Highly tunable plasmon-induced transparency with Dirac semimetal metamaterials∗
2021-09-28ChunzhenFan范春珍PeiwenRen任佩雯YuanlinJia贾渊琳ShuangmeiZhu朱双美andJunqiaoWang王俊俏
Chunzhen Fan(范春珍),Peiwen Ren(任佩雯),Yuanlin Jia(贾渊琳),Shuangmei Zhu(朱双美),and Junqiao Wang(王俊俏)
1School of Physics and Microstructures,Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450001,China
2College of Science,Henan University of Engineering,Zhengzhou 450001,China
Keywords:plasmon-induced transparency,Dirac semimetal metamaterials,optical switch,slow light
1.Introduction
Electromagnetically induced transparency(EIT)represents a quantum interference phenomenon,which can dramatically modulate the optical properties of the propagated medium.[1–3]It induces an obvious transmission window in the absorption spectra and has a wide application in nonlinear optics and quantum communications.However,the realization of EIT requires severe restrictions,such as cryogenic temperatures and noble gas.Once the atomic system is set up,the propagating properties cannot be dynamically tuned.[4,5]Recently,with the prompt rise of metamaterials,plasmoninduced transparency(PIT)is realized by virtue of its distinctive electromagnetic properties,which is an analogue electromagnetically induced transparency.[6–8]PIT demonstrates a clear narrow transparency window within a broad absorption spectrum,[9–11]leading to huge applications in optical switchers,[12]sensors,[13]and slow light devices.[14]It can evade the harsh experimental requirements and achieve much progress in terahertz(THz),[15–17]mid infrared,[18,19]and radio frequency range.[20,21]In the early stage,novel metallic materials are the primary choice to achieve PIT effect.To overcome the intrinsic loss of the metals,the defects of actively tuning and poor coupling strength,graphene,black phosphorus,[22,23]and topological insulators have attracted extensive attention.In recent years,much research on adjustable PIT is carried out with the two-dimensional(2D)material.They can embody the dynamic regulation of PIT by virtue of its distinct photoelectric characteristics.[24–26]Regrettably,the traditional 2D materials constitute a conspicuous class of atomically thin layered materials.The external dielectric environment not only affects the properties of graphene-based materials,but also has a weak light absorption owing to its high transmittance larger than 90%.Consequently,the exploration of Dirac semimetal metamaterials has become a new research aspect.
Dirac semimetal metamaterials represent a new state of quantum matter,which is also regarded as three-dimensional(3D)analogue graphene.[27,28]The preponderances of it is able to avoid the large metallic loss of traditional metal metamaterials and tune the resonant frequency via non-contact external stimuli.[29–32]In this way,the original structure is modulated by external means to obtain different transmission spectra without reconstructing the structure.Specifically,the response of the Dirac semimetal metamaterials is 5.9 mA/W,up to 10 times of the graphene detector(0.5 mA/W).[33]The carrier mobility reaches up to 9×106cm2·V−1·s−1(5 K),[34]about 45 times of the best graphene 2×105cm2·V−1·s−1(5 K),[35]which is better than any semiconductor.Therefore,Dirac semimetal metamaterials provide an excellent opportunity for new material platform in the fields of optics,electronics,and various plasmonic devices.Recently,Chen et al.designed two types of H-shaped structures and got the multiple transparency windows in 2018.[36]A structure composed of a strip and two L-shaped resonators based on Dirac semimetal metamaterials by Wang et al.exhibited a polarization nonsensitive PIT effect in 2019.[37]Recently,Liu et al.proposed a tunable PIT based on asymmetric split ring resonator of Dirac semimetal metamaterials and obtained a positive group delay of about 0.75 ps.[38]Therefore,realization of highly tunable PIT effect is still a hot research topic.
In this work,actively tunable PIT effect is investigated with Dirac semimetal metamaterials consisting of a strip and a square bracket.The physical mechanism and dispersion behavior are analyzed in detail.With the varied Fermi energy,the spectral response realizes an effective non-contact modulation.Quite different from other studies,an on-to-off optical switch can be achieved through the external polarization angle.The slow light phenomenon is also examined and a large group delay of 1.022 ps can be achieved.Moreover,dynamically regulated PIT transparency window is achieved by setting different geometric parameters.With a small variation of the substrate,the transparency window embodies an obvious movement and causes a distinct red shift.Therefore,our research provides a new route to achieve efficient manipulation of the PIT effect.
