成果。余健明等[11]提出了一种配电网动态分时段重构方法,将研究时段分成多个连续的时间间隔,以网损最小为目标函数,分别进行各时间间隔静态重构。Shariatkhah等[12]根据负荷波动聚类进行时段划分,以损耗成本、中断成本和切换成本为优化目标,通过分时段静态重构实现动态重构。赵静翔等[13]提出了一种基于信息熵时段划分的等效日负荷曲线分段方法,建立了以日损失费用最低为目标的动态重构模型,利用基于十进制编码的改进杂草混合算法进行求解。李振坤等[14]考虑到负荷的波动特性,提出了一种基于多代理技术的配电网动态重构方法,利用混合粒子群算法进行多时段静态重构求解。王淳等[15]采用最优模糊C均值聚类技术进行负荷聚类,将配电网动态重构转换为以聚类中心表示负荷状态的多个静态重构问题。Zhu等[16]在实时调度阶段考虑了负荷的时变特性,研究了配电网每小时动态重构对DG消纳的效用。易海川等[17]考虑了DG在不同时段出力不同的特性,以提高配电网对DG的接纳能力为优化目标构建了动态重构模型,并用遗传算法对其进行求解。文献[11-17]仅考虑了负荷或者DG的时变特性,这种假设导致了次优的解决方案。文献[18-19]充分考虑DG与负荷时变特性,构建了多目标配电网重构模型,但是仅适用于静态重构。傅晓飞等[20]综合考虑DG与负荷的不确定性,建立了配电网动态重构模型,并利用差分进化入侵杂草优化算法进行求解。唐浩等[21]综合考虑DG与负荷的时变特性,以网损费用和开关操作费用为目标函数,将配电网进行分时段动态重构。文献[21]的优化目标不包含DG消纳。Zhu等[22]考虑DG与负荷的随机特性,从DG规划的角度分析了每小时动态重构对于促进DG消纳的作用。付洋洋[23]提出了通过最小数目的开关操作来提高DG消纳能力的配电网多时段重构模型。上述文献大部分是基于时段划分进行的多时段静态重构合并来实现动态重构,时段的划分与合并存在一定的主观性。此外,常规的动态重构研究通常采用智能优化算法求解构建的数学模型以获得最优解,解的精度依赖于算法对优化模型的求解计算,存在一定程度的寻优误差,难以保证解的最优性。
基于上述背景,本文提出了一种基于区域划分的农村有源配电网动态重构方法。首先,提出了一种区域初始划分方法,对配电网主干线路、分支线路进行区域初始划分;然后,提出了一种基于图论的区域动态优化划分方法,对初始区域划分结果进行动态优化,以寻找所有的DNR可行方案;其次,采用快速非支配排序策略以确定最优方案;最后,通过算例验证所提方法的有效性。
1 农村有源配电网动态重构模型
本节描述了农村有源配电网动态重构问题的目标函数及其相关约束。
1.1 目标函数
1)DG消纳利用率
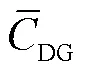

2)线路损耗
电力系统的线损是反映电力系统经济性的重要指标,在满足系统安全稳定运行的条件下,应尽最大可能降低系统的线损。系统总线损定义为[24]
1.2 约束条件
1)功率平衡约束
2)节点电压约束为
3)支路电流约束为
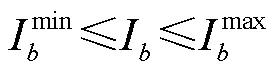
4)DG有功功率输出约束为
5)开关动作次数约束为
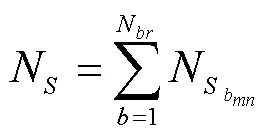

2 基于区域划分的农村有源配电网动态重构方法
配电网动态重构中描述开关状态的是离散整数变量,是一种复杂的非线性组合优化问题[25]。在综合考虑算法效率和全局寻优性能的基础上,本文提出了一种基于区域划分的农村有源配电网动态重构方法,并设计了相应的动态重构流程,实现步骤主要包括3部分,如图1所示。
