A network pharmacology-based study on the anti-hepatoma effect of Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex
2021-11-05QiulinYanGuodongYao
Qiulin Yan,Guodong Yao
Key Laboratory of Computational Chemistry-Based Natural Antitumor Drug Research&Development,Liaoning Province,School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China
Abstract Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex (PCC) has been used for the treatment of human hepatocellular carcinoma,but the underlying mechanisms are still unclear.In this study,15 active compositions of PCC were obtained from Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database (TCMSP),and 505 putative identified targets of PCC were screened by Swiss Target Prediction server.Next,HCC data was downloaded from Drugbank and GeneCards databases.Furtherly,45 common targets were revealed.The network diagrams of the active component-target network,proteinprotein interaction (PPI) network and active component-target-pathway network were constructed using Cytoscape software.The analysis of the network results showed that the active ingredients of PCC,such as berberine,obacunone,rutaecarpine,candletoxin A,palmatine,isocorypalmine,quercetin,and (S)-Canadine,had a good binding activity with more targets.Additionally,Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses revealed that common targets were significantly enriched in Ras signaling pathway,ErbB signaling pathway,and Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)signaling pathway.Altogether,the multi-component,multi-target,and multi-pathway characteristics of PCC provided a reference for the in-depth study of the mechanism of PCC in the treatment of HCC.
Keywords:network pharmacology;Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex;human hepatocellular carcinoma;traditional Chinese medicine
1 Introduction
The etiologies of hepatocellular carcinoma(HCC) are diverse,involving many factors,such as HBV and HCV infection,genetics,diet,obesity,and environment.HCCs are primarily composed of cells with hepatic differentiation [1].According to Global Cancer Statistics 2020,liver cancer becomes the sixth leading cause of cancer incidence in 2020 and the third leading cause of cancer death in the world [2].At present,patients with hepatoma are usually treated with surgical resection or transplantation [3].However,most hepatoma patients are diagnosed with advanced disease,usually accompanied by micrometastases [4].Under such circumstances,chemotherapy has become an irreplaceable strategy in the treatment of hepatoma.
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has been playing a key role in improving the quality of life and curing disease.In recent years,Chinese herb medicine has attracted increasing attention worldwide for the treatment of disease.Phellodendri Chinensis
Cortex,the dried bark ofPhellodendron chinense
Schneid has multiple functions such as clearing away heat,eliminating edema,antioxidative stress,and regulating immunity,and is widely used in clinical practice in China.In addition,it has been proved to have antitumor effects,and some compounds have obvious cytotoxic activity on hepatoma cell line [5].Studies have shown that some components of PCC,such as berberine andβ
-sitosterl,have an inhibitory effect on HepG2 cells [6,7].The ability of PCC to inhibit hepatoma cells has been validated,but the pharmacological mechanisms and material bases related to HCC remain obscure.Network pharmacology can not only explain the relationship between compounds,targets,and diseases,but also visually present the drug target network on the whole [8].It has become a comprehensive tool to systematically reveal the complex network relationship between the bioactive components and potential mechanisms of TCM formulas [9].The purpose of this study was to explore the potential mechanism of PCC on HCC by using network pharmacology means,including active compound screening,target prediction,proteinprotein interaction (PPI) network construction,enrichment analysis and active component-targetpathway network construction,so as to clarify the medicinal value of PCC.The workflow of the study was shown in Fig.1.
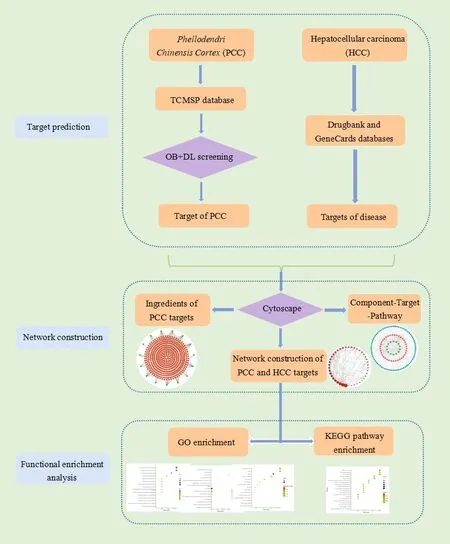
Fig.1 Flowchart of determining the pharmacological mechanisms of PCC on HCC with network pharmacology
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Database Building and Active Compound Screening
All compound data of PCC were obtained from Traditional Chinese Medicine System Pharmacology Database (TCMSP,http://lsp.nwu.edu.cn/tcmsp.php).The TCMSP Database analysis platform is a comprehensive Chinese medicine analysis platform that captures the relationship between herbal ingredients,targets,and diseases [10].It includes more than 13731 pure compounds isolated from 505 TCM herbs.The database provides 12 ADME parameters,such as oral bioavailability (OB),halflife (HL),drug-likeness (DL),Caco-2 permeability(Caco-2),blood-brain barrier (BBB),corresponding targets and related diseases for each compound [11].PCC compounds were screened based on absorption,distribution,metabolism,and excretion (ADME),and OB ≥ 30% and DL ≥ 0.18 were used as the cutoff of bioactive compounds for further analysis [12].
2.2 Predicting the targets of PCC
Information on PCC-related target genes was obtained from the Swiss Target Prediction tool (http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/),developed and maintained by Molecular modelling group of Swiss Institute of bioinformatics (SIB).Swiss Target Prediction tool,a data platform that is used to estimate macromolecular targets of small molecules [13].We uploaded the Canonical SMILES structural formula of the active ingredients of PCC in turn,selected Homo sapiens as the species,and clicked Predict targets to accurately predict the targets related to PCC.In addition,we used UniProt database (http://www.uniprot.org/) to obtain the gene names of all targets,with the selected species being human.
2.3 Construction of active component-target network
A visual network was constructed through Cytoscape (version 3.6.1;https://www.cytoscape.org/) software based on the active compounds and potential targets.Nodes represent the components and targets,while edges represent the intermolecular interactions between compounds and targets.
2.4 Searching HCC-related targets
HCC-related genes were collected from two databases.GeneCards (http://www.genecards.org) is an automated integrative database of human genes that provides genomic maps,proteomic,diseases,transcriptomic,genetic,and disease information.The database automatically integrates gene-centric data from 125 web sources,such as HGNC,NBCI,and Ensemble [14,15].Drugbank (https://www.drugbank.ca/) is a free web-enabled database that combines detailed drug data with comprehensive drug-target and drug-action information.It was specifically designed to facilitate silico drugtarget discovery,drug design,drug-metabolism prediction,drug-interaction prediction,and general pharmaceutical education [16].In these two databases,we used the keywords“hepatocellular carcinoma”as the query to search for known therapeutic targets of diseases.
2.5 Collecting compound-disease common target
The screened compound targets and disease targets database were imported into the ImageGP(http://www.ehbio.com/ImageGP/index.php)platform for analysis.The Venn diagram was drawn,and the common targets of compound and disease were obtained as the potential targets for further analysis.
2.6 PPI network map of compound-disease common targets
Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was derived based on STRING database (https://stringdb.org/),an online database of known and predicted protein-protein interactions,with the species set to“Homo sapiens”and the confidence score >0.4.The target interaction information,obtained according to the analysis results were put into the Cytoscape software where the interaction network was drawn and analyzed [12].The size of the nodes was used to reflect the degree value which represents the number of the combined targets.
