Study on Virus-free Breeding Technology of Potato Microtuber
2021-12-30ChunLIYuanjingXU
Chun LI, Yuanjing XU
Zaozhuang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Zaozhuang 277300, China
Abstract It is the simplest, fastest and effective way to improve the yield level of potato by selecting high quality virus-free seed potato for field production and maintaining the original characters of virus-free minituber. Microtuber is featured by small volume, no pathogen, convenient storage and transportation, which can be induced in summer with high temperature and humidity, and overcome a series of problems such as poor survival rate of transplanted test-tube plantlets, and easy pollution of cutting tips. Therefore, it can replace conventional test-tube plantlets directly for reproduction. Meantime, if minitubers are sown ahead of time using cold frame, the growth stage of potato minituber will avoid the occurrence period of aphids. The use of gauze cover for insect prevention has good effect on maintaining the excellent characters of microtuber. The yield and quality of virus-free potato are greatly improved by means of virus-free culture of shoot tip seedlings, subculture propagation of virus-free seedlings, induction of microtubers by dark culture, cultivation of breeder’s seeds in greenhouse and screenhouse to preserve the characters of potato.
Key words Potato, Virus-free, Microtuber, Induction, Breeder’s seed, Seed character
1 Introduction
Zaozhuang City is the largest potato production area in Shandong Province and the largest potato double crop area in China. In 2016, the planting area of potato in Zaozhuang reached nearly 80 000 ha, and a large-scale potato production base had been formed. Zaozhuang is named as "Hometown of Potato in China" and "Advanced Potato Production City in Shandong Province" by the Ministry of Agriculture. The commodity potatoes are sold at home and abroad, with very optimistic market prospect. However, low yield per unit area and heavy degradation of potato in China are the main factors restricting farmers’ economic income at present. Especially in recent years, when most farmers use self-propagating virus-free seed potato in potato double crop areas in South Shandong, due to high temperature and humidity, large occurrence of aphids, and continuous cropping in the old base, virus-free seed potato has seriously degraded. Meantime, since the detection means and detection standards of virus-free varieties are not popular in seed potato production management department, the quality of virus-free potato varieties is poor, bringing huge economic losses to farmers. Therefore, it is the simplest, fastest and effective way to improve the yield level of potato by selecting high quality virus-free seed potato for field production and maintaining the original characters of virus-free minituber. Microtuber is featured by small volume, no pathogen, convenient storage and transportation, which can be induced in summer with high temperature and humidity, and overcome a series of problems such as poor survival rate of transplanted test-tube plantlets, and easy pollution of cutting tips. Therefore, it can replace conventional test-tube plantlets directly for reproduction, or replace conventional potatoes for commercial potato production, which is very beneficial to accelerate the application of virus-free potato seed in production, and is conducive to potato planting and production. How to produce fast propagation microtuber with high quality is discussed in this paper.
2 Virus-free culture of shoot tip seedlings
