Palladium-catalyzed cascade synthesis of spirocyclic oxindoles via regioselective C2-H arylation and C8-H alkylation of naphthalene ring
2021-05-14XiiLuoWengungLiHiynLuGuoboDengYunYngChunmingYngYunLing
Xii Luo,Wengung Li,Hiyn Lu,Guobo Deng,Yun Yng,*,Chunming Yng,*,Yun Ling,*
a National & Local Joint Engineering Laboratory for New Petro-chemical Materials and Fine Utilization of Resources, Key Laboratory of Chemical Biology and Traditional Chinese Medicine Research, Ministry of Education, Key Laboratory of the Assembly and Application of Organic Functional Molecules of Hunan Province, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hunan Normal University, Changsha 410081, China
b Hunan University of Medicine, Huaihua 418000, China
ABSTRACT A simultaneous C2-H arylation and C8-H alkylation of naphthalene ring has been achieved by palladiumcatalyzed cascade reaction of N-(2-halophenyl)-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)acrylamides with aryl iodides,which provides an efficient method for synthesizing various aryl-substituted spirocyclic oxindoles.The protocol enables three bonds formation via an intramolecular Heck reaction and sequentially regioselective bond activation.
Keywords:Palladium-catalyzed Cascade reaction Regioselective C-H activation Naphthalene ring Spirocyclic oxindoles
Naphthalenes as the simplest fused arenes,whose site-selectivefunctionalization have been widely studied based on the presence of C1-directing groups 12–15].However, the vast majority of methods have focused on single C2-H [12], C3-H[13], and C8-H activation [14] of naphthalenes under transitionmetal catalysis (Scheme 1A-a).In contrast, the reports on their doublefunctionalization are relatively rare.Despite the fact that the You group has recently demonstrated a palladiumcatalyzed regioselective C7-H and C8-H arylations of 1-naphthamides for the construction of carbohelicenes via a directing groupassisted strategy (Scheme 1A-b) [15], the development of new efficient methods for doubleactivation of naphthalenes is urgently needed and extremely intriguing.Our group reported a series of palladium-catalyzed tandem reactions of aryl iodides involving C(aryl)-H activation in recent years [11,16].In continuation of our interest in this field, we envision that doublefunctionalization of naphthalene ring could be achieved by the domino reaction of N-(2-iodophenyl)-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)acrylamides with aryl iodides.Herein,we present a new transformation between N-(2-iodophenyl)-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)acrylamides and aryl iodides for the synthesis of aryl-substituted spirocyclic oxindoles,which allows threebonds formation by sequential C2-H arylation and C8-H alkylation of naphthalene ring(Scheme 1B).
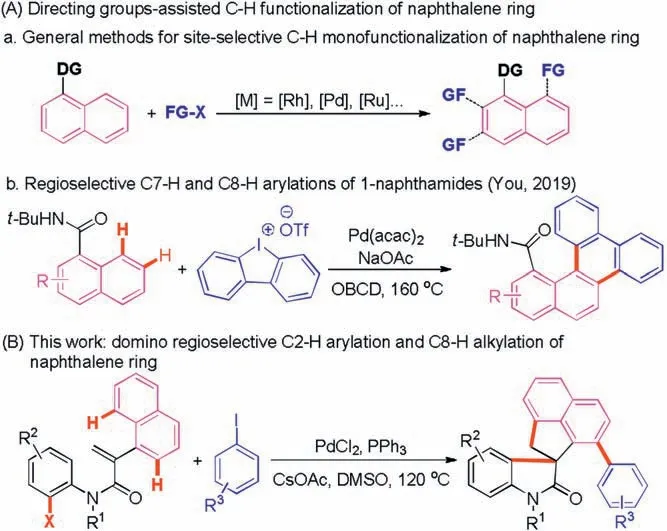
Scheme 1.Two different strategies for transition-metal-catalyzed functionalization of naphthalene ring.
We began our investigation with the tandem reaction of N-(2-iodophenyl)-N-methyl-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)acrylamide 1a with iodobenzene 2a (Table 1).Unexpectedly, the product 3aa, rather than 3aa0, was obtained exclusively in 52% yield via sequentially selective CH activation under the reaction conditions reported by our previous work(entry 1).Inspired by this intriguing result,ascrupulous screening of various reaction parameters was performed.Evaluation of palladium catalysts (Pd(dba)2, PdI2, and PdCl2)and P-ligands(P(o-tol)3and dppf)showed that a combination of PdCl2with PPh3was the best choice (entries 2–7).Unfortunately, replacing PdCl2and PPh3with PdCl2(PPh3)2displayed lower catalytic efficiency(entry 8).Subsequently,CsOAc was found to be the most competent base in terms of yield(entries 9–13).Finally, Inferior results were afforded by performing the reaction with other solvents (DMF and MeCN) or reaction temperature (110and 130) (entries 14–17).Accordingly, the optimal reaction conditions were shown as entry 13 in Table 1.Gratifyingly, a gram-scale experiment of 1a (3 mmol,1.24 g) with iodobenzene 2a could afford the product 3aa in 62% yield (entry 18).
