Development of the general chapters of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition: A review
2021-09-14XinyiXuHuayuXuYueShangRanZhuXiaoxuHongZonghuaSongZhaopengYang
Xinyi Xu, Huayu Xu, Yue Shang, Ran Zhu, Xiaoxu Hong, Zonghua Song, Zhaopeng Yang
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, Beijing,100061, China
Keywords:Chinese pharmacopoeia 2020 edition General chapter Development Review
ABSTRACT The Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition was reviewed and approved by the National Medical Products Administration and the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China in July 2020. The current edition was officially implemented on December 30, 2020. The general chapters of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia discuss the general testing methods and guidelines, which are the common requirements and basis for the implementation of drug standards in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia.Owing to adherence to the principles of scientificity, versatility, operability,and sustainable development, there is an improvement in the general chapters of the 2020 edition over those of the previous editions.Further,the application of advanced and mature analytical techniques has expanded,the development of testing methods for exogenous pollutants in traditional Chinese medicines has been strengthened,and technical requirements are now better harmonized with international standards. The updated edition provides technical and methodological support to ensure safety, effectiveness, and control of pharmaceuticals in China and will play an important and active role in encouraging the application of advanced technologies, improving the quality control of medicines, and strengthening the means of drug regulation in China. This review provides a comprehensive introduction of the main features of and changes to the general chapters in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition and aims to provide reference for its correct understanding and accurate implementation.
1. Introduction
The Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition was reviewed and approved by the National Medical Products Administration(NMPA)and the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China in July 2020. This edition was officially implemented on December 30, 2020. The Chinese Pharmacopoeia is a statutory technical specification that must be implemented for drug development, production, use, and regulation in China. The general chapters in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia are the basis for the accurate implementation of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. The 2020 edition contains 360 general chapters, including 23 new and 83 revised chapters.This updated edition reflects not only the current level of technology used in the pharmaceutical industry in China but also the technologies used for international drug quality control.
2. Application of advanced and mature analytical techniques has been expanded
Method 0451, “X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy”, was added to guide the application of X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy in the qualitative and quantitative analyses of elemental impurities[1-9].Oscillating transducer density meter application and instrumentation were added in method 0601, “Determination of Relative Density” [10,11]. In method 0713, “Tests of Fat and Fatty Oil”, the melting range,saponification value,and iodine value were revised,and information concerning unsaponifiable matter, fatty acid composition,alkaline impurities,anisidine value,sterols,and trans fatty acids was added [12-16]. Methods 1001, “Polymerase Chain Reactions”; 1021, “Identification of Bacterial DNA Sequences”; and 9108, “DNA Sequencing”, were added. These methods are used to ensure the accurate identification and clinical safety of drugs[17-22].In vitro methods,which involve the use of an instrument to determine endpoints, have replaced in vivo biological methods,which is in line with the goal of reducing, replacing, and refining laboratory animal use.The anti-factor IIa and anti-factor Xa assays were added to method 1208,“Biological Assay of Heparin”[23-27].The heparin-binding capacity assay was added to method 1213,“Biological Assay of Protamine Sulfate” [28-32]. New sterilization methods (vapor-phase sterilization and liquid-phase sterilization)were added to method 1421,“Methods of Sterilization”,to guide the sterilization/filtration-based production of drugs to ensure that the sterility level meets the requirements [33-36]. The monocyte activation test was added in guideline 9301, “Application of Safety Tests for Injection” [37-42]. Based on research detailing the technical requirements for the verification and transfer of analytical methods from the United States Pharmacopoeia (USP) and the American Association of Analytical Chemists [43-49] to the Chinese Pharmacopoeia,guidelines 9099,“Verification of Compendial Procedures”, and 9100, “Transfer of Analytical Procedures”, were added.
The applicability requirements of the analytical methods were enhanced. In method 1105, “Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products: Microbial Enumeration Tests”, an improved method for the preparation of aerosol test samples was included,and information regarding the quantities of small-dose, low-content, and small-batch samples to be tested was added. In method 1107, “Microbiological Acceptance Criteria of Nonsterile Pharmaceutical Products”, the microbiological acceptance criteria for semisolid preparations were modified to ensure strict control,as is required for liquid preparations. The definition and scope of antimicrobial preservatives in method 1121, “Antimicrobial Effectiveness Testing”,have been revised to enhance accuracy.The recovery rates of the suitability test for the medium and test microorganisms used in the operational suitability test were revised to ensure consistency with method 1105[50].Other newly added and revised general testing methods are detailed in Table 1.
