Technical Regulations for Production of Apple ‘Jiping 1’
2021-12-01XiangminSUOJinxinWANGJingmiaoHUANGJieHAOJianzhongFENGXinminYANJianmingLIXiangeWANGXueyingLI
Xiangmin SUO, Jinxin WANG, Jingmiao HUANG, Jie HAO, Jianzhong FENG, Xinmin YAN, Jianming LI, Xiange WANG, Xueying LI
Shijiazhuang Pomology Institute, Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences, Shijiazhuang 050061, China
Abstract Apple ‘Jiping 1’ is a new early maturing apple variety bred by Shijiazhuang Pomology Institute, Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences. To further normalize the standardized production technology of ‘Jiping 1’, realize improvement and upgrading of fruit quality, and improve sustainable development of apple industry, according to national and industrial standards, specific requirements on selection of production orchard, planting, soil, fertilizer and water management, shaping and pruning, flower and fruit management, pest control, and fruit harvesting of ‘Jiping 1’ are put forward, and technical regulation for production of ‘Jiping 1’ (standard number: DB 13/T 5167-2020) is made. The regulation has important guiding significance for the production of early maturing apple in Hebei Province.
Key words Apple, Jiping 1, Technical regulations for production
1 Introduction
Apple ‘Jiping 1’ is an excellent early maturing apple variety independently bred by Shijiazhuang Pomology Institute, Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences. In December of 2013, it was approved by Hebei Forest Variety Approval Committee. The cultivation of ‘Jiping 1’ makes up for the defects of existing early maturing apple varieties. After several years of field cultivation, there is excellent performance, and it has become early maturing series mainly promoted in the main apple producing areas of Hebei Province. The cultivation of ‘Jiping 1’ is of great significance to promote the adjustment of apple planting structure, promote the healthy and sustainable development of apple industry in Hebei Province, and realize the structural reform of agricultural supply side.
With planting area of ‘Jiping 1’ continuously enlarges, there is an urgent need for a set of perfect technical regulations to guide production, thereby providing scientific theoretic support for fruit farmers, and standardizing the standardized production of apple ‘Jiping 1’. According to scientific research foundation of apple cultivation and many years of production practice experience, Shijiazhuang Pomology Institute, Hebei Academy of Agriculture and Forestry Sciences formulates production technical regulations of apple ‘Jiping 1’ (local standards of Hebei Province DB 13/T 5167-2020), which has an important significance for standardized production of apple ‘Jiping 1’, realizing fruit quality improvement and upgrading, and promoting the sustainable development of apple industry.
2 Range
In the standard, orchard selection and planning, seedling and planting, soil, fertilizer and water management, tree shape selection and high spindle shaping and pruning, pollination, flower and fruit thinning, pest control and fruit harvesting of apple ‘Jiping 1’ are stipulated. The standard is suitable for the production of suitable area of ‘Jiping 1’ in Hebei Province.
3 Normative references
The following documents are essential for the application of this standard. For dated references, only the dated version is applicable to this standard. For undated references, the latest edition (including all amendments) is applicable to this standard.
GB 9847-2003Apple
Nursery
Plants
.NY/T 5012-2002Pollution
-free
Food
—Apple
Production
Technical
Specification
.NY/T 1084-2006Regulations
of
Production
Technique
on
Red
Fuji
Apples
.NY/T 441-2013Technical
Code
for
Producing
Apples
.NY/T 394-2013Green
Food
—Fertilizer
Application
Guideline
.DB13/T 1446-2011Technical
Manual
for
Water
-saving
Irrigation
of
Apple
Orchard
.4 Orchard selection and planning
4.1 Environmental conditions of orchard
The orchard is located in an agricultural production area far away from pollution sources, with good ecological conditions and sustainable production capacity.4.2 Climatic conditions
It should correspond with the stipulations of Section3
.1
.1
in NY/T 441-2013.4.3 Soil conditions
It should correspond with the stipulations of Section3
.1
.2
in NY/T 441-2013.4.4 Topography
It should select flat ground or low and gentle hills with a slope of 5-15° or mountains with a slope of 15-30°. Mountain orchards should choose the south slope out of the wind and facing the sun, and terraces are built, to do a good job in water and soil conservation.4.5 Orchard planning
Orchard planning should be implemented according to Section3
.2
in NY/T 441-2013.5 Nursery stock and planting
5.1 Selection of nursery stock
Dwarf rootstock seedlings are preferred, and selection of nursery stock is implemented according to GB 9847-2003 standard. When the 3-year-old big seedlings with branches are used to build the garden, the standards of nursery stock are: robust and free of quarantine diseases and pests; stem diameter > 1.2 cm at 10 cm above the variety interface and seedling height > 1.5 m; 6-9 effective branches in the reshaping belt, with a length of about 40-50 cm and uniform distribution; strong root system and more than 5 lateral roots over 20 cm.
