Effect of Gully Land Reclamation on Soil Organic Matter and Carbon Contents
2021-08-02PanpanZHANGTingyuZHANG
Panpan ZHANG Tingyu ZHANG
Abstract [Objectives] This study was conducted to investigate the effects of Yanan gully land reclamation project on farmland soil organic matter and carbon contents.
[Methods]Through indirect sampling and random sampling methods, soil samples were collected from six areas of Baota District, Ansai District, and Zichang County in Yanan City, before and after gully land reclamation, and the organic matter and soil organic carbon contained in them were determined.
[Results] Through sampling experiments, we initially analyzed the changes of the above components in the land consolidation areas after different years and the reasons for the changes: ① after the Yanan gully land reclamation project was implemented, the soil organic matter and carbon contents increased; ② directing at the improvement of soil organic matter and carbon content different years after the consolidation, the improvement ranked as 5 a>2 a>1 a; and ③ correlation analysis showed that there was a significant positive correlation between soil organic matter and carbon contents.
[Conclusions]This study provides scientific decision-making and theoretical basis for the construction of high-standard farmland in gully areas and the implementation and promotion of gully land reclamation projects.
Key words Gully land reclamation; Soil organic matter; Soil organic carbon; Effect
Received: March 11, 2021 Accepted: May 12, 2021
Supported by Internal Scientific Research Project of Shaanxi Provincial Land Engineering Construction Group (DJNY2021-35, DJNY2021-10); Fundamental Research Fund for Central Universities (300102351502).
Panpan ZHANG (1990-), female, P. R. China, engineer, master, devoted to research about land engineering.
*Corresponding author. E-mail: 410207176@qq.com.
In response to problems such as the reduction of arable land in Yanan area and the inability to guarantee food security, combined with the soft soil of the Loess Plateau conducive to farming and abundant land resources in Yanan City, Yanan City promotes the vigorous development of gully land reclamation and rapidly increases the area of high-standard basic farmland[1].
Gully land reclamation projects are bound to have an impact on soil nutrients[2]. Soil organic matter is an important constituent of the solid phase of soil, which has extremely important significance for soil formation, soil fertility, environmental protection and sustainable development of agriculture and forestry[3]. Soil organic carbon is the core of soil nutrient conversion and is closely related to soil nutrient. At present, the related research on gully land reclamation is mostly focused on benefit evaluation analysis and cultivated land quality research, and there are few studies on the impacts on soil organic matter and organic carbon[4]. Therefore, in this study, we explored the response of soil organic matter and soil carbon contents to gully land reclamation in the same area and to remediation of the same land type after different years and revealed the characteristics of the effects of gully land reclamation on soil organic matter and soil carbon contents. This study can provide scientific decision-making and theoretical basis for the construction of high-standard farmland in gully areas and the implementation and promotion of gully land reclamation projects.
Materials and Methods
General situation of the study area
The gully land reclamation project area is located in Yanan City, Shaanxi Province. Yanan belongs to the hilly and gully area of the Loess Plateau, with an arid and semi-arid inland climate. The landform is dominated by loess plateau and hills. The terrain is high in the northwest and low in the southeast. The test soil samples were taken from Yangjuangou Watershed, Gutun Village and Madongchuan of Baota District, Yanqiao area of Ansai District, and Jiuyugou and Nanzhenggou of Zichang County, in Yanan City, Shaanxi Province. The research area was planted with maize, one crop a year, and chemical fertilizer was applied in one time.
Sample collection
In view of the convenience of operation, this study adopted an indirect method, which was to sample the consolidated soil and adjacent slope soil free of land consolidation at the same time as the soil samples before and after treatment and compare and study the soil samples. A sample plot with a size of 10 m×10 m was set up in the upper, middle and lower reaches of Yangjuangou in Baota District of Yanan City, respectively, and soil samples in the range of 0-20 cm cultivated layer were collected according to a five-point mixing method. Soil was collected from five points in each plot for mixing, and at the same time, samples were collected in the same way in adjacent gullies that had not been consolidated, avoiding point pollutants such as fertilization and dung piles when collecting. The sampling method for other areas was the same as that of Yangjuangou. A total of 36 soil samples were collected from the six locations, and each sample was about 1 000 g. After removing the debris, the soil was air-dried, ground and sieved for later use. Each sample had three replicates. The sampling time was May 2020.
Determination method and data analysis
The data were processed by Excel, and the origin software was used for drawing. Soil organic matter was determined by potassium dichromate volumetric method, and soil organic carbon was determined by TOC/TN analyzer (MultiC/N3100).