3. Development of testing methods for exogenous pollutants in traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) has been strengthened
Methods for determining exogenous pollutants in TCMs have been improved in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition.Qualitative screening and quantitative analytical methods,including gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (GCMS/MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS), were added to method 2341,“Determination of Pesticide Residues”. Qualitative screening methods are used for the rapid qualitative testing,risk monitoring,and early warning testing of pesticides. Pesticides with limited requirements can be directly determined using a quantitative analytical method. In the 2020 edition, the number of pesticides tested has increased to 592.Eighty-eight pesticides were identified using GC-MS/MS and 523 pesticides were determined using HPLCMS/MS.For pesticides that can be determined with GC-MS/MS and HPLC-MS/MS,the preferred method is provided,and the maximum possible number of characteristic ions is recommended [51-56].
Accurate and low-detection-limit methods,including HPLC-MS/MS analysis of aflatoxin and patulin; HPLC and HPLC-MS/MS analyses of ochratoxin A, zearalenone, and vomitoxin; and HPLC-MS/MS analysis of multiple mycotoxins, were added to method 2351,“Determination of Mycotoxins”. Considering that the abovementioned methods require complex sample pretreatment, specific instruments, and specialized personnel training, they will be subject to limitations for being used in quality control of TCMs. A fast, sensitive, simple, and low-cost aflatoxin ELISA method was added as a new technique for the quality control of TCM in China(Table 2) [57-63].
As the development of acceptable microbiological criteria for TCM decoction pieces was a breakthrough,strategies and methods for specific microbial contamination control in TCMs with different uses were introduced. Compared with the medicines produced according to good manufacturing practices, TCM decoction pieces contain microorganisms in high abundance,with a wider variety of species and a more uneven distribution. Further, the microbial analysis requirements are unique to each type of medicinal material. Therefore, method 1108, “Microbiological Examination of Traditional Chinese Medicine Decoction Pieces”, was added. The enumerated microbial parameters include total aerobic microbial counts,total combined yeast/mold counts,and the number of heatresistant bacteria; the parameters for specified microorganismsinclude the number of bile-tolerant gram-negative bacteria,Escherichia coli, and Salmonella. The quantity of the product to be tested, the preparation method for the test solution, and the suitability test of the counting method are specified; and the uncertainty in the interpretation of the results can be greater for TCMs than that for other products.

Table 1 Additions and revisions in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition general testing methods.
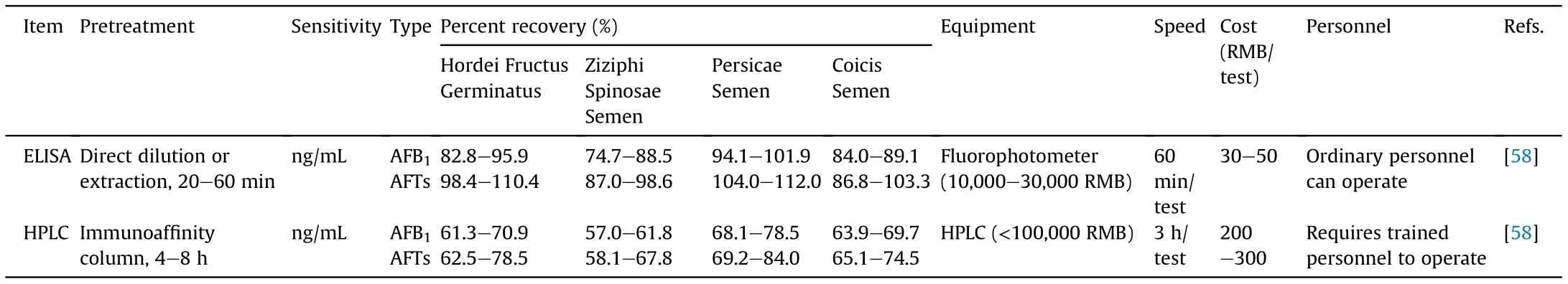
Table 2 Comparison of immunological and chemical methods for the determination of aflatoxins.
In method 2322, “Determination of Mercury and Arsenic Speciation and Valence States”, the method of test solution preparation was improved to address the difficulties in determining the valence states of arsenic and mercury in marine- and animalderived TCMs. Notably, information regarding the preparation of the test solution, determination of the sample amount, and principle of the method application, was added.
4. Technical requirements are better harmonized with the International Council for Harmonization (ICH) of technical requirements for pharmaceuticals for human use guidelines
In 2017, the NMPA joined the ICH. In the process of compiling the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition, the implementation of international standards was further strengthened (Table 3)[64-67]. Considering the current status of drug production andquality control and the current applicability of products already on the market in China, the newly added general technical requirements are consistent with the ICH guidelines,and the revised general technical requirements are better harmonized with the ICH guidelines as much as possible.
