Role of Nrf2 signaling pathway in manganese-induced oxidative damage in TM3 cells
2021-04-25,,
, ,
(Department of Hygienc Toxicology,School of Public Health,Zunyi Medical University,Zunyi Guizhou 563099,China)
[Abstract]Objective To explore whether manganese(Mn)mediated the regulation of Nrf2 signal pathway to playan anti-oxidative effect in the TM3 cell.Methods Efficacy of low,medium and high doses of Mn were included.The experimental inhibitor was ATRA and the agonist was TBHQ,at a final concentration of 10 μmol/L.The cell experiment was divided into 12 groups,namely:high,medium and low concentration of Mn groups(100,200,300 μmol/L); agonist with high,medium and low concentration of Mn groups; inhibitor with high,medium and low concentration of Mn groups; blank control group,agonist control Group and inhibitor control group.The Mn exposure time was 24 h.In this experiment,the cell apoptosis rate,cell ROS level,MDA content and other oxidative stress indicators were detected.Western blot and RT-qPCR assays were used to measure the expression of Nrf2,HO-1,GSTpi,SOD,NQO1 and other oxidative stress-related proteins and genes.Results The IC50 of Mn in TM3 cells was 300 μmol/L.With the dose of Mn increased,the survival rate of cells was decreased.The higher concentration of Mn produced, more ROS and MDA.The expressions of oxidative stress-related proteins of HO-1,NQO1,SOD,GSTpi and Nrf2 were decreased after exposure to Mn,which caused cell oxidative damage.Consistent results were shown in western blot and RT-qPCR assays.After Nrf2 was inhibited,ROS generation was increased in all doses of Mn groups,with dose-effect relationship.On the contrary,when Nrf2 was activated,ROS and MDA were increased.Conclusion Mn could damage TM3 cell with a dose-dependent relationship and one of the underlying mechanism might be related to oxidative damage,and activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway might play anti-oxidant role in the cell damage.
[Key words]manganese; TM3 cells; Nrf2; oxidative damage
A damaged Nfr2 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various diseases such as tumor,inflammation and neurodegenerative diseases[7-8].The Nrf2 signal pathway regulates the expression of antioxidant protein so that it can protect cell against oxidative damage.The Nrf2 signal pathway is now a crucial drug target
For its antioxidant effect,researchers used Nrf2 agonists to activate this pathway in order to enhance the antioxidant ability of the body.Among Nrf2 agonists,tertiary butylhydroquinone(TBHQ)is commonly used of its high efficiency,low toxicity and good stability.KhodagholiF[9]found that TBHQ could inhibit cell injury and death caused by lipopolysaccharides.Meanwhile,it can significantly increase the expression of Nrf2 protein and its downstream gene transcription,and it reduces the expression of caspase-3.Results byNouhiand his colleagues[10]first showed that TBHQ has a neuro-protective effect by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway.ATRA(Total trans-sulfonic acid),an inhibitor of Nrf2 signaling pathway,has been shown to inhibit the binding of Nrf2 to ARE(Antioxidant homeopathic components).
To explore Mn-induced cytotoxicity,we set out the hypothesis that Mn exposure may damage the regulation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway,which contributes to Mn-induced cellular oxidative stress and cell death.We chose TM3 cells as the model system in this study.By determining cell morphology,cell vitality,and intracellular Nrf2,HO-1(heme oxygenase-1),GSTpi(Glutathion S-transferase),SOD(superoxide dismutase),NQO1(NAD(P)H dehydrogenase quinone 1)levels,we observed a Mndose-dependent activation of Nrf2 signaling pathways in TM3 cells.The results may help to understand the mechanism of Mn-induced male reproductive toxicity.
1 Materials and methods
1.1 Material Reagents were purchased from the following sources:reagents and kits routinely used in RPMI 1640 culture medium(Gibco)from Sigma; all antibodies used from Abcam; and retinoic acid and TBHQ from(MCE).All reagents were of analytical,HPLC or the best available pharmaceutical grade.
1.2 Cell grouping and cell processing TM3 cell(Shanghai College of Life Science,Chinese Academy of Sciences,CHINA)was used in this study.Cells were cultured with a 1640 complete medium,under the humidity 95%~100%,at 37℃,with 95%-air and 5%CO2.The cells were in logarithmic growth phase.The IC50of TM3 cells after Mn treatment for 24h was determined by MTT assay.There were three Mn concentration(with low,medium and high Mn levels).The inhibitor was ATRA,and the agonist was TBHQ.The final concentration was 10 μmol/L,and the pretreatment was 1.5h.The experiment was divided into 12 groups(Table 1),namely:blank control group(MnCl2:0 μmol/L,group C),low-dose Mn group(MnCl2:100 μmol/L,group L),medium-dose Mn group(MnCl2:200 μmol/L,group M),high-dose Mn group(MnCl2:300 μmol/L,group H),agonist control group(TBHQ:10 μmol/L,TC group),agonist and low-dose Mn group(TBHQ:10 μmol/L+MnCl2:100 μmol/L,TL group),agonist and medium-dose Mn group(TBHQ:10 μmol/L+MnCl2:200 μmol/L,TM group),agonist and high-dose Mn group(TBHQ:10 μmol/L+MnCl2:300 μmol/L,TH group).Inhibitor control group(ATRA:10 μmol/L,RC group),inhibitor and low-dose Mn group(ATRA:10 μmol/L+MnCl2:100 μmol/L,RL group),inhibitor and medium-dose Mn group(ATRA:10 μmol/L+MnCl2:200μmol/L,RM group),inhibitor and high-dose Mn group(ATRA:10μmol/L+MnCl2:300 μmol/L,RH group).The Manganese exposing time of all groups was 24 hours.
