Villagers’ Satisfaction Evaluation of Rural "Toilet Revolution" in Qinghai Province: A Case Study of Huzhu Tu Autonomous County
2021-12-30XiaomingLIU
Xiaoming LIU
Qinghai University School of Finance and Economics, Xining 810016, China
Abstract With the effect of rural toilet improvement and villagers’ satisfaction as the evaluation targets, the evaluation index system was constructed by mastering the actual situation of rural toilet improvement in Huzhu County, including villagers’ acceptability of rural toilets, construction of toilets after improvement, treatment methods and effects of fecal sewage, management of toilet equipment after toilet improvement. The indexes were assigned with weights by expert scoring, and the evaluation model of the effect of rural toilet improvement in Huzhu County was established by entropy weight method and fuzzy evaluation analysis method. The result is of great significance to the follow-up management and protection of rural toilets.
Key words Toilet improvement, Rural revitalization, Toilet revolution, Huzhu County
1 Introduction
The "toilet revolution" in rural areas is not only an important part of rural revitalization, but also closely related to the implementation of beautiful rural construction. The "toilet revolution" has developed rapidly in rural areas across the country. With the continuous advancement of rural "toilet revolution", there will be problems in the middle and late stage of toilet improvement. With the effect of rural toilet improvement and villagers’ satisfaction as the evaluation targets, the evaluation index system was constructed by mastering the actual situation of rural toilet improvement in Huzhu County from the aspects of villagers’ acceptability of rural toilets, construction of toilets after improvement, treatment methods and effects of fecal sewage, and management of toilet equipment after toilet improvement and combining with field visits and research. The evaluation model was established by entropy weight method and fuzzy evaluation analysis method, and case analysis was conducted to explore the problems of rural toilet improvement, paving the way for follow-up perfection of countermeasures for toilet improvement system.
2 Basic situation of toilet improvement in Huzhu County, Qinghai Province
Huzhu Tu Autonomous County locates in the east of Qinghai Province, north of Haidong City, which is under the jurisdiction of Haidong City, Qinghai Province. It is the only Tu autonomous county in China and also the county with the largest number of Tu ethnic groups. Affected by economic, natural, folk and other factors, the villagers of the vast rural households of Huzhu County have been using pit toilets for a long time, which are very simple, with poor sanitary conditions, and it is difficult to achieve water-flush harmless treatment of feces. The three-year battle of "toilet revolution" was launched in 2018. By December 2020, the 18 villages and towns in Huzhu County had undertaken the task of 333 284 toilet improvement in three years, 30 127 of which had been completed. At present, there are 42 024 traditional pit toilets and 35 357 sanitary toilets, among which 18 047 are harmless toilets.
3 Thinking of toilet improvement evaluation
3.1 Selection of model
The construction of beautiful countryside is an important task in the process of urban and rural integration, among which the "toilet revolution" is particularly important. In order to better understand the convenience of toilet improvement for rural residents, as well as rural residents’ needs for toilets, this evaluation came into being.However, for the evaluation of villagers’ satisfaction after "toilet improvement" in rural areas of Huzhu County, its satisfaction or not is a fuzzy concept, which is non-deterministic. To make a deep research on villagers’ satisfaction, uncertain fuzzy concept should be quantitatively analyzed. The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model in fuzzy mathematics was used to analyze villagers’ satisfaction.
3.2 Calculation process
In this paper, the evaluation of villagers’ satisfaction after "toilet improvement" in rural Huzhu County was analyzed by fuzzy comprehensive evaluation model from the following aspects. (i) The object that needed to be evaluated should be clearly defined, that is, the factor set of the study should be clearly defined. (ii) The evaluation levels of the research objects were established, that is, the evaluation level rangeS
={S
,S
,S
,…S
.
} was determined. The final evaluation result was a vector containing several levels, which was the design comment set. (iii) The data were statistically analyzed by fuzzy evaluation method, and then the membership degree of single factor index was determined. Afterwards, the evaluation matrix was established, and finally the fuzzy relation matrix was determined. (iv) By multiplying the weights of indexes at all levels by the corresponding fuzzy evaluation matrix, the evaluation results at all levels (scores) were obtained. (v) The comprehensive score of the index system was calculated by weighted average method, and the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation result was obtained. (vi) The results of fuzzy comprehensive evaluation were summarized and analyzed.4 Construction of evaluation index system
4.1 Selection of index system
4.1.1
Basis of index selection. Following the principle of typicality, systematicness and simplicity, the evaluation indexes were selected from different levels according to the principle of "few, precise, simple and easy to operate" in combination with the relevant policies of the state, the opinions of government officials and experts of university professors.(i) Actual situation of toilet improvement. In the process of implementing the "toilet revolution" in rural areas of Huzhu County, the prominent toilet problems concerned by the government and villagers were selected as evaluation indexes, and then the aspects closely related to the use of toilets by villagers were selected as evaluation indexes. The evaluation indexes were directly or indirectly related to the effect of rural toilet reconstruction and played a leading role in the evaluation effect.