2.Structure design and theoretical analysis
Figure 1 depicts the 3D configuration of the proposed Dirac semimetal metamaterials,which is deposited on SiO2substrate.The unit cell consists of a strip and a square bracket.It is arranged periodically along x and y directions,where Px=57µm and Py=50.1µm.The length of the strip is l1=50µm and the width is w1=6µm.The length and width of square bracket are l2=30µm and w2=6µm.The short arm length is l3=9µm.The coupling distance between the two resonators is taken as s=9µm.θis the polarization angle of incident light in Fig.1(b).The thickness of Dirac semimetal metamaterials is fixed as 0.2µm.
In our numerical calculation,the commercial software COMSOL Multiphysics is employed to study the properties of the multi-functional PIT effect.According to the solution of Maxwell equation to obtain the required physical quantities.To model the Dirac semimetal metamaterials,the designed structure includes four layers,the air layers are set above and below the main structure.The computation domain consists of only a unit cell with perfectly matched layer applied to the boundary along the propagation direction(z-axis direction)and periodic conditions imposed on the four lateral boundaries in the x-axis and y-axis directions.A perfect matching layer is used in the z direction to eliminate the non-physical reflection at the boundary.The Dirac semimetal can be characterized by permittivity values under different frequencies in the simulation processes.At present,Na3Bi and Cd3As2are the most frequently investigated 3D Dirac semimetal materials.[39,40]Take Cd3As2as an example,topological insulator Cd3As2materials can be grown on a substrate by CVD.[41]Subsequently,the Dirac semimetal film is patterned through a photolithography process.[42]Exposure and development are used to depict the geometric pattern structure on the photoresist layer,and then the pattern on the photomask is processed through an etching process to obtain the desired structure.[43]
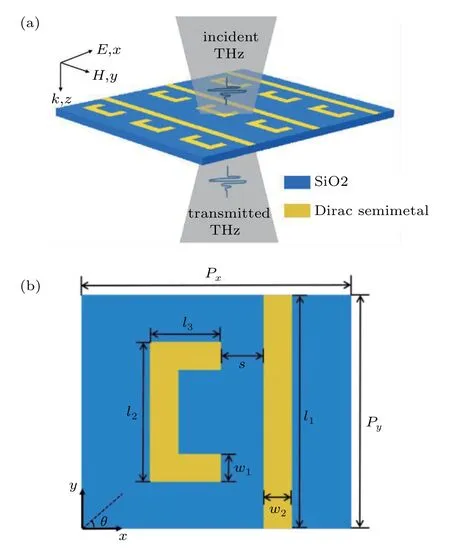
Fig.1.Schematic view of our proposed structure,which consists of a strip and a square bracket.(a)Overall view of structure.The incident light propagates in the z direction and its electric field polarization is along x direction.(b)Top view of the unit cell with defined geometrical parameters.l1=50µm,w1=6µm,l2=30µm,w2=6µm,l3=9µm,s=9µm,Px=57µm,Py=50.1µm,and T=300 K.The refractive index of substrate is 1.5.
The conductivity of Dirac semimetal metamaterials can be obtained with Kubo formula.According to the random phase approximation at long wavelength limit,the real and imaginary parts of conductivity can be derived as[28]

where e and¯h denote the charge of an electron and reduced Planck constant respectively.G(E)=n(−E)−n(E),where n(E)represents Fermi distribution function,kF=EF/¯hvFdenotes the Fermi momentum,EFand vF=106m/s stand for the Fermi energy and Fermi velocity.ε=E/EF,Ω=¯hω/EF,εc=Ec/EF.Ec=3 represents the cut off energy.g is the degeneracy factor and it is taken as 40.At low temperature restriction,the conductivity can be simplified as[28]


Fig.2.Real and imaginary parts of the conductivity in Dirac semimetal metamaterials with different EF Fermi energies.

Fig.3.(a)Transmission spectra of only strip(red line),only square bracket(black line),and combined structure(blue line)are illustrated.Panels(b)–(d)represent the electric field distribution at dip I,peak II,and dip III of the blue curve in Fig.3(a).