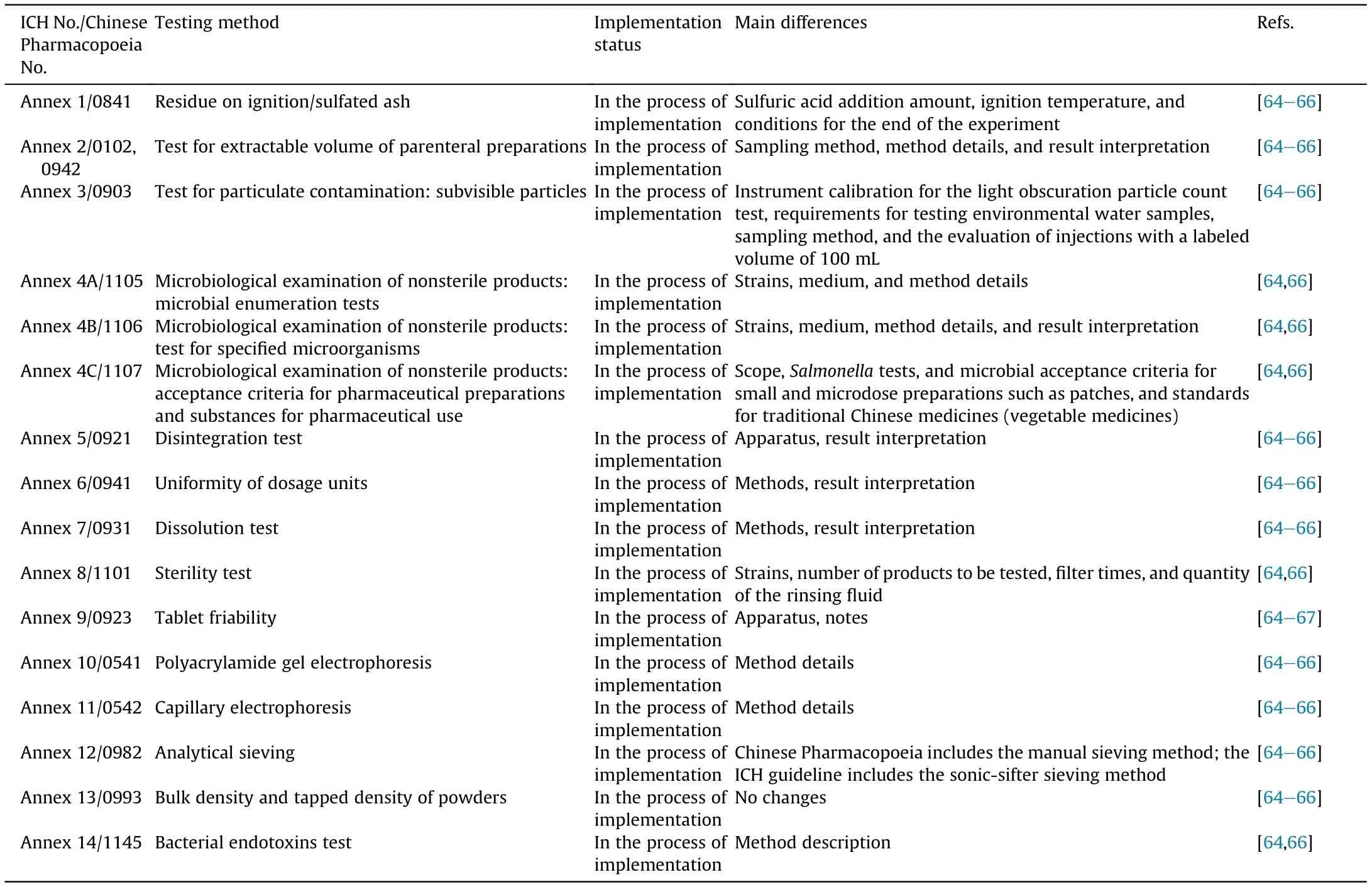
Table 3 Implementation status of the ICH Q4B in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition.