2.7 Gene ontology (GO) and KEGG pathway enrichment
The proteins in PPI network were placed in the DAVID (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/) database for GO enrichment and pathway enrichment analyses.Enrichment analysis results of the study were screened according toP
<0.05 to exclude specific disease pathways.2.8 Construction of active component-targetpathway network
The active components of PCC,common targets and pathways were uploaded to the cytoscape 3.6.1 software to construct a network diagram of active component-target-pathway network.
3 Result
3.1 Chemical compositions and the targets of PCC
Thirty-seven compounds of PCC were collected from the TCMSP,with OB ≥ 30% and DL ≥ 0.18.Among the 37 compounds obtained,15 ingredients were selected as candidate compounds (Table 1)which yielded 505 putative targets (Supplementary Table S1).
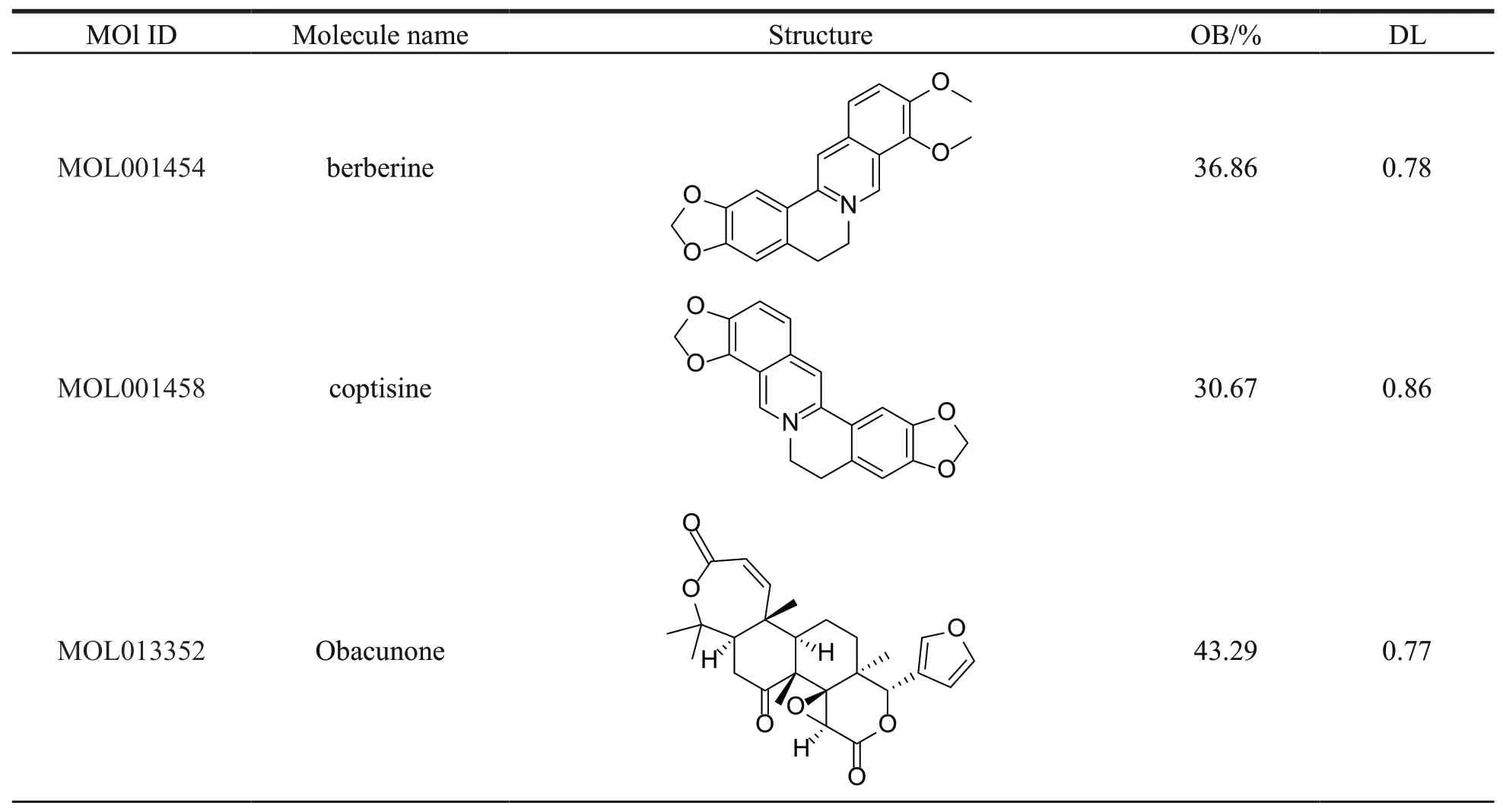
Table 1 Basic information of PCC compound ingredients
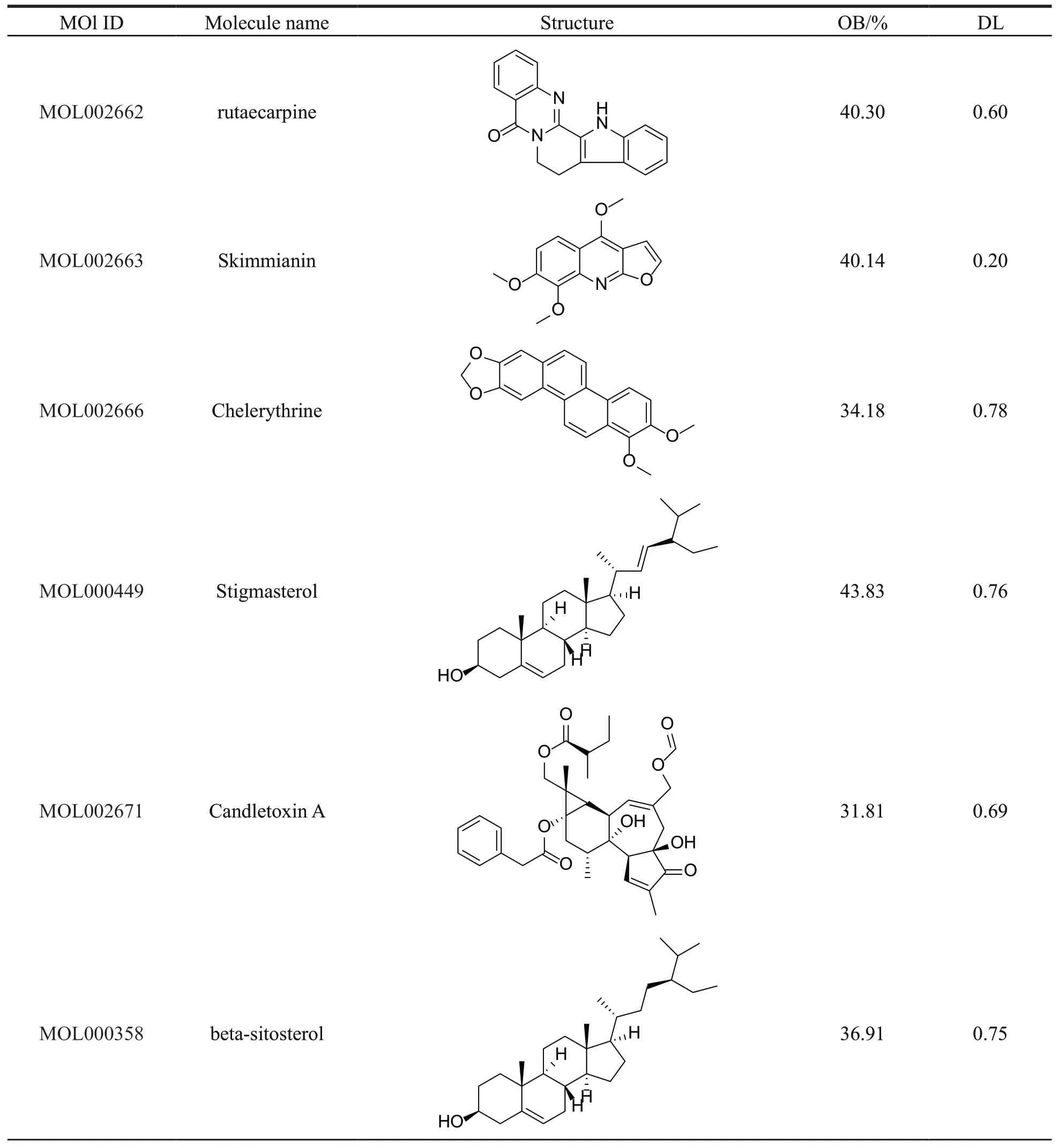
Continued table 1
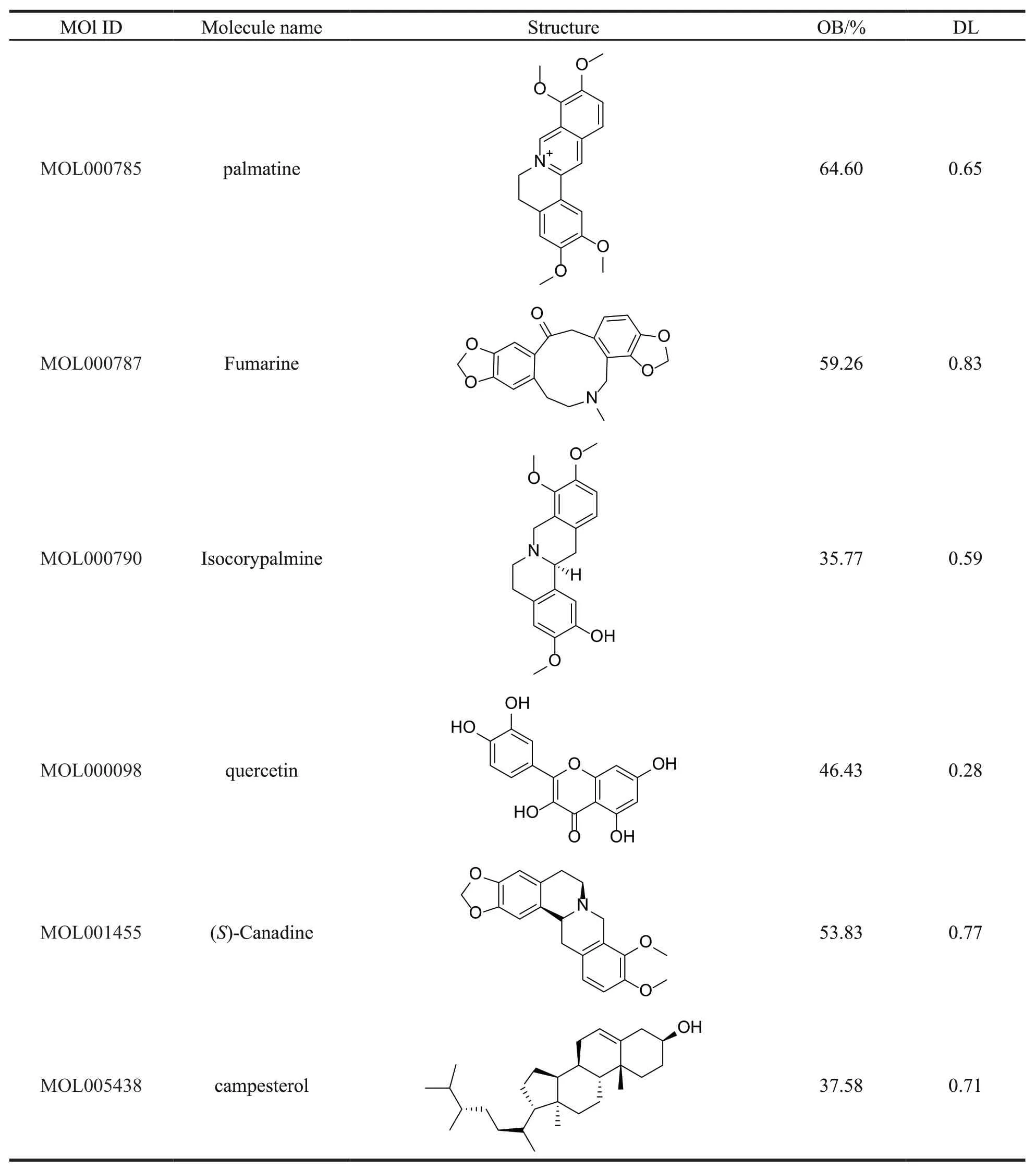
Continued table 1
3.2 Compound-target network
