Investigation of Cultivated Woody Plant Resources in Ping’an District of Qinghai Province in China
2021-12-01YingHUHuipingJIAPengmaodejiJingjingWEIHaoranZHANGHuichunWANG
Ying HU, Huiping JIA, Pengmaodeji, Jingjing WEI, Haoran ZHANG, Huichun WANG,2,3*
1. College of Life Sciences, Qinghai Normal University, Xining 810008, China; 2. Key Laboratory of Medicinal Animal and Plant Resources on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Xining 810008, China; 3. Key Laboratory of Tibet Plateau Biodiversity Formation Mechanism and Comprehensive Utilization, Xining 810008, China; 4.College of Geography Sciences, Qinghai Normal University, Xining 810008, China
Abstract [Objectives] To investigate and find the characteristics and distribution of woody plant resources in Ping’an District of Qinghai Province. [Methods] The investigation was carried out by interview method, literature method and route method. [Results] There were 22 families, 40 genera and 84 species of woody plants in Ping’an District of Qinghai Province, and their life forms were mainly shrubs. Cultivated woody plants in the study area were dominated by trees; the distribution of families and genera were mainly concentrated in single families, few families, single genera and few genera, the families and genera were narrow; economic value was mainly manifested in ornamental value. [Conclusions] The investigation results are expected to provide a certain reference for the economic development of cultivated woody plants in the study area.
Key words Cultivation, Economic value, Woody plants, Ping’an District of Qinghai Province
1 Introduction
Cultivated plants, as the products of long-term domestication, selection and improvement of wild plants by humans, exert a huge impact on human survival and development. Mastering the overall situation of cultivated plants and proposing scientific and reasonable production and structural adjustments are particularly important in improving the healthy and coordinated development of the regional economy and promoting the regional economic development to get rid of poverty. In recent years, domestic scholars have paid little attention on the integrity of cultivated plants, and most of them have focused on research on cultivated plant genomes, breeding of high-quality cultivars, insect resistance and disease resistance characteristics. In this context, taking Ping’an District, Haidong City, Qinghai Province as the study area, we investigated and counted the types, quantities, and flora distribution of cultivated woody plants, and came up with some pertinent recommendations and strategies, so as to provide a certain reference for the economic development of the study area.
2 Overview of study area and investigation methods
2.1 Overview of study area
Ping’an District. located in the eastern area of Qinghai Province, is the central hinterland of Haidong City. It borders Ledu District of Haidong City to the east, Xining City and Huangzhong County to the west, Hualong County to the south, and Huzhu County to the north across Huangshui River. Pingan District is 33.6 km long from north to south, 23 km wide from east to west, with an average altitude of 2 066-2 300 m. It has a continental climate with long sunshine, strong solar radiation, dry and windy spring, cool summer, cold winter, and not distinct seasons; the annual average temperature of 7.6 ℃, the annual rainfall of 310.1 mm, and the frost-free period of 218 d. Within the district territory, most of the area is mountainous, with complex topography and vertical ravines. The Huangshui River flows through the whole district from west to east. The terrain is high in the south and low in the north, sloping from southwest to northeast. In the district, there are mainly plants ofPotentilla