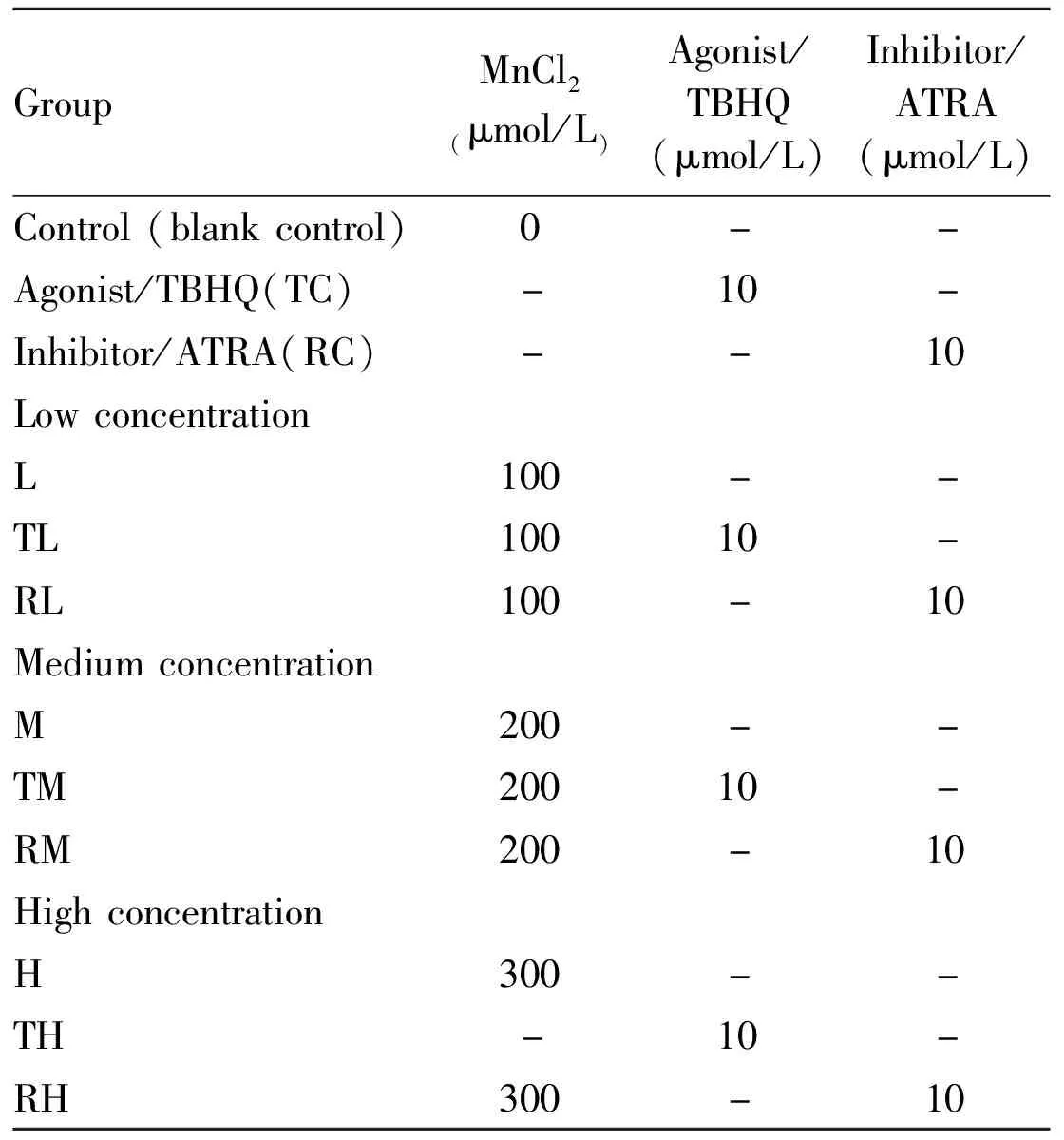
Table 1 Cell grouping and cell processing
1.3 Cell viability When drawing the cell growth curve,we adjusted the cell concentration to 5 × 104/ml,100 μl per well.After Mn adding for 6,12,24,36,48,60 and 72 h,MTT assay was used to test the cell viability.Bliss method in Graph-pad software was used to calculate the IC50.
The old woman had appeared to be most friendly, but she was really an old witch39 who had waylaid30 the children, and had only built the little bread house in order to lure31 them in
1.4 The cell apoptosis After treating with Mn,0.25% Trypsin(without EDTA)was used to digest and collect the cells.The culture solution and the cells were collected into a centrifuge tube,and centrifuged for 5 min,at 1 500 r/min.The supernatant was poured.Every sample included about 8 × 105cells.Cells apoptosis was tested by FCM following the instructions.
1.5 ROS content detection The probe 2 ′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate(DCFH-DA)was diulted with serum-free cell culture medium at a ratio of 1∶1 000,so its final concentration reaches 10 μmol/L.Detection conditions:the emission wavelength is 525nm,and the excitation wavelength is 488nm.Each group had 6 duplicate wells and the detection repeated 3 times.
1.6 Intracellular MDA levels measurement The malondialdehyde concentration in plasma samples was measured by using a lipid peroxidation assay kit(BC0025,Solarbio,Shanghai,China).MDA can be condensed with thiobarbituric acid to produce red product,which has a maximum absorption peak at 532 nm.The content of lipid peroxide in the sample could be calculated by colorimetry.The absorbance was set at 600 nm.The content of MDA was calculated by the difference of absorbance at 532 nm and 600 nm.