To clarify the complex interactions of PCC constituents with their corresponding targets at the system level,we constructed a compoundtarget network,as shown in Fig.2.The network embodied 151 nodes and 296 edges,in which the inverted triangles represent the potential active compounds in PCC,and the round shapes represent the corresponding targets of the compounds.Among the compounds,six compounds have relatively more targets,they are rutaecarpine,Candletoxin A,(S
)-Canadine,Obacunone,palmatine and quercetin,with 111,110,110,107,103 and 103 targets respectively.The result suggests that these six components probably are of great significance in the therapy of HCC.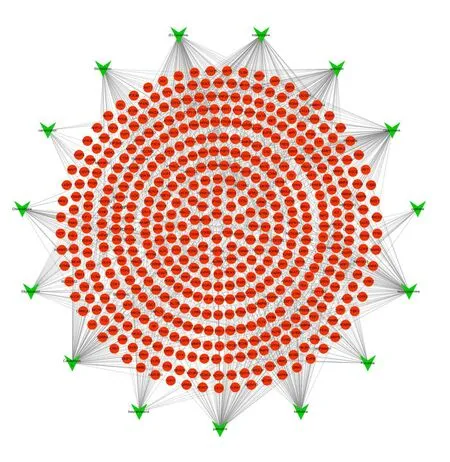
Fig.2 Compound-target network of potential targets in PCC.The inverted triangles represent the potential active ingredients in PCC,and the round shapes represent the corresponding targets of the ingredients
3.3 Retrieval of potential disease targets
From the GeneCards database,we obtained 3464 HCC-related targets,and 185 HCC-related targets were collected from Drugbank database.In total,3528 HCC-related targets were identified after the deletion of duplicate targets.Subsequently,the intersection between the potential target gene in HCC and the disease target genes was obtained using the ImageGP platform,and a Venn diagram was drawn (Fig.3).A total of 45 potential targets were obtained based on the intersection shown on the Venn diagram (Table 2).