fruticosa
L.,Lancea
tibetica
Hook. f. et Thoms.,Valeriana
officinalis
L.,Elsholtzia
feddei
Lévl.,Populus
davidiana
Dode,Hippophae
rhamnoides
subsp.sinensis
Rousi.2.2 Investigation methods
In this study, we mainly adopted the interview method, literature consultation, and route survey. For the interview method, we mainly visited local orchards, nursery stock nursery bases, forestry management and protection stations and other locations to survey and count the types and number of cultivated woody plants. For the literature, we mainly consulted the cultivation of woody plants in the area by consulting the relevant archives and documents of the local forestry department. Route survey was a comprehensive coverage of the cultivated plant distribution area in the study area based on interview and literature survey, and the survey of the cultivation of woody plants in the study area. On this basis, with reference toGuide
Price
for
the
Main
Afforestation
Seedlings
and
Seeds
in
the
Autumn
of
2020
in
Qinghai
Province
, we calculated the economic output value of cultivated plants in the study area by the following formula:A
=∑(α
×β
×δ
+α
×β
×δ
+…+αi
×β
×δ
)(1)
whereA
denotes the total economic benefit (yuan);α
represents the average annual number of plants per square kilometer of a single plant;β
indicates the planting area of a single plant (km), andδ
represents the average price of a single plant (yuan). In addition, there are overlaps between ecological plants and timber plants, in which ecological plants are mainly calculated with tree age of 3 to 5 years, while timber plants are mainly calculated with tree age of more than 20 years.3 Results and analysis
3.1 Species composition
Through the investigation, we found that there were 22 families, 40 genera and 84 species of cultivated woody trees in Ping’an District, Haidong City, Qinghai Province, including 9 gymnosperms, accounting for 10.71% of the total species, and 75 angiosperms, accounting for 89.92% of the total species, indicating that angiosperms are the majority of cultivated woody plants in this area (Table 1).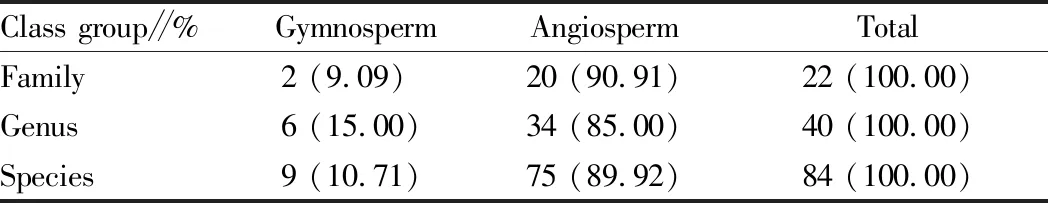
Table 1 Species composition of cultivated woody plants in the study area
3.2 Plant life form
The life forms of cultivated forest plants were divided into two types in the study area: tree and shrub, among which there were 58 species of trees, accounting for 69.05%, includingPicea
crassifolia
Kom.,Pinus
tabuliformis
Carriere,Populus
davidiana
Dode,etc.
; there were 26 species of shrubs, accounting for 30.95%, includingSyringa
oblata
Lindl.,Viburnum
farreri
W. T. Stearn,Sorbaria
kirilowii
(Regel) Maxim.,etc.
, as shown in Fig.1.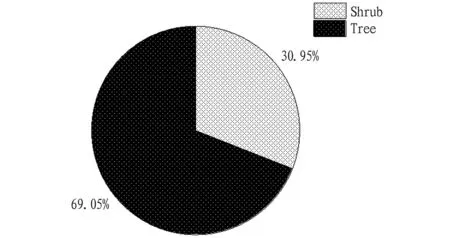
Fig.1 Statistical chart for life form of cultivated woody plants in the study area
4 Distribution of families, genera, and flora
4.1 Distribution of families
As shown in Table 2, among the cultivated woody plants in the study area, Rosaceae was the only big family with more than 20 species, while Salicaceae was the only larger family with 11 to 20 species. Medium families with 6 to 10 species were only Leguminosae; there were 9 families with 2 to 5 species, accounting for 40.91% of the total number of families, including Buxaceae, Celastraceae, Elaeagnaceae,etc.
, and 10 single families, such as Juglandaceae, Ranunculaceae, Saxifragaceae,etc.
, accounting for 45.45% of the total number of families. These indicate that the cultivated woody plants are mainly concentrated in rosaceae and salicyliae, of which Rosaceae mainly has economic value, which is reflected in fruit value in the study area. such asMalus
pumila
Mill.,Prunus
salicina
Lindl.,Armeniaca
vulgaris
Lam.,etc.
