Effectiveness of Rain Classroom Intelligent Teaching Design: A Case Study of the Course of Spring Water Tourism Resources
2021-12-01WeijunZHAOYungangWEIXiaomeiLIUDongmeiZHANGMinDINGWenxinDUAN
Weijun ZHAO, Yungang WEI, Xiaomei LIU, Dongmei ZHANG, Min DING, Wenxin DUAN
School of Tourism, Taishan University, Taian 271000, China
Abstract [Objectives] To evaluate the effectiveness of Rain Classroom intelligent teaching in the course of Spring Water Tourism Resources. [Methods] The course of Spring Water Tourism Resources in the course of Overview of Tourism Resources was taken as an example, the pre-class preparation, in-class teaching, and after-class evaluation links were designed separately through the Rain Classroom platform. Then, a questionnaire survey was carried out for the students of Spring Water Tourism Resources. [Results] About 58.3% of the students believed that the greatest advantage of using the Rain Classroom teaching platform is that the learning method is flexible and can improve the ability of independent learning; 61.78% of students stated that playing 3D animation in the classroom has the best effect for learning different tourism resources; with the aid of the Rain Classroom platform, the communication between teachers and students becomes more timely, and the students’ ability to deal with practical problems can be practiced. [Conclusions] This study is intended to build an intelligent classroom model suitable for tourism management department based on the Rain Classroom platform. It is recommended to promote and apply this model in the teaching of tourism management.
Key words Rain Classroom, Intelligent classroom, Teaching design, Spring Water Tourism Resources (SWTRs)
1 Introduction
Intelligent education is an education method and it takes advantage of various intelligent network technologies to guide, assist, and inspire learners to self-learn and discover, create, and apply their wisdom. The outbreak of COVID-19 promoted the progress of online education. The Ministry of Education of China launched an initiative entitled "ensuring learning undisrupted when classes are disrupted". Up to 300 million students realized learning through online education platform. Such new technologies as artificial intelligence, big data, and 5G have shown people the potential of education. The Rain Classroom platform well integrates PowerPoint and WeChat, and covers the pre-class, in-class, and after-class links in a scientific manner. This platform can record, collect, analyze, process, evaluate and improve teaching activities, teaching behavior, teaching status and teaching effectiveness. With the aid of data analysis on the platform, teachers can teach students in accordance with their aptitude. The content of the Rain Classroom platform is vivid. Through 3D animation in class, it is able to simulate the formation process of tourism resources, so as to help students better understand tourism resources. At present, the foreign literature mainly focuses on the integration of Rain Classroom and discipline classrooms to explore teaching modes, mainly including English, Accounting, Computer and other disciplines; the research on the effectiveness of learning by the Rain Classroom platform. In this study, we constructed Flipped Classroom teaching mode based on the Rain Classroom and evaluated its application effectiveness. The results show that the combination of Rain Classroom platform and course practice can realize multi-channel communication and interaction inside and outside the classroom, fully mobilize students’ enthusiasm, and improve students’ comprehensive ability. For the Rain Classroom involved in the Chinese literature, the research objects involved elementary school, junior high school, high school, secondary vocational and higher education, and the research disciplines mainly involved English, mathematics, and information technology, indicating that the intelligent teaching design of Rain Classroom is a hot spot in the current research of various disciplines, while there are few studies about the tourism education. Under the premise that students have a high usage rate of mobile smart phones and WeChat, the Rain Classroom platform connects the entire pre-class, in-class, and after-class process of teachers and students, and play a positive role in optimizing the teaching effect. In this study, we combined the Tourism Resource Management course with the Rain Classroom, and analyzed the teaching process and methods of the intelligent classroom, to reform tourism education and promote the innovation of tourism teaching methods. Taking the Spring Water Tourism Resources (SWTRs) as an example, we studied the effectiveness of Rain Classroom intelligent teaching, to explore a suitable intelligent classroom teaching mode for Tourism Management department.