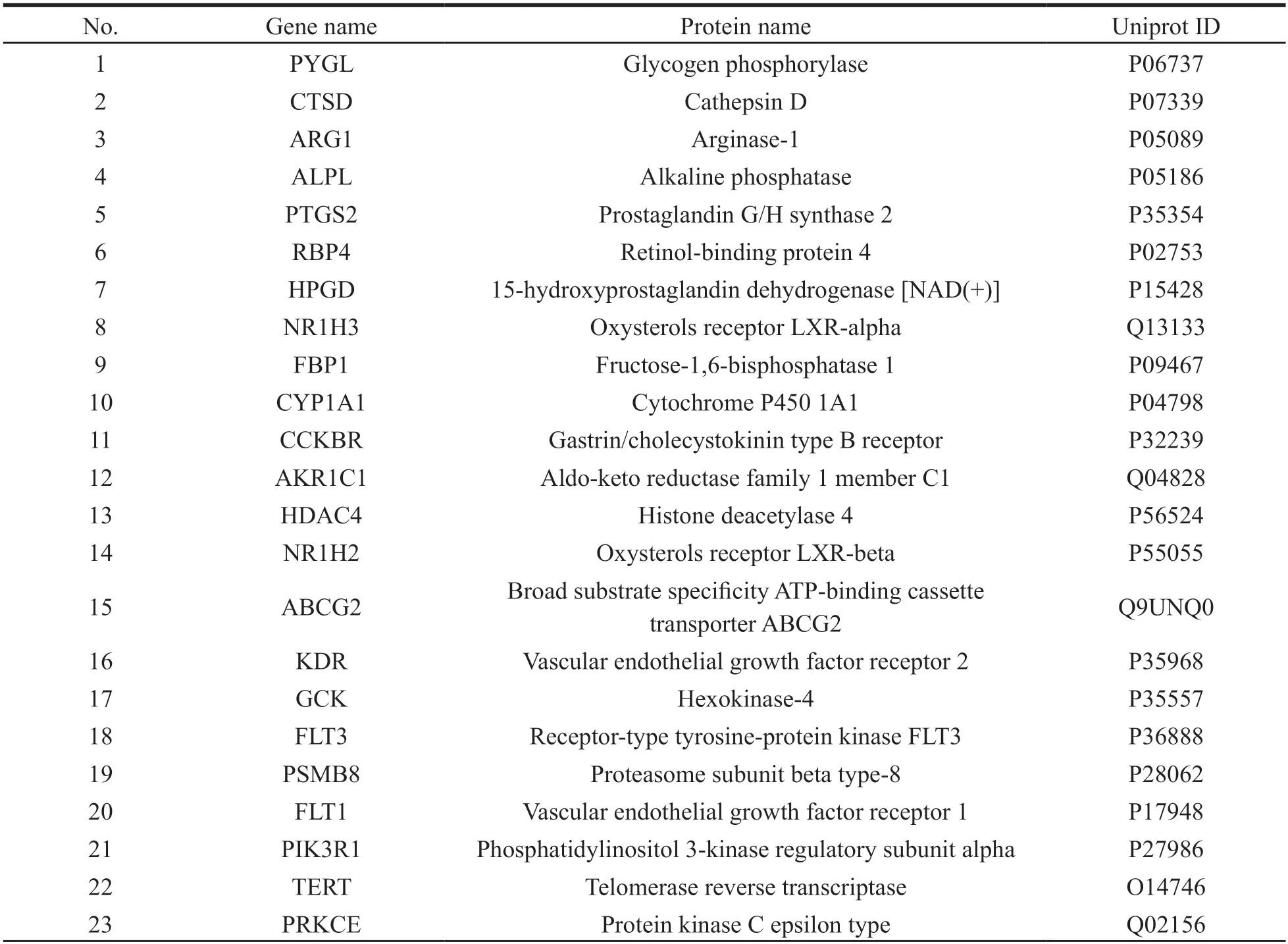
Table 2 Information on potential targets
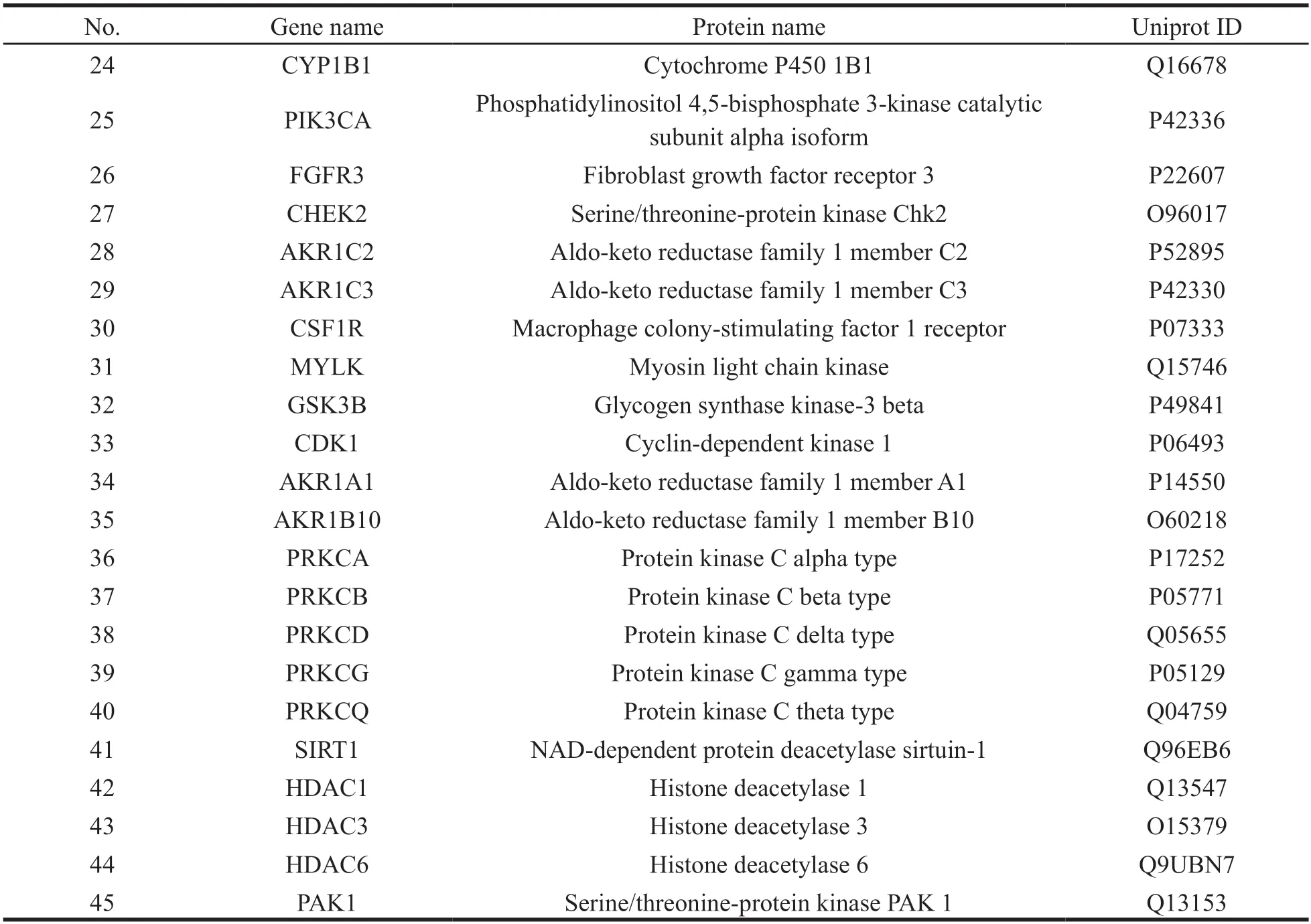
Continued table 2
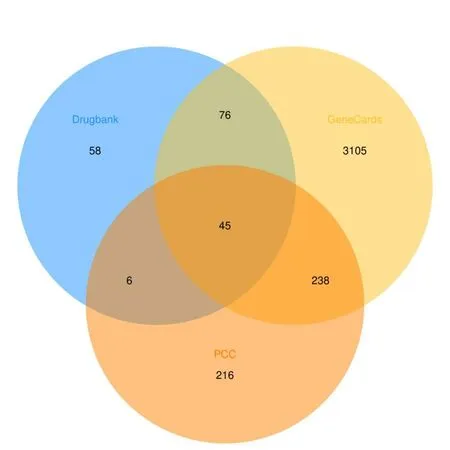
Fig.3 Common targets for PCC and HCC
3.4 PPI network
The 45 potential genes were uploaded to the STRING database for analysis.The protein targets with a medium confidence score of 0.400 were selected to construct the interaction network.The network of protein-protein interactions (PPI)(Fig.4),which embodied 42 nodes and 240 edges,was established through the STRING database.The results were used for further analysis through Cytoscape software,and the network was constructed as Fig.5.The edges represent the association between a pair of action targets,the nodes represent the action target,and the size of the node area in the network is positively correlated with the magnitude of its degree in the PPI network.Moreover,the protein nodes such as SIRT1,PIK3CA,PTGS2,PIK3R1,GSK3B,TERT,PRKCD,and PRKCA have higher degrees in the PPI network,which indicates that these protein targets are the key targets of PCC against HCC.