1.7 Related proteins detection by Western blot First,the total protein was extracted.BCA assay was used to quantify the proteins.Second,electrophoresis was set at 80V,and increased to 120V when the red bar of Marker was separated.Third,PVDF membrane was used for transfer.Condition of electric transfer was as follows:constant current 300 mA,90min.After all the above steps were completed,the all-energy imaging system dark box was put in,the configured luminous working liquid was add to the film,then the dark box was closed and allowed exposure.The obtained Image was scanned using image-pro Plus 6.0 software.The internal reference protein was GAPDH,and the data was input into SPSS20.0 software for analysis.
1.8 The target gene detection by RT-qPCR Total RNA was extracted from TM3 cells and operated according to the instructions.Step one:95 ℃ for 30 s.Step two:95 ℃ for 5 s.Step three:Gradient 61.0 ~ 65.0 ℃,30 s + Plate Read.Step four:GOTO Step 2,39 more times.(39).Step 5:Melt Curve 65.0 ℃ to 95.0 ℃,0.5 ℃ increment for 5 s + Plate Read.Step 6:4.0 ℃.The primers of these genes were listed in table 1.With GAPDH as the internal reference,the differences in expression were compared using the 2-ct method,and each gene in the group was set with 3 wells and repeated for 3 times.
The forward and reverse primer sequences for selected genes were designed and synthesized by the Invitrogen company(Table 2).

Table 2 Forward and reverse primer sequence
1.9 Statistical analysis SPSS20.0 statistical software was used to analyze the experimental data,and one-way ANOVA was used to compare the means.Lsd-t test was used to compare between groups,and test level was equal to 0.05.
2 Results
2.1 Effect of MnCl2on TM3 cell viability and IC50As shown in Fig 1A,the OD value of TM3 cells gradually increased with the extension of culture time.After 24 hours in the culture,it entered the logarithmic growth stage.After 60 hours,the cell growth reached the plateau.Therefore,we chose the cells whose cultured cycle was greater than 24 hours and less than 60 hours for this study.
The IC50used in this experiment is calculated by the OD value of 10 manganese dyes in 24 hours.The survival rate of TM3 cells was shown in Fig 1B.It showed that IC50was 300 μmol/L.
A:TM3 cells were treated by 0,25,50,100,200,400,800,1 200,1 600,and 2 000 μmol/L MnCl2 for 6,12,24,36,48,60,and 72 h;B:The survival rate of TM3 cells were measured by MTT assay.TM3 cells were treated by 0,25,50,100,200,400,800,1 200,1 600,and 2 000 μmol/L MnCl2 for 72 h.The survival rate of TM3 cells were measured by MTT assay.
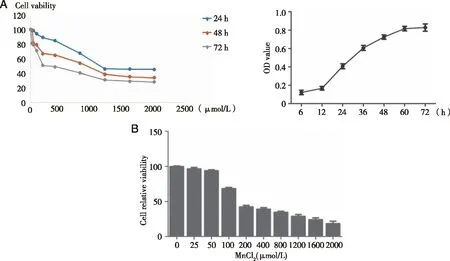
2.2 The effects of Mn on the levels of ROS and MDA in TM3 cell Compared with the control group,the ROS content in low,medium and high doses of Mn groups were all increased(Fig 2A,B).With the increase of Mn content,the ROS content also increased(P<0.05).Compared with group C,MDA contents in the low,medium and high dose manganese groups all increased,and MDA contents also increased with the increase of manganese dose(P<0.05).