2 Research method
2.1 Questionnaire survey
Taking the SWTRs in the course of Overview of Tourism Resources of the Tourism Management department of Taishan University, we practiced the application of Rain Classroom in the teaching. Through distributing questionnaires to students of different grades of the course, we made a statistical analysis of the learning situation of the intelligent teaching of Rain Classroom, and accordingly made proper improvement of the classroom.2.2 Mathematical statistical method
With the aid of statistical analysis software SPSS, we carried out descriptive statistics and reliability and validity tests of survey data.3 Questionnaire and analysis based on the study situation of Overview of Tourism Resources
3.1 Purpose and objects of survey
The questionnaire objects were undergraduates from the Tourism Management department of Taishan University in the 2017, 2018, 2019, and 2020 grades and students from Tourism Service department in 2017 and 2018 grades. Basic information of survey objects is shown in Table 1. The questionnaire was completed in Wenjuanxing (https://www.wjx.cn) and a total of 259 copies of questionnaire were collected.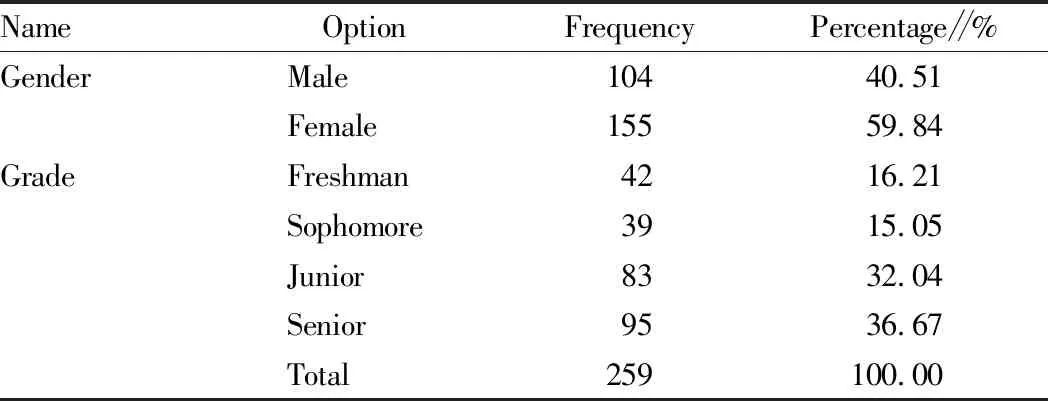
Table 1 Basic information of questionnaire objects
3.2 Questionnaire design
The questionnaire was designed with 18 questions, including multiple-choice questions (choosing one answer and several answers) and an open-ended short-answer question. The question types involve pre-class preparation, in-class teaching, and after-class evaluation. The questionnaire contents mainly included: (i) Personal information of the surveyed students, including gender, grade, and whether they have used Rain Classroom. (ii) Students’ attitude and experience of using Rain Classroom intelligent classroom design in the class of SWTRs. (iii) Advantages and disadvantages of Rain Classroom functions. (iv) Weak aspects that need to be improved in the Rain Classroom design of SWTRs, as well as the statistics of students’ learning situation and process evaluation. (v) Factors influencing students’ learning in the design of Rain Classroom.3.3 Analysis of questionnaire data
3.3.1
Students’ learning experience of using Rain Classroom for the SWTRs. Among the surveyed students, 36.89% said that they liked the application of Rain Classroom in the study of Tourism Resources, 45.4% showed that general attitudes towards the Rain Classroom, and 17.71% said they did not like (Fig.1). we cross-analyzed whether the Rain Classroom has a positive effect on the students’ learning, and whether the students like the application of Rain Classroom in the Overview of Tourism Resources. Among the students who did not like to use Rain Classroom, 84.37% still held that Rain Classroom has a positive effect on the mastery of classroom knowledge (Fig.2). Among the students who liked Rain Classroom, 98.25% believed that Rain Classroom has a positive effect on the mastery of classroom knowledge. Students preferred to use the Rain Classroom platform to learn the Overview of Tourism Resources and contended that this teaching method is more conducive to learning than traditional teaching methods.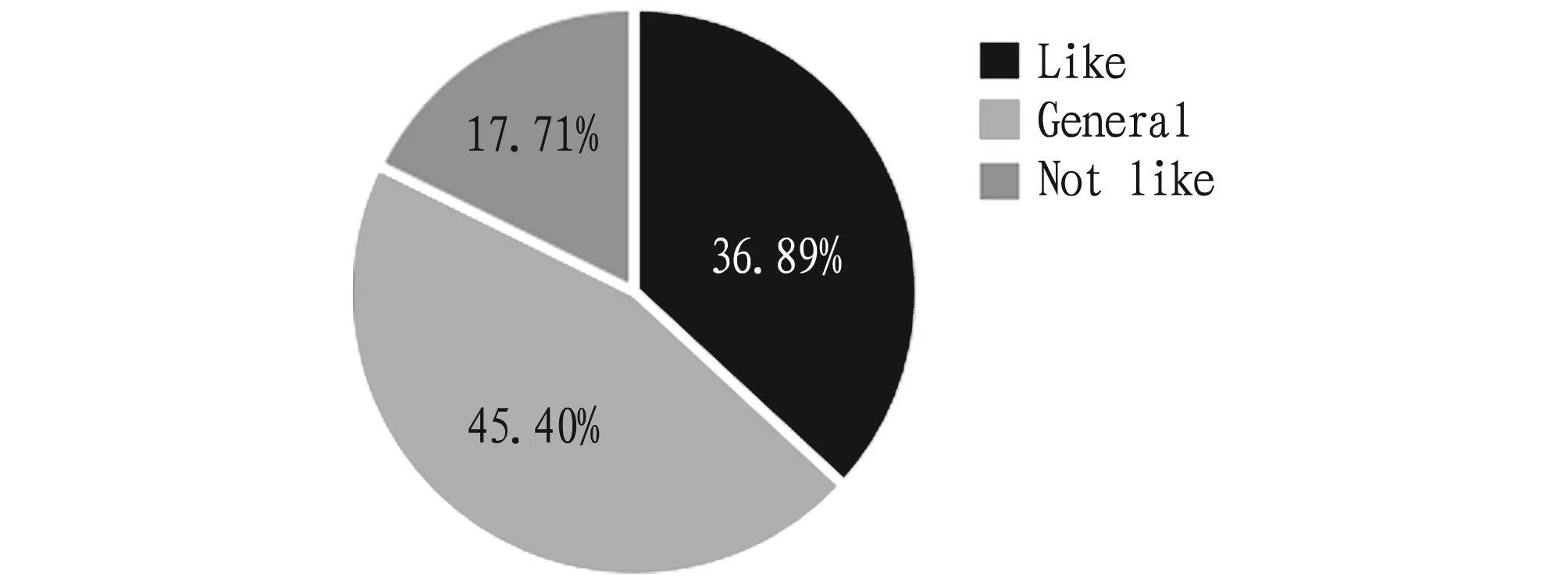
Fig.1 Whether students like the application of Rain Classroom in the study of Tourism Resources

Fig.2 Attitudes of students towards the Rain Classroom
3.3.2
Survey of use of Rain Classroom platform functions. In the surveyed students, 50% stated that they have used "classroom blackboard (PPT and blackboard two in one)" and "feedback for PPT slides not clear". Among them, the most frequently used function is "class blackboard (PPT and blackboard two in one)" (Fig.3A). Next, in the function of Rain Classroom, the frequency of random roll call in class, push of in-class exercises, and check of class notice was relatively high. On this basis, we surveyed which function of the Rain Classroom has the greatest help for students (Fig.3B). Among the surveyed students, 54.83% believed that the function of using Rain Classroom to push exercises in time to complete the teaching evaluation is the most helpful to the teaching effect, and 54.08% held that the PPT in the classroom synchronized to the mobile WeChat terminal helps the teaching effect the most. Compared with traditional classrooms, 58.3% of students stated that the biggest advantage of using the Rain Classroom intelligent teaching model is the flexibility of learning and it can improve the independent learning ability; 50.97% of the students said that the biggest advantage is that they can watch the teaching content repeatedly (Fig.3C); 57.53% stated the platform lacks effective supervision during the course of using Rain Classroom, and they are easily attracted by other mobile interfaces (Fig.3D).3.3.3
