Hippo/YAP通路在血管紧张素Ⅱ诱导的高血压肾损伤中的作用机制研究
2021-05-08张君杰徐茜方天明张丽周明生
张君杰 徐茜 方天明 张丽 周明生

【摘要】 目的:本文探討了Hippo/YAP通路在血管紧张素Ⅱ(AngⅡ)诱导的高血压肾损伤中的作用。方法:研究时间为2018年5月-2019年12月,将18只雄性C57BL/6小鼠随机分为正常对照组、模型组、治疗组(Verteporfin),模型组和治疗组通过植入胶囊渗透压泵连续灌注AngⅡ持续21 d,治疗组从造模后第1天开始,隔天1次,腹腔注射Verteporfin至实验结束。比较各组SBP、尿蛋白/尿肌酐结果,比较各组YAP、P-LATs、纤维化因子[TGF-β1、CTGF及纤维连接蛋白(FN)]、炎症因子(TNF-α、MCP1及IL-1β)蛋白表达量。结果:三组SBP和尿蛋白/尿肌酐结果比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。三组肾小球纤维化面积百分比、肾小球硬化面积百分比比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。三组YAP、P-LATs蛋白相对表达量比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。三组各纤维化因子蛋白相对表达量结果比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。三组各炎症因子蛋白相对表达量结果比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:AngⅡ诱导的高血压肾损伤存在有Hippo/YAP通路的激活,该通路可能通过介导肾脏的炎症及纤维化引起肾损伤和高血压。
【关键词】 Hippo/YAP通路 高血压 肾损伤
The Role of Hippo/YAP Pathway in Angiotensin Ⅱ-Induced Hypertension and Its Associated Renal Injury/ZHANG Junjie, XU Qian, FANG Tianming, ZHANG Li, ZHOU Mingsheng. //Medical Innovation of China, 2021, 18(05): 0-024
[Abstract] Objective: To explore the role of the Hippo/YAP pathways in angiotensin Ⅱ (AngⅡ) induced hypertension renal injury. Method: From May 2018 to December 2019, 18 male C57BL/6 mice were randomly divided into normal control group, model group and treatment group (Verteporfin). In the model group and the treatment group, AngⅡ was continuously perfused by implanting capsule osmotic pump for 21 days. In the Verteporfin treatment group, Verteporfin was injected intraperitoneally every other day, starting from the first day after modeling, until the end of the experiment. SBP and urinary protein/urinary creatinine were compared, the expressions of YAP, P-LATs, TGF-β1, CTGF and Fibronectin (FN), TNF-α, MCP1 and IL-1β were compared. Result: There were statistically significant differences in SBP and urinary protein/urinary creatinine among the three groups (P<0.05). There were statistically significant differences in the percentage of glomerular fibrosis area and glomerular sclerosis area among the three groups (P<0.05). There were statistically significant differences in the relative expression levels of YAP and P-LATs among the three groups (P<0.05). There were statistically significant differences in the protein expression levels of fibrosis factors among the three groups (P<0.05). There were statistically significant differences in the relative expression levels of inflammatory cytokines among the three groups (P<0.05). Conclusion: There is activation of Hippo/YAP pathway in AngⅡ induced hypertensive renal injury, which may cause renal injury and hypertension by mediating renal inflammation and fibrosis.