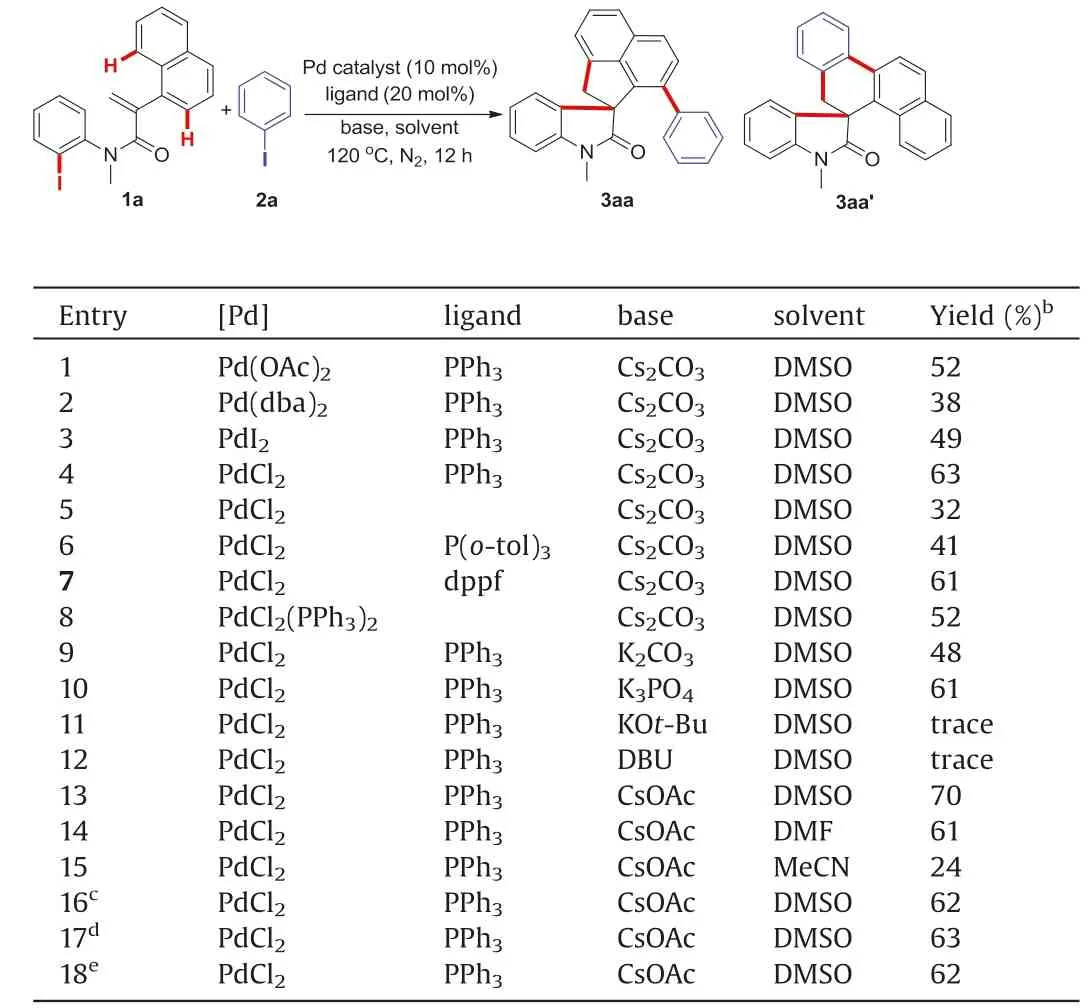
Table 1 Optimization of the reaction conditions.a
Having the optimized reaction conditions in hand,we set out to examine the substrate scope of this cascade reaction.A variety of substituted N-(2-iodophenyl)-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)acrylamides 1 were initially investigated (Scheme 2).Acrylamides bearing different substituents on the nitrogen atom could undergo this cyclization/cross coupling cascade to produce the target products 3ba-3da in moderated to good yields.The structure of the product 3ba was clearly verified by single-crystal X-ray analysis.Delightedly,substitution with electron-withdrawing(F,Cl,CF3and NO2)as well as electron-donating groups (Me and OMe) on the aromatic ring of the aniline moiety were well tolerated under the standard conditions, and the desired products 3ea-3na were afforded in 42%–90% yields.It was noteworthy that acrylamides 1o from heterocyclic arylamine could be smoothly converted into the product 3oa, albeit only with a 28% yield.
