The Program Construction Method of Navigation Format Files GPX and KML Based on Geological Exploration Point Information
2021-08-02SongshiXIE
Songshi XIE
Abstract GPX and KML are open and multi-purpose, which are widely used in many fields such as basic geological survey, geochemical survey, geophysical survey, engineering survey and so on. Based on the analysis of the syntax features, basic structure and expression of GPX and KML files, this paper discussed the construction methods of GPX and KML files by taking the construction of navigation files of point information as an example. According to the specifications of GPX and KML files, an automatic construction program of GPX and KML files is designed and compiled, which realizes the automatic generation of batch point navigation files and supports in related software, and shows good effects of holding and displaying, which is helpful to simplify work flow and improve work efficiency.
Key words GPX; KML; Navigation file; Conversion program; Survey point
Received: December 26, 2020 Accepted: March 2, 2021
Songshi XIE (1981-), male, P. R. China, senior engineer, devoted to research about agricultural geology and environmental geochemistry.
*Corresponding author.
GPX and KML are widely used and have good supportability. They are common navigation and data storage formats used by geological survey software and equipment, and have a wide range of applications in field work in many fields such as basic geological survey, geochemical survey, geophysical survey and engineering survey[1-3]. GPX (GPS eXchange Format) is a general-purpose GPS data storage and exchange format based on XML (eXtensible Markup Language), which can be used to describe the location, altitude, time, and trajectory of waypoints. It can be used to exchange data between different GPS devices and software, such as viewing trajectories, embedding geographic data in the exif data of photos. It is a positioning data format commonly supported by current mainstream maps, navigation software, and handheld locator devices such as MapSource, Ovi Interactive Map, Google Earth, and GISoffice. The GPX format is free and can be used without paying any license fees. KML (Keyhole Markup Language) is an XML-based markup language originally developed and maintained by Keyhole. It uses XML syntax format to describe geospatial data (such as points, lines, areas, polygons and models), and is suitable for geographic information collaboration and sharing under the network environment[4]. KML was announced as an open geographic information coding standard by OGC (Open Geospatial Consortium, Inc.) in 2008, and is currently widely supported by Ovi Interactive Maps, Google Earth, Google Maps and other software, as well as unmanned aerial vehicles. As far as field work in the geological survey industry is concerned, a small number of points can be navigated by manually inputting coordinates on a handheld locator, but for a large number of points, this method is quite cumbersome and even not operable. At present, GPX and KML formats are the most commonly used navigation file storage formats[5], and it is of significant practical significance to deeply understand their characteristics and to edit and produce navigation files based on this.
Methods
Definitions of GPX and KML formats
According to the GPX architecture document, all coordinates are relative to the WGS84 datum, and all measurements are in metric units. The GPX file contains a metadata header, followed by waypoints, routes, and tracks. The metadata header contains GPX version, creator information, copyright information, etc., which are essential, but do not require special attention. Waypoints, routes, and tracks are represented by
Basic KML files can describe location marks, overlays, routes, and polygons. They are created using
Theoretically speaking, GPX and KML files with a small amount of information can be constructed directly by writing, but in actual work, it is often necessary to convert a large amount of point information into GPX and KML, because it is inconvenient to write directly, and the characters and tags are not standardized and easily lead to format reading error. Obviously, it is a more feasible way to use program design to realize the conversion of survey point information to GPX and KML files. In the past, a variety of program design methods and ideas have been used in previous studies, and significant results have been achieved[6-9], which is of great practical significance for simplifying the work process and improving work efficiency.