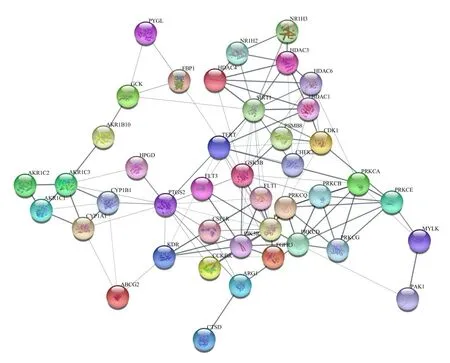
Fig.4 Common target PPI network between PCC and HCC.Each bubble node represents a protein,and the 3D structure in the bubble nodes represents whether the protein spatial structure is known or predicted.The lines between the inner nodes display the relationship between different proteins
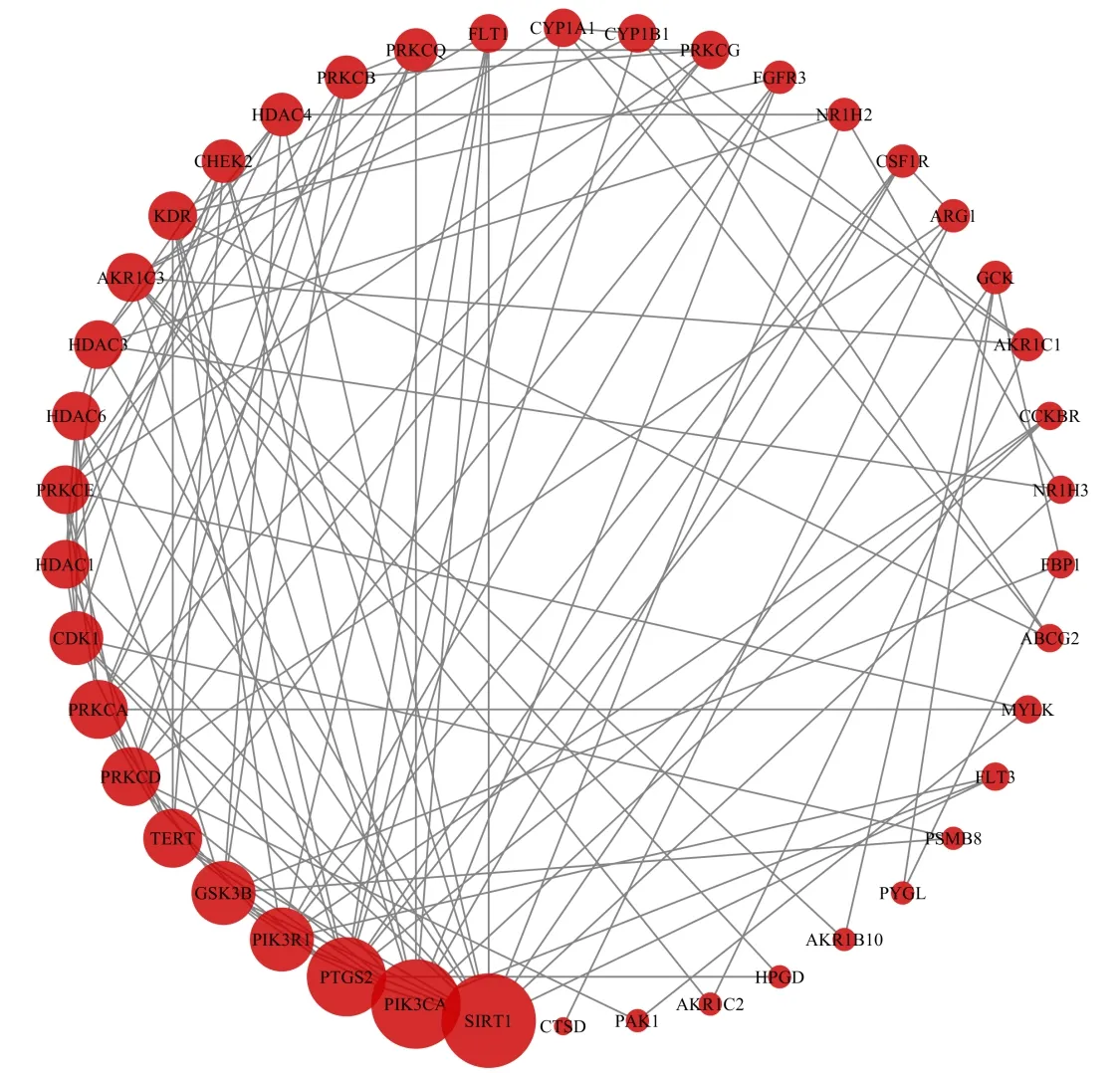
Fig.5 The PPI network of targets for PCC in the treatment of HCC.The layout of the outer ring is based on the area of nodes.The nodes represent the potential targets of PCC in HCC.The size of the nodes is shown in a gradient from large to small in descending order of the degree value.And the lines between the inner nodes display the relationship between different proteins
3.5 Gene ontology enrichment analysis
To elucidate the biological characteristics of putative targets,we imported the selected potential 45 target genes into the DAVID system for GO analysis.The results indicated that the functions of these potential targets were related to many biological processes (BP),molecular functions (MF),and cellular components (CC).A total of 110 biological processes were enriched,and the top 15 remarkably enriched BP terms were selected for analysis,such as cellular response to hypoxia,intracellular signal transduction,and positive regulation of macroautophagy (Fig.6).A total of 17 molecular functions (Fig.7) were enriched,and the top 15 entries were selected for analysis.These molecular functions mainly involved ATP binding,core promoter binding,protein serine/threonine kinase activity,protein kinase C activity,etc.Altogether,19 cell component GO terms (Fig.8) were enriched,and the top 15 entries were selected.These targets were closely related in nucleus,plasma membrane,and cytosol.These results are of great significance for further understanding of the mechanism of PCC on the HCC.