(ii) Refer to relevant policies, norms and standards. In 2009, in accordance with theLaw
of
the
People
’s
Republic
of
China
on
the
Prevention
and
Treatment
of
Infectious
Diseases
, the National Patriotic Health Committee formulated theAdministrative
Measures
for
Improving
Toilets
in
Rural
Areas
(Trial
) and theTechnical
Specifications
for
Improving
Toilets
in
Rural
areas
(Trial
), in order to standardize the work of improving toilets in rural areas and speed up the process of improving toilets in rural areas. In 2012, the Ministry of Health and the Standardization Administration of China issued theSanitary
Standards
for
Rural
Toilets
, providing a basis for the sanitary standards of rural toilets across the country. In 2018, the No.1 Central DocumentOpinions
on
the
Implementation
of
the
Rural
Revitalization
Strategy
proposed to promote the "toilet revolution" in rural areas, vigorously carry out the renovation of rural households’ sanitary toilets, and carry out the work of fecal sewage treatment. On February 5 of the same year, the General Office of the State Council issued theThree
-year
Action
Plan
for
the
Improvement
of
Rural
Living
Environment
, which took the treatment of toilet fecal sewage as one of its key tasks and encouraged local governments to make resource utilization of toilet feces and livestock and poultry waste in accordance with local conditions. In 2019, the No.1 Central Document mentioned that rural living environment improvement tasks focusing on rural garbage and sewage treatment, toilet revolution and village appearance improvement should be comprehensively carried out by learning from the toilet improvement experience of "demonstration of thousands of villages and renovation of ten thousands of villages" in Zhejiang Province. In 2020, the No.1 Central Document proposed that the harmless transformation of rural household toilets should be basically completed in the eastern regions and the inner suburbs of central and western cities, while other areas should set goals and tasks realistically. In 2021, the No.1 Central Document mentioned that the "toilet revolution" in rural areas should be promoted in a classified and orderly manner; the research and development of sanitary toilet technology and products suitable for dry and cold areas should be accelerated; and the renovation of rural household toilets in central and western regions should be strengthened. These policies and standards on toilet improvement involved the evaluation and management of rural toilets. By referring to these normative policies and requirements, more reasonable indexes could be selected.4.1.2
Determination of influencing factors of rural toilet improvement. According to the actual situation of rural toilet improvement in Huzhu County, relevant materials and policies, visits to villagers in Huzhu County, and the demonstration of teachers and experts in relevant universities, four main influencing factors were formulated, including villagers’ acceptability of rural toilets B(toilet environment after improvement C, villagers’ use experience after improvement C, cost of toilet improvement C), construction of toilets after improvement B(reasonable layout of toilet space C, structure of toilet C), treatment methods and effects of fecal sewage after improvement B(feces treatment and sewage discharge C, harmless treatment effect C, environmental threat C), management of toilet equipment after toilet improvement B(system improvement and personnel management C, late maintenance and cost of toilet C, daily consumption of toilet C). The evaluation index system of rural toilet improvement in Huzhu County was composed of 4 criterion layers and 11 index layers (Table 1).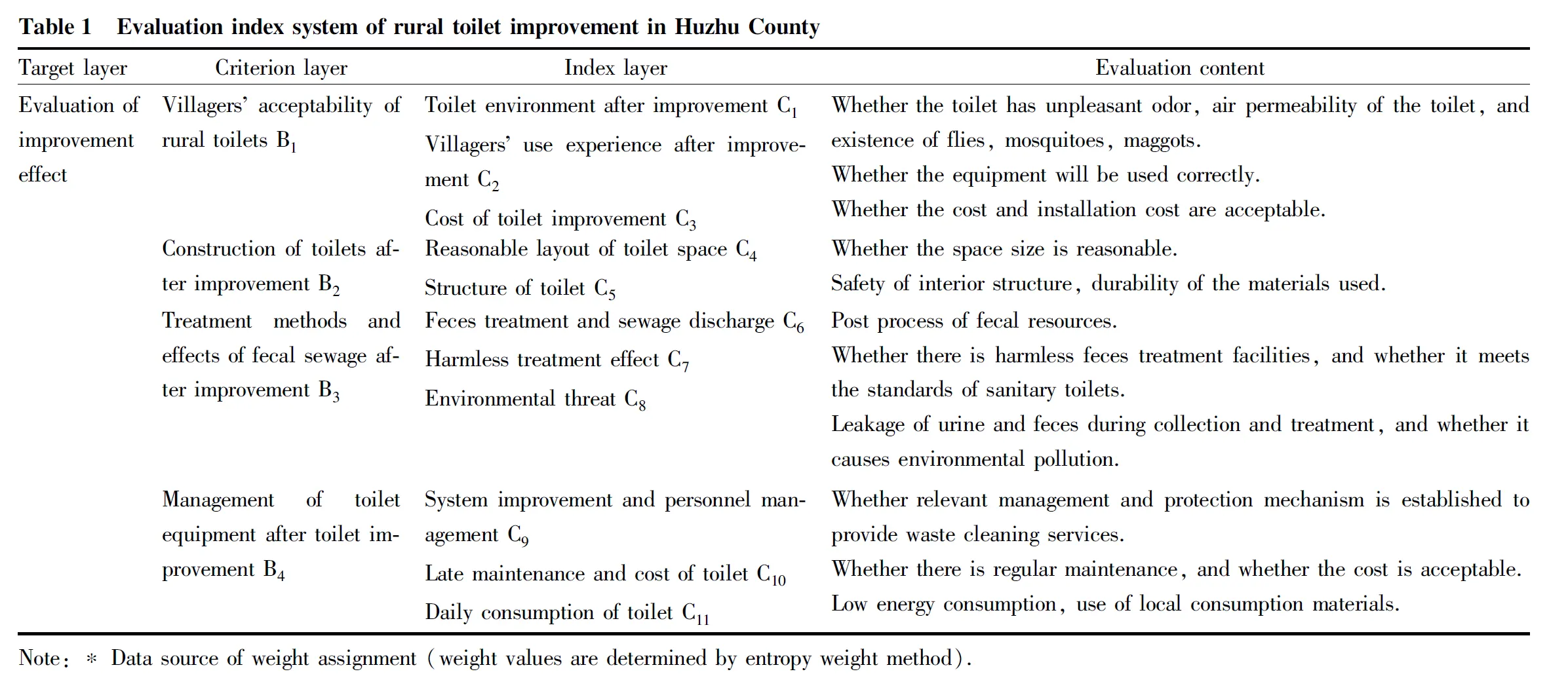