2.1 农村有源配电网区域初始划分
本文依照以下2个原则针对存在环路的线路进行区域初始划分:
1)主干线路的区域初始划分原则
如果主干线路上包含可控DG,以DG接入节点前的开关为区域划分界线,从根节点到线路末端依次划分为一个独立的区域。即划分后的区域内最多包含一个DG。如果主干线路上不包含可控DG,则从根节点到主干线路末端划为一个独立的区域。
2)分支线路的区域初始划分原则
如果分支线路上包含可控DG,则分支线路的区域初始划分原则与主干线路的区域初始划分原则一致;如果分支线路上不包含可控DG,则从分支界定开关到支路末端划分为一个独立的区域。
基于上述区域初始划分原则,可将整个配电网络结构划分为多个初始区域(Initial Region,IR)。
2.2 基于区域动态优化划分方法寻找DNR可行方案
基于区域动态优化划分方法获取DNR可行方案,主要包括以下3个步骤:
1)区域电力供需分析
首先,基于区域初始划分结果和源-荷历史数据,根据公式(11)、(12)分别计算各区域的源-荷不平衡度与DG充裕度,分析当前各区域的电力供需平衡情况。
区域源-荷不平衡度是指研究区域内总DG与总负荷之间的差值占总负荷的比重。各区域源-荷不平衡度可以表示为
各区域的DG充裕度可以表示为
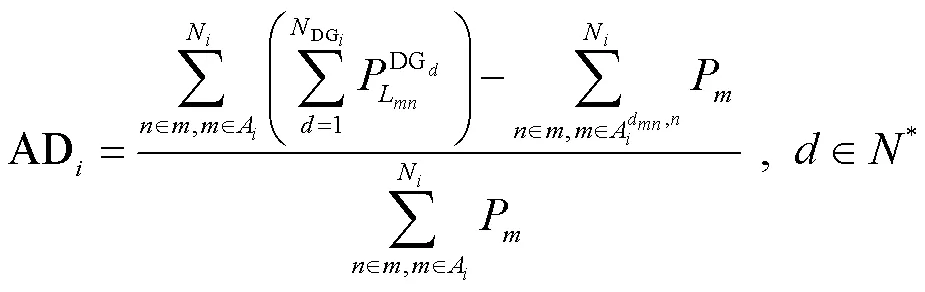
2)基于图论算法的区域动态优化划分
首先,采用图论算法中的广度优先遍历算法[26],确定各IR的邻接区域(Adjacent Region,AR)。然后,根据区域电力供需分析结果,筛选出具有电力互补特性的AR集合。假设配电网各线路的单位阻抗一致,则线路损耗与线路长度成正相关关系。再次,采用图论算法中的深度优先遍历算法[27],从具有电力互补特性的AR集合进一步中筛选出符合配电网潮流正向且距离相近的AR集合。最后,通过开关的优化控制实现若这些AR之间的灵活组合,形成多个新的区域,以最小各AR的源-荷不平衡度,即求解以下数学模型
式中1表示IR集合中相邻的A和A合并后的区域源-荷不平衡度;2表示A、A之间的线路长度,km。
3)DNR可行方案的检验与修正
为了保证配电网中不存在环网结构和孤岛,首先基于区域动态优化划分结果,采用图论中的深度优先遍历算法对合并区域之后的配电网络结构进行连通性和辐射性检验。然后,基于检验结果对环网进行解环、对孤岛进行连接,以满足配电网拓扑约束,从而可获得所有的DNR可行方案。
2.3 确定DNR最优方案
1)基于有源配电网动态重构模型的约束条件确定DNR有效方案
为避免DG接入可能引起电压越限的问题,遍历所有的可行方案,从中选取满节点电压约束条件的DNR方案。在此基础上,为了降低开关动作对其使用寿命以及电压稳定的影响,进一步筛选出满足开关动作次数约束条件的可行方案。
2)基于快速非支配排序策略确定最优方案
采用快速非支配排序遗传算法 2[28]中的快速非支配排序策略,对DNR有效方案进行非劣排序,可获得非劣排序层级最高的DNR最优方案。
根据上述的农村有源配电网区域初始划分原则、基于图论算法的配电网区域动态划分方法以及DNR最优方案搜索方法求解配电网动态重构问题,可根据配电网的实际运行工况对任意时间段的网络拓扑结构进行优化调整。如此反复循环,直至获得整个研究时段内的DNR最优方案集合。
3 算例分析
3.1 算例1:IEEE 33节点配电系统
3.1.1 测试数据