Construction programs of GPX and KML
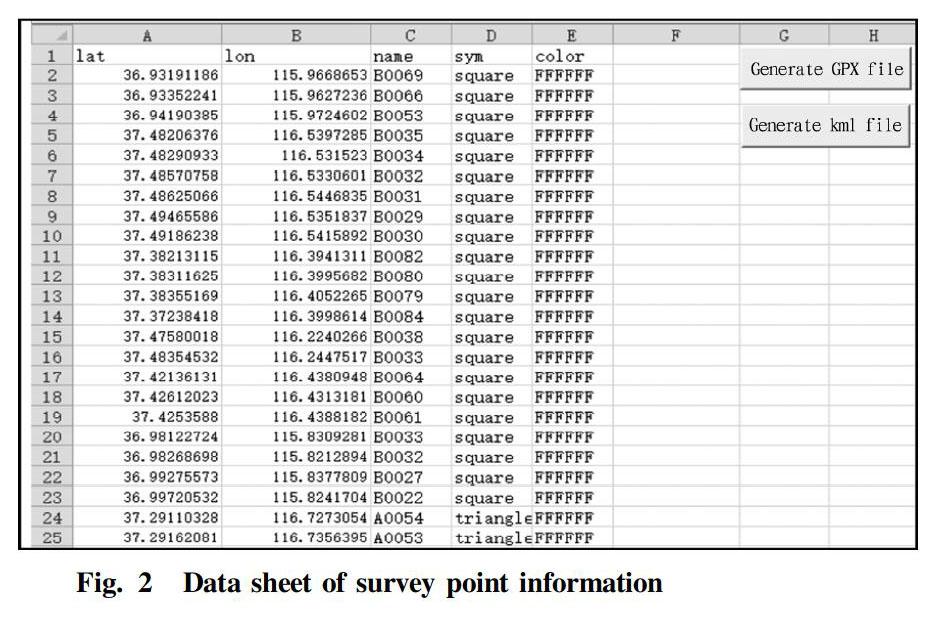
The grammatical formats of GPX and KML files are similar, so the construction methods are similar. Here we take the commonly used point information-based GPX and KML format file construction as an example to design the program. First of all, data preparation is required. The excel table should include at least the four columns of "longitude", "latitude", "point number" and "symbol" under WGS84 coordinates. If there is a requirement for the color of the point symbol in the generated KML, a "color" column will be needed. Secondly, the GPX and KML files are created and named, and the file header was written according to the rules; and then the point information is read from the specified data column position, and written according to the rules; and finally the end of the file is written, and the corresponding file is closed. The specific program code is implemented in VBA, and the KML conversion code is as follows:
Public Sub xls2xml()
If Dir(ActiveWorkbook.Path& "\KML", vbDirectory) <> "" Then
MsgBox "The generated folder already exists, click OK to overwrite the original file!"
Else: MkDirActiveWorkbook.Path& "\KML" ‘Create output folder
End If
Set rmyrange = ActiveSheet.UsedRange.Cells
latClm = Application.InputBox(prompt:="Enter the serial number of the latitude (N) column", Default:=1, Type:=1)
lonClm = Application.InputBox(prompt:="Enter the serial number of the longitude (E) column", Default:=2, Type:=1)