4.2 Principles of index construction
4.2.1
All-rounded principle. Combined with comprehensive analysis of main factors affecting the effect of rural toilet improvement, the comprehensive effect of rural toilet improvement should be comprehensively evaluated, and then these main factors should be completely integrated into the evaluation index system.4.2.2
Universality principle. The evaluation method should be suitable enough for the evaluation of rural toilet improvement effect in other areas, and the adopted index system and evaluation content should have universal applicability. Index is a common phenomenon and key concern in the process of toilet improvement, so it should have good applicability.4.2.3
Villager-centered principle. The direct profit object of rural toilet improvement is the rural villagers. Through toilet improvement, the living environment of villagers can be improved, and the home health level of villagers can be improved. The "toilet revolution" can also improve the basic sanitation services in rural areas, improve the comprehensive level of rural living environment, promote the change of farmers’ ideas and lifestyles, and improve the quality of life of farmers. Therefore, the improvement of rural toilets is closely related to the villagers’ quality of life, so the selection of evaluation indexes of toilet improvement quality should follow the villager-centered principle.4.3 Construction of evaluation index system for effect of rural toilet improvement
The evaluation of the effect of rural toilet improvement is a complex system with multiple factors and indexes. The evaluation of villagers’ satisfaction after rural toilet improvement needs to be comprehensively evaluated by multiple indexes. Therefore, it is necessary to classify the comprehensive evaluation indexes of the effect of rural toilet improvement according to certain principles and form a clear index framework chart.The evaluation structure of rural toilet improvement effect was divided into three layers. The first layer was the target layer, referring to evaluation of the effect of rural toilet improvement in Huzhu County; the second layer was the criterion layer, including villagers’ acceptability of rural toilets, construction of toilets after improvement, treatment methods and effects of fecal sewage after improvement and management of toilet equipment after toilet improvement. The third layer was the index layer, which broke down the criterion layer into specific indexes. Villagers’ acceptability of rural toilets was further divided into toilet environment after improvement, villagers’ use experience after improvement, and cost of toilet improvement; construction of toilets after improvement was subdivided into reasonable layout of toilet space, structure of toilet; treatment methods and effects of fecal sewage after improvement was subdivided into feces treatment and sewage discharge, harmless treatment effect, and environmental threat; management of toilet equipment after toilet improvement was subdivided into system improvement and personnel management, late maintenance and cost of toilet, and daily consumption of toilet (Table 1).