Analysis of learning process of the Rain Classroom. According to the survey, in the pre-class preview part of SWTRs, 75.29% students stated that they would read and complete the exercises in the preview video or text materials pushed before the class, but still 24.71% students said they would not preview (Fig.4A). In the use of Rain Classroom platform, 32.05% students believed that the most helpful content presentation form for the understanding of the teaching content is animation, and only 8.49% students thought that the form of blackboard writing is conducive to the understanding of the learning content (Fig.4B). In the interaction with the teacher, 25.48% students who have never asked the teacher for help when encountering difficulties, and only 24.33% said that they would ask the teacher for help (Fig.4C).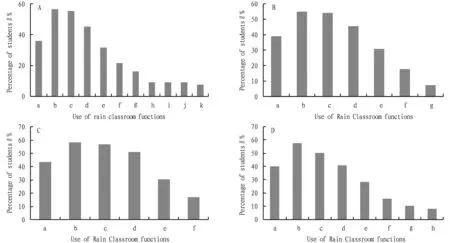
Note: A: a. use of Rain Classroom functions, b. random roll call, c. feedback of PPT slides not clear, d. classroom blackboard (PPT and blackboard two in one), e. push of exercises, f. check of classroom announcements, g. scroll through the teaching contents, h. answering class questions, i. making bullet-screen comments, j. after-class homework, k. participating in discussion, l. watching the replay of teaching contents;
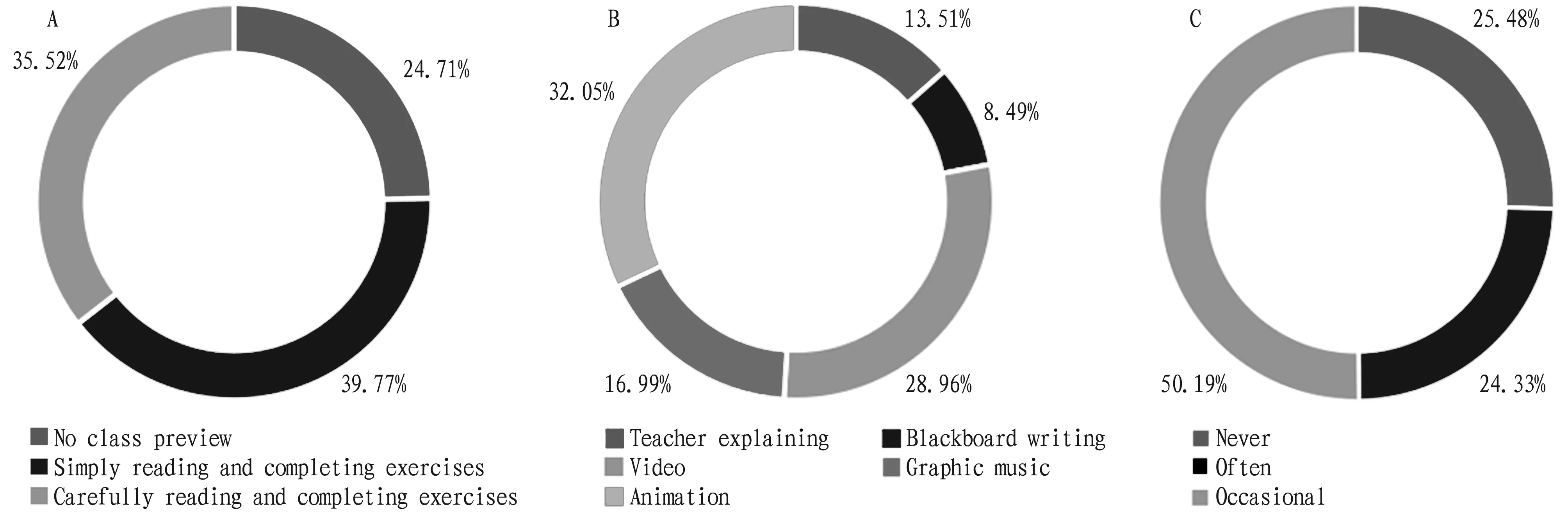
Note: A. Completion of class preview; B. Most helpful teaching content for knowledge understanding; C. Students asking help for teacher.
In the survey of process evaluation methods, 28.96% of the surveyed students stated that random testing in class is the most conducive to learning, while 22% believed that random classroom roll call can increase the classroom attendance and is the most favorable for learning (Fig.5). In the use of Tourism Resources in Rain Classroom, 61.39% students stated that they cannot find their knowledge blind spots and shortcomings in a timely manner in process evaluation, and 47.88% thought that the test method of teaching effect is relatively simple (Fig.6).