A:TM3 cells were treated by 0,100,200,or 300 μmol/L of MnCl2 for 24 h;B:The levels of ROS were detected by probe DCFH-DA assays kit.The levels of MDA were measured with lipid peroxidation assay kit.*:P<0.05,significantly different compared with control TM3 cells.
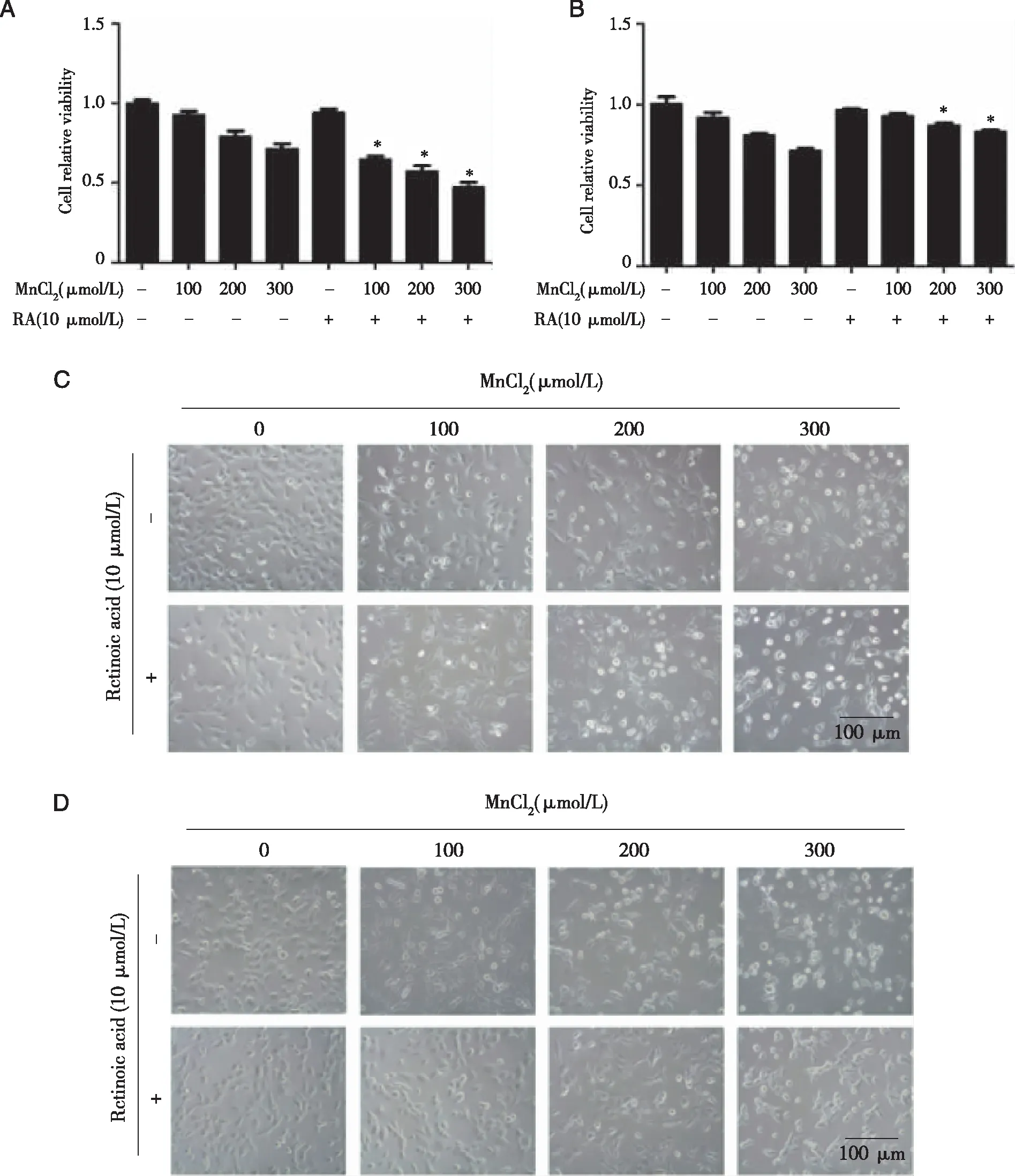
2.3 Effects of Nrf2 inhibitor or activator on cell viability and cell morphology in TM3 cells As shown in Fig 3A and B,the survival rate of TM3 cells gradually decreased with the increase of manganese dose compared with the control group(P<0.05).The cell survival rate of the same dose group was increased after the addition of activator.After adding inhibitor,the cell survival rate of the same dose group was decreased.All the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).
Observed under inverted phase contrast microscope we found that the exposure of the cell in ifferent doses of manganese(0,100,200,300 μmol/L)caused significant change of TM3 cell.Inhibitor ATRA(10 μmol/L),or activator TBHQ(10 μmol/L)also exerted effect on the cell morphology.Cells in group C and RC group had firm adherence.The cell was plump and well differentiated.The proliferated cells were connected into a single reticular formation,cytoplasmic was spreading uniformly and protruding.With the increase of Mn dose,the cells gradually retracted and became round,and the cells were floating more and obviously.The cell fragments were gradually increasing.
After using the inhibitor,cells were also exposed to Mn.It was found that the floating cells were more prominent,the cells retracted and became round,and the resulting cell fragments were increased.The cells of group C and activator group TC were firmly adhered to the wall,well differentiated,full cell body.The proliferated cells connected into a single layer network,and the cytoplasm spread and protruded.The cells of group TC were in a better condition.With the increasing concentration of manganese,the changes were more obvious.After agonist treatment,it was found that the cells became round and the suspended cells were not obvious,and the amount of cell debris generated was less than that of the group without agonist(Fig 3C,D).
2.4 Effects of Nrf2 inhibitor or activator on ROS and MDA levels in TM3 cells As shown in Fig 4A and B,compared with group C,ROS content in cells of all groups before and after adding of activator was significantly increased.The higher the Mn dose,the more the ROS content in the cells.Comparing with groups without the activator,ROS content in groups exposed to the activator was significantly lower(P<0.05).ROS content in the same dose group were increasing with the addition of inhibitor(P<0.05).
As shown in Figure 4C and D,compared with group C,MDA content in each group was significantly increased before and after the addition of the activator,and the higher the Mn dose,the more the MDA content.Compared with the medium and high dose group,MDA content in the group with the same dose of activator decreased significantly(P<0.05).Compared with the low-medium dose group,the MDA contents in the group with the inhibitor were significantly increased(P<0.05).