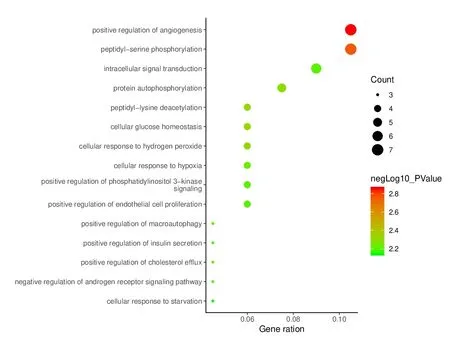
Fig.6 Enriched GO terms for the biological process (BP) of potential targets.The color of the nodes is shown in a gradient from red (deep) to green (light) in descending order of the P value.The size of nodes is arranged in ascending order of the number of genes
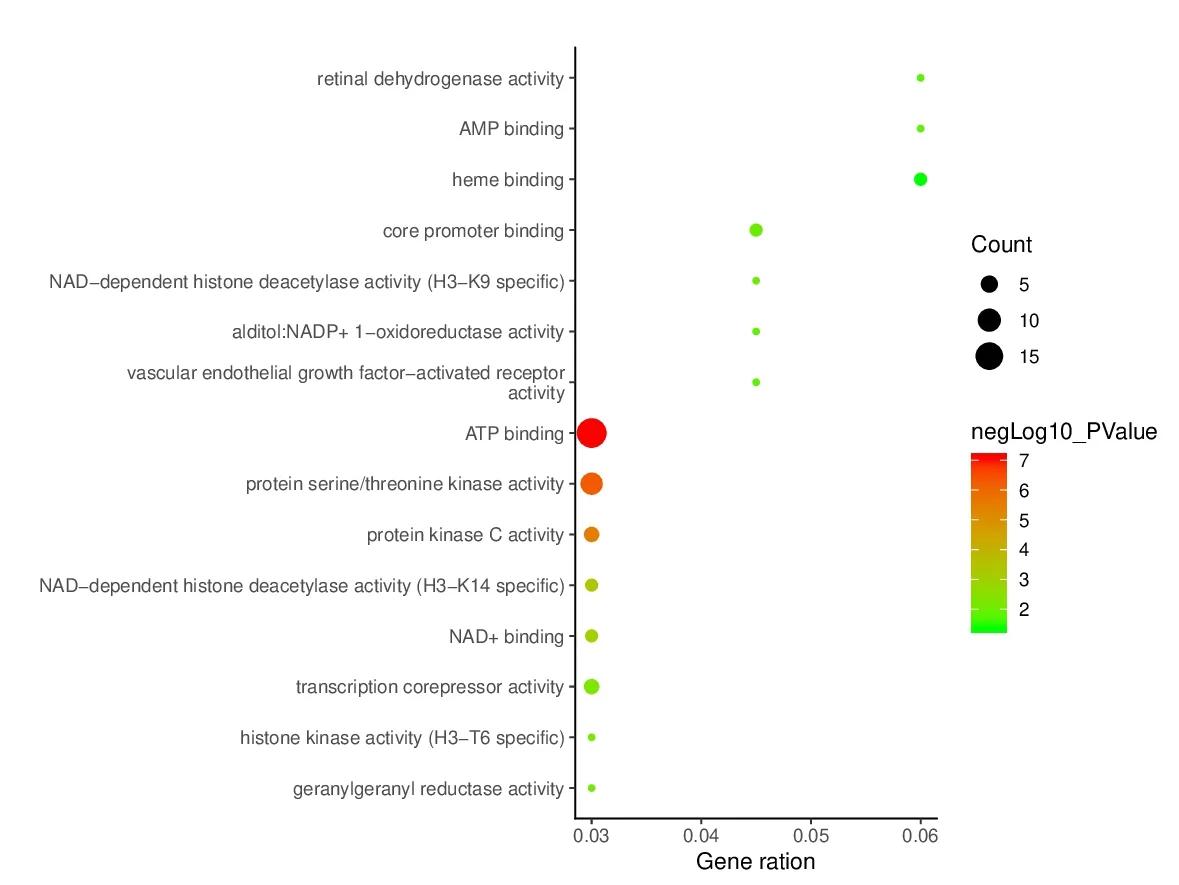
Fig.7 Enriched GO terms for molecular function (MF) of potential targets.The color of the nodes is shown in a gradient from red (deep) to green (light) in descending order of the P value.The size of nodes is arranged in ascending order of the number of genes
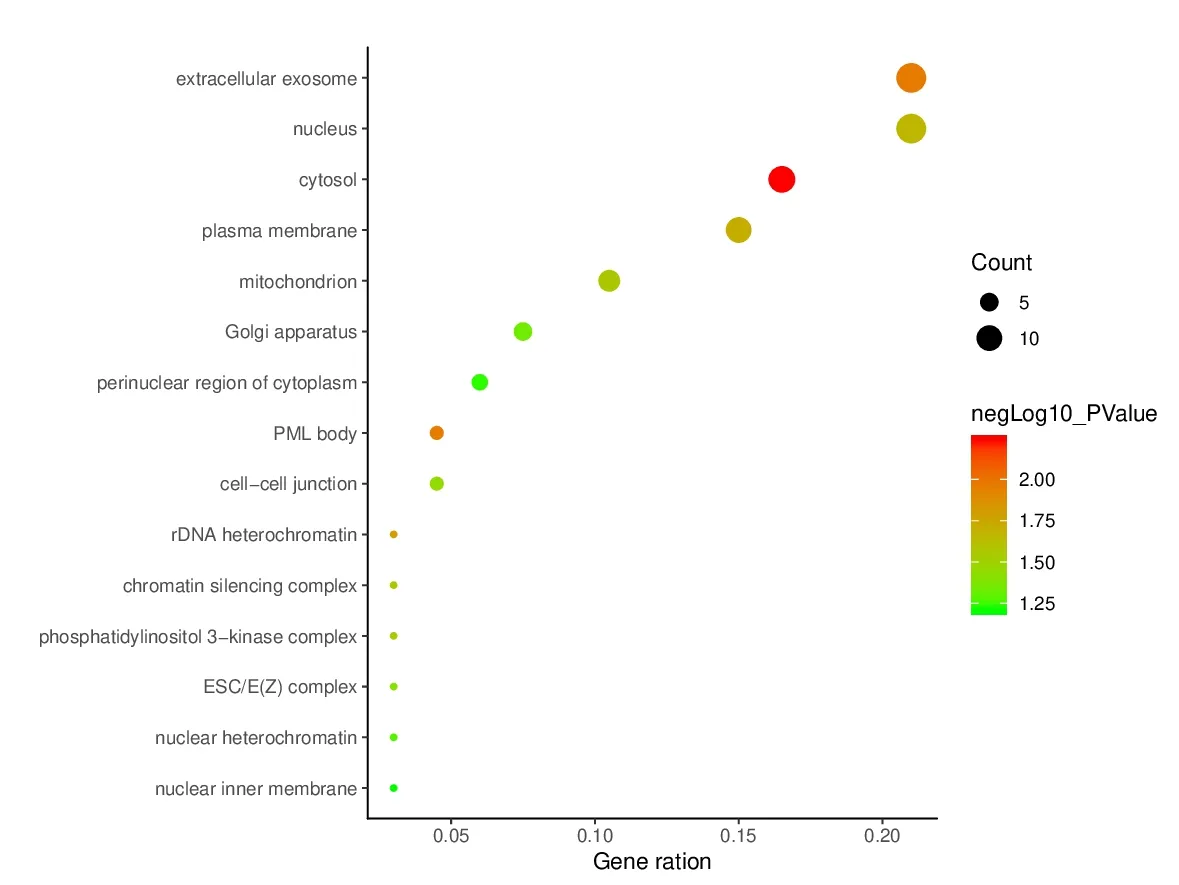
Fig.8 Enriched GO terms for cell component (CC) of potential targets.The color of the nodes is shown in a gradient from red (deep) to green (light) in descending order of the P value.The size of nodes is arranged in ascending order of the number of genes
3.6 KEGG pathway enrichment analysis
To further reveal the potential mechanism of the PCC on HCC,we performed KEGG pathway enrichment analysis on 45 genes and screened out top 20 pathways for analysis (Fig.9).These genes are involved in many pathways,including pathway in cancer,Ras signaling pathway,Rap1 signaling pathway,ErbB signaling pathway,HIF-1 signaling pathway,mTOR signaling pathway,and non-small cell lung cancer.Among them,pathway in cancer and Ras signaling pathway displayed the highest number of target connections(degree=10).ErbB signaling pathway involved 7 targets,mTOR signaling 5 targets,and non-small cell lung cancer 3 targets.Ras plays an important role in the occurrence and development of liver cancer [17].ErbB signaling pathway regulates cell proliferation,differentiation,migration,and apoptosis.ErbB participates in some physiological activities in normal tissues,and its mutations are associated with cancer [18].MTOR controls the translation of mRNA in cells and participates in a series of physiological and pathological processes such as membrane protein transport,protein degradation,and ribosome synthesis [19].MTOR signaling pathway is considered to be a signal convergence point that regulates cell cycle progression and cell growth.The results provided theoretical evidence that PCC might act on Ras signaling pathway,ErbB signaling pathway and mTOR signaling pathway in HCC treatment.