本文基于IEEE 33节点配电网标准算例[29],加入了分布式光伏、风力发电和EV充电站,来模拟源、荷具有时变特性的农村有源配电网,如图2所示。在节点6、9、15、22上分别接入了小型风机、风电场、小型光伏电站和光伏电站。各DG的额定容量见表1。在节点12上接入了EV充电站,额定容量为1MW。基于区域初始划分方法可以将配电网划分为4个主干线区域(A1~A4)和3个分支线区域(A5~A7),如图2所示。

表1 DG配置参数
假设在相同的地区、时间条件下,相同类型的DG出力特性一致,则相同类型的DG有功功率输出值与其额定容量呈正相关关系。本文将DG有功功率输出数值与DG额定容量的比值,定义为DG出力率。本文通过DG额定容量乘以DG出力率的变化值来模拟随时间变化的DG出力值,通过节点原始负荷乘以节点变化率来模拟随时间变化的负荷值。需要说明的是,采用其他方法来模拟各个节点负荷以及DG的出力时序变化情况,不会影响使用本文所提方法。重构前DG出力率以及负荷变化曲线如图3所示。
由图3可以看出,光伏与风力发电以及EV充电负荷皆存在很强的波动性、间歇性与随机性。源-荷侧的不确定性容易导致弃风弃光现象以及电压越限等问题,增加了配电网优化运行控制的难度。
3.1.2 结果分析
各时段重构得到的最优开关组合见表2,其中每个开关用其对应线路两端的节点编号表示。本文设定研究时段内每个开关的操作次数和所有开关的总操作次数上限分别为3和16次,可保证配电网动态重构的安全稳定性。由表2可知,随着负荷需求与DG出力的时序变化,相应时段的配电网重构最优开关组合也在不断调整。

表2 不同时段最优开关组合
本文对24 h内配电网动态重构前后的仿真结果进行对比分析。其中,线路损耗如图4所示;配电网总DG平均消纳利用情况,如图5所示。
由图4可以看出,配电网线损在网络结构经过优化之后有一定程度降低,在11:00至17:00时间段内降损效果明显,尤其是在14:00线路损耗降低了71.41%,降损效果尤为显著,说明该方法能有效提高配电网运行的经济性。
由图5所知,配电网络结构经过动态优化之后总DG的平均消纳率得到了较大幅度的提升,说明该方法能有效提高配电网的电力供需平衡能力和经济运行水平。
为了深入分析本文所提网络结构动态优化方法对各DG消纳利用的影响,因此对网络结构动态优化前后各DG的日平均消纳利用率进行了对比,如表3所示。

表3 配电网动态重构前后各DG日平均消纳利用对比分析
由表3可知,配电网络结构优化后每个DG的日内平均消纳率均有一定程度的提升,其中,DG4实现了完全消纳。网络结构优化后各DG消纳利用水平的上升,意味着该方法能降低弃风弃光现象出现的概率,因此该方法能有效提高配电网运行的经济性以及环保性。
上述是针对24 h时间段内配电网络结构优化前后仿真结果进行的分析,为了进一步分析本文所提方法在时间断面上对配电网运行的优化效果,基于图3显示的DG总发电在上午11:00左右达到顶峰,本文选取11:00时刻重构前后的配电网运行情况进行细致分析。其中,各DG消纳利用的变化情况见表4。经过潮流计算进行电压校验,配电网重构前后33个节点电压分布,如图6所示。
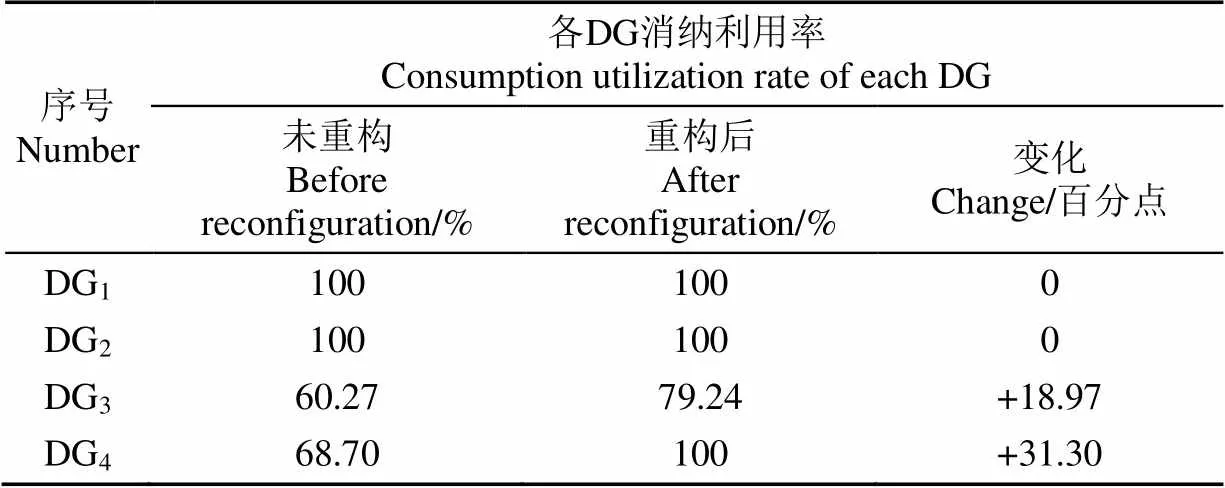
表4 11:00 DNR前后各DG消纳利用情况
由表4可知,在11:00根据区域动态优化划分方法得到的配电网络结构内部分DG的消纳利用率升高了。其中,DG1和DG2的消纳利用率在网络结构优化前后均达到了完全消纳,DG1和DG2在初始网络结构下实现了完全消纳,这与DG1和DG2的接入容量以及研究时间段内DG有功出力以及负荷大小相关;连接在22节点的DG4消纳利用率提升最显著,上升了31.30个百分点;DG3消纳利用率的提升效果也很明显,上升了18.97个百分点。
假设配电网线电压的基准值以根节点为准,则根节点电压标幺值为1.0。由图6可知,网络结构优化后各节点电压的标幺值都在0.95到1.05之间,符合节点电压上下限的要求。此外,配电网络结构优化后的节点电压有了一定的提升,尤其是DG接入点附近的电压提升最为显著。
结合表4与图6可知,虽然DG1和DG2的消纳利用率在网络结构优化前后均达到了完全消纳,但是初始网络结构下的节点电压存在越限问题,经过区域优化划分方法得到的网络结构下各节点电压均符合电压质量要求。
3.2 算例2:PG&E 69节点配电系统
3.2.1 测试数据
为进一步验证本文所提方法的有效性,本节采用复杂的PG&E 69节点配电系统[30]进行测试,系统的结构如图7所示。本文分别在节点23、38上接入了额定容量分别为0.8、1MW的光伏电站,在节点53、59上分别接入了额定容量均为0.8MW的风电场。基于区域初始划分方法可以将配电网络划分为2个主干线区域(A1、A2)以及6个分支线区域(A3~A8),如图7所示。
为保证配电网动态重构的安全稳定性,设定每个开关的操作次数和所有开关的操作次数上限分别为3次和20次。计算所采用的DG出力率的变化情况与图3中的DG变化曲线一致,负荷率变化曲线如图8所示。
3.2.2 结果分析
69节点配电系统动态重构结果对比见表5。
由表5可知,与未重构相比,动态重构后的配电网对DG的消纳利用率整体上升了16.09个百分点,线损降低了55.32%。
可以看出,该结果与采用IEEE 33节点测试系统所得结论一致,同样表明了所提方法能够促进DG消纳、提升系统运行的经济安全运行能力。

表5 69节点系统动态重构前后结果对比
4 结 论
在大规模DG和EV接入农村配电网的新形式下,本文围绕农村有源配电网的动态重构问题,提出了一种新的基于区域划分的农村有源配电网动态重构方法。主要研究工作及结论如下:
1)计及DG与负荷的双重时变特性,提出了一种农村有源配电网区域初始划分原则。根据区域初始划分原则,可以对主干线路和分支线路进行区域初始划分,形成初始配电网络划分图,为快速求解动态重构问题奠定基础。
2)提出了一种基于图论算法的区域动态优化划分方法,可根据农村有源配电网的实际运行工况对区域初始划分结果进行动态优化,从而获得区域间开关控制方案,有助于提高动态重构问题的求解效率。
3)基于IEEE 33节点和PG&E 69节点算例进行了仿真验证,仿真结果表明:所提方法在33节点算例中损耗降低效果很好,尤其是14:00时的网络损耗显著降低了71.41%,此时提高DG消耗的效果也是最明显的;在69节点算例中提升了系统日DG平均消纳率16.09个百分点,日线损降低了55.32%。这说明本文所提方法能够实现农村有源配电网提升DG消纳、降低线损以及改善电压质量等技术要求。
[1] Oureilidis K O, Bakirtzis E A, Demoulias C S. Frequency-based control of islanded microgrid with renewable energy sources and energy storage[J]. Journal of Modern Power Systems & Clean Energy, 2016, 4(1): 54-62.