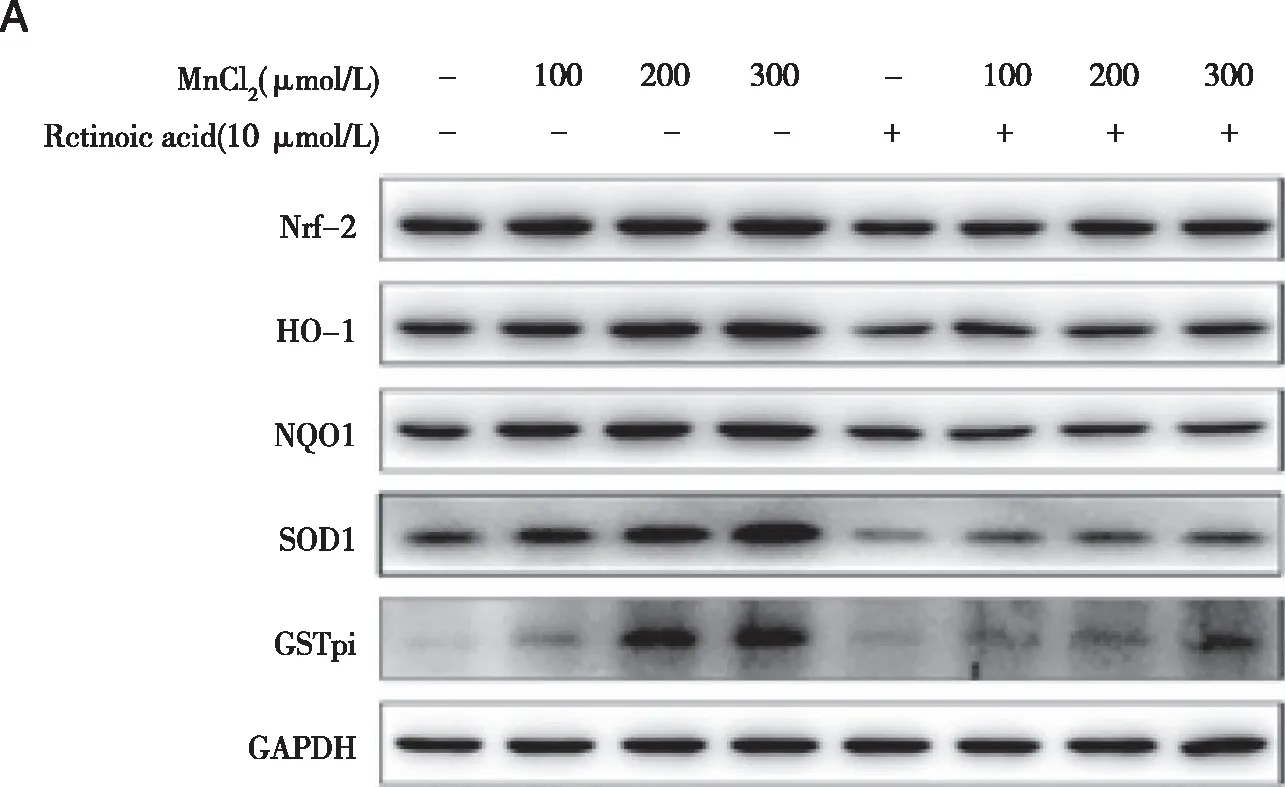
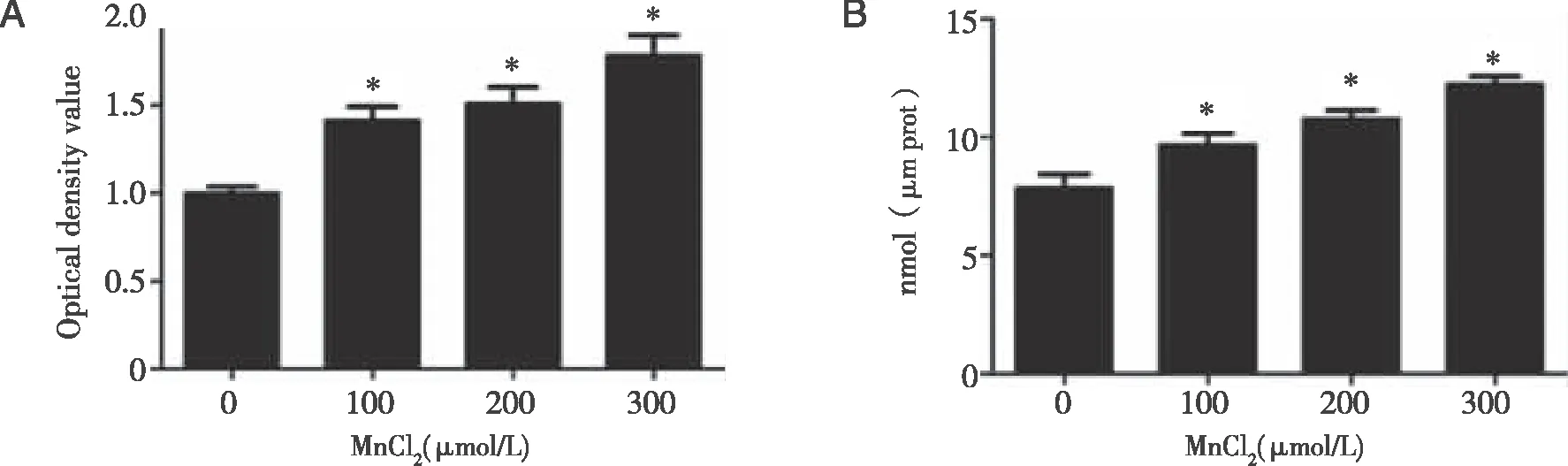
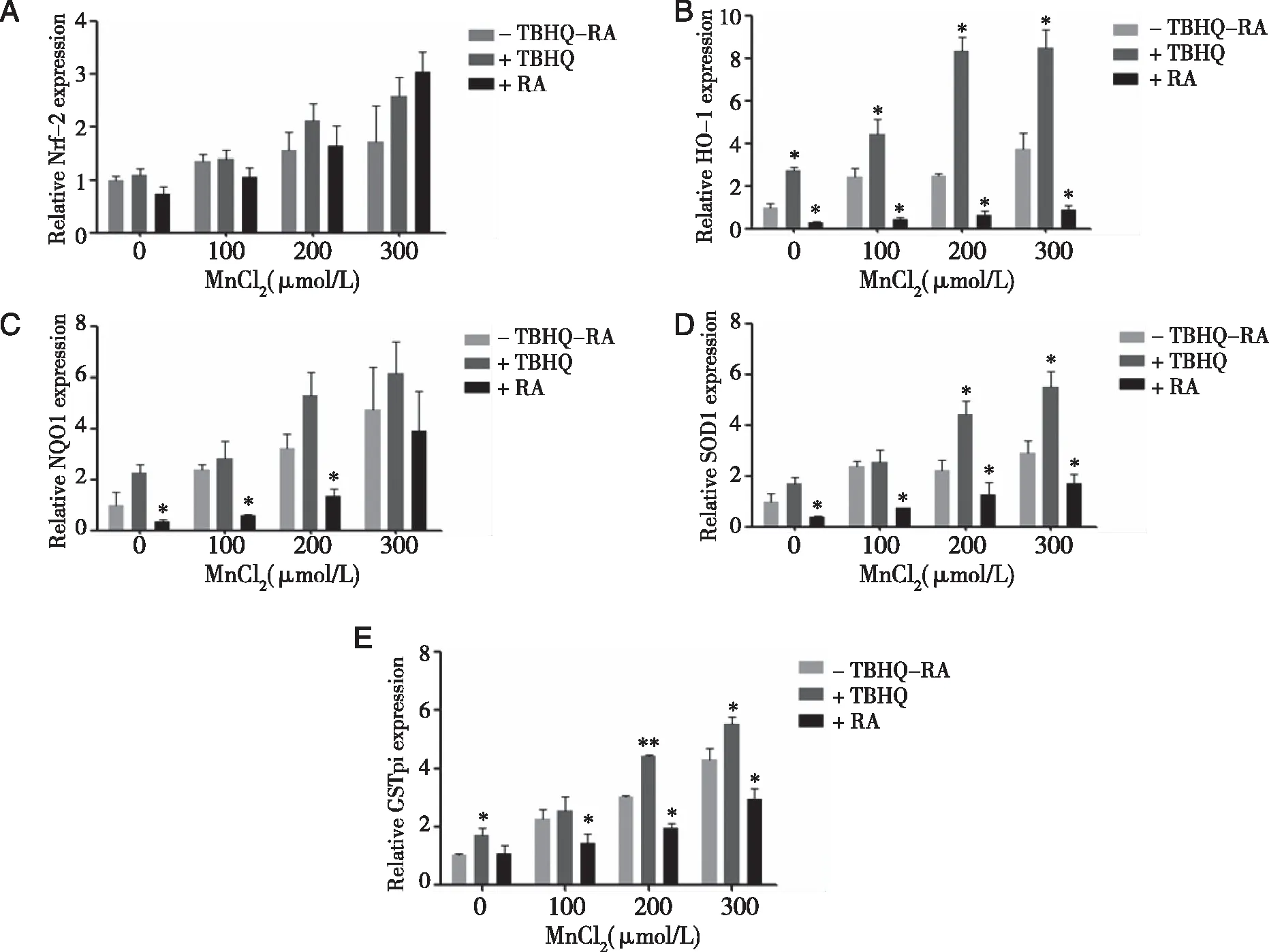
Densities of bands were quantified by Image J software.GAPDH levels,measured in parallel,served as controls.After TM3 cells were treated by 0 or 10 μmol/L ATRA(Nrf2 inhibitor)or TBHQ(Nrf2 activator)for 1.5 h,they were exposed to 0 ,100,200,or 300 μmol/L MnCl2 for 24 h.A,B,D:Western blots were performed;C,E:relative protein levels of Nrf2,HO-1,NQO1,SOD,and GSTpi were determined.*:P<0.05,significantly different compared with control TM3 cells.
A:After TM3 cells were treated by 0 or 10 μmol/L ATRA(Nrf2 inhibitor)for 1.5 h;B:After TM3 cells were treated by 0 or 10 μmol/L TBHQ(Nrf2 activator)for 1.5 h.Cells of(a)and(b)were exposed to 0,100,200,or 300 μmol/L MnCl2 for 24 h.The survival rate of TM3 cells were measured by MTT assay;C ,D :Cell morphology of TM3 cells were observed.*:P<0.05,significantly different compared with control TM3 cells.

A,B:After TM3 cells were treated by 0 or 10 μmol/L ATRA(Nrf2 inhibitor)or TBHQ(Nrf2 activator)for 1.5 h,they were exposed to 0,100,200,or 300 μmol/L MnCl2 for 24 h.The levels of ROS were detected by probe DCFH-DA assays kit;C,D:The levels of MDA were measured with lipid peroxidation assay kit.*:P<0.05,significantly different compared with control TM3 cells.
2.5 Effects of Nrf2 inhibitor or activator on Nrf2,HO-1,NQO1,SOD,and GSTpi levels in TM3 cells As shown in figure 5A~E,cfor the low and middle dose groups,Nrf2 inhibitors addition decreased the expression of Nrf2,HO-1,NQO1,SOD and GSTpi(P<0.05).Compared with the M,H group,in TM,TH group ,the expression of SOD and GSTpi,Nrf2,HO-1,NQO1 was increased(P<0.05).Compared with group TC,the expression levels of Nrf2,HO-1,NQO1,SOD,GSTpi in TM and TH groups were increased,depending on manganese concentration(P<0.05).
2.6 Effects of Nrf2 inhibitor or activator on apoptosis in TM3 cells As shown in Figure 6A and B,compared with group C,all the treated groups had increased apoptosis rate(P<0.05).Compared with group L,M and H,the apoptosis rate in the RL,RM and RH groups increased(P<0.05),and the apoptosis rate in the TL,TM and TH groups decreased(P<0.05).Compared with the RC group,apoptosis rate in the RL,RM and RH groups was increased(P<0.05).Compared with the TC group,the cell apoptosis rate was increased for the TL,TM and TH groups(P<0.05).