Results and Analysis
Effect on soil organic matter before and after gully land reclamation
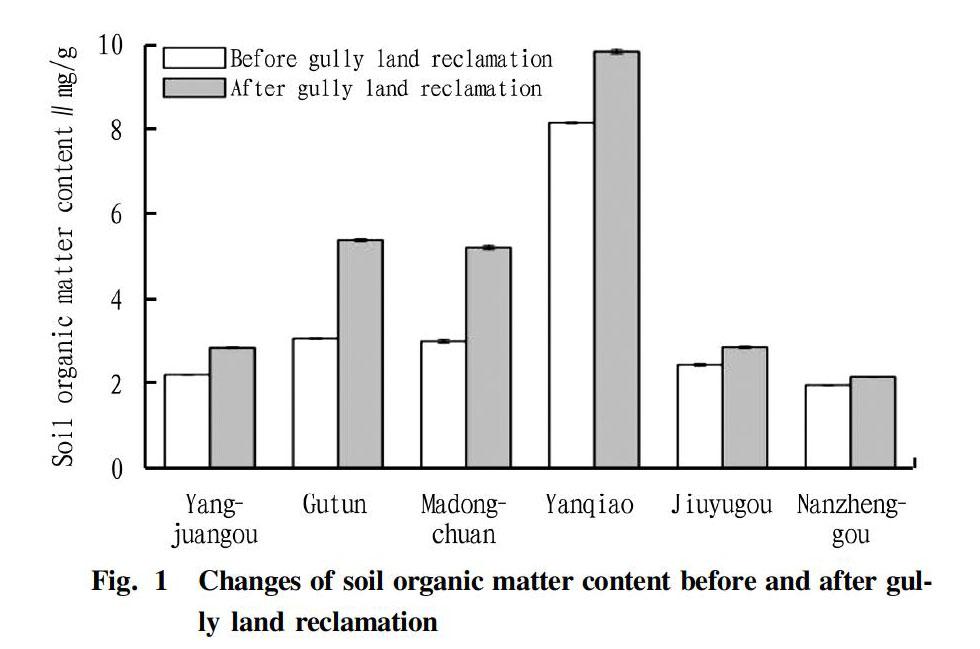
Changes in soil organic matter content before and after gully land reclamation are shown in Fig. 1. It can be seen from Fig. 1 that the content of soil organic matter in the study area after gully land reclamation increased compared with before, with an amplitude of variation of 0.41-2.32 mg/g. In Baota District, the content of soil organic matter increased by 28.38% in Yangjuangou, 75.78% in Gutun, and 72.53% in Madongchuan. Yanqiao area of Ansai district showed a content of soil organic matter increased by 20.71%; and the soil organic matter of the sampling area of Zichang County increased by 0.315 mg/g averagely, and the contents in Jiuyugou and Nanzhenggou increased by 16.73% and 11.28%, respectively.
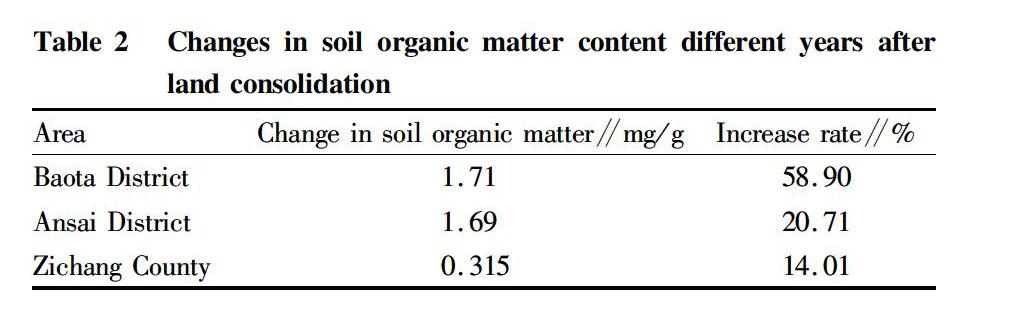
The changes in soil organic matter content different years after land consolidation in the study area are shown in Table 2. The soil organic matter in the sampling area of the gully land reclamation project in Baota District increased by 1.71 mg/g on average after consolidation compared with before consolidation, that is, an increase of about 58.90%; the soil organic matter in the sampling area of Ansai District increased by an average of 1.69 mg/g, with an increase rate of approximately 20.71%; the soil organic matter in the sampling area of Zichang County increased averagely by 0.315 mg/g, with an increase rate of approximately 14.01%. The improvement of soil organic matter ranked as 5 a>2 a>1 a.