4.4 Selection of evaluation methods
The main research objective of this paper was the evaluation of villagers’ satisfaction after "toilet improvement" in rural Huzhu County. Satisfaction is a standard fuzzy concept, which is characterized by uncertainty, multi-dimension and complexity. In order to accurately quantify the fuzzy concept of villagers’ satisfaction degree, this paper mainly chose fuzzy comprehension evaluation method based on fuzzy mathematics, and used entropy weight method to determine the objective weight of each index. The fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method could accurately express the subjective feelings of farmers, decompose "satisfaction" into multiple indexes to judge one by one, and then integrate the qualitative concept into quantitative concept according to the objective weight of each index. This method is featured by strong systematicness, explainability and definite results. In addition, the weight of each index is determined through expert advice and communication with farmers in the traditional method, which inevitably has strong subjective color. In this paper, the weight was determined by entropy weight method, an objective value assignment method based on information theory. The basic idea was to determine the objective weight according to the variability of each index, which reduced the subjective color and increased the scientificity and accuracy.4.5 Evaluation factor set and comment set according to evaluation index system
For the 4 second-level indexes and 11 third-level indexes divided in the early stage, corresponding factor sets were designed according to their respective inclusion relationships as follows.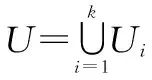
U
∩U
=Φ
(i
≠j
)Different subset had different elements.
U
={U
,U
,U
,U
}whereU
stands for the villagers’ acceptability of rural toilets;U
stands for the construction of toilets after improvement;U
stands for the treatment methods and effects of fecal sewage after improvement; andU
stands for the management of toilet equipment after toilet improvement.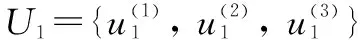
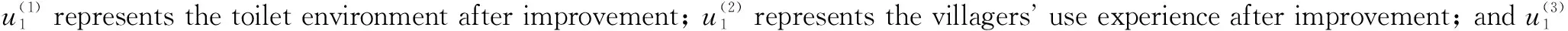
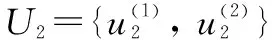
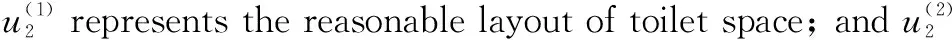
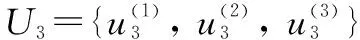
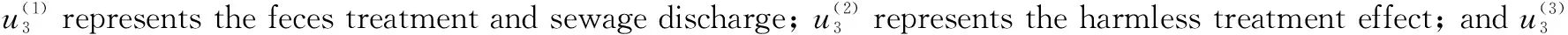
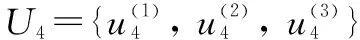
The comment set was divided into the levels of excellent, good and poor.
V
={v
,v
,v
}wherev
stands for poor;v
stands for good; andv
stands for excellent.The scores of villagers on the above 11 index were collected in each set. The scores were set from 1 to 9, with 1 being the worst and 9 being the best, and each evaluation was specified through the scores.
4.6 Determination of fuzzy set matrix of evaluation level standard
The determination of fuzzy set matrix of evaluation level standard mainly refers to selection of membership function and determination of comprehensive evaluation matrix of three-level index.4.6.1
Selection of membership function. The membership function defined in the paper was:φ
∶ω
→[0, 1]wherev
stands for the fuzzy set, including poor, good, excellent;ω
is the domain set, a classical set. The membership function ranges from 0 to 1, and each number within the value range represents a membership degree. The higher the membership degree is, the higher the degree of the element in thev
domain. Each element ofω
domain corresponds to a membership degree in the value range.Membership function has a variety of choices, and common membership functions include double S-shaped membership function (dsigmf), S-shaped membership function (sigm), trapezoidal membership function (trapmf), triangular membership function (trimf), Z-shaped membership function (zmf),etc.
Each membership function has its different characteristics, and the membership function will present different forms according to different scoring situation, with strong subjectivity. Although membership functions are different, they can be generally divided into three types: small, intermediate and large. In order to correspond to the three levels of poor, good and excellent in the fuzzy set in this paper, the trapezoidal membership function was finally selected in this paper (Table 2).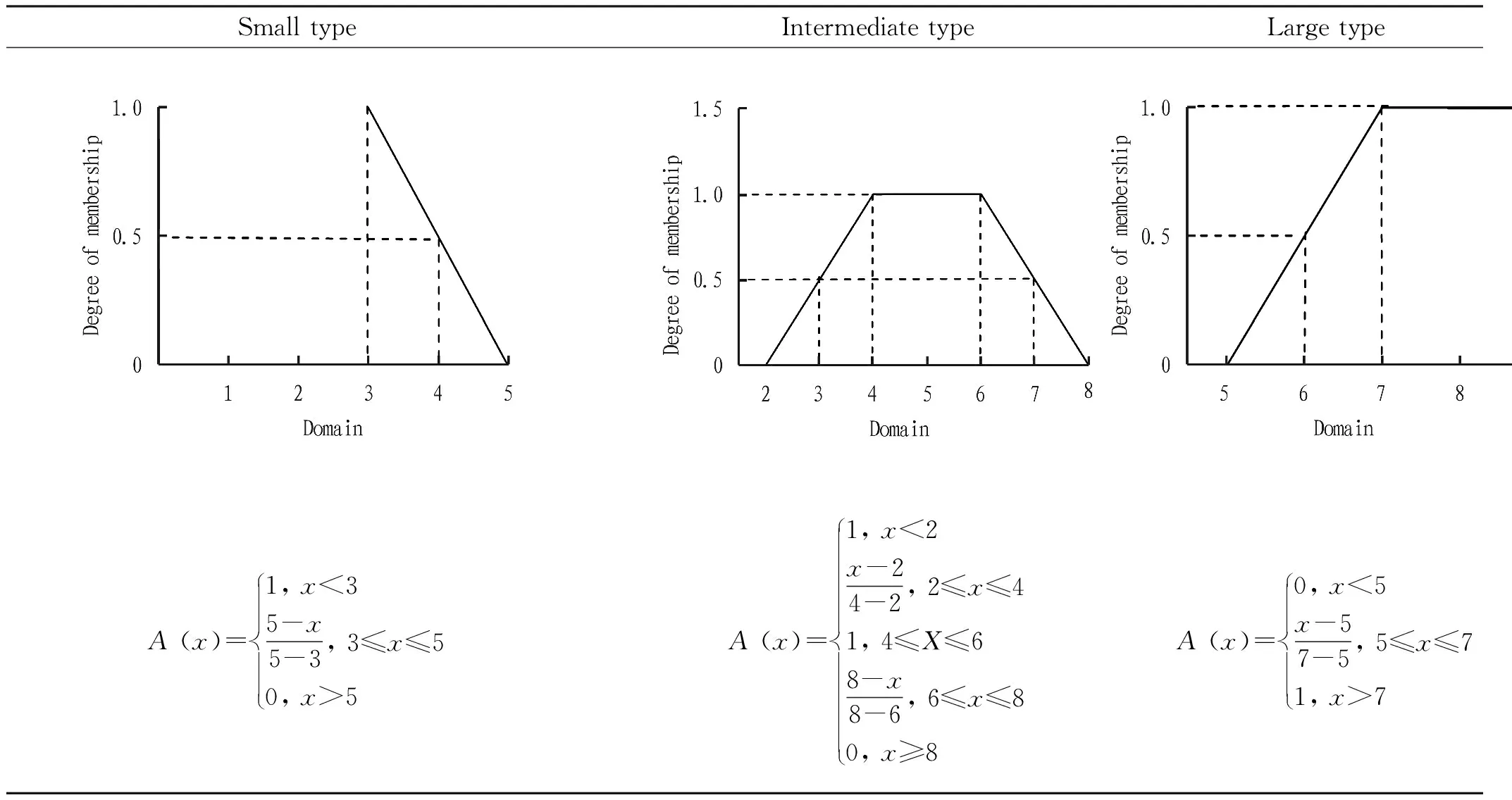
Table 2 Trapezoidal membership function
After sorting, the membership function was:
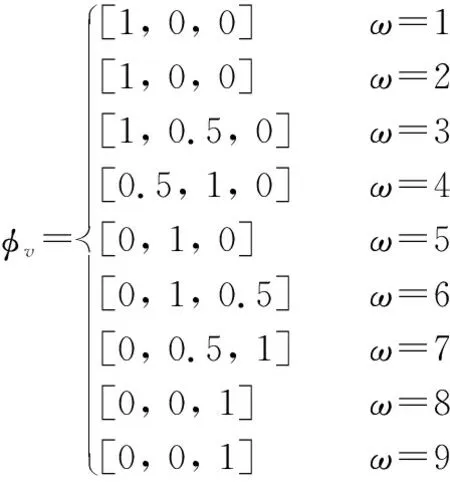
4.6.2
Determination of comprehensive evaluation matrix of three-level index. For each three-level index, the membership vector of all villagers to this index was obtained according to the membership function. On this basis, the next task was to obtain the overall evaluation of all farmers on this index. Different integration methods will lead to different effects. Common integration methods include standard intersection, weak intersection, bounded difference, standard union, weak union, bounded sum, arithmetic mean and weighted average. In this paper, arithmetic mean was adopted to calculate the overall evaluation of each index by using codes.4.7 Selection of weight of each index and comprehensive evaluation matrix of second-level index
In this paper, entropy weight method was mainly used to determine the weight of each index. Entropy weight method (EWM) is a method to determine the objective weight of an index according to its variability. It is an objective weighting method with higher reliability and accuracy than subjective weighting method. Entropy is a physical concept of thermodynamics, and it is a measurement of chaos or disordered degree of a system. A higher entropy means a more chaotic system (that is, it carries less information), while a lower entropy means a more orderly system (that is, it carries more information). Referring to the concept of entropy in thermodynamics, information entropy is used to describe the amount of information of an event on average. Generally speaking, the smaller the information entropy of an index is, the greater the variation degree of the index value is, the more information it provides, the greater the role it can play in the comprehensive evaluation, and the greater its weight is, and vice versa.The entropy weight method mainly determines the index weight from the following steps.