The Salicaceae is mainly of ecological value, such as windbreak and sand fixation, soil and water conservation, and also has economic value, mainly reflected in the sale of seedlings.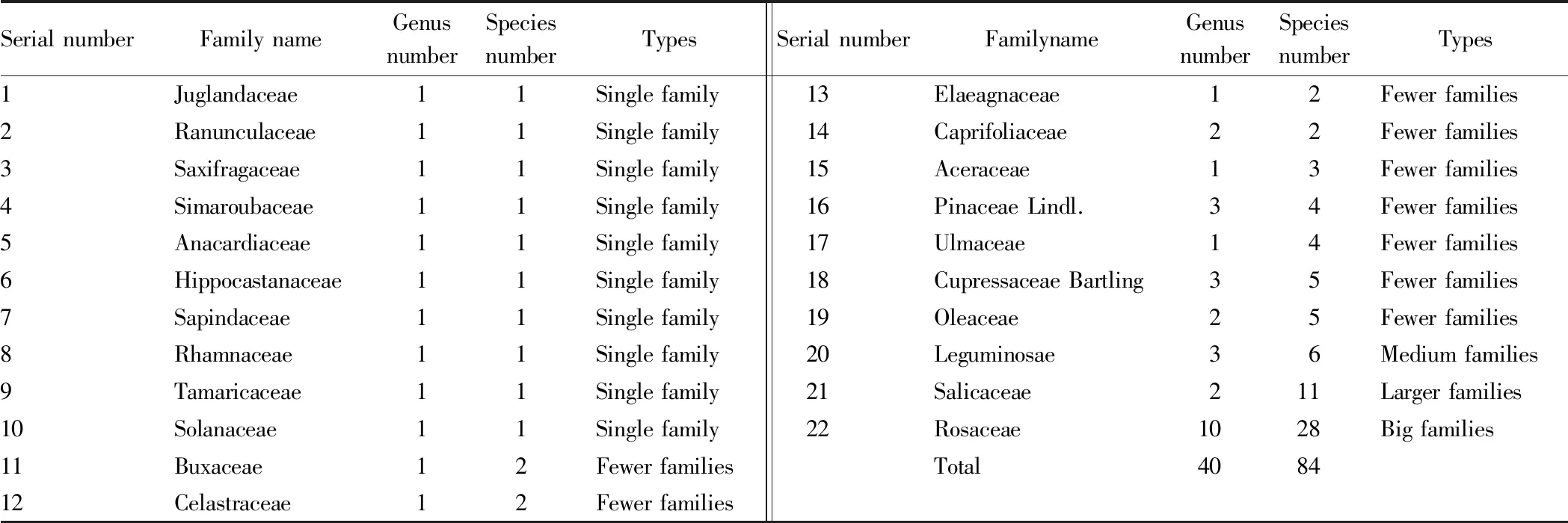
Table 2 Distribution of germplasm families of cultivated trees in the study area
4.2 Distribution of genera
Among the cultivated woody plants in the study area, there were no larger (with 11-20 species) or big (more than 20 species) genera. Medium genera (with 6-10 species) includePyrus
L.,Populus
L. andMalus
Mill., accounting for 7.50% of the total number of genera; few species (with 2-5 species) includePinus
L.,Cedrus
Trew andPlatycladus
Spach, accounting for 15 of the total 37.50% of the number of genera, 22 single genera, accounting for 55.00% of the total number of genera (Table 3). These show roughly the trend as the species within the family. In other words, the plants in the study area are narrow in the composition of families and genera, and the plant species are concentrated in a small number of families and genera.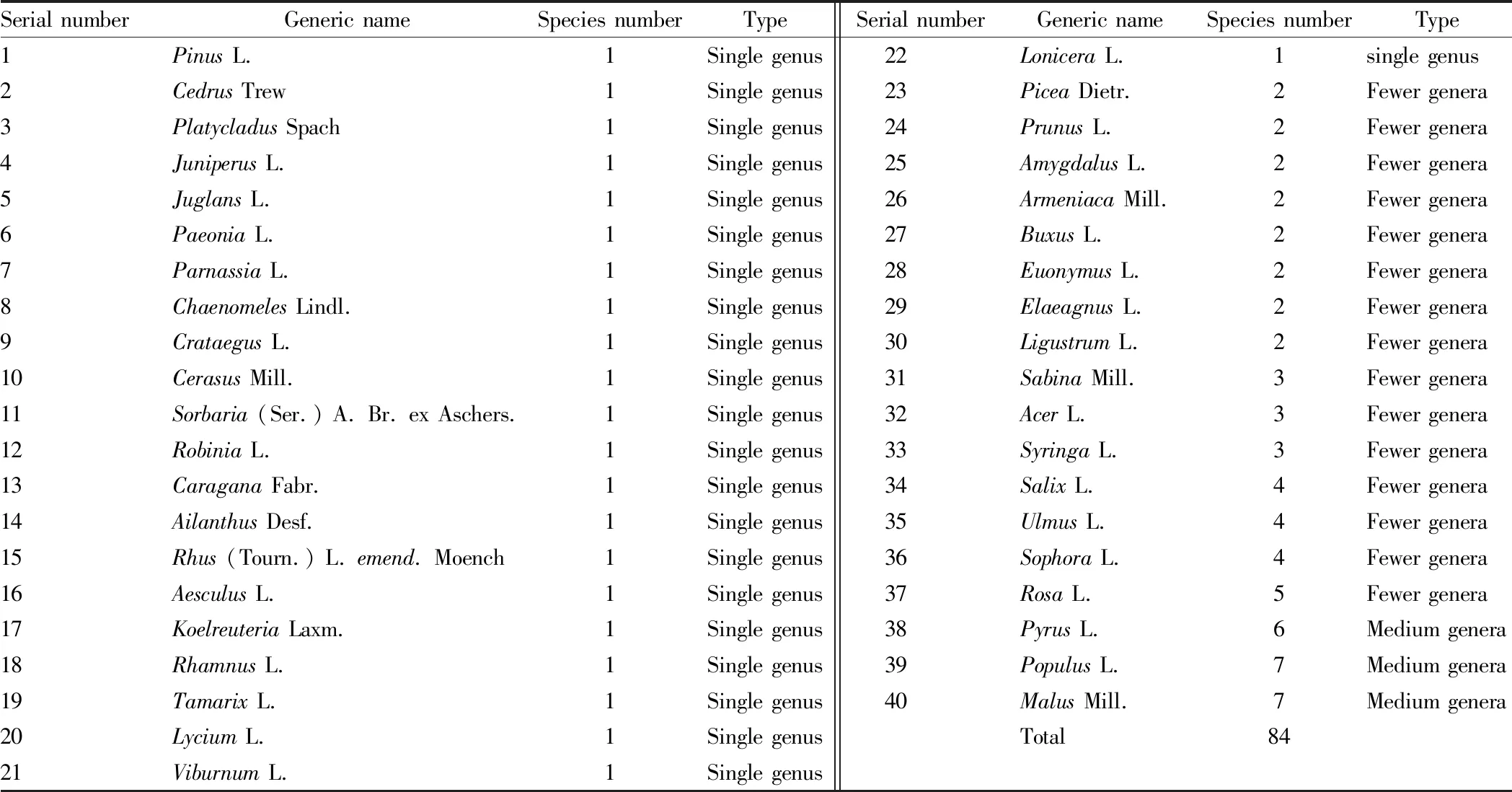
Table 3 Distribution of cultivated woody plant families in the study area
4.3 Flora distribution of genera
According to the classification principle of Spermatophyta genera in China, cultivated woody plants in the study area were divided into 10 types, including distribution in the north temperate, distribution in the East Asia and distribution in the old world temperate, as shown in Table 4. Apart from distribution in the Cosmopolitan, distribution in the north temperate was the majority, accounting for 56.41%, mainly including 22 genera, such asJuglans
L.,Lonicera
L. andPopulus
L. The second was East Asia, accounting for 10.26%, includingSyringa
L.,Koelreuteria
Laxm. andPlatycladus
Spach. The rest of the composition was relatively small, but there were a weak tropical component invasion. On the whole, the cultivated woody plants showed the characteristics of north temperate in the study area.
