右美托咪定与咪达唑仑在机械通气重症患者镇静中的效果比较
2021-11-13钟盛华鄢志磊吴乐峰危雪晖
钟盛华 鄢志磊 吴乐峰 危雪晖
[關键词] 右美托咪定;咪达唑仑;机械通气;重症;镇静;血流动力学
[中图分类号] R614 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-9701(2021)25-0035-04
Comparison of the effects of dexmedetomidine and midazolam in the sedation of severely ill patients with mechanical ventilation
ZHONG Shenghua1 YAN Zhilei1 WU Lefeng1 WEI Xuehui2
1.Department of Critical Care Medicine, Fuzhou First People's Hospital in Jiangxi Province, Fuzhou 344000, China; 2.Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Fuzhou First People′s Hospital in Jiangxi Province, Fuzhou 344000, China
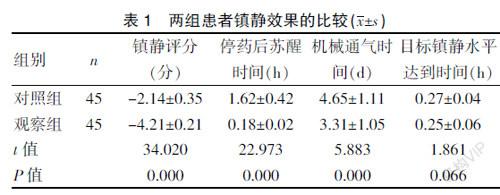
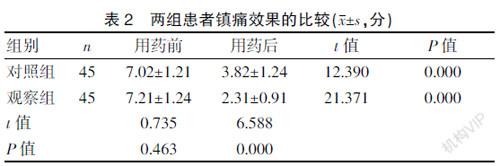
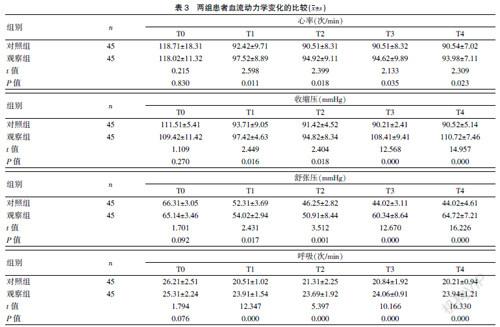
[Abstract] Objective To explore the value of dexmedetomidine and midazolam for sedation in severely ill patients with mechanical ventilation. Methods From January 2019 to December 2020, 90 mechanically ventilated critically ill patients admitted to Fuzhou First People′s Hospital were selected as the research objects. They were divided into the observation group and the control group according to a 1:1 ratio, with 45 cases in each group. The observation group was sedated with dexmedetomidine, and the control group was sedated with midazolam. The sedative effect, analgesic effect, hemodynamic changes, and the incidence of adverse reactions were compared between the two groups. Results ①Sedation effect: the observation group′s sedation score (-4.21±0.21) points, wake-up time after stopping the drug (0.18±0.02) h, mechanical ventilation time (3.31±1.05) d were shorter than those of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The time to reach the target sedation level (0.25±0.06) h in the observation group was no different from the control group. ②Analgesic effect: The VAS score (2.31±0.91) of the observation group was lower than that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). ③Changes in hemodynamics: The heart rate, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and respiration of the observation group during T1, T2, T3, and T4 were higher than those of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). ④The incidence of adverse reactions of the observation group (4.44%) was lower than the control group (22.22%), and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion Dexmedetomidine in sedation of severely ill patients with mechanical ventilation has a significant effect. It can improve the patient′s sedative and analgesic effect, improve the changes in hemodynamics, and avoid fluctuations in blood pressure and heart rate, which greatly affect the sedative effect. And it is worth learning.