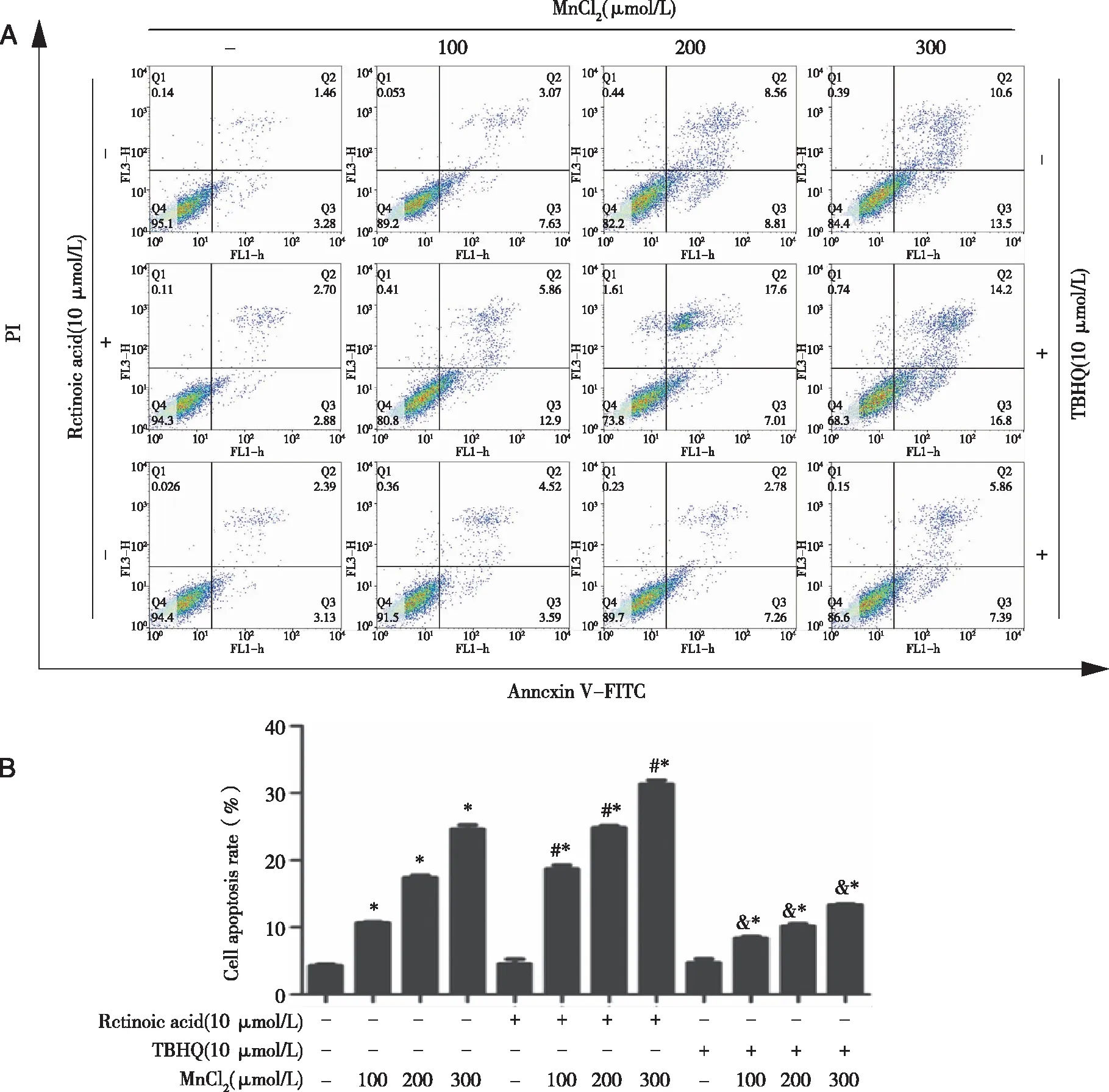
Densities of bands were quantified by Image J software.GAPDH levels,measured in parallel,served as controls.After TM3 cells were treated by 0 or 10 μmol/L ATRA(Nrf2 inhibitor)or TBHQ(Nrf2 activator)for 1.5 h,they were exposed to 0,100,200,or 300 μmol/L MnCl2 for 24 h.A:Flow cytometry analysis ; B:cell apoptotic percentage were performed.*:P<0.05,significantly different compared with control TM3 cells.
2.7 The effects of Nrf2 inhibitor or activator on the mRNA level of key proteins in Nrf2 pathway in TM3 cells after MnCl2treatment As shown in Figure 7A~E,the difference in Nrf2 mRNA expression between groups after the manganese exposed in TM3 cells was not obvious(P> 0.05).Compared with group C,HO-1mRNA expression in TC,TL,TM and TH groups all increased(P<0.05),and HO-1mRNA expression in RC,RL,RM and RH groups decreased(P<0.05).Compared with group C,L,M and H,HO-1mRNA expression in TC,TL,TM and TH groups increased(P<0.05),and HO-1mRNA expression in RC,RL,RM and RH groups decreased(P<0.05).The expression level of NQO1-mRNA in the RC,RL and RM group was lower than that in the C,L and M group(P<0.05).SOD-mRNA expression in the RC,RL,RM and RH groups was lower than that in the C,L,M and H groups.The expression of GSTpi-mRNA in RL,RM and RH groups was lower than that in L,M and H groups(P<0.05).Compared with the M and H groups,the GSTpi-mRNA expression in TM and TH groups was higher than that in M and H groups(P<0.05).
Densities of bands were quantified by Image J software.GAPDH levels,measured in parallel,served as controls.After TM3 cells were treated by 0 or 10 μmol/L ATRA(Nrf2 inhibitor)or TBHQ(Nrf2 activator)for 1.5 h,they were exposed to 0,100,200,or 300 μmol/L MnCl2 for 24 h.A~ E:The mRNA levels of Nrf2 ,HO-1,NQO1 ,SOD),and GSTpi were determined by qRT-PCR.*:P<0.05,significantly different compared with control TM3 cells.