The buds of 3-4 cm on tubers that have germinated at 32-35 ℃ for 20 d are rinsed with running water for 30 min, soaked in 75% alcohol for 30 min, soaked in 0.1% HgClfor 5-8 min, rinsed with sterile water for 4-5 times, and dissected on ultra-clean table under an anatomical lens. The young leaves at the bud tip are peeled off layer by layer using a scalpel or an anatomic needle. After 1-2 leaf primordia and growth cones are exposed, the growth cones with 1-2 leaf primordia are cut off by a scalpel, and immediately inoculated onin
vitro
medium supplemented with MS+1 mg/L6-BA+1 mg/L IAA+2% sugar. Each tube (agar 1%, pH 5.7-5.8) is inoculated with only one shoot tip. The culture medium is sterilized at 121 ℃ for 20 min, inoculated and then cultured at 20-25 ℃, light intensity 1 600-3 000 lx, 16 h light per day. The growth of shoot tip could be observed about 30 d after survival. If leaf primordium is not rooted after leaflets are formed, the shoot tip could be transferred to the medium without growth regulator, and the seedlings would quickly form root system. After about 100-120 d when the shoot tip grows to 4-5 segments with 5-6 leaves, single segment is inoculated on MS flask medium marked with serial number. After about 30 d, the seedlings in the triangular flasks are inoculated into 3-4 triangular flasks in single sections. When the height of the seedlings in flasks is about 10 cm, 2-3 flasks of seedlings are directly performed virus detection, or transplanted in the greenhouse for virus detection. One flask is kept in culture room for propagation after detection.3 Virus detection of shoot tip seedlings
Visual inspection and indicator plant detection method are commonly used for detection. In visual inspection, the shoot tip seedlings with fast growth, thick leaf color, flat leaf and robust growth are selected, and the shoot tip seedlings with weak growth, light leaf color and chlorotic spots on leaves are removed. Indicator plant detection is to use the plant with suspicious symptoms as scion, and then inoculate with the juice of the indicator plantGomphrena
globosa
. At 2 weeks post inoculation, if diseased spots appear on the leaves of the indicator plant, the corresponding shoot tips should be removed.4 Subculture propagation technology of virus-free seedlings
Under aseptic conditions, the virus-free seedlings to be propagated are cut into sections with one leaf and one segment, and inserted into 1/2MS medium. It takes about 3 d for 50% of the cuttings generating roots and 5 d for all cuttings rooting, and axillary buds germinate after 3-5 d. The test-tube plantlets with 5-7 leaves are grown after about 30 d, which could be recycled for propagation.
5 Comprehensive induction technique of microtuber
5.1 Strong seedling culture
The top and base of virus-free seedlings are removed, and the stem segments that grow to 3-4 segments are cultured in liquid medium, 10 segments each flask. The liquid medium is MS basal medium supplemented with 0.5 mg/L 6-BA, 0.1 mg/L NAA, 0.15% activated carbon and 3% sucrose, which is placed in triangular flask for shallow liquid static culture. The temperature of the culture room is 20-25 ℃, and the light intensity is above 2 000 lx for 16 h a day. As stem segments are cultured for 3-5 d, axillary buds begin to sprout. The flasks are full of young seedlings after about 4 weeks, which could be transferred to dark culture to induce microtuber.5.2 Induction of microtuber
After strong seedling culture, test-tube plantlets could be added with special induction medium for dark culture to induce microtuber. The medium for induction of microtuber is as follows: MS+5 mg/L 6-BA+100 mg/L chlormequat chloride + 0.5% activated carbon + 8% sucrose. Medium should be replaced in a sterile room to prevent contamination in dark culture. The original liquid medium is discarded, and induction medium is added. After sealed, the medium is cultured in dark culture room. Dark culture should be dominated by scattered light, and the temperature must be kept at 18-20 ℃. Microtubers appear at 5 d post inoculation, and could be harvested after 55-70 d.6 Breeding technology of microtuber