The dielectric function of Dirac semimetal material can be obtained throughε=1+iσ(ω)/ε0ω.ε0andωrepresent the permittivity of vacuum and the angular frequency of the incident light.According to the homologous conductivity expression,the relation of the conductivity with the incident light frequency in THz is numerically calculated in Fig.2.Here EFis taken as 0.11 eV,0.14 eV,0.17 eV and 0.20 eV respectively.In the frequency range from 0 THz to 5 THz,Fermi energy is directly proportional to the real part of the conductivity and inversely proportional to the imaginary part.Namely,the real part of conductivity diminishes and the imaginary part increases with a larger EF,which shows a marvelous adjustability of conductivity.In addition,the loss effect can be ignored in the higher frequency region.
3.Results and discussion
In order to achieve the PIT effect with Dirac semimetal metamaterials,the transmission spectra with different structures are illustrated for comparisons in Fig.3.Here the Fermi energy is fixed as 0.11 eV and the polarized electric field is along the x direction.For the normal incidence,a classical transmission dip emerges at 1.99 THz owing to the strong interaction of patterned strips with the incident plane wave in red line in Fig.3(a).The square bracket resonator can directly excite with the incident wave and form a broad discrete spectrum at 2.58 THz in black line.However,due to the near field coupling between two bright modes resonators(strip and square bracket),an apparent transparency window at 2.20 THz exits in blue line.The corresponding transmittance can reach up to 98.5%.To further demonstrate the physical origin of the transparency window,the electric field distribution at dip I(1.90 THz),peak II(2.20 THz)and dip III(2.77 THz)are also illustrated.As shown in Fig.3(b),the electric field mainly distribute on the strip,showing a typical bright mode.Similarly,the electric field intensity distributes around the square bracket and reveals a bright mode in Fig.3(d).The interaction between the two modes makes the electric field redistribute around the two resonators at peak II in Fig.3(c)and induces a representative transparency window.