[2] 董逸超,王守相,闫秉科. 配电网分布式电源接纳能力评估方法与提升技术研究综述[J]. 电网技术,2019(7):2258-2266.
Dong Yichao, Wang Shouxiang, Yan Bingke. Summary of research on evaluation method and improvement technology of distributed power supply acceptability in distribution network[J]. Power System Technology, 2019(7): 2258-2266. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 孟晓芳,朴在林,王英男,等. 中压配电网网架优化规划方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(11):164-164.
Meng Xiaofang, Piao Zailin, Wang Yingnan. Optimal planning method for medium voltage distribution network[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2011, 27(11): 164-164. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 苏向敬,陈思利,米阳,等. 分布式电池储能在含高比例可再生能源不平衡配电网中的序次优化配置[J]. 电网技术,2019,43(10):3698-3707.
Su Xiangjing, Chen Sili, Mi Yang, et al. Sequential optimization configuration of distributed battery energy storage in unbalanced distribution network with high proportion of renewable energy[J]. Power System Technology, 2019, 43(10): 3698-3707. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 牛焕娜,杨明皓,井天军,等. 农村主动型配电网优化调度线性模型与算法[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(16):190-197.
Niu Huanna, Yang Minghao, Jing Tianjun, et al. Linear optimal operation model and algorithm for active distribution network in rural areas[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(16): 190-197. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 孟晓芳,朴在林,王英男,等. 考虑分布式电源影响的配电网降损分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(25):128-131.
Meng Xiaofang, PiaoZailin, Wang Yingnan, et al. Analysis of distribution network loss considering influence of distributed generation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(25): 128-131. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 唐巍,薄博,丛鹏伟,等. 含分布式发电接入的农村电网多目标规划[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(增刊):132-137.
TangWei, Bo Bo, Cong Pengwei, et al. Multi-objective planning of rural power network incorporating distributed generation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(Supp1. ): 132-137. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 高燕,杨仁刚,李伟. 考虑分布式电源的农村配电网网络重构[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(9):162-169.
Gao Yan, Yang Rengang, Li Wei. Rural distribution network reconfiguration with dispersed generation[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(9): 162-169. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] Hamida I B, Salah S B, Msahli F, et al. Optimal network reconfiguration and renewable DG integration considering time sequence variation in load and DGs[J]. Renewable Energy, 2018, 121(6): 66-80.
[10] 翟鹤峰,杨明,赵利刚,等. 提升分布式电源接纳能力的配电网三相鲁棒动态重构[J]. 电力系统自动化,2019,43(18):35-42.
ZhaiHefeng, Yang Ming, Zhao Ligang, et al. Three-phase robust dynamic reconfiguration of distribution network to improve acceptance ability of distributed generator[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(18): 35-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 余健明,王征,许苗. 考虑负荷变化的配电网动态分时段重构[J]. 高电压技术,2007,33(9):125-128.
YuJianming, Wang Zheng, Xu Miao. Dynamic reconfiguration of distribution network with dividing time and considering load changes[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2007, 33(9): 125-128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] Shariatkhah M H, Haghifam M R, Salehi J, et al. Duration based reconfiguration of electric distribution networks using dynamic programming and harmony search algorithm[J]. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2012, 41(1): 1-10.
[13] 赵静翔,牛焕娜,王钰竹. 基于信息熵时段划分的主动配电网动态重构[J]. 电网技术,2017,41(2):402-408.
ZhaoJingxiang, Niu Huanna, Wang Yuzhu. Dynamic reconfiguration of active distribution network based on information entropy of time intervals[J]. Power System Technology, 2017, 41(2): 402-408. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 李振坤,陈星莺,赵波,等. 配电网动态重构的多代理协调优化方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2008,28(34):72-79.
Li Zhenkun, Chen Xingying, Zhao Bo, et al. Dynamic reconfiguration of the distribution network based on multi-agent systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2008, 28(34): 72-79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 王淳,高元海. 采用最优模糊C均值聚类和改进化学反应算法的配电网络动态重构[J]. 中国电机工程学报,2014,34(10):1682-1691.
Wang Chun, Gao Yuanhai. Dynamic reconfiguration of distribution network based on optimal fuzzy C-means clustering and improved chemical reaction optimization[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2014, 34(10): 1682-1691. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] Zhu J, Wu Z, Jiang P, et al. An improved PSO algorithm based on statistics for distribution network reconfiguration to increase the penetration of distributed generations[J]. 2015, DoI: 10.1049.CP.2015.09.02.
[17] 易海川,张彼德,王海颖,等. 提高DG接纳能力的配电网动态重构方法[J]. 电网技术,2016,40(5):1431-1436.
Yi Haichuan, Zhang Bide, Wang Haiying, et al. Distribution network dynamic reconfiguration method for improving distribution network’s ability of accepting DG[J]. Power System Technology, 2016, 40(5): 1431-1436. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 丛鹏伟,唐巍,张璐,等. 基于机会约束规划考虑DG与负荷多状态的配电网重构[J]. 电网技术,2013,37(9):2573-2579.
Cong Pengwei, Tang Wei, Zhang Lu, et al. Chance-constrained programming based distribution network reconfiguration considering multi-states of distributed generation and load[J]. Power System Technology, 2013, 37(9): 2573-2579. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 赵晶晶,李新,彭怡,等. 基于粒子群优化算法的配电网重构和分布式电源注入功率综合优化算法[J]. 电网技术,2009,33(17):162-166.
Zhao Jingjing, Li Xin, Peng Yi, et al. A comprehensive optimization algorithm for injection power of distributed generation and distribution network reconfiguration based on particle swarm optimization[J]. Power System Technology, 2009, 33(17): 162-166. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 傅晓飞,纪坤华,廖天明,等. 含间歇性DG的主动配电网动态重构研究[J]. 浙江电力,2018,37(11):73-81.
Fu Xiaofei, Ji Kunhua, Liao Tianming, et al. Study on dynamic reconfiguration of active distribution network considering intermittent DG[J]. Zhejiang Electric Power, 2018, 37(11): 73-81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 唐浩,周步祥,彭章刚,等. 采用改进细菌觅食算法的含分布式电源配电网动态重构[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报,2017,29(4):122-128.
Tang Hao, Zhou Buxiang, Peng Zhanggang, et al. Dynamic reconfiguration of distribution network with distributed generations using improved bacterial foraging algorithm[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2017, 29(4): 122-128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] Zhu J, Gu W, Lou G, et al. Learning automata based methodology for optimal allocation of renewable distributed generation considering network reconfiguration[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 14275-14288.
[23] 付洋洋. 提高可再生能源消纳能力的配电网多时段重构研究[D]. 天津:天津大学,2018.
Fu Yangyang. Research on Multi-period Network Reconfiguration for Increasing the Hosting Capacity of Distribution Networks[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] Singh J, Tiwari R. Real power loss minimisation of smart grid with electric vehicles using distribution feeder reconfiguration[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2019, 13(18): 4249-4261.
[25] 陈正鹏,黄纯,张亚萍,等. 基于改进双种群遗传算法的含分布式电源配电网重构[J]. 电力系统及其自动化学报,2017,29(4):78-83.
Chen Zhengpeng, Huang Chun, Zhang Yaping, et al. Distribution network reconfiguration with different distributed generations based on improved dual population genetic algorithm[J]. Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2017, 29(4): 78-83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] Peng J, Wenli D. Multi-objective modeling and optimization for scheduling of cracking furnace systems[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2017, 25(8): 992-999.
[27] 汤旻安,张凯越,许希元. 基于启发式规则与AHP-CRITIC算法的配电网故障恢复策略[J]. 电力系统保护与控制,2020,48(14):1-9.
Tang Wenan, Zhang Kaiyue, Xu Xiyuan. Service restoration strategy of a distribution network based on heuristic rules and the AHP-CRITIC algorithm[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(14): 1-9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 徐成司,董树锋,孙洲,等. 基于网络简化和深度优先遍历的配电网路径搜索算法[J]. 电力系统自动化,2017,41(24):170-176.
Xu Chengsi, Dong Shufeng, Sun Zhou, et al. A path searching algorithm for distribution network based on network simplification and depth first traversal[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2017, 41(24): 170-176. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] Nguyen T T, Nguyen T T, Nguyen N A. Optimal network reconfiguration to reduce power loss using an initial searching point for continuous genetic algorithm[J]. Complexity, 2020, 2020(6): 1-21.
[30] Moghaddam M J H, Kalam A, Shi J, et al. A new model for reconfiguration and distributed generation allocation in distribution network considering power quality indices and network losses[J]. IEEE Systems Journal, 2020, 14(3): 1-9.
Dynamic reconfiguration method of rural active distribution network based on regional division
Liu Zhihong, Sheng Wanxing, Du Songhuai, Su Juan※, Xia Yue
(,,100083,)
In recent years, under the guidance of China's green energy development strategy, a large number of photovoltaic, wind power and other DGs have been connected to the rural distribution network. The current rural distribution network structure, DG grid-connected location and capacity, line transmission capacity and other system conditions are in conflict with the ever-increasing rural power demand. DG output and load demand are continuously changing with time. The large-scale access of DGs and EVs has made the “source-load” side of the rural distribution network present significant uncertainty. The traditional topology of rural distribution network cannot cope with the impact of this “source-load” double uncertainty. Therefore, it is urgent to study a new method of dynamic reconfiguration for rural active distribution network. This paper establishes a dynamic reconfiguration model of active distribution network with DG consumption and line loss as objective functions. Taking into account the time-varying characteristics of “source-load”, this paper proposes a new method of dynamic reconfiguration of rural active distribution network based on regional division, and designs the process of this dynamic reconfiguration method. In order to improve the efficiency of solving the problem of dynamic reconfiguration of active distribution network, a regional division method is proposed for the first time. The regional division method includes two parts: The initial division of regions and the optimized division of regions. The dynamic reconfiguration method of active distribution network based on area division mainly includes the following four steps. Firstly, the distribution network structure is divided into several initial regions which include main line regions and branch line regions based on the regional initial division method. Secondly, with the goal of promoting the flexible and efficient combined application of DGs between regions, the result of regional initial division is optimized dynamically based on the breadth-first traversal algorithm in the graph theory algorithm. Thirdly, based on the obtained results of dynamic regional optimization, the depth-first traversal algorithm is used to test and modify the DNR scheme to meet the topology constraints of the distribution network. At this time, all feasible DNR schemes can be obtained. Finally, the fast non-dominated sorting strategy is adopted to select the best network reconfiguration scheme that meets the constraints such as node voltage. To validate the performance of the proposed method, it is tested on the well-known IEEE 33-node and PG&E 69-node distribution system. The simulation result of 33-node distribution system shows that the loss reduction effect of the proposed method is very good. Especially at 14:00, the loss reduction effect of the distribution network was the most obvious, which was reduced by 71.41%. At this time, the effect of increasing the utilization rate of DG consumption is also obvious. On this basis, the proposed method on the consumption of each DG was deeply analyzed in this article. Result shows that the proposed method can achieve complete consumption of DG. The voltage of each node under the network structure obtained by the regional optimization division method meets the voltage quality requirements. In addition, the average daily DG consumption rate of the PG&E 69-node distribution system was increased by 16.09 percent point, and the daily line loss was reduced by 55.32%. The effectiveness of the proposed method is verified by the simulation of these two case studies. The simulation results show that the proposed method can fully switch and adjust the ability to improve the absorption capacity of the distributed power, reduce the line loss, suppress the fluctuation of the distributed power, and keep the node voltage smooth.
energy; algorithm; rural active distribution network; regional division; network dynamic reconfiguration
刘志虹,盛万兴,杜松怀,等. 基于区域划分的农村有源配电网动态重构方法[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(20):248-255.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.20.028 http://www.tcsae.org
Liu Zhihong, Sheng Wanxing, Du Songhuai, et al. Dynamic reconfiguration method of rural active distribution network based on regional division[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2021, 37(20): 248-255. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.20.028 http://www.tcsae.org
2021-07-15
2021-10-11
国家自然科学基金项目(52007194);国家电网公司总部科技项目(SGXJWL00YJJS1801742);中国农业大学2115人才工程资助
刘志虹,博士研究生,研究方向为配电网优化运行与控制。Email:zhihongliu@cau.edu.cn
苏娟,博士,副教授,博士生导师,研究方向为农业电气化与自动化、电力市场等。Email:sujuan@cau.edu.cn
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2021.20.028
TM761
A
1002-6819(2021)-20-0248-08