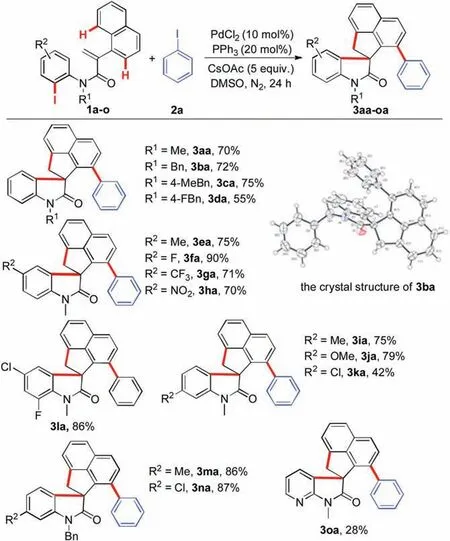
Scheme 2.Scope of the N-(2- iodophenyl)-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)acrylamides.Reaction conditions: 1 (0.2 mmol), 2a (0.4 mmol), PdCl2(10 mol%), PPh3(20 mol%),CsOAc (5 equiv.), DMSO (1 mL) at 120under nitrogen atmosphere for 24 h.
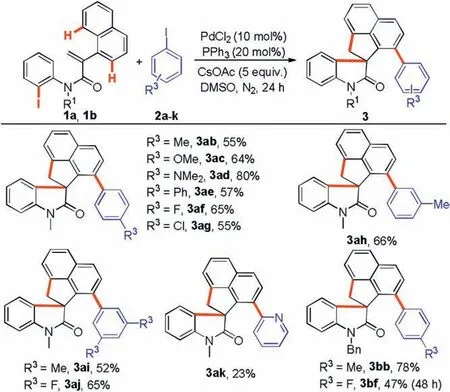
Scheme 3.Scope of the aryl iodides.Reaction conditions: entry 13 in Table 1 and Scheme 2.
The substrate scope of aryl iodides 2 was explored next, as demonstrated in Scheme 3.We were pleased to found that monosubstituted aryl iodides possessing Me,OMe,NMe2,Ph,F and Cl groups at the para or meta position could be efficiently coupled producing the aryl-substituted spirocyclic oxindoles 3ab-3ah,3bb and 3bf in moderate to good yields.Unfortunately, orthosubstituted aryl iodides, such as 1-iodo-2-methylbenzene and 1-fluoro-2-iodobenzene, could not be converted into the desired products.The results demonstrated that the cascade reaction was dramatically affected by the steric effect of the substituents on aryl iodides.Disubstituted aryl iodides (2i and 2j) proved to be also amenable substrates,producing 3ai and 3aj in 52%and 65%yields,respectively.However, the reaction of 2-iodopyridine 2k with acrylamides delivered the product 3ak in a lower yield in comparison with other aryl iodides.
Finally,the generality of this protocol was further examined by using N-(2-bromophenyl)-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)acrylamides and aryl iodides as the reaction substrates (Scheme 4).Gratifyingly,the reaction of N-(2-bromophenyl)acrylamide 4a with iodobenzene could afford 65%of the target product 3aa under the standard conditions.Subsequently, several N-(2-bromophenyl)acrylamide(4b,4e,and 4h)and aryl iodides(1c and 1f)were investigated.All of them were subjected to the cascade cyclization to provide the desired products (3ba, 3ea, 3ha, 3ac and 3af) in 63%–79% yield.
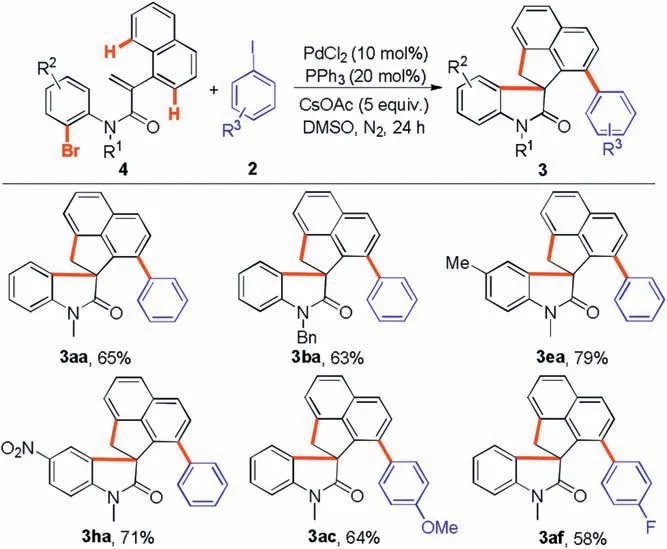
Scheme 4.The reaction of N-(2-bromophenyl)-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)acrylamides with aryl iodides.Reaction conditions: entry 13 in Table 1 and Scheme 2.