4.7.1
Determine the amount of information. In general, the amount of information contained in an object is determined by its probability of occurrence. The higher the probability of occurrence, the smaller the uncertainty and the amount of information contained. Conversely, the smaller the probability of occurrence, the greater the uncertainty and the amount of information contained. Therefore, we specified the amount of informationI
as:I
=log(1/P
)=-log(P
)whereP
is the probability of occurrence of events, and the amount of information is the logarithm of the reciprocal of the probability of occurrence.4.7.2
Information entropy normalization processing. Information entropy is a comprehensive reflection of the amount of information contained in an event. The value of information entropy is the expected amount of information of each index.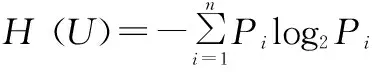
H
stands for the information entropy;U
stands a specific index;n
stands for the number of elements in domainω
, which was 9 in this paper;P
stands for the probability of occurrence of each element.After the information entropy was calculated, 0-1 normalization was required to normalize the score of the data into [0, 1].
The formula was as follows:
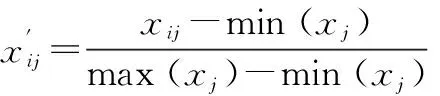
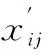
4.7.3
Determination of weight by information entropy. First, the proportion of thei
user’s score on thej
index to all the scores of this index was calculated.
Second, the information entropy of the index was calculated.
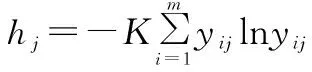
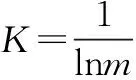
h
stands for the information entropy of thej
index;K
stands for the constant coefficient;m
stands for the total number of samples. The base of the logarithm is the natural constante
.Finally, the weight setsA
,A
,A
,A
andA
corresponding to factor setsU
,U
,U
,U
andU
were obtained according to the indexes of different levels.The weight of thej
index wasa
.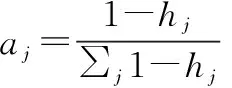
4.7.4
Determination of the weight of villagers’ acceptabilityU
.The raw data were:
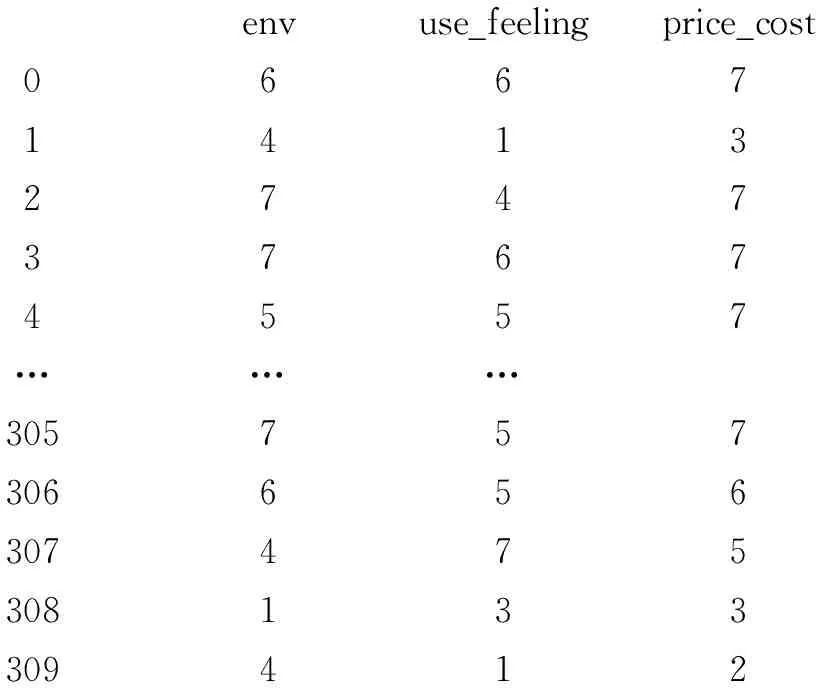
envuse_feelingprice_cost06671413274737674557………305757306656307475308133309412
The normalized data were:
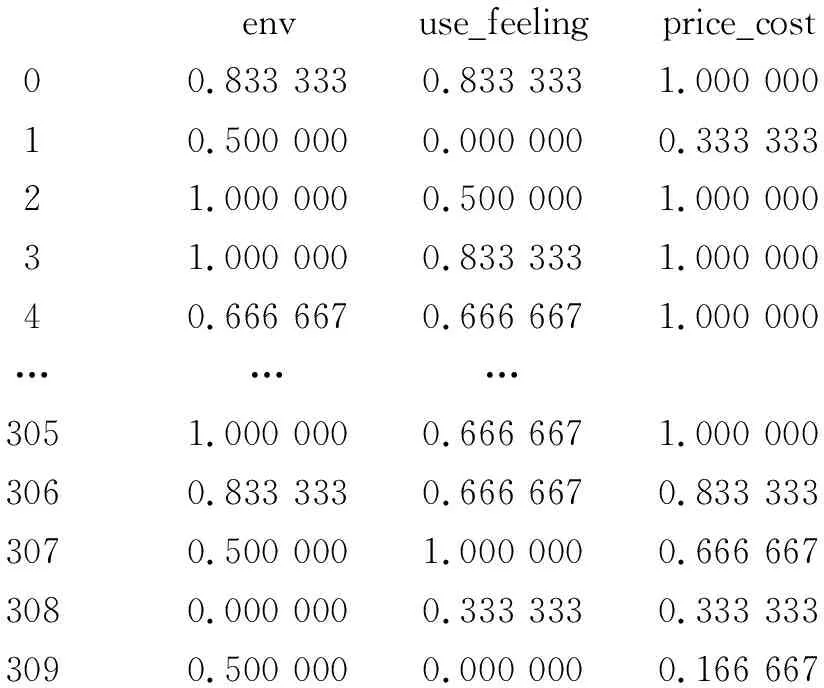
envuse_feelingprice_cost00.833 3330.833 3331.000 00010.500 0000.000 0000.333 33321.000 0000.500 0001.000 00031.000 0000.833 3331.000 00040.666 6670.666 6671.000 000 ………3051.000 0000.666 6671.000 0003060.833 3330.666 6670.833 3333070.500 0001.000 0000.666 6673080.000 0000.333 3330.333 3333090.500 0000.000 0000.166 667
The proportion of the score of each index to its total data was:
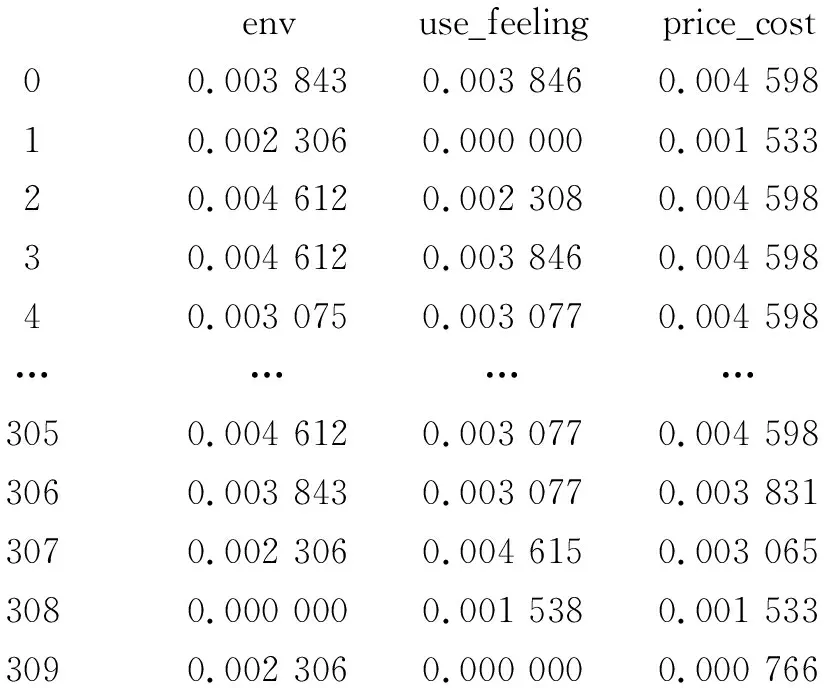
envuse_feeling price_cost00.003 8430.003 8460.004 59810.002 3060.000 0000.001 53320.004 6120.002 3080.004 59830.004 6120.003 8460.004 59840.003 0750.003 0770.004 598… ………3050.004 6120.003 0770.004 5983060.003 8430.003 0770.003 8313070.002 3060.004 6150.003 0653080.000 0000.001 5380.001 5333090.002 3060.000 0000.000 766