Dirac semimetal materials have band structures similar to graphene.The conductivity of Dirac semimetals is closely related to Fermi energy.The dielectric properties of Dirac semimetals can also be dynamically adjusted by changing the Fermi energy through an external gate voltage or doping.[44,45]To initiate it,metal electrodes are deposited on both sides of the Dirac semimetal material structure.Dirac semimetal is designed to cover with a layer of transparent conductive medium and the Fermi level of the Dirac semimetal material is adjusted by the grid voltage at both ends of the electrode,which avoids direct contact with the sample.The modulation of PIT transparency window at different EFis explored in Fig.4.Here the polarization angle is set as 0°.The PIT window demonstrates a distinct blue shift with a higher EFfrom 0.11 eV to 2.0 eV.Namely,the PIT transparency window is moving into the high frequency region with enhanced Fermi energy.It is worth noting that the resonant frequency in Dirac semimetal metamaterials can be well regulated with the applied external electric gate voltage.And this feature facilitates dynamic control of the PIT effect without re-optimizing or re-fabricating the structure.
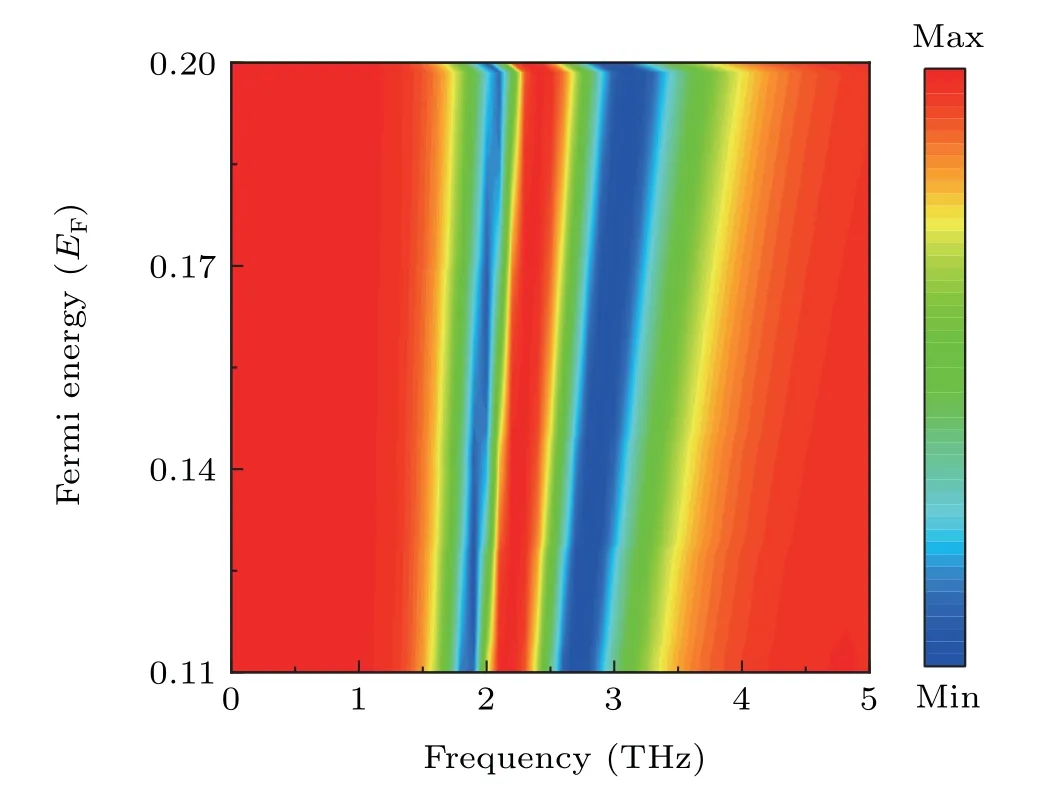
Fig.4.Contour plot of the Dirac semimetal metamaterials with different EF in THz region.
The tunable PIT effect in Dirac semimetal metamaterials as a function of the applied polarization angle is also numerically calculated and demonstrated in Fig.5.In our calculation,the polarization angle is considered from 0°to 90°with a step of 15°.As shown in Fig.5(a),the intensity of the two dips undergoes an apparent transformation.It is getting diminished with a larger polarization angle,resulting in an on-to-off modulation at the specific resonant frequency.For instance,when the polarization angle is set as 0°,the transmission of dip I and dip III are 0.18 and 0.14.The system is in the on state.The transmission spectra of two dips approach up to 1.0 and transparency window disappears when the polarization angle is 90°,indicating an off state.Thus,the vanishing process of the transparent window is realized