5.1.2
Pollination variety. Special pollination trees are recommended to be configured in the row, and one plant is configured every 15-20 m. Or Gala, Wanglin, Xinhongxing, Jinguan, Huaguan, Fuji,etc.
are selected as pollination varieties, using determinant or configuration along contour lines.5.2 Planting
5.2.1
Planting density. Spacing in the rows and spacing between rows of arborization planting is (3.0-4.0) m×(4.0-5.0) m, while spacing in the rows and spacing between rows of dwarf planting is (1.0-2.0) m×(3.0-4.0) m.5.2.2
Soil preparation. Soil preparation is implemented according to the stipulations of Section5
.1
in NY/T 441-2013. In autumn, ditch land preparation is carried out for the planting garden, and the specification of the ditch is 60 cm×80 cm (width×depth); when trenching, the topsoil and subsoil shall be stacked separately. After mixing organic fertilizer, phosphorus fertilizer and potassium fertilizer with topsoil, it is backfilled to be level with the ditch. After that, it is watered and settled, and then a layer of topsoil is covered to be level with the ground to preserve moisture.5.2.3
Planting time. From middle March to middle April, it is planted after soil thawing to before germination (before and after Qingming).5.2.4
Pre planting treatment. The root system is pruned, and then the seedling root system is soaked in clean water for 12-24 h.5.2.5
Planting method. Dwarf self rootstock seedlings should be planted with 5-10 cm dwarf rootstock exposed on the ground. It is suitable to plant dwarf intermediate rootstock seedlings to expose 10-15 cm intermediate rootstock on the ground.5.3 Post planting management
5.3.1
Plastic film mulching. It is watered immediately after planting, and the gap at the seedling base is covered with a small amount of soil after water seepage. It is watered for the second time after 3-5 d, and the tree tray is covered with black plastic film to preserve moisture in time, and it is removed in time in mid and late May.5.3.2
Heading. Large seedlings without branches: headed immediately after planting in spring. For nursery stock <1.5 m, heading height is between 1.0 and 1.2 m. For nursery stock >1.5 m, there is no heading. After heading, protective agent is applied to the cut. At the place where the seedling trunk is more than 50 cm away from the ground, a bud is cut or hair branching element is applied every 2-3 buds until it is 20-30 cm away from the top.Large seedlings with branches: the branches with the thickness of the base exceeding 1/3 of the thickness of the insertion and the length > 60 cm can be removed. If number of lateral branches after thinning is more than or equal to 5, branch could be retained. If number of lateral branches after thinning is less than 5, all branches could be removed, and there is no seedling heading. If there is no branch on central stem, one bud is cut every 2-3 buds to 30 cm below the top of the extended branch of the central stem.
5.3.3
Setting up support. For dwarf rootstock orchard that plant spacing is less than 1.5 m, it needs conducting erect cultivation. One galvanized steel pipe (6-8 cm of diameter) or cement pile (10-12 cm of diameter) is set at a spacing of 10-15 m, and is buried 70 cm underground, and the frame height is 3.5-4.0 m. 4-5 steel wires with diameter of 2.2 mm shall be set evenly, and the lowest wire shall be 0.8 m from the ground. The end of each row of frame is installed with ground anchor and branch pulling steel wire (inclined outward by about 15°). A bamboo pole with a height of about 3.0 m is selected as the pillar, and one bamboo pole is erected for each plant. The planted seedlings are bound to the bamboo pole, and the central stem is bound with growth.5.3.4
Tree anti freezing. Antifreeze or whitening agent is used during defoliation.6 Soil, fertilizer and water management
6.1 Soil management
Soil management is implemented according to the stipulations of Section6
.1
in NY/T 441-2013 and Section6
.1
in NY/T 5012-2001. At soil management, the soil management system of covering horticultural land cloth after ridging in the row, natural grass or artificial grass between rows can be adopted.6.2 Fertilizer application
Fertilizer application is implemented according to NY/T 394-2013. Fertilization is dominant by autumn base fertilizer, and the application amount of organic fertilizer is increased. Generally, application amount of high-quality organic fertilizer in full fruit stage is between 37 500 and 45 000 kg/ha, and it can also be applied in the proportion of 1 kg organic fertilizer per 1 kg apple. Organic fertilizer is applied in the middle and late September, and an appropriate amount of quick acting fertilizer is applied after germination, flowering, fruit expansion and fruit harvest to meet the needs of tree body and fruit growth. It should timely water after topdressing.6.3 Water management
6.3.1
Irrigation. Irrigation is implemented according to DB13/T 1446-2011, and water management takes "early guarantee and later control" as principle. Irrigation period should be determined according to soil moisture, mainly including four key periods: germination stage, rapid growth stage of spring shoot, rapid expansion stage of fruit and before freezing. Water saving irrigation is advocated.6.3.2
Draining. Drainage ditches shall be dug in flat orchards, and the depth shall reach below the live soil layer. The ditch under the weir shall be dredged in the terrace to ensure smooth drainage.7 Tree shape selection and high spindle shaping and pruning
Tree shape selection is related to planting density, frame type, rootstock type, soil, fertilizer and water conditions. In the region with fertile soil, more rainfall or irrigation condition, high spindle shape can be selected for wide row dense planting. In the region with drought or poorer soil condition, the planting density is low, and the tree shape can be high spindle shape or slender spindle shape. Trunk height of high spindle is 80 cm, and tree is 3.5-4.0 m high, and crown diameter is 150 cm. The central trunk is upright and strong, and 35-45 small main branches directly grow on the central trunk, which are evenly arranged in a spiral rising shape. The upper and lower spacing of the main branches on the same side is about 30 cm. The opening angle of the main branch is 110-120°, extending uniaxially, and fruiting branches are directly attached to the main branch. The subordinate relationship between the small main branch and the central stem is obvious, and the branch stem ratio is between 1∶3 and 1∶5. Average length of small main branch does not exceed 75 cm, and their lengths up and down the canopy are basically consistent. The tree crown is long and narrow, and the tree shape is compact, showing high spindle.