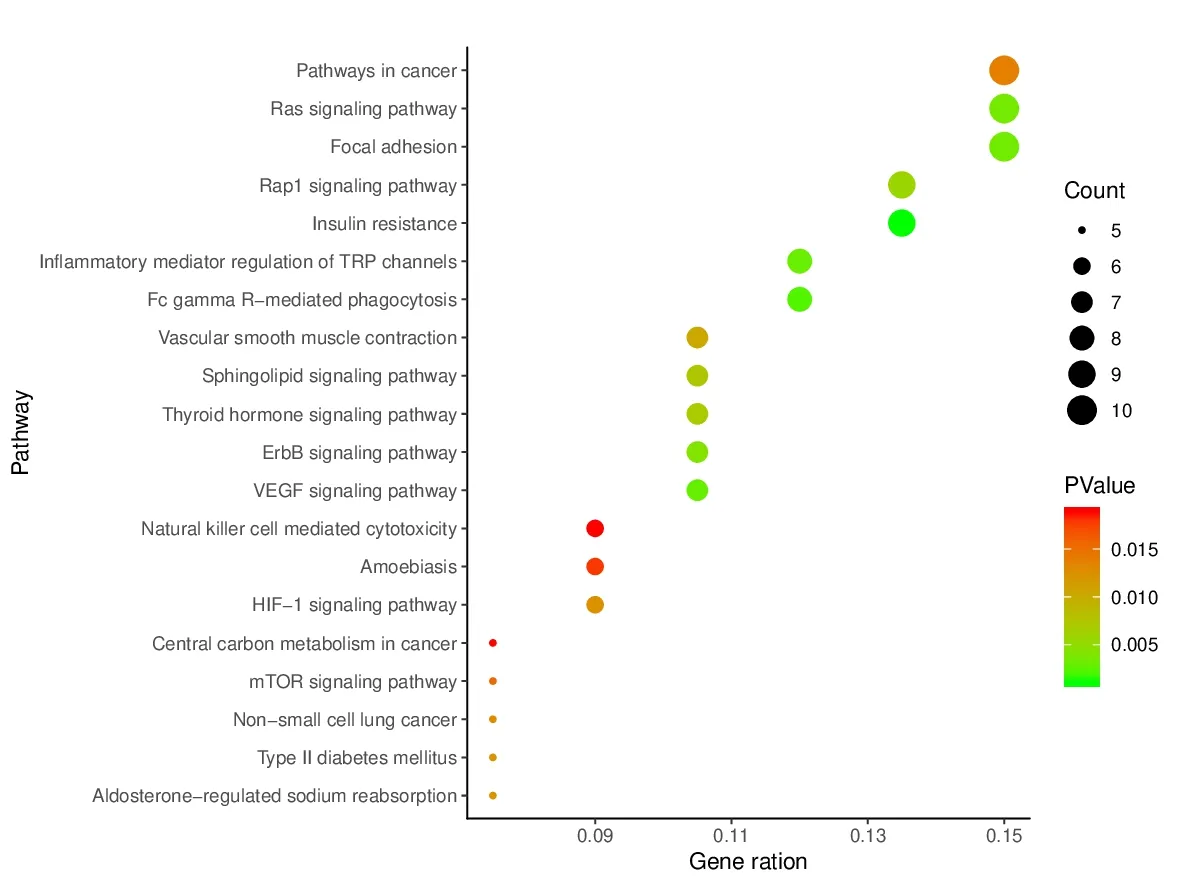
Fig.9 KEGG pathway analysis of putative target genes of PCC.The color of the nodes is shown in a gradient from red (deep) to green (light) in descending order of the P value.The size of nodes is arranged in ascending order of the number of genes
3.7 Active component-target -pathway network
We used Cytoscape software to establish the active component-target-pathway network,as shown in Fig.10.The network embodied 138 nodes and 2182 edges,in which the green nodes represent the potential active compounds in PCC,the red nodes represent the potential targets,and the light blue nodes represent the pathways for potential target genes.As shown in Fig.10,the active ingredients,targets,and pathways have a complex network relationship.The active ingredients play an important role in different metabolic pathways through different protein targets,and coordinate with each other,which is in line with the“multicomponent-multi-target-multi-channel”feature.
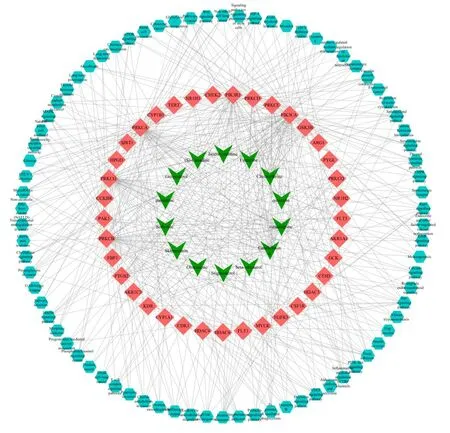
Fig.10 Active ingredient-target-pathway network of PCC.The inverted triangles represent the active ingredients in PCC,the regular quadrilateral represent the potential targets,and the regular octagons represent the corresponding pathways for potential target genes
4 Discussion
HCC is one of the common malignant tumors.At present,the incidence of HCC increases year by year,which seriously threatens the quality of life and even the lives of HCC patients.In recent years,much attention has been focused on the Chinese herb medicine for the treatment of cancer.It is reported that traditional Chinese medicine such as herbal medicine is more effective in HCC.The active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine with coordinated intervention effects at multiple levels and multiple targets are expected to become ideal medicines for the treatment of HCC.In this study,the active ingredient-target network shows that the main active ingredients of PCC (such as berberine,quercetin and palmatine) play an important role in the network,indicating that they have potential research value in the treatment of HCC.