nameClm = Application.InputBox(prompt:="Enter the serial number of the name column", Default:=3, Type:=1)
symClm = Application.InputBox(prompt:="Enter the serial number of the symbol column", Default:=4, Type:=1)
clrClm = Application.InputBox(prompt:="Enter the serial number of the color column", Default:=5, Type:=1)
sfilename = ActiveWorkbook.Path& "\KML\" &ActiveSheet.Name&sfilename& ".kml"
ifilenum = FreeFile()
The following rules for writing GPX and KML files are different
Open sfilename For Output As #ifilenum
Print #ifilenum, ""
Print #ifilenum, "
Print #ifilenum, "
Print #ifilenum, "
Print #ifilenum, "
Print #ifilenum, "
For i = 2 Tormyrange.Rows.Count
Print #ifilenum, "
Next
Print #ifilenum, ""
Close #ifilenum
End Sub
The conversion code of GPX is similar to the KML file. The methods of obtaining the data information columns and creating the file are the same, while the rules for writing the files are different. The specific code is as follows:
sfilename = ActiveWorkbook.Path& "\GPX\" &ActiveSheet.Name&sfilename& ".gpx"
ifilenum = FreeFile()
Open sfilename For Output As #ifilenum
Print #ifilenum, ""
Print #ifilenum, "
For i = 2 Tormyrange.Rows.Count
Print #ifilenum, "
Next
Print #ifilenum, " "
Close #ifilenum
Songshi XIE. The Program Construction Method of Navigation Format Files GPX and KML Based on Geological Exploration Point Information
Results and Application
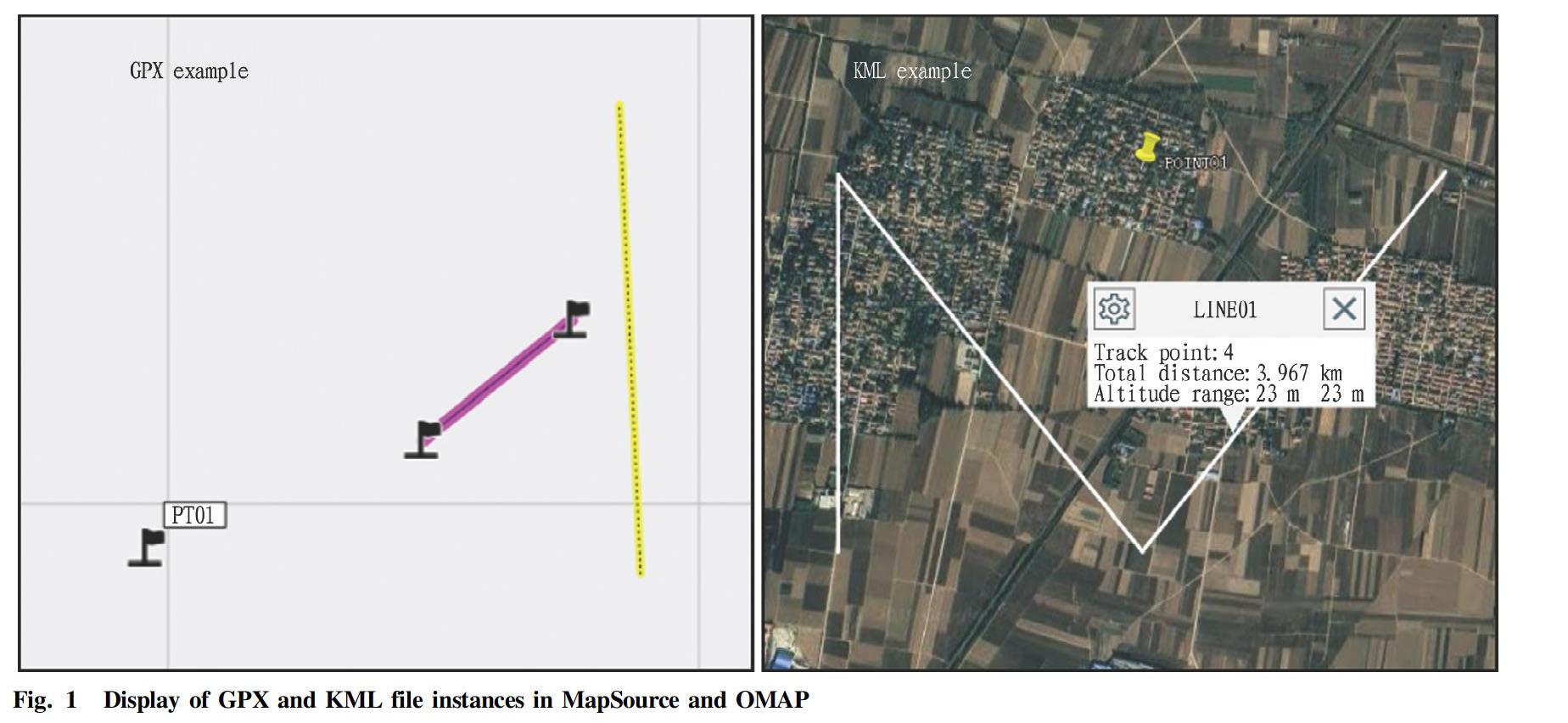
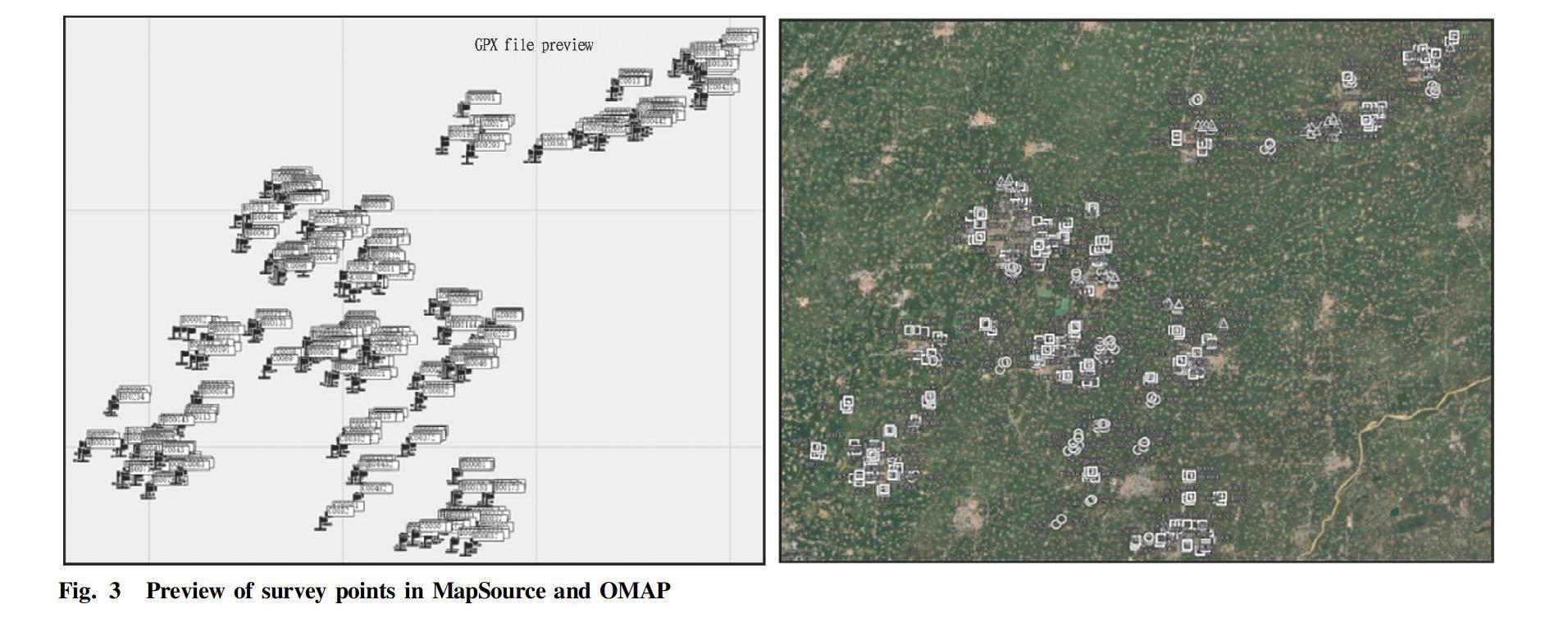
Taking a certain surface soil survey point as an example, the total number of sample points was 470. First, the survey point coordinates were converted to WGS84 coordinates, and the coordinate unit was "degree". The conversion parameters in the conversion of the commonly used Beijing 54 coordinate system or Xian 80 coordinate system coordinates to WGS84 coordinates should be used correctly, otherwise it is easy to cause navigation deviation. By default, the first four columns in the survey point information data table were latitude, longitude, point number, symbol, and color. Different types of survey points could be distinguished by different symbols or colors. Different software may have different interpretations of symbol tags, which need to be determined according to the specific conditions of the symbol library provided by the software. The preparation of the point data information table is shown in Fig. 2. After clicking the "Generate GPX file" or "Generate KML file" button, the sub process in the corresponding module was executed, by which the program created a folder named "GPX" or "KML" in the directory where it was located, and the created navigation point file was saved into the corresponding folder. The display effect of the converted survey point GPX file in MapSource and the display effect of KML file in Ovi Interactive Map are shown in Fig. 3. It can be seen that the files generated by this program could be imported and displayed normally.
Conclusions
For batch and repetitive point information processing processes, the application of programmed processing methods is an effective means to improve work efficiency, and there are many successful precedents in the field of geological exploration[10-13]. Here we take the construction of the most commonly used navigation files based on point location information as an example to discuss the construction method of procedural GPX and KML files. In the actual work of geological survey, information such as survey line or survey area range needs to be expressed based on line or graphic information, and its file construction method is similar to that of point files. If you have actual needs, you can rewrite the program using line or graphic tags referring to the structure of this program.
Both GPX and KML files use a grammatical format based on tags (names and attributes) to describe geographic labeling information. Their plain code format makes them easy to construct and modify, and have good readability, and it is easier to implement lightweight software design based on them. In fact, in addition to the commonly used tags, the two data formats both provide rich attribute information tags, which can be easily queried and used in related public documents, and they have high practical value for further enriching the content of the created GPX and KML files.
References
[1] WU XY, MA XH. Application of GPX data to design of geophysical exploration projects[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2016, 31(3): 456-460. (in Chinese)
[2] ZHANG SY, SUN HJ. Application of WGS84 coordinates and KML file in route engineering survey[J]. Industrial Technology Innovation, 2015, 02(5): 542-546. (in Chinese)
[3] YANG SF, WANG L, HAI YQ. Method and skills of geophysical exploration measuring network data fast import into hand-held GPS[J]. Guizhou Geology, 2014, 31(2): 136-140. (in Chinese)
[4] DU YJ, YU CC, LIU J. On GIS system based on KML and its application[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2010, 27(10): 49-51, 116. (in Chinese)
[5] SHI XQ, CHANG Y. Application of GPX data format in geophysical prospecting measurement[J]. Equipment for Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 20(1): 61-64. (in Chinese)
[6] LIU XL, MA J. The method for transforming ArcGIS vector data to KML file based on ArcEngine[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, 2007(3): 98-101. (in Chinese)
[7] DING P. Application of GISOffice and Coord in conversing data of plane rectangular coordinate system to Kml files of Google Earth[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 2015, 22(3): 213-214, 185. (in Chinese)
[8] WU SS, CHEN T, WU YR. Design and realization of KML file automatic generation software[J]. Mechanical and Electrical Information, 2019(24): 98-99. (in Chinese)
[9] LIU GP, XU M, CHEN XD. Batch generation of KML files for power lines based on Excel VBA[J]. Low Carbon World, 2017(33): 79-80. (in Chinese)
[10] ZHANG DE, XIE QF, HE Z, et al. The automatic generation of large lattice coding in the sampling point layout map for regional geochemical exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 35(3): 406-408, 430. (in Chinese)
[11] CHEN KZ. Methods of automatic numbering of geochemical exploration sampling points and automatic generation of waypoints[J]. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 2014, 34(S1): 60-65. (in Chinese)
[12] SONG BJ. Discussion on geochemical data batch transfer to GPS based on the GPX exchange documents[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2010, 33(3): 111-113, 119. (in Chinese)
[13] YANG XP, GENG XM, CHU QF. A method of points batch mark in google earth based on KML[J]. Geomatics & Spatial Information Technology, 2012, 35(4): 92-93. (in Chinese)
杂志排行
农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Anti-inflammatory Activity and Mechanism of Total Flavonoids from the Phloem of Paulownia elongate S.Y. Hu in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages
- Comparative Genomic Analysis of Boron Transport Gene Family in Arabidopsis and Five Crops
- Effects of Different Water-saving Irrigation Methods on Fruit Quality and Yield of Snow Melon
- Field Control Effects and Crop Safety Assessment of Triazole Fungicides on Apple Rust
- Effects of Acetylacetone Solution Soaking on Agrobacterium-transformed Maize Seed Buds
- Effects of Meteorological Factors on Overwintering Ability, Yield and Quality of Forage Rape