The value ofK
was:K
=0.174 320 125 005 559 07The information entropy of each index was:
h
=[0.979 970 69, 0.979 913 27, 0.980 601 74]The weight of each index was:
A
=[0.336 546 17, 0.337 510 96, 0.325 942 88]4.7.5
Determination of weight of each index. According to the above methods, four weight vectorsA
,A
,A
andA
of second-level indexes to third-level indexes and weight vectorA
of second-level indexes to first-level indexes were obtained:A: [0.249 090 04, 0.247 990 42, 0.252 710 49, 0.250 209 05];A
: [0.336 546 17, 0.337 510 96, 0.325 942 88];A
: [0.517 982 38, 0.482 017 62];A
: [0.321 967 62, 0.344 130 21, 0.333 902 17];A
: [0.341 722 85, 0.300 079 07, 0.358 198 08].4.7.6
Comprehensive evaluation matrix of second-level indexes. Comprehensive judgment matrix is the product of weight vector and fuzzy comprehensive judgment matrix.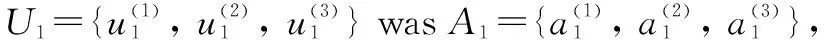
B
=A
×R
.whereB
is the membership degree of the first second-level indexU
to each element in the comment set.5 Empirical evaluation of farmers’ satisfaction with toilet improvement quality
5.1 Data sources
For the empirical evaluation of farmers’ satisfaction with the quality of toilet improvement, the paper selected Heyu Town, Shizimiao Town, Sanchuan Town, Tantou Town and Lengshui Town as the research objects. According to the status quo of toilet improvement in local area, questionnaires were distributed to local residents, including the elderly, youth and children. For different subjects, different survey methods were adopted, including but not limited to telephone survey, online questionnaire, offline interview,etc.
, to ensure the comprehensiveness. Finally, a total of 500 questionnaires were distributed in the survey, among which 310 were valid.5.2 Evaluation conclusions
After sorting out the data of the returned questionnaires, they were imported into the fuzzy evaluation analysis model, and the following results were obtained.5.2.1
Villagers’ acceptability of rural toilets (hereinafter known as matrixR
).
According to the analysis, the villagers appraised the toilet environment as good; for the feeling of using the toilet, the villagers rated as excellent; and for the cost of toilet reconstruction, the villagers also regarded as excellent. On the whole, the villagers’ acceptability of rural toilets was high, and the feeling of use was good.
5.2.2
Construction of toilets after improvement (hereinafter known as matrixR
).
According to the above results, the villagers accepted the spatial layout of toilets. Most of the villagers thought the layout was acceptable, and only a few people did not approve of the layout. The villagers quite approbated the structure of toilets.
5.2.3
Treatment methods and effects of fecal sewage after improvement (hereinafter known as matrixR
).