7.1 Pruning in forming period
7.1.1
Pruning in dormancy period. The elongated branches of the central trunks of 1-2-year-old trees are mainly light and short cut, and the lateral branches on the central trunk are not short cut. The competitive branches and near ground branches are cut off to promote the vertical growth of the central trunk. The extended branches of the central trunks of 3-year-old trees are not truncated, but the large fruiting branches on the central trunk and new shoots that the thickness exceeds 1/3 of the thickness of the inserted part are dredged. The angle between the fruiting branch and the central trunk should be maintained at 110-120°, and the dorsal branch and elongated head competing branch on the small main branch should be removed.7.1.2
Pruning in growth period. In the first and middle of May, when the length of new shoots at the top of the central trunk of 1-2-year-old young trees is more than 20 cm, the one with the strongest growth is selected as the extension branch of the central trunk. The second, third and fourth bud branches below the extended branch of the central trunk shall be removed or re shortened. When re shortened, the cut length shall be 3-5 cm. When the length of new shoots on the central trunk is more than 30 cm, the base angle shall be opened in time. In the growing season, the main branches shall be kept drooping by taking and pulling branches, and the length shall be controlled at 70-80 cm in combination with coring.7.2 Pruning in early fruit stage (4-6-year-old)
It is mainly to remove the long and dense branches, and cultivate the strong fruiting branch group dominated by the small and medium fruiting branch group, so as to adjust the amount of fruit and reasonably load. In addition to winter pruning, measures such as cutting buds, pulling branches, twisting tips, and picking hearts should also be taken to strengthen flower promotion and pruning in the growing season. The tree height is kept at 3.5-4.0 m, and the crown diameter is about 150 cm. The small main branches on the central trunk that are too dense and whose thickness exceeds 1/3 of the thickness of the growing part are removed year by year. It should timely remove the branches on the back and competitive branches.7.3 Tree pruning at full fruit stage
After 7 years, the tree enters the full fruit stage. In this stage, the tree shape pruning work is mainly to remove 2-3 too thick small main branches with a diameter of more than 3 cm every year to maintain the balance of the tree structure. It should remove over dense branches or upright branches on the back to ensure ventilation and light transmission in the tree crown and between rows. It should retract the branches with long fruiting years and weak growth, so as to maintain the momentum of the golden mean tree and prolong the fruiting years.8 Pollination
Pollination by bees or wall bees is used to improve fruit setting rate and fruit uniformity.
9 Thinning flowers and fruits
By thinning flowers and fruits, the load is reasonably controlled, making the yield stable at about 37 500 kg/ha. When thinning flowers, it should remove the edge flowers and leave the center flowers, remove the axillary flower buds and leave the top flower buds, remove the back flowers and leave the lateral and drooping flowers, to ensure the correct fruit shape. During fruit thinning, the spacing of young fruits is between 10 and 20 cm.
10 Pest control
Pest control is implemented according to Chapter 9 in NY/T 441-2013, Chapter 9 in NY/T 5012-2002, and Chapter 9 in NY/T 1084-2006. Taking agricultural, physical and artificial control as the basis, and biological control as the core, according to economic threshold of pest occurrence, it should rationally use chemical control technology to economically, safely and effectively control diseases and insect pests. Methods of pest control refer to Table 1.