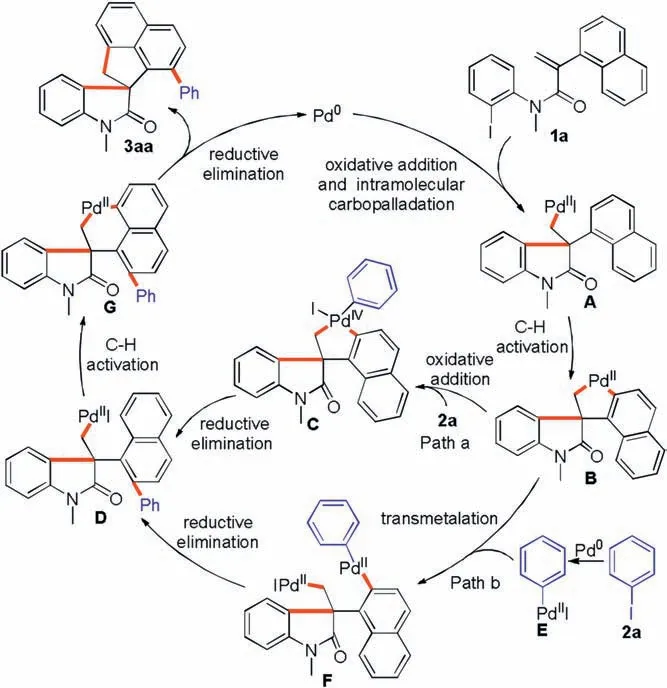
Scheme 5.Possible reaction mechanism.
On the basis of Lautens ’s work [10e] and our previous report[11c], a possible mechanism for this palladium-catalyzed cascade reaction is depicted in Scheme 5.First,oxidative addition of N-(2-iodophenyl)acrylamide 1a to Pd(0) species followed by an intramolecular Heck reaction forms the intermediate A.Next,the C2-H activation of the aryl Pd(II)species A to the naphthalene ring produces the spiropalladacycle B,which inserts into thebond of iodobenzene 2a via oxidative addition to give spiropallada(IV)cycle C.Intermediate D was then formed by the reductive elimination of intermediate C.Finally, intermediate D undergoes the secondactivation of naphthalene ring followed by reductive elimination to give product 3aa and regenerate Pd(0)(path a).Furthermore,the transmetelation pathway of spiropalladacycle B with intermediate E generated from iodobenzene 2a cannot be ruled out (path b).
In summary, we have disclosed a new palladium-catalyzed cascade reaction for the assembly of a variety of aryl-substituted spirocyclic oxindoles from N-(2-halophenyl)-2-(naphthalen-1-yl)acrylamides with aryl iodides, which enables regioselective C2-H arylation and C8-H alkylation of naphthalene ring through an intramolecular carbopalladation/twiceactivation sequence.Notably,this approach showcases broad substrate scope and good functional group tolerance.Further studies toward exploring this type of cascade reaction are still in progress in our laboratory.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Nos.21572051, 21602057, 21901071, and 21971061), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (Nos.2020JJ5350 and 2020JJ5347), Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (Nos.18A002, 19B359 and 17C1137), and Science and Technology Planning Project of Hunan Province (No.2018TP1017) for financial support.
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementarymaterialrelatedtothisarticlecanbefound,inthe online version,at doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2020.07.005.
杂志排行
Chinese Chemical Letters的其它文章
- Quantitative assessment of rhodamine spectra
- One-step straightf oward solid synthesis of high yield white fluorescent carbon dots for white light emitting diodes
- Free-standing nitrogen doped graphene/Co(OH)2composite films with superior catalytic activity for aprotic lithium-oxygen batteries
- Amorphous silicon from low-temperature reduction of silica in the molten salts and its lithium-storage performance
- Two 2D uranyl coordination complexes showing effective photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B and mechanism study
- Recent advances in electrochemical sensors for antibiotics and their applications