6.1 Breeding of float tray
The virus-free microtuber inducedin
vitro
could be planted in greenhouse or screenhouse after a dormant period of 3-4 months. The weeds in the greenhouse (screenhouse) must be cleared before planting, and dimethoate should be sprayed to kill aphids. Meanwhile, the culture substrates such as vermiculite are sterilized by spraying 0.1% potassium permanganate. Microtuber could be directly sown in the float tray, 50 seedlings each tray. After emergence, water and nutrient solution is sprayed regularly. The compositions of nutrient solution are KHPO350 mg/L, MgSO·2HO 490 mg/L, (NH)SO170 mg/L, Ca(NO)100 mg/L, Na-EDTA 37.5 mg/L and FeSO·7HO 27.8 mg/L. The breeder’s seeds could be harvested after 2 months, with an average of 3-4 tubers per plant. The weight of each minituber is about 2-3 g, and 150-200 virus-free minitubers could be harvested from each tray.6.2 Planting and breeding of breeder’s seeds in greenhouse and screenhouse
Due to small volume, microtuber has high technical requirements in production and application, so it can be used after planting and propagating breeder’s seeds and stock seeds in greenhouse and screenhouse. After indoor induction, virus-free microtuber could not be planted in greenhouse and screenhouse unless experienced a dormant period of 3-4 months. The weeds in the greenhouse (screenhouse) must be cleared before planting, and dimethoate should be sprayed to kill aphids. Meanwhile, the culture substrates such as vermiculite are sterilized by spraying 0.1% potassium permanganate. Microtuber could be directly sown in the float tray, 50 seedlings each tray. After emergence, water and nutrient solution is sprayed regularly. The composition of nutrient solution is shown in Table 1. The breeder’s seeds could be harvested after 2 months, with an average of 3-4 tubers per plant. The weight of each minituber is about 2-3 g, and 150-200 virus-free minitubers could be harvested from each tray.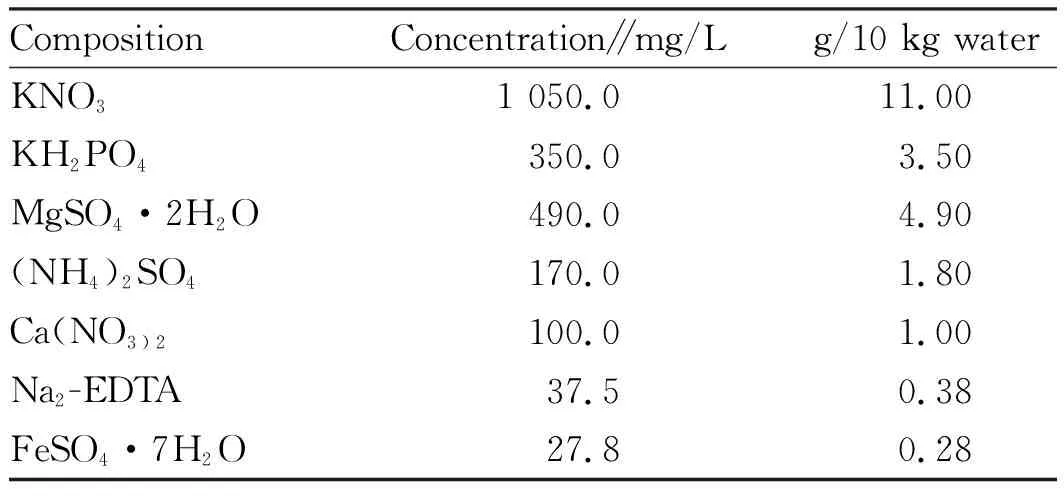
Table 1 Nutrient solution composition for soilless culture of virus-free potato
The breeder’s seeds of virus-free potato bred by this way have to be sprayed with water every day and nutrient solutions every other day. The management is cumbersome, and seedling growth is not robust enough to obtain higher yields. Therefore, the author has improved this breeding method since 2009. First, the soil is ploughed and raked, and then decomposed organic fertilizer is applied at the dose of 35-37.5 t/ha. Approximately 8-10 g of Diaveridine is applied for sterilization per square meter, and vermiculite is spread with the thickness of 10-12 cm; 1 kg of ammonium phosphate is added per cubic meter vermiculite to ensure the robust growth of seedlings. The seeds are sown according to the row spacing of 15 cm×10 cm and the depth of 5-7 cm, and vermiculite is covered after sowing. In this way it generally requires only water management during the growth process. In special cases, certain amount of micronutrient fertilizer should be sprayed, which is easy to manage and could get higher yield of breeder’s seeds. The contrast is direct sowing in vermiculite, and the results are shown in Table 2.
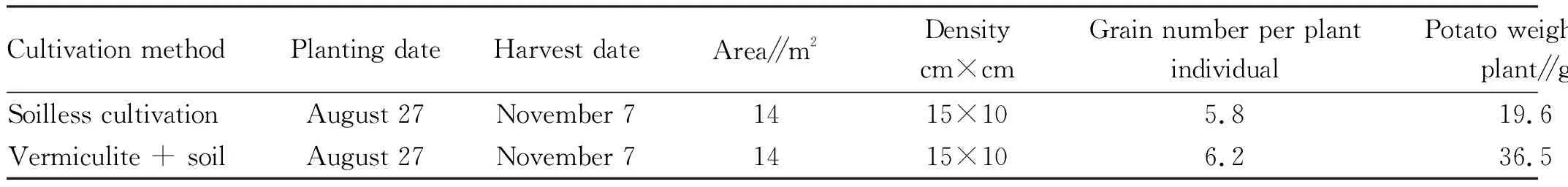
Table 2 Comparison of yields of virus-free potato breeder’s seeds under different cultivation conditions
As shown in Table 2, the plot yield of virus-free potato breeder’s seeds was increased from 13.4 to 23.5 kg after the cultivation method was improved, with an increase of 42.9%, and the difference was extremely significant. The weight of potato per plant increased from 19.6 to 36.5 g. The cultivation method greatly increases the yield of virus-free potato and lays a good foundation for the production of potato breeder’s seeds.