The changes in soil organic carbon content before and after gully land reclamation are shown in Fig. 2. It can be seen from Fig. 2 that the soil organic carbon content in the study area increased after gully land reclamation, with an amplitude of variation of 0.05 to 0.80 mg/g. In Baota District, the content of soil organic carbon increased by 0.19‰ in Yangjuangou, 1.48‰ in Gutun, and 1.09‰ in Madongchuan; the soil organic carbon in Yanqiao area of Ansai District increased by 0.52‰; and in Zichang County, the soil organic carbon increased by 0.19‰ in Jiuyugou, and 0.09‰ in Nanzhenggou.
The changes of soil organic carbon content different years after land consolidation in the study area are shown in Table 3. The soil organic carbon in the sampling area of the Baota District increased by 0.50 mg/g after the gully land reclamation project on average compared with before land consolidation, that is, an increase of about 9.19%; the soil organic matter in the sampling area in Ansai District increased by 0.42 mg/g on average, that is, an increase of approximately 5.15%; and the soil organic matter in the sampling area of Zichang County increased by an average of 0.08 mg/g, with an increase rate of about 1.36%. The increases in soil organic carbon ranked as 5a>2a>1a.
Relationship between soil organic matter and soil carbon content
The correlation between soil organic matter and organic carbon in the study area after gully land reclamation is shown in Table 4, and there was a significant positive correlation between the two.
Discussion and Conclusions
In the gully land reclamation project, the surface soil was peeled off, but the soil organic matter content and nutrient status increased in a short period of time, which is consistent with previous research results. With the improvement of production conditions, it is conducive to the growth of crops and the accumulation of biomass. The implementation of farmland protection and ecological protection projects increase the area of forest land, which is conducive to the formation of a farmland protection ecological forest system, which has a positive effect in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem, retaining water and soil and ensuring ecological safety[5].
Discussing the impact of gully land reclamation engineering measures on soil organic matter and soil carbon content can reveal changes in soil environmental quality under gully land reclamation measures. Soil organic matter and carbon contents affect crop yields. Soil active organic carbon is the most sensitive component in soil organic carbon pool that responds to various disturbance factors such as physical and chemical factors. It plays an important role in soil nutrient cycling. Gully land reclamation projects can promote the improvement of soil environmental quality indicators. In-depth study of the relationship of soil organic matter and carbon contents with soil environmental quality indicators is of great significance for evaluating soil environmental quality functions of gully land reclamation engineering measures and guiding actual production.
① After the implementation of the Yanan gully land reclamation project, the content of soil organic matter increased, within a range of 0.41-2.32 mg/g; and the increases of soil organic matter ranked with the years after land consolidation as 5 a>2 a>1 a.
② The content of soil organic carbon increased to a certain extent, within 0.05-0.80 mg/g; and the increases of soil organic carbon ranked with the years after land consolidation as 5a>2a>1a.
③ The changes of soil organic matter and organic carbon were significantly different from those before land consolidation. After correlation analysis, soil organic matter and organic carbon had a significant positive correlation. It can be seen that the gully land reclamation project helps to increase the soil organic matter and carbon content.
References
[1] WANG CL, YANG JL, WANG ZL, et al. Effect of green manure rape turning over on soil moisture and fertilizer in the gully region of the Loess Plateau[J/OL]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2021(2): 1-8. (in Chinese)
[2] QIU HJ, CAO MM. Land-use change in gully region of Loess Plateau: A case study of Luochuan County, Shaanxi Province[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 31(2): 207-210, 251. (in Chinese)
[3] DU PC, XU Q, ZHAO KY, et al. Impacts of gully reclamation project on cropland distribution and vegetation restoration in North Shaanxi Province: A case study at Gutun Watershed of Yanan City[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 39(6): 1-8. (in Chinese)
[4] LIE N. Effect of Yanan gully land reclamation project on soil organic carbon[C]//Editorial Department of Environmental Engineering. Environmental Engineering, 2017 Supplement 2, Volume 2: Industrial Construction, 2017: 6. (in Chinese)
[5] XU XL, ZHANG KL, XU XL, et al. Spatial distribution and estimating of soil organic carbon on Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2003(3): 13-15. (in Chinese)
杂志排行
农业生物技术(英文版)的其它文章
- Anti-inflammatory Activity and Mechanism of Total Flavonoids from the Phloem of Paulownia elongate S.Y. Hu in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 Macrophages
- Comparative Genomic Analysis of Boron Transport Gene Family in Arabidopsis and Five Crops
- Effects of Different Water-saving Irrigation Methods on Fruit Quality and Yield of Snow Melon
- Field Control Effects and Crop Safety Assessment of Triazole Fungicides on Apple Rust
- Effects of Acetylacetone Solution Soaking on Agrobacterium-transformed Maize Seed Buds
- Effects of Meteorological Factors on Overwintering Ability, Yield and Quality of Forage Rape