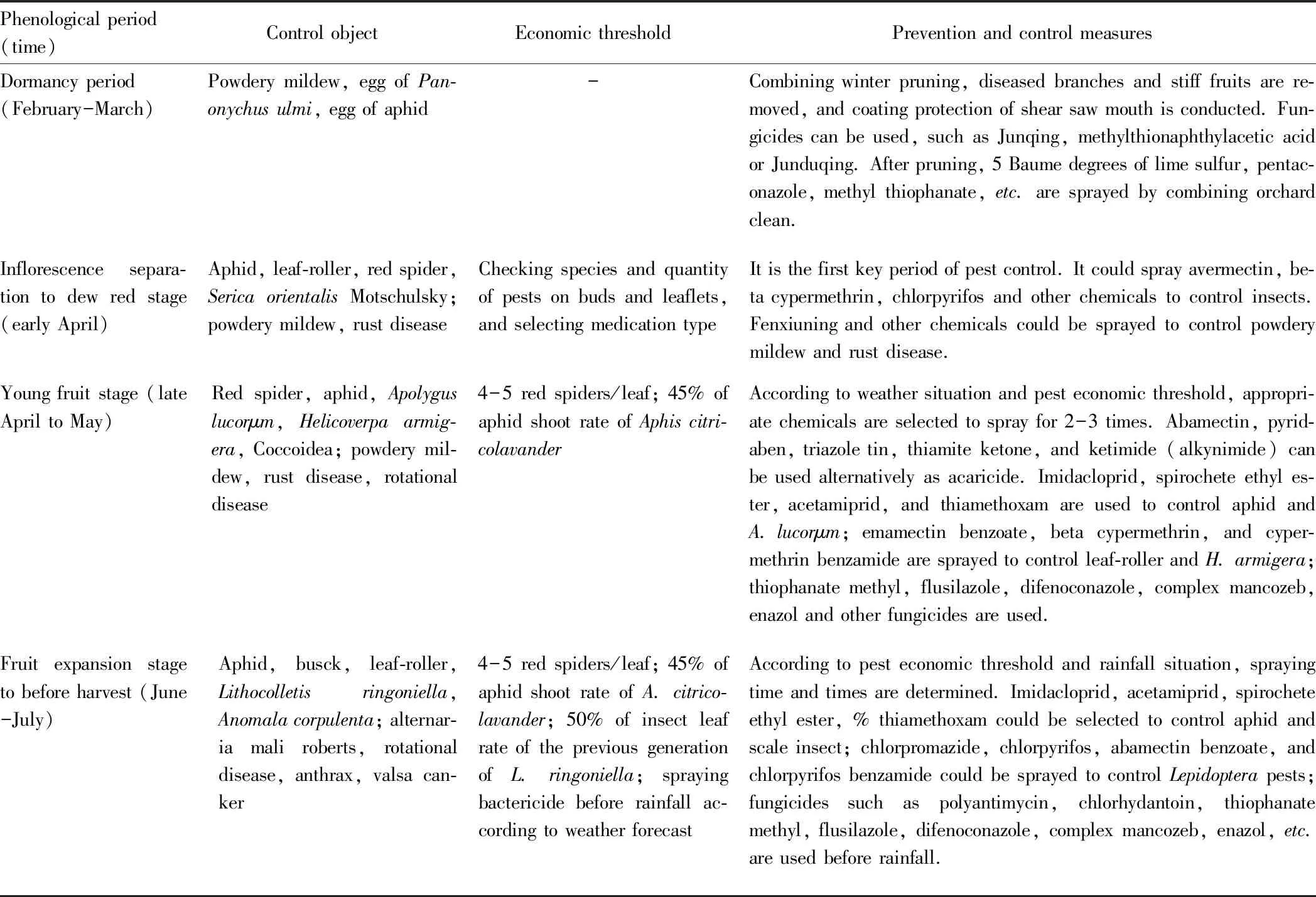
Table 1 Integrated pest management of apple ‘Jiping 1’
11 Fruit harvesting
It is harvested from late July to early August, to supply fresh food market. When harvest, it is handled with care to avoid damage, so as not to reduce the marketability of the fruit.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Effectiveness of Rain Classroom Intelligent Teaching Design: A Case Study of the Course of Spring Water Tourism Resources
- Investigation of Cultivated Woody Plant Resources in Ping’an District of Qinghai Province in China
- Effect of Labor Skills Training on Industrial Development and Economic Benefits of Winter Potato in Regions Inhabited by Ethnic Minorities: A Case Study of Lancang Lahu Autonomous County
- Strategies for Prioritizing Ecological Construction with Consideration of Agricultural Industry Development in Northern China’s Agro-pastoral Ecotone: A Perspective of Opportunity Cost
- Construction Path of Farmer Education and Training System in the Context of Rural Revitalization
- Certification and Conversion Mode of Learning Achievement Based on Credit Bank under the Background of Higher Vocational Enrollment Expansion