[Key words] Hippo/YAP pathway Hypertensive Kidney injury
First-authors address: Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110000, China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2021.05.006
高血压是危害人类健康的常见病,可引起心脑肾等靶器官损害。高血压是引起终末期肾病(end stage renal disease, ESRD)的一个最主要危险因素[1]。高血压肾病的主要病理特征包括肾脏炎症,肾小球基底膜增厚、硬化,肾小球及间质纤维化[2]。高血压肾病发病机制十分复杂,尽管进行了深入的研究,但其发病机制目前尚未完全阐明[3-4]。
近期研究发现一些心血管和肾脏疾病的发生可能与改变Hippo/YAP信号通路有关[5-6]。Hippo通路是在进化过程中高度保守的信号通路,Yes-associated protein(YAP)是一个生物转录调控因子,参与调控组织生长,协调细胞增殖、死亡和分化等[7],该通路早期研究主要集中在抗肿瘤领域[5]。目前有关该通路在肾脏中的作用所知甚少,近年来备受关注,最新研究提示Hippo/YAP通路参与肾小球和下尿道胚胎发育中的信号传导,维持肾脏足细胞稳态平衡以及肾小球滤过屏障的完整性[8-10]。改变肾脏Hippo/YAP信号通路可能与一些肾脏疾病的发生,如糖尿病肾上皮损伤和肾脏纤维化发生等有关[8]。但有关该通路与高血压及高血压肾病的研究尚未见文献报道。通过灌注血管紧张素Ⅱ(AngⅡ)诱导小鼠高血压是一种常见的高血压动物模型[10-11]。给予小鼠灌注3周升压剂量的AngⅡ可以诱导稳定性的高血压和高血压肾损伤。本研究将使用该模型,通过腹腔注射YAP抑制剂维替泊芬(Verteporfin, Ve,Ve是一个被广泛应用的YAP激活抑制剂)治疗,探讨Hippo/YAP通路在高血压及其肾损伤中的作用及可能机制。现报道如下。
1 材料与方法
1.1 仪器与材料 大小鼠无创血压仪,超声波破碎仪,高速台式离心机,SDS电泳仪,化学发光成像系统,水平摇床,正置荧光显微镜,半封闭脱水机,自动组织包埋机,手动石蜡切片装置[12]。SPF级C57BL/6小鼠18只。
1.2 实验动物分组及实验方案 研究时间为2018年5月-2019年12月,将8~10周龄雄性C57BL/6小鼠18只随机分為正常对照组、模型组、治疗组。正常对照组6只,平均体重(23.73±1.31)g;模型组6只,平均体重(23.88±1.05)g;治疗组6只,平均体重(24.07±0.89)g。模型组和治疗组通过植入胶囊渗透压泵连续灌注AngⅡ, 1.1 mg/(kg·d)持续21 d,治疗组腹腔注射Verteporfin(Selleck,Cat No.S1786,50 mg),注射浓度60 mg/kg,剂量
0.15 mL,隔日注射一次至实验结束。用尾动脉法分别测定小鼠实验前、实验第1、2、3周的尾动脉收缩压(systolic blood pressure, SBP);3周后,处死动物,从膀胱中收集尿液并解剖收集肾组织样品。
1.3 模型制备 计算每个泵需要的AngⅡ的量,麻醉小鼠,埋泵,待小鼠苏醒后,放回饲养笼。
1.4 尾动脉血压测量 使用无创尾动脉血压仪测量小鼠尾动脉血压,反复测量5次,求平均值。
1.5 尿蛋白和肌酐测定 将收集到的尿液按照BCA法测定尿蛋白的浓度,用酶标免疫法测定尿样品中的肌酐含量,计算尿蛋白与肌酐比值。
1.6 肾组织PAS和Masson染色 肾脏组织的石蜡切片,PAS染色后用显微镜对样品进行拍照以评估肾小球损伤,最后计算出肾小球硬化面积占整个肾小球面积的百分比。Masson染色对肾脏组织中胶原蛋白含量的进行半定量分析,以评估肾纤维化。对Masson染色分析使用胶原容积分数,即胶原阳性的蓝色面积与组织总面积的百分比。
1.7 Western blot 检测YAP、P-LATs、纤维化因子[TGF-β1、CTGF及纤维连接蛋白(FN)]、炎症因子(TNF-α、MCP1及IL-1β)蛋白表达量。(1)制样提前打开离心机4 ℃预冷。将收集好用于Western blot的肾脏组织置于EP管中,依据组织重量,按比例加入配制好的裂解液,4 ℃ 12 000 r/min离心30 min并吸取上清;(2)BCA法测定蛋白浓度;(3)配制SDS-PAGE胶;(4)电泳;(5)湿转法转膜;(6)杂交;(7)ECL显色,PVDF膜滴加配置好的AB发光液后孵育1 min,显影摄片,Image J统计灰度值。
1.8 统计学处理 图像分析使用Image J,数据统计分析及作图使用GraphPad Prism 5。结果用(x±s)表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA),P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
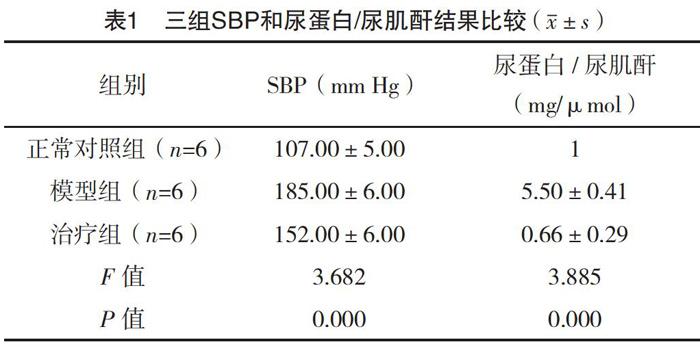