As for the method and effect of feces treatment, the villagers in the villages that had established sewage treatment plants considered that the situation of feces treatment and sewage discharge was good, but because of the terrain problem, some villagers were worried about the difficulty of pumping feces and other problems. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out continuous exploration and improvement. As for the effect of harmless water treatment and en-vironmental threat, the villagers agreed that it was well done.
5.2.4
Management of toilet equipment after toilet improvement (hereinafter known as matrixR
).
According to current situation of toilet equipment management, the villagers reflected that there was no better perfect system and unified personnel management after toilet improvement, while some villagers had to pay their own expenses for drawing out dung and late maintenance of toilet, which needs to be improved by the government. All the villagers believed that the treatment effect was good, and a better maintenance mechanism should be further developed.
5.2.5
The final result. After determining the weight of each index with entropy weight method, the comprehensive evaluation results of the overall situation were as follows:[0.063 845 0.295 102 0.430 228].
6 Conclusions
Based on the analysis of various data imported into the model, it can be seen that the villagers generally approve of the toilet improvement, and the overall evaluation is excellent. Through the final scoring result of the evaluation of rural toilet improvement effect, it can be seen that rural toilet improvement has fundamentally solved the toilet problem that villagers have been facing for a long time. The development and implementation of toilet improvement work has brought many positive effects. Through the "toilet revolution", the home environment of rural villagers has been really improved, and the overall hygienic living standard of rural villagers has been improved. The improvement of toilets not only solves the problem of dirty and messy environment of pit toilets, but also improves the happiness and life quality of villagers and promotes the change of their ideas and lifestyles. The "toilet revolution" has also become an important project for the benefit of the people and has positive significance for the development of China’s rural areas.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Evaluation of Antibiotic Pollution in Soil of Vegetable Base in Yangling District, Shaanxi Province
- Niche Characteristics of Herbaceous Plants under Pinus tabuliformis Plantation Forest in Feldspathic Sandstone Area
- Design of Trinity Framework for Cultivated Land Protection
- Current Situations and Recommendations for Development of Agricultural Sci-Tech Park District of Luzhou City
- Study on Virus-free Breeding Technology of Potato Microtuber
- Labor Flow Characteristics of Taian City in the Context of Rural Revitalization