Table 4 Flora distribution of cultivated woody plants in the study area
5 Classification of economic use
The cultivated woody plants in the study area can be divided into five categories according to economic use: ornamental, ecological, medicinal, edible and timber (Table 5). Among them, ornamental woody plants had 83 species and accounted for 98.81%, includingPrunus
×cistena
N.E.Hansen ex Koehne (0.9×10yuan/year),Malus
×micromalus
Makino (1.6×10yuan/year), Sorbaria kirilowii (Regel) Maxim (0.5×10yuan/year); ecological woody plants had 33 species and mainly refer to tree species used for tree planting and afforestation, playing the ecological functions of windbreak and sand fixation, water and soil conservation, accounting for 39.29% of the total number of plants in the study area, includingPinus
tabuliformis
Carr. (3.3×10yuan) /year),Picea
wilsonii
Mast. (2.5×10yuan/year), andPopulus
davidiana
Dode (1.2×10yuan/year); medicinal (30 species) and edible (30 species) both accounted for 35.71%. Medicinal woody plants mainly includedPinus
tabuliformis
Carr. (7.9×10yuan/year),Lycium
barbarum
L. (3.5×10yuan/year),Rosa
rugosa
Thunb. (1.3×10yuan/year),etc.
Edible woody plants mainly includedPyrus
bretschneideri
Rehd. (9.6×10yuan/year),Crataegus
pinnatifida
Bge.) (8.5×10yuan/year),Juglans
regia
L. (0.8×10yuan/year),etc.
The timber woody plants had 15 species and accounted for the lowest proportion, includingPicea
wilsonii
Mast. (1.2×10yuan/year),Picea
crassifolia
Kom. (1.9×10yuan/year), andPopulus
davidiana
Dode (2.8×10yuan/year), accounting for 17.86%. The contribution of cultivated woody plant resources in the study area to the area’s annual average economic output value was about 2.323×10yuan.
Table 5 Economic plant classification and economic benefit estimation of the study area
6 Discussion and conclusions
Through this investigation, we found that there are 84 species of cultivated woody plants in Ping’an District, Haidong City, Qinghai Province. These species belong to 22 families and 40 genera. The species composition is dominated by angiosperms, and the life form is mainly tree. Flora is an important manifestation of plant evolution, and is a foundation of regional plant diversity protection, ecological restoration, introduction and domestication and other technologies. The flora of the cultivated plants in the study area is dominated by the northern temperate zone, which is consistent with the characteristics of the wild plants in Nanmenxia in the adjacent areaand also consistent with the flora characteristics of the seed plants in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, indicating that the plant cultivation in the study area is scientific in terms of species selection. In the study area, the distribution of families and genera of cultivated plants has distinct hierarchical characteristics, and it has the most obvious in the distribution of families. The cultivated woody plants belonging to the ornamental and timber categories are mainly composed of a single family and a few families, while the edible cultivated woody plants are mainly distributed in Rosaceae, with 10 genera and 28 species, which are related to the artificial selection of cultivated species. Among the plants in the economic output value of the study area, ecological and timber resources have made greater contributions to the total economy. The former is mainly related to the enhancement in ecological engineering governance in Qinghai Province in recent years, and the latter may be related to the study area being a main timber production area in Qinghai Province.
The study area should make further scientific adjustment, optimize economic structure, reinforce the ecological sustainable resources, and reduce the types with slow resource production, such as timber (at least 30 years) and ornamental (5 years on average) resources, and properly increase the edible resources with rapid efficiency (the average investment in the early stage is 5 years, and there is income every year in the later stage). In summary, we reached the following conclusions. (i) The cultivated plant flora in the study area is consistent with the general environment, and the species selection is scientific. (ii) The distribution of families and genera is obvious, mainly because the families and genera of edible cultivated woody plants are widely distributed, and the distribution of other types of families and genera is narrow. (iii) It is necessry to adjust the structure of cultivated plants, and concentrate on resources with fast economic returns such as edible resources.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Effectiveness of Rain Classroom Intelligent Teaching Design: A Case Study of the Course of Spring Water Tourism Resources
- Technical Regulations for Production of Apple ‘Jiping 1’
- Effect of Labor Skills Training on Industrial Development and Economic Benefits of Winter Potato in Regions Inhabited by Ethnic Minorities: A Case Study of Lancang Lahu Autonomous County
- Strategies for Prioritizing Ecological Construction with Consideration of Agricultural Industry Development in Northern China’s Agro-pastoral Ecotone: A Perspective of Opportunity Cost
- Construction Path of Farmer Education and Training System in the Context of Rural Revitalization
- Certification and Conversion Mode of Learning Achievement Based on Credit Bank under the Background of Higher Vocational Enrollment Expansion