Stability is one of the critical factors influencing competivity in the drug market and is an important field of technological innovation. Guideline 9001, “Stability Testing of Drug Substances and Preparations”, was revised according to the ICH Q1A [68]. The definition of “significant changes” in preparation quality was proposed to guide manufacturers to focus on critical quality attributes.Additionally, the requirements for the transportation of temperature-sensitive drugs have been clarified. For special preparations, such as sustained- and controlled-release preparations and inhalations, the important parameters affecting their stability test are listed. Guideline 9101, “Validation of Analytical Methods”,was revised to be consistent with the ICH Q2 [69]; the contents regarding the correction factor were deleted and the methods for accuracy and precision were revised. The reporting, identification,and qualification thresholds for drug impurities and the decision tree of the ICH Q3A and Q3B [70,71] were introduced in guideline 9102,“Analysis of Impurities in Drugs”.To ensure consistency with the ICH Q3C[72],cumene and methyl isobutyl ketone were revised from class 3 solvents to class 2 solvents,and triethylamine,a class 3 solvent, was added to method 0861, “Determination of Residual Solvents”. The flow-through cell and reciprocating cylinder methods were added to method 0931, “Dissolution and Drug Release Test”. The instruments, methods, and interpretations related to the ICH Q4B Annex 7[73-82]and the research results on specific preparations, such as compound ketoconazole cream and lithium carbonate sustained-release tablets, were introduced.Method 1101,“Sterility Tests”,was improved,based on the ICH Q4B Annex 8, to be more instructive and practical [83]. The scope of environmental monitoring, the storage and use of culture media and strains, the culture time of the medium sensitivity test, the number and quantity of products to be tested, and the requirements of incubation and observation were revised. The bulk density and tapped density are important functionality-related characteristics of pharmaceutical excipients in powder form.These densities are commonly used to calculate the Hausner ratio and compressibility index of the powders.Referring to the ICH Q4B Annex 13[84-86],method 0993,“Bulk Density and Tapped Density of Powders”, was added. Referring to the ICH M7 [87], guideline 9306, “Genotoxic Impurities Control”, was added, and the general principles, assessment methods, and calculation methods of acceptable intakes and limits were introduced.
However, some general testing methods in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition still differ from those in the ICH Q4B(Table 3). The general testing methods in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia were originally drafted according to the British Pharmacopoeia and the World Health Organization, and these general chapter methods have a long history of use and a wide variety of applications in China. However, the current mainstream drug standard harmonization is based on the Pharmacopoeia Discussion Group and the ICH. Moreover, due to limited information and the complexity of regulatory adjustments, the information in international standards referenced by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia is not comprehensive, and the revisions are not timely. Despite these challenges, harmonization with international standards is still vigorously promoted by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission(ChPC).In October 2018,the ICH Q4 symposium was held in Beijing.More than 20 experts from the ICH Expert Working Group and ChPC discussed strategies for implementing ICH Q4 in China. In 2020, the ICH Q4B implementation status of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia was added to the official ICH website for the first time[64].
5. Summary and prospects
The general chapters of the Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition are based on science, risk, and applicability, and refer to the ICH guidelines. New technologies and requirements developed in recent years were introduced to provide technical and methodological support to ensure the safety, effectiveness, and controllability of pharmaceuticals in China.The current edition will play an active role in encouraging the application of advanced technologies, improving quality control of drugs, and strengthening the means of drug regulation in China.
As observed from the history of other pharmacopoeias, the development of drug standards is a process of gradual and continuous improvement owing to the limitations of scientific cognition. The concept of quality by design and life cycle management will be further implemented in the general chapters of the 2025 Chinese Pharmacopoeia [88-96]. For example, analytical procedure lifecycle guidelines and process analysis technologies will be introduced, and the roles of statistical methods in data evaluation, interpretation, and processing for the development,validation, transfer, and verification of analytical methods will be strengthened.The system for microbiological control based on risk assessment will also be improved.
Widely used analytical technologies, such as HPLC, GC, and atomic spectroscopy, will be revised. Moreover, additional scientific, objective, and convenient techniques will be introduced in a timely manner.The development of personalized microbial testing methods for specific preparations and research detailing rapid microbiological methods will be further elaborated [97-101]. The testing methods for active and toxic ingredients, exogenous pollutants in crude TCMs, and the microbiological examination requirements for TCM decoction pieces will continue to be improved.
In 2020,the revision of the Q4B guidelines was initiated by the ICH. The ChPC will continue to expand its participation in the harmonization of drug standards and actively promote harmonization/interchangeability with ICH Q4 based on validation. Other ICH guidelines, such as the ICH Q3D, will also be harmonized.Further, the general chapter of “Elemental Impurities Limits and Procedures” in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia will be developed to better assess and control elemental impurities in drugs in China.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission Drug Standard Promoting Funds and Comprehensive Reform of the Chinese Drug and Medical Device Review and Approval System Funds (2015-2020).
杂志排行
Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis的其它文章
- Plasma-metabolite-based machine learning is a promising diagnostic approach for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma investigation
- Reducing SARS-CoV-2 pathological protein activity with small molecules
- UHPLC-MS/MS analysis of cAMP and cGMP in rat plasma as potential biomarkers of Yin-Yang disharmony in traditional Chinese medicine
- Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the quantification of an anti-sclerostin monoclonal antibody in cynomolgus monkey serum
- Simultaneous determination of fourteen components of Gumiganghwal-tang tablet in human plasma by UPLC-ESI-MS/MS and its application to pharmacokinetic study
- A simplified LC-MS/MS method for the quantification of the cardiovascular disease biomarker trimethylamine-N-oxide and its precursors