7 Purity-conservation of seed characters
Based on successful induction of microtuber and breeding of breeder’s seeds, it is very important to select suitable seed preservation technology. Since aphid occurs in middle May in double crop areas, how to take measures to prevent aphids, prevent seed potato degradation, and maintain seed characters is a new topic. Therefore, it is necessary to choose suitable breeding sites. The breeding sites of stock seed should be selected in the land with high and cold terrain, few aphids, good natural isolation conditions and no transmission of viruses and bacterial diseases. The plots where the previous stubble is graminaceous crop and potatoes have not been planted for more than three years are generally selected. There is no other potato production field within 500 m, and fine breed production fields should be strictly separated from commercial potato production fields.
According to the characteristics of potato production in Zaozhuang City, the following seed conservation and breeding techniques should be adopted.
7.1 Cold frame seed conservation
Seed germination is accelerated around January 20 for cold frame breeding, and seeds are sown in middle February. The leeward and sunny location in north-south direction can be selected as the border, with the width of 1.2 m and the depth of 33 cm. The length depends on the need and area. In the border, 25 kg of fermented fertilizer is applied per square meter, and deeply ploughed. Sufficient bottom water is irrigated, and arches with the height of 1 m are built. Before sowing, 800 times dilution dimethoate emulsion is sprayed to prevent and control aphids. Three ridges of seed potato are sown in the border in the north-south direction, 2 rows each ridge, with the ridging spacing of 40 cm and plant spacing of 16 cm. After sowing, the gauze net is first covered and then the thin film is covered, and the shed is sealed. When the temperature is stabilized at 15-20 ℃, the film is removed, leaving only the insect proof net until harvest.7.2 Early sowing and early harvest in spring, late sowing and seed reproduction in autumn
According to the production characteristics of Zaozhuang City and the occurrence regularity of aphids, seeds can be sown in mid-late January with three film mulching or in mid-February with double film mulching, and harvested in late April or early May, in order to avoid the occurrence period of aphids. Seeds can be sown in the middle and late August in autumn breeding. The density in early spring sowing can be raised up to 10 000-20 000 plants/ha, and that in autumn sowing is 8 000 plants/ha. The plants are harvested before Frost’s Descent. In the breeding process, it is necessary to achieve fine management and timely prevention and control of diseases, insects and weeds.8 Vermiculite and nutrient soil breeding
The soil is ploughed and raked, and then decomposed organic fertilizer is applied at the dose of 35-37.5 t/ha. Appropriately 8-10 g of Diaveridine is applied for sterilization per square meter, and vermiculite is spread with the thickness of 10-12 cm; 1 kg of ammonium phosphate is added per cubic meter vermiculite to ensure the robust growth of seedlings. The seeds are sown according to the row spacing of 15 cm×10 cm and the depth of 5-7 cm, and vermiculite is covered after sowing. In this way it generally requires only water management during the growth process. In special cases, certain amount of micronutrient fertilizer should be sprayed, which is easy to manage and could get higher yield of breeder’s seeds. This cultivation method greatly increases the yield of virus-free potato and lays a good foundation for the production of potato breeder’s seeds.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Evaluation of Antibiotic Pollution in Soil of Vegetable Base in Yangling District, Shaanxi Province
- Niche Characteristics of Herbaceous Plants under Pinus tabuliformis Plantation Forest in Feldspathic Sandstone Area
- Design of Trinity Framework for Cultivated Land Protection
- Current Situations and Recommendations for Development of Agricultural Sci-Tech Park District of Luzhou City
- Labor Flow Characteristics of Taian City in the Context of Rural Revitalization
- Villagers’ Satisfaction Evaluation of Rural "Toilet Revolution" in Qinghai Province: A Case Study of Huzhu Tu Autonomous County