with a larger polarization angle.To better quantitatively and intuitively characterize the variation process of transparency window,the transmittance of the two dips at each polarization angle is shown in Fig.5(b).These two dips are getting larger with the increased polarization angle and both of them reach up to 1.0 finally.This highly tunable capability provides us an effective way to design optical switchers.
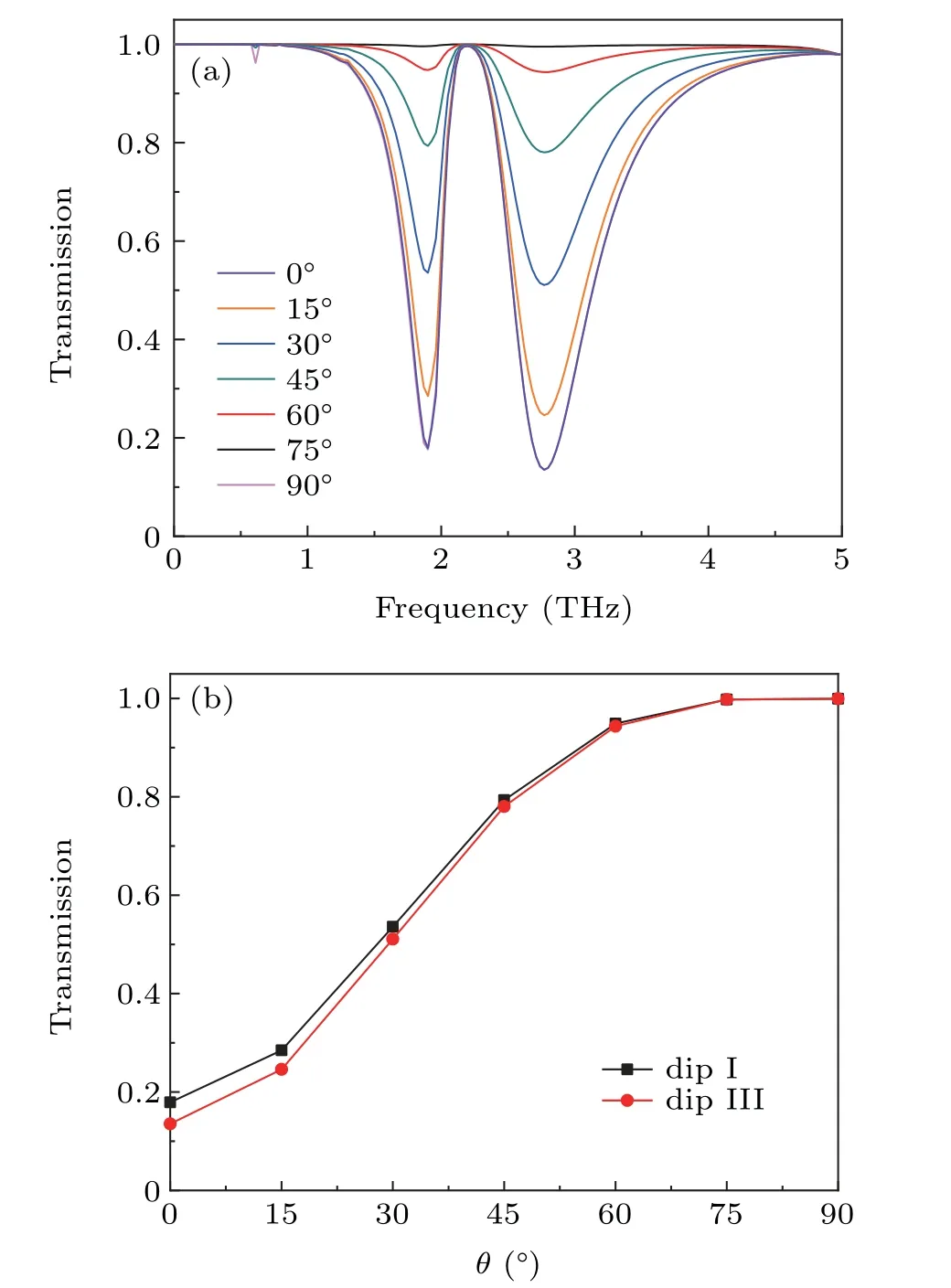
Fig.5.(a)Transmission spectra of the Dirac semimetal metamaterials as a function of polarization angles.(b)The corresponding transmittance of dip I and dip III with different polarization angles.
The transmittance of the PIT transparency window is closely related to the incident polarization angle,which can be employed to get tunable optical effect.It can be clearly observed that an abrupt phase change is obtained when the incident angle is varying from 0 to 90°in Fig.6(a).In order to clearly indicate the effect of polarization angle on the phase,enlarged view and the position of phase change with differentθis shown in Fig.6(b).And the phase change is slightly getting larger whenθis in the range of 15°–75°in Fig.6(c).Namely,the phase shifts slightly with a larger polarization angle.The dispersion behavior is investigated with the calculation of group delay by setting different polarization angles in Fig.6(d).The group delay(τg)is introduced to evaluate the slow light capabilityτg=−dφ/dω.[47–50]The corresponding group delay at each polarization angle is illustrated in Fig.6(d).It increases first and then decreases with the change of corresponding frequency of the transparent window.Evidently,a larger group delay of 1.022 ps at 2.2 THz can be realized at the extreme 45°polarization angle,which is much larger than 0.75 ps in the work.[38]This non-contact dynamic control of PIT effect lays the foundation in slow light equipment.
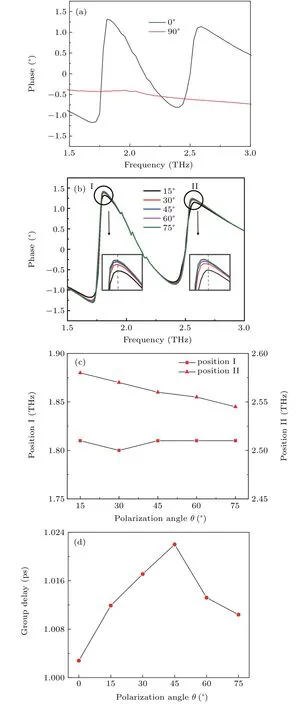
Fig.6.(a)and(b)The phase shift(φ)of our proposed metamaterials with different polarization angles.(c)The change of position I and position II at different polarization angles.(d)The group delay(τg)with different polarization angles.