3 Discussion
Manganese is essential for human,animal and plant survival.It is involved in the stability of the intracellular environment and several enzyme-catalyzed reactions[11].However,excessive manganese will affect the normal operation of various systems in the body,particularly the reproductive system.Excessive manganese will cross the blood testis barrier,induce severe and irreversible reproductive damage.The direct result is affecting the male sex organ growth and reducing the sperm quality.The indirect effect is reducing some biochemical indicators(such as SOD,GST,etc.)in testicular cells and causing damage to the reproductive system[12].
Nrf2 belongs to C 'n' C family of transcription factors,which are considered to be key transcription factors in the endogenous antioxidant injury system.Combination of Nrf2 with motorcycle can start the Nrf2/Keap1/motorcycle signal pathway,and can regulate its downstream target genes,including antioxidant enzymes and detoxification enzymes.So we used TBHQ and ATRA to activate and inhibit the Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling pathway.Thereby,we could determine the signal pathways which induced the oxidative damage of MnCl2exerted on TM3 cells and its protection mechanism.
The present study showed the following facts.(1)Manganese can activate Nrf2 signaling pathway in TM3 cells.(2)The mechanism of Nrf2 signaling pathway in Mn-induced TM3 cell injury may be the up-regulation of Nrf2 signaling.The expression of genes downstream in this pathway plays an antioxidant role.These observations support the view that Mn exposure can alter the Nrf2 signal pathway,which causes oxidative damage to the TM3 cells.Thus,Mn-induced male reproductive toxicity is partly due to Mn interaction with the Nrf2-mediated cellular defense mechanism.
Under normal physiological conditions,there is a dynamic equilibrium between the oxidation and antioxidant system in the body.Once free radical is excessive,the dynamic equilibrium will break,and the oxidative stress reaction will be triggered.And it can induce Leydig cell degeneration and other cellular disorders in the reproductive system[13].In this experiment,the effects of different doses of Mn on TM3 cells were observed by three methods:cell morphology observation,MTT experiment,and flow cytometry.The results of the three methods are consistent.The cell damage is Mn-dose dependent.Within the same Mn concentration,after ATRA pretreatment,the cell damage became severe.The cellular damage was reduced after pretreatment with TBHQ,which suggested that Mn can induce the oxidative damage of TM3 cells,and the Nrf2 signal pathway has antioxidant effect in TM3 cells.
Manganese reproductive toxicity mechanism involves mitochondrial dysfunction,oxidative stress,inflammation,and apoptosis.At the molecular level,damage in various kinase,nuclear transcription factors and protein changes can cause the reproductive toxicity.Although the detailed mechanism at the molecular level has not been confirmed,a large number of experiments showed that the formation of ROS and MDA and oxidative stress change are the key to the reproductive toxicity[14].For example,an important cell for reproduction,the Leydig cells are highly metabolized and can produce large amounts of ROS enzymes.Melatonin can inhibit oxidative stress by activating the AKT-Nrf2 pathway,thereby inhibiting Leydig cell apoptosis[15].The MDA level can reflect the level of membrane lipid peroxidation.MDA is an aldehyde that is not oxidized,decomposed or released by fatty acids in the process of lipid peroxidation.MDA is the final product of lipid peroxidation,which can connect proteins,lipids and sugars,denature cell membranes and reduce membrane fluidity,thus causing cell damage[16].In this study,we found that the ROS and MDA contents of TM3 cells increased in all concentrations of manganese exposure groups without ATRA or TBHQ treatment.In a certain dose range,the higher the concentration of manganese,the more ROS and MDA produced.After Nrf2 was inhibited,ROS production increased in the low,middle and high dose groups with a dose-response relationship.On the contrary,when Nrf2 was activated,the production of ROS and MDA decreases,and also has a dose-response relationship.These results suggest that manganese can increase ROS and MDA in TM3 cells.Activation of Nrf2 pathway can clear the products of ROS and MDA in TM3 cells,and reduce oxidative damage.
Domestic and foreign researches showed that Nrf2 signaling pathway is the most important antioxidant pathway in cells[17].Some studies showed that,the importance of Nrf2/Keap1/ARE signaling pathway is due to its ability to activate downstream gene expression,such as HO-1,NQO1,SOD,GST,gamma-cysteine ligase(γ-GCL),etc[18].In this experiment,after adding the agonist TBHQ,the experimental results showed that the expression of oxidative stress-related proteins was significantly increased,and after the addition of the inhibitor RA,those related proteins decreased.Regardless of whether agonists or inhibitors were added,the expression of oxidative stress-related proteins decreased with the increase of manganese exposure,which was consistent withKUKDU[19]and other studies.
These above results showed that,ATRA,a Nrf2 inhibitor,can enhance the oxidative damage of TM3 cells at a dose of 10 umol/L after treating for 1.5 h.On the other hand,Nrf2 activator TBHQ can reduce oxidative damage of TM3 cells.This is consistent with research fromWuresearches[3]andWang’s[20].Manganese poisoning can reduce the expression of oxidative stress-related proteins HO-1,NQO1,SOD,GSTpi and Nrf2 in TM3 cells,which may lead to oxidative damage in TM3 cells,suggesting that the Nrf2 signaling pathway may also be involved.The results of RT-qPCR were similar to the results of Western Blot,which confirmed the reliability of this experiment.The difference of Nrf2 protein may be caused by many factors,such as phosphorylation,nuclear translocation and transcription process.
In summary,this study made in clear that,the activation of Nrf2 pathway may play an antioxidant role in TM3 cells when it is treated with MnCl2.However,the antioxidant effect of Nrf2 may not be sufficient to antagonize a relatively high concentration of manganese-induced severe damage to germ cells.The results of this study indicate that Nrf2 signaling pathway plays a key role in the survival of Leydig cells in the testis.Future studies will further examine the nuclear translocation and phosphorylation of Nrf2.This experiment also highlights the potential clinical relevance of Nrf2 pathway targeted therapy.