There is increasing evidence that some compounds found in this study have anti-HCC effect.It was reported that berberine could inhibit the proliferation of HepG2 cells and induce cells apoptosis [20].It also reduced HCC cell growth [21].Previous studies have indicated that quercetin effectively inhibits human HCC cell proliferation and induces apoptosis [22].Quercetin also blocks Notch and Hedgehog,regulates the apoptotic and proliferative pathways,and inhibits CK2α
in HCC [23].PPI network analysis revealed that SIRT1,PIK3CA,PTGS2,PIK3R1,GSK3B,TERT,and PRKCD might represent hub genes against HCC.SIRT1 (Silent information regulator 1) is an NADdependent deacetylase essential for normal embryonic development,differentiation and homeostasis,and SIRT1 plays an important role in health and disease.Interacting with histone and nonhistone such as P53 and PGC-1α
,SIRT1 plays an important role in mammalian metabolism [24].The deacetylation effect of SIRT1 on the histone and nonhistone plays a part in cell growth,apoptosis,and the occurrence and development of tumor.It is worth mentioning that the effect of SIRT1 varies with organs [25].Studies have shown that,compared with normal liver or surrounding tumor tissues,SIRT1 is strongly overexpressed in HCC,and inhibition of SIRT1 in HCC cells impairs their proliferationin vitro
and tumor formationin vivo
.This has suggested that SIRT1 expression positively influences the growth of HCC [26].PIK3CA is an oncogene.In tumor cells,its kinase activity is enhanced,stimulating downstream AKT,making cells proliferate independent of growth factors,and increasing cell invasion and metastasis [27].PIK3CA gene plays an important role in tumorigenesis and development,and is a better target for intervention therapy [28].Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases/AKT pathway plays a pivotal role in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mutant PIK3CA,encoding the p110a catalytic subunit,stimulates the AKT pathway and promotes cell growth in various cancers [29].The expression of PIK3CA gene in carcinomas tissue and corresponding adjacent tissues of 67 patients with HCC was detected,and the results showed that the expression of PIK3CA gene in carcinomas was higher than that in the corresponding adjacent tissues and its expression was related to the size of tumor and the integrity of capsule [30].Therefore,these results indicate that our screened targets are consistent with the literature reports.In order to predict the mechanism of PCC in the treatment of HCC,we analyzed the candidate targets by performing KEGG pathway enrichment analysis.The pathway analysis results suggested that pathways in cancer,including Ras signaling pathway,ErbB signaling pathway,and mTOR signaling pathway,might be closely related to HCC progression.Ras signaling pathway is associated with the development and progression of multiple human malignancies.Ras gene is one of the most easily activated oncogenes [17].Humans have three kinds of Ras genes,including K-Ras,H-Ras and N-Ras,which are distributed on different chromosomes and can encode p21 protein.Mutations in the Ras gene prevent GTP from being hydrolyzed and keep the Ras protein in the GTP activated form,thereby stimulating downstream effectors [31].Quercetin,an active compound of PCC,has been shown to induce autophagy specifically in Ha-Ras-transformed cells and reduce the half-life of oncogenic Ras protein levels by a process that is inhibited by the proteasome inhibitor MG132 [32].MCF-10A cells are normal human breast epithelial cells,but H-Ras-transformed MCF-10A cells have cancer properties.Quercetin could also inhibit the H-Ras-induced invasion and migration of MCF10A human breast epithelial cells by acting on the molecular target PI3K [33].The mutation of the Ras gene causes the continuous activation of Ras,which causes the high activation of downstream Raf,and ultimately leads to the rapid proliferation of cells leading to malignant transformation.Studies have indicated that quercetin can induce apoptosis of NCI-H460 and inhibit the EGFR-Ras-Raf-MEK/ERK1/2 pathway by inhibiting the activation of c-Raf [34].Quercetin can specifically inhibit the proliferation and colony formation of K-Ras mutant colorectal cancer cells [35].
ErbB signaling pathway has been studied in cancer.ErbB family includes four tyrosine kinase receptors,namely,HER1 (ErbB1,EGFR),HER2(ErbB2,NEU),HER3 (ErbB3) and HER4 (ErbB4).After being combined with the ligands (EGF,TGF,AR,etc),ErbB family activates downstream related genes (Akt,MAPK,etc) to regulate cell proliferation,differentiation,migration,and apoptosis [36].ErbB participates in some physiological activities in normal tissues.Its mutations are related to the occurrence of a variety of cancers.Low expression leads to neurodegeneration,such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease [18],and high expression is also related to a variety of solid tumors,such as non-Small cell lung cancer [37],breast cancer [38],gastric cancer,etc.Studies have shown that quercetin inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells by downregulating ErbB2/ErbB3 signaling and the Akt pathway [39].In addition,inhibition of ErbB-2 and ErbB-3 by pharmacological doses of quercetin may provide a new approach for the treatment of prostate cancers [40].
MTOR is a serine/threonine protein kinase,which plays an important role in cell growth,differentiation,proliferation,migration and survival.Because mTOR signal transduction pathway plays an important role in the cell cycle process and the abnormal regulation of cell cycle process is related to the occurrence and development of many diseases,especially cancer,the dysregulation of the mTOR signal pathway can cause a variety of cancers [41].In addition,mTOR is also related to the autophagy process.Activation of autophagy is sensitized by inactivation of the mechanistic target of rapamycin,which is a major cellular nutrition and energy sensor kinase [42].Berberine,an active compound of PCC,has been shown to be combined with rapamycin and improve HCC therapy by synergistically inhibiting the mTOR signaling pathway,which is at least in part,mediated by CD147 [43].Berberine has sensitized gastric cancer cells to DDP by enhancing apoptosis and repressing PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling [44].In addition,recent data has revealed that quercetin can inhibit mTOR activity in cancer cells.The ability of quercetin to interfere with both mTOR activity and activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway gives quercetin the advantage to function as a dual-specific mTOR/PI3K inhibitor.The ability of quercetin to inhibit mTOR activity by multiple pathways makes this otherwise safe bioflavonoid an interesting tool for the treatment of cancers and other diseases associated with mTOR deregulation [45].Studies have shown that quercetin can promote the apoptosis process of human breast cancer cell line T47D by inhibiting EGFR/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway [46].Therefore,our results revealed that PCC played a significant anti-HCC role,which was mediated by Ras signaling pathway,ErbB signaling pathway,and mTOR signaling pathway.
5 Conclusion
Our study shows that PCC exerts a multicomponent and multi-pathway synergetic efficacy and has significant advantages in the treatment of HCC.The results are consistent with those reported in the published studies.At the same time,the biological functions of active compounds and their corresponding targets of PCC were analyzed by network pharmacological method,which further revealed the molecular biological mechanism of PCC in treating HCC.This study provides a theoretical basis for clinical treatment of HCC.
杂志排行
Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines的其它文章
- Network pharmacology-based analysis on three amicoumacintype isocoumarin compounds from an endophytic bacterium in Houttuynia cordata
- Compounds from the flowers and fruits of Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench
- Research progress on the main chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Piper betle L.
- Research progress on chemical constituents in Sophora alopecuroides L.and their pharmacological activities
- Contribution Regulations for Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines