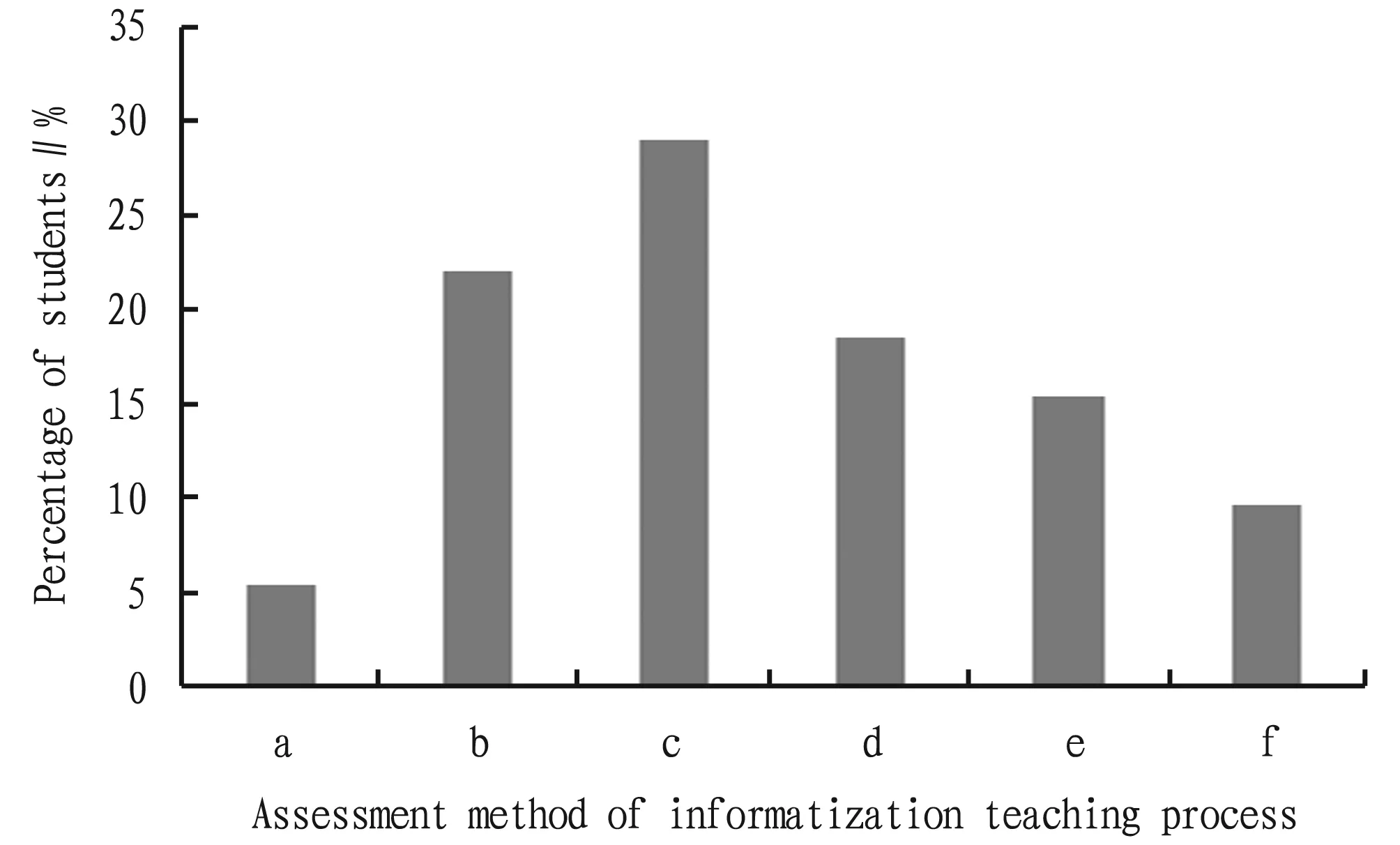
Note: a. questionnaire of learning, b. online feedback of understanding, c. team representative speaking, d. in-class exercise, e. classroom random roll call, f. after-class homework completion.
3.3.4
Analysis of the survey results of classroom improvement opinions. Among the surveyed students, 61.78% believed that playing 3D animation in the classroom has the best effect (Fig.7A). In the learning process of the Rain Classroom platform taking SWTRs as an example, 37.07% students believed that whether the learning materials are vivid and easy to understand are important factors influencing their learning (Fig.7B). The problems that students hope to improve in descending order of proportions were: vivid learning materials, enriching pre-class preview and video materials, and increasing the communication time between teachers and students and between students themselves during class (Fig.7C).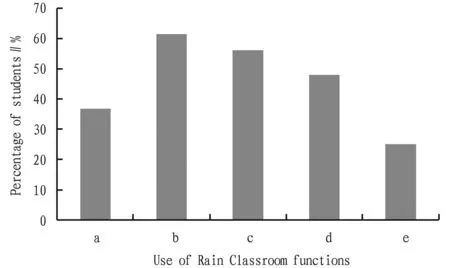
Note: a. learning effect assessment, b. failing to find knowledge blind spots and shortcomings, c. filing to receive prompt answer from teacher, d. single teaching effect assessment method, e. long assessment cycle, failing to guide next stage study.

Note: A: a. push of video materials, b. play of 3D animation, c. update of PPT blackboard, d. random roll call, e. making bullet-screen comments;
4 Teaching design and application research based on the Rain Classroom platform
4.1 Objects of teaching experiment
The experiment objects were undergraduates from the Tourism Management department of Taishan University. Taking the knowledge points of SWTRs as an example, we carried out the experiment of WeChat Rain Classroom platform.4.2 Teaching practice process
Students and teachers can use Rain Classroom platform under Windows and MacOS systems, and can also use the platform’s independent mobile client. It covers all teaching scenarios, can be used online and offline before class, during class and after class, and can connect microphone for interaction and can use cloud recording function. This teaching practice uses Windows and WeChat mobile platforms as teaching tools, and Rain Classroom as the technical support for intelligent classroom. Taking the chapter of SWTRs in Overview of Tourism Resources as example, we carried out the teaching practice and quantified various learning behavior data.4.2.1
Design of pre-class process. This mainly refers to the preview before the class. The ideal classroom is that both teachers and students are prepared and there is sufficient interaction in the classroom, but this is not easy to achieve for a big class. Rain Classroom can help teachers provide presentation materials in class, including video and text materials. Through online feedback from students, teachers can promptly adjust the key explanations in the classroom and grasp the learning situation of students, so as to obtain better teaching effect. Before students formally enter the classroom, teachers can use Rain Classroom platform to assign learning tasks: (i) through playing short videos, asking students to join in and enter the platform to preview; (ii) logging on to the online course platform to view the teacher’s online courses, and preview the river landscape and SWTRs; (iii) based on the contents of the preview, getting a simple understanding of river landscape and SWTRs. Students can log on to the platform to view the learning tasks, collect and download learning materials, watch teaching videos, which will stimulate their learning interest. The teacher can clearly define the scope of the preview through issuing the announcement (Fig.8A), and pushing the corresponding pre-class discussion (Fig.8B), and also can use Rain Classroom platform to review the students’ learning situation (Fig.8C). Through the data in the backstage of Rain Classroom platform, the teacher can see the students’ preview status, such as whether they have previewed the content or not, the preview time and duration (for the default of Rain Classroom, each slide of PPT would stay three seconds for preview records), so as to count the students’ pre-class preview status. The teacher can use the feedback of Rain Classroom to explain the content of the course for pre-class preparation (Fig.9). In the course of the class, students can also communicate with the teacher about their questions.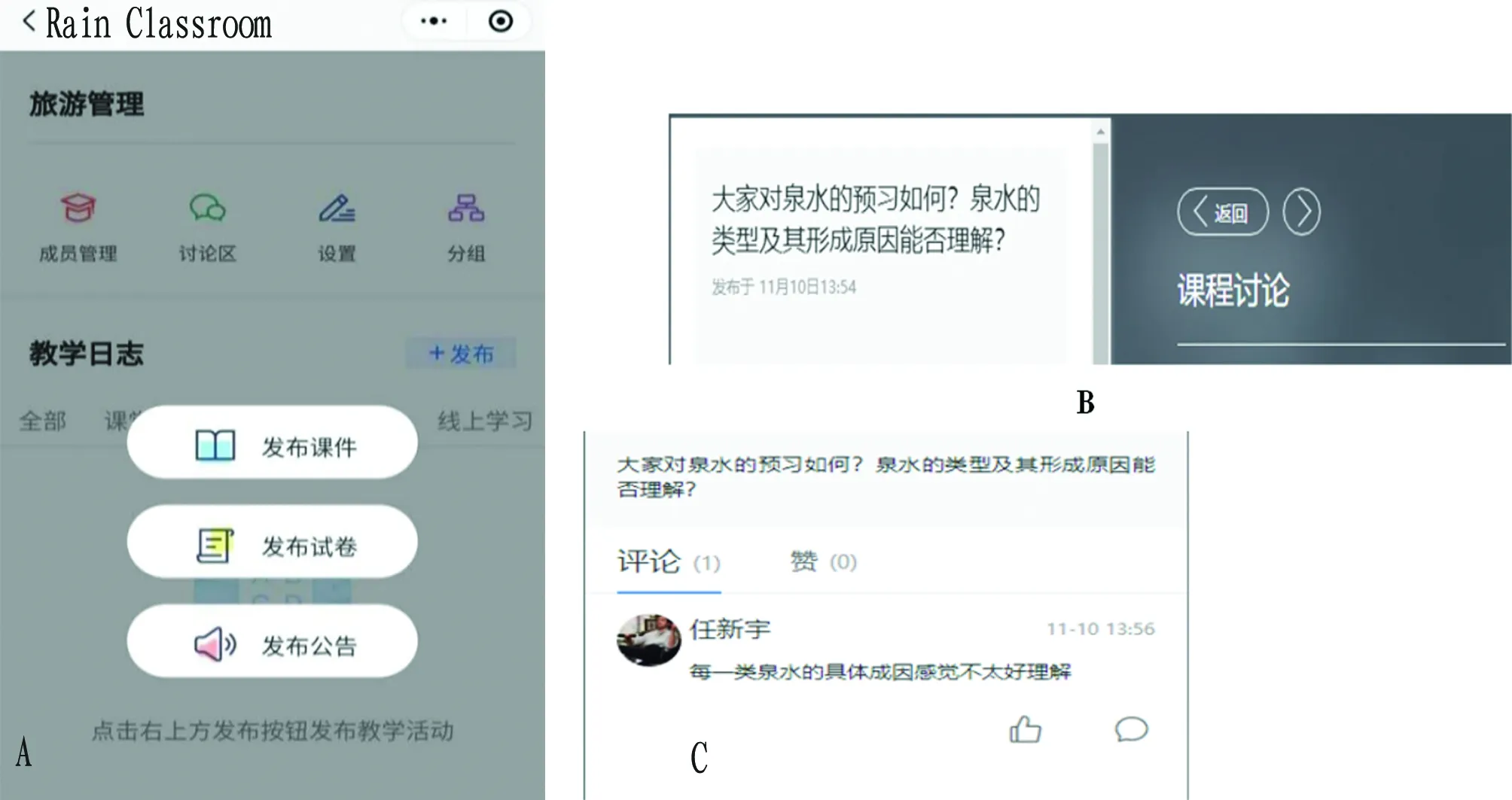
Note: A. Issue announcements; B. Course discussion; C. Pre-class preview feedback.

Fig.9 Rain Classroom learning data
4.2.2
Design of in-class process. (i) Organizing students to log onto the Rain Classroom. The teacher asks students to scan the QR code to log onto the Rain Classroom and sign in randomly. The Rain Classroom backstage monitors the student’s sign-in rate through data to help the teacher make a record of the attendance rate of the students, which changes the traditional classroom roll call method and saves their time, and take full advantage of the classroom teaching time.(ii) Teaching process of Rain Classroom intelligent classroom. The teacher first uses the Rain Classroom platform to discuss online, so that students can recall the previous learning content. The students can summarize the learning content of this course by consulting course materials and online course teaching materials before class. Subsequently, the teacher used short videos of SWTRs to create a situation and introduce a new lesson (Fig.10). Video importing is more intuitive and can break the limit of imagination. Through videos, students can observe the characteristics of SWTRs from multiple angles, which is helping for understanding concepts and mastering methods. The combination of sound and video can make students more quickly concentrate their attention in the classroom.

Fig.10 Short video examples of Spring Water Tourism Resources
The teacher uses the Rain Classroom platform to assign the learning tasks in this chapter: the main types of river landscapes; the reasons for the formation of SWTRs; the main types of SWTRs. During the task implementation, the teacher uses video materials, consult network platform materials, and use the Rain Classroom platform and teaching animation to explain in detail the theoretical knowledge of SWTRs. During guiding the interaction between teachers and students, through the Rain Class platform, the teacher can start the function of making bullet-screen comments, organize classroom discussions, activate the classroom atmosphere, and strengthen the interaction between teachers and students in real time. Besides, the teacher can make a random roll call, to check the mastering of knowledge. In addition, the teachers can design in-class quizzes on the knowledge points of SWTRs. The platform can show the results of the quizzes in real time. On the basis of this, the teacher can analyze the data and give his answers to the questions. The teacher can judge students’ mastery of knowledge points based on students’ real-time answering questions, so as to adjust the teaching rhythm in time in class. For knowledge points with a high error rate in the question, the teacher can explain the exercises in time.
In the course of student learning, the teacher uses the Rain Classroom platform to send subjective questions based on the teaching goals, such as "Please search the well-known Spring Waters through network resources, please give 3-5 well-known Spring Waters, and state their tourism functions?" (Fig.11). Through the Rain Classroom platform, the teacher makes online grouping and divide the students into four groups (Fig.12). The grouping function can only be used to answer subjective questions. After class discussion, each group submits answers, and the teacher evaluates the completion of the tasks of each group, and uploads the evaluation results to the Rain Classroom platform.

Fig.11 Subjective question pushed by Rain Classroom platform

Fig.12 Online grouping on the Rain Classroom platform
In the process of learning on the Rain Classroom platform, students can give feedback and communicate with the teacher in time. Also, they can make anonymous bullet comments, or click "not understand" to give feedback on the courseware that is difficult to learn, and also can click "Favorite" to review after class (Fig.13). During the teaching process on the Rain Classroom platform, the teacher can check the "not understand" status of students in real time, adjust the teaching progress in time, and provide targeted explanations or special guidance. After the class is completed, both students and the teacher can view the teaching log, and the Rain Classroom platform will send detailed student learning statistics to the teacher’s mailbox (Fig.14).

Fig.13 Teaching log
Fig.14 Learning situation data of students
4.2.3
Design of after-class process. After class, the teacher can make online homework through the Rain Classroom platform: assign homework, search network resources, combine practice, and fully understand the types of river landscape and SWTRs, listen carefully, make a record and accept homework. The teacher customizes the display time of the answer and sets the delayed answer display, so that students can view the answers and analysis immediately after completing the exercises. Besides, the teacher can set the time and deadline for answering the exercises. Students who have not completed the exercises before the deadline will receive a reminder. The Rain Classroom platform will present the completion of the students’ exercises after class. The platform automatically corrects objective questions and calculates points. The teacher can intuitively see the data of students’ answers to exercises and obtain the correct rate of each question, so that the teacher can adjust the next teaching plan and grasp the change of learning situation of students. In addition, students can obtain the prompt evaluation of the teacher during the use of the Rain Classroom platform. Furthermore, the teacher can also send the link of the course learning expansion materials (audio/video/document/web articles) to students anytime and anywhere, and students can view these materials on their mobile phones. The teacher’s courseware will be uploaded to the student’s mobile phone WeChat simultaneously, and students can download and review at any time (Fig.15).
Fig.15 Download of materials
5 Conclusions
Taking the SWTRs as an example, we studied and analyzed the design and application of the Rain Classroom platform. We arrived at the following conclusions.
(i) Online learning becomes gradually in-depth. Especially, the professional knowledge of tourism management is characterized by strong application, strong practicality and high comprehensiveness. Taking the Overview of Tourism Resources as an example, in traditional classrooms, teachers use language explanation as the main teaching method. The students’ auditory, visual and other sensory systems are restricted, and their learning effect could not reach the ideal state. By comparison, the Rain Classroom teaching platform combines a variety of intelligent teaching tools in teaching, provides users with a variety of terminals, and provides learning materials according to students’ personal needs and learning characteristics, so it can raise learning interest of students.
(ii) In the Rain Classroom intelligent classroom design taking SWTRs as an example, teachers and students use the Rain Classroom platform to communicate and interact. The interaction of the intelligent classroom is based on the function of making bullet comments of the learning platform, which realizes efficient, instant and multi-dimensional interaction between teachers and students during the interaction process, and promotes the generation of deep learning results. The intelligent classroom further exercises students’ ability to deal with practical problems through group cooperation and multimedia scenario simulation.
(iii) Intelligent classroom is an intelligent and efficient classroom supported by a new generation of information technology. A prerequisite for implementing intelligent classroom teaching is to build an intelligent teaching service platform based on intelligent information technology. In the Rain Classroom intelligent classroom design taking SWTRs as an example, the application of information technology plays a supporting role in the teaching process. The Rain Classroom platform takes advantage of the big data to analyze the data of students’ learning process and feed back to teachers.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Investigation of Cultivated Woody Plant Resources in Ping’an District of Qinghai Province in China
- Technical Regulations for Production of Apple ‘Jiping 1’
- Effect of Labor Skills Training on Industrial Development and Economic Benefits of Winter Potato in Regions Inhabited by Ethnic Minorities: A Case Study of Lancang Lahu Autonomous County
- Strategies for Prioritizing Ecological Construction with Consideration of Agricultural Industry Development in Northern China’s Agro-pastoral Ecotone: A Perspective of Opportunity Cost
- Construction Path of Farmer Education and Training System in the Context of Rural Revitalization
- Certification and Conversion Mode of Learning Achievement Based on Credit Bank under the Background of Higher Vocational Enrollment Expansion