2.1 三组SBP和尿蛋白/尿肌酐结果比较 三组SBP和尿蛋白/尿肌酐结果比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1。
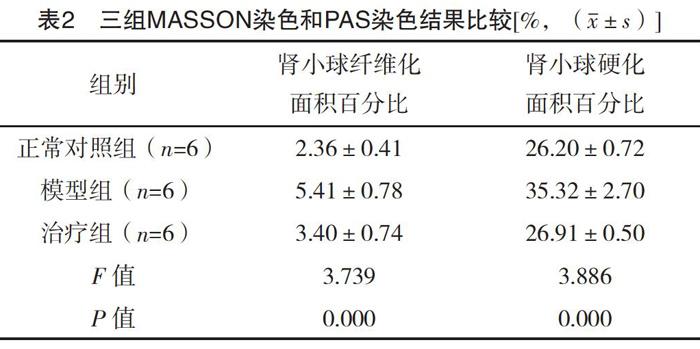
2.2 三组MASSON染色和PAS染色结果比较 三组肾小球纤维化面积百分比、肾小球硬化面积百分比比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表2。
2.3 三组YAP、P-LATs蛋白相对表达量比较 三组YAP、P-LATs蛋白相对表达量比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表3。
2.4 三组各纤维化因子蛋白相对表达量 三组各纤维化因子蛋白相对表达量结果比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表4。
2.5 各炎症因子蛋白相对表达量比较 三组各炎症因子蛋白相对表达量结果比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表5。
[11] Panciera T,Azzolin L,Cordenonsi M,et al.Mechanobiology of YAP and TAZ in physiology and disease[J].Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,2017,18:758-770.
[12] Moya I M,Halder G.Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling in organ regeneration and regenerative medicine[J].Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,2019,20(4):211-226.
[13] Wang C,Zhu X,Feng W,et al.Verteporfin inhibits YAP function through up-regulating 14-3-3σ sequestering YAP in the cytoplasm[J].Am J Cancer Res,2015,6(1):27-37.
[14] He J,Bao Q,Yan M,et al.The Role of Hippo/YAP Signaling in Vascular Remodeling and Related Diseases[J].Br J Pharmacol,2018,175(8):1354-1361.
[15] Ishihara E,Nishina H.Role of Hippo-YAP/TAZ signaling pathway in mechanotransduction[J].Clin Calcium,2016,26(12):1751-1756.
[16] Lei H,Aimei W,Yun H,et al.Macrophage Depletion Lowered Blood Pressure and Attenuated Hypertensive Renal Injury and Fibrosis[J].Frontiers in Physiology,2018,9:473.
[17] Szeto S G,Narimatsu M,Lu M,et al.YAP/TAZ Are Mechanoregulators of TGF-β-Smad Signaling and Renal Fibrogenesis[J].J Am Soc Nephrol,2016,27(10):3117-3128.
[18] Liang M,Yu M,Xia R,et al.Yap/Taz Deletion in Gli+ Cell-Derived Myofibroblasts Attenuates Fibrosis[J].J Am Soc Nephrol,2017,28(11):3278-3290.
[19] Xu J,Li P X,Wu J,et al.Involvement of the Hippo pathway in regeneration and fibrogenesis after ischaemic acute kidney injury: YAP is the key effector[J].Clinical Science,2016,130(5):349-363.
[20] Chen J,Harris R C.Interaction of the EGF Receptor and the Hippo Pathway in the Diabetic Kidney[J].J Am Soc Nephrol,2016,27(6):1689-1700.
(收稿日期:2020-06-03) (本文編辑:姬思雨)
