阴茎部分切除加延长术治疗早期阴茎癌的临床效果
2021-11-13刘春生卢华荣
刘春生 卢华荣

[關键词] 阴茎部分切除术;阴茎全切术;阴茎延长术;早期阴茎癌
[中图分类号] R737.27 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)25-0058-03
Clinical effect of partial penectomy and penile lengthening in the treatment of early penile cancer
LIU Chunsheng LU Huarong
Department of Urology, the Second Hospital of Longyan in Fujian Province, Longyan 364000, China
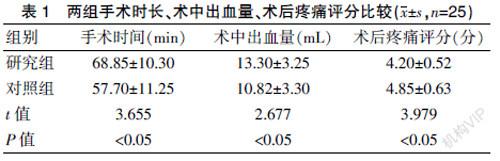
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the clinical effect of partial penectomy and penile lengthening in the treatment of early penile cancer. Methods A total of 50 patients with early penile cancer admitted to our hospital from January 2018 to January 2020 were divided into two groups by random number table. Twenty-five cases in the control group underwent total penile resection, and 25 cases in the study group underwent partial penectomy and penile lengthening. The operation time, intraoperative blood loss, postoperative pain score, postoperative tumor recurrence, incision infection, external urethral stenosis, urination, preoperative and postoperative SAS score, and SDS score were compared between the two groups. Results The operation time of the study group was longer than that of the control group. The amount of intraoperative blood loss of the study group was higher than that of the control group, and the postoperative pain score was lower than that of the control group. The difference was statistically significant, P<0.05. There was no tumor recurrence, incision infection or external urethral stenosis in the two groups after the operation. The control group cooperated with the urethral perineum fistula after the operation, and the patients squatted to urinate normally. The study group stood to urinate normally after the operation, and the voiding function was not affected. The preoperative SAS score and SDS score of the two groups were significantly different between the two groups(P>0.05). The SAS score (48.3±4.5) and SDS score (52.2±4.0) of the postoperative study group were lower than those of the control group [(64.2±5.8) and (63.3±4.8)]. The difference was statistically significant(t=10.830, t=8.883, P<0.05). Conclusion In the clinical treatment of early penile cancer, partial penectomy, and penile lengthening can restore normal urination function, reduce postoperative pain, improve the negative emotion of patients and promote the improvement of patients′ quality of life.
[Key words] Partial penectomy; Total penectomy; Penile lengthening; Early penile cancer