Moreover,the transmission spectra with different geometrical parameters are explored.The position of the transmission spectra in relation with the strip length and width are presented in Fig.7.The resonance intensity of dip I diminishes and it moves into the higher frequency region as the length of l1decreasing from 50µm to 44µm.Meanwhile,the transmission of dip III increases from 0.19 to 0.65,which shows a flexible adjustment of the PIT effect in Fig.7(a).With the increase of w1from 4µm to 10µm,the bandwidth of transparency window gets broader and its resonant peaks are moving into lower frequency region in Fig.7(b).Thus,with the carefully chosen geometry parameters,the desired transmission spectra can be obtained.

Fig.7.Transmission spectra of our proposed metamaterials with different geometry parameters:(a)the strip length l1,(b)the strip width w1.EF is kept as 0.11 eV.

Fig.8.(a)The transmission of our proposed structure with different substrates.(b)The value of FWHM as a function of refractive index and its linear fit.(c)The sensitivity at the transparency window(black dots)and its linear fit(red line).(d)FOM of peak II with different n1.
To extend the application of our proposed metamaterials in sensing,the transmission spectra with different refractive indices of the substrate are fully investigated in Fig.8.To initiate it,the patterned Dirac semimetal surface can be transferred onto different substrates.The two most popular methods for transferring are using thermal release tape and the PMMA method.[51,52]Using PMMA method,a layer of PMMA is spin-coated onto the patterned surface to act as a support.An etchant is then used to remove the metal catalyst,after which the PMMA/Dirac semimetal is transferred to another substrate.Solvents are then used to remove the PMMA,completing the transfer.Five different substrates are investigated in our calculation.Namely,silica(n1=1.440),[53]agate silicon dioxide(n1=1.544),malachite(n1=1.655),aluminum oxide(n1=1.670),[54]and ceylanite(n1=1.770).With the increase of refractive index,the transparency window is always more than 98.5% and shows an obvious red shift in Fig.8(a).Thus,a small variation of the substrate can induce an obvious shift of the PIT transparency window.Particularly,the sensing ability is better quantified adopting the full width at half maximum(FWHM)and FOM of the resonant frequency[39,40]and it embodies an excellent linear fit with the variation of the different substrate.Based on the above calculation,the minimum FWHM value can reach up to 0.45 THz with n1=1.77.In order to assess the sensing properties of the PIT transparency window,the sensitivity to its surrounding environments(S)and the corresponding sensing FOM are presented clearly in Figs.8(c)and 8(d).The refractive index sensitivity is defined as the wavelength shift per refractive index unit(RIU),and the corresponding FOM equals the ratio of the sensitivity to FWHM.The calculated sensitivity of peak II at 2.20 THz is 0.781 THz/RIU.In addition,the quality factors corresponding to the peak II is also presented with different refractive indexes n1in Fig.8(d).It can be observed that the FOM is got increased with a larger n1.The quality factor achieves a high value of 1.734,which can be served as a highly efficient sensor.
4.Conclusion
In summary,adjustable PIT effect based on the Dirac semimetal metamaterials is realized in THz region.The transmission spectra and corresponding electric field distributions demonstrate that near field coupling of two bright modes results in a pronounced transparency window.This brilliant performance of PIT effect can be adjusted with EFand geometry parameters EF.Furthermore,an on-to-off switch of the PIT effect can be realized with different polarization angles for the first time with Dirac semimetal materials.Meanwhile,the corresponding phase and group delay are fully examined with different polarization angles.Finally,the performance of sensing embodies a liner relation with different substrates.Thus,this active modulation of PIT effect opens up its potential application in tunable optical switchers,sensing devices,and slow light devices.
杂志排行
Chinese Physics B的其它文章
- Origin of anomalous enhancement of the absorption coefficient in a PN junction∗
- Protection of isolated and active regions in AlGaN/GaN HEMTs using selective laser annealing∗
- First-principles study of plasmons in doped graphene nanostructures∗
- Probing thermal properties of vanadium dioxide thin films by time-domain thermoreflectance without metal film∗
- An improved model of damage depth of shock-melted metal in microspall under triangular wave loading∗
- Signal-to-noise ratio of Raman signal measured by multichannel detectors∗