Research on the Curriculum Construction by Promoting Teaching Using Competition Based on Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives
2021-02-18XiuLIHuiWANG
Xiu LI, Hui WANG
Taishan University, Tai’an 271000, China
Abstract Based on Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives, this paper puts forward the construction of curriculum system in the primary stage, intermediate stage and advanced stage by promoting teaching using competition, and provides a theoretical and practical basis for the curriculum construction by promoting teaching using competition, which is of great practical significance to promoting the construction of applied universities.
Key words Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives, Promoting teaching using competition, Curriculum construction
1 Introduction
Since the 18CPC National Congress, China has put forward development strategies such as "craftsman spirit" and "skills power". InOutline
of
the
National
Medium-and
Long-term
Education
Reform
and
Development
Plan
(2010-2020
), the Ministry of Education puts forward: "testing teaching quality through skills competitions, and as one of the important means to improve the quality of education and teaching". The skill competition is not only conducive to the curriculum construction, curriculum reform and the construction of experimental training conditions in colleges and universities, but also capable of reflecting the quality of talent training in colleges and universities to a certain extent, which is leading the teaching reform to a new height. Therefore, how to make the skill competition lead the reform of professional courses and teaching mode to make the two promote and integrate each other has become the focus of research in colleges and universities.The tourism management major of Taishan University was rated as a national first-class undergraduate major in 2019. In the process of building a national first-class major, the skill level of students has become one of the important indicators. Although the tourism management major of Taishan University has made some achievements in the competition in the past ten years, there are still some problems in promoting teaching using competition, such as a poor effect of competition on the promotion of talent training, a low proportion of teachers and students participating in the competition, uneven allocation of resources, and uncoordinated combination of schools and enterprises. Therefore, how to promote teaching by competition, meet the requirements of first-class majors, and improve students’ applied comprehensive quality and ability has become an urgent problem to be solved in the construction of national first-class major of tourism management in Taishan University. This study is of great practical and theoretical significance.
2 Present situation of the research on promoting teaching using competition
In recent years, the research results of domestic related skills competitions are also relatively rich, but from the point of view of the research object, most of them are aimed at vocational and technical colleges. At present, many colleges and universities are defined as "application-oriented undergraduate universities", and further research is needed for the research of application-oriented undergraduate universities.
2.1 Analysis of the connotation of skill competition
The connotation of the skill competition is mainly analyzed from two angles. First, from the perspective of the effect of the process and results of the competition on the participants, the functions of the competition are summarized as display function, publicity function, evaluation function and guidance function, and a kind of derivative function-development function is derived. This is a comprehensive function with higher and more positive value. Second, the value of the competition is integrated into the function of the competition, and it is concluded that the competition has three functions: improving the vocational education and teaching quality, enhancing the social attention to vocational education, and testing the quality of moral and talent training in vocational education. There is also a lot of research on the dispersion of the functions of the competition into the value of the competition, which can be divided into four types of values: educational value, innovative value, aggregate value and social value.2.2 Influence of skill competition on the quality of education
Li Mingliang and Li Yuanyuan (2012) pointed that the requirements and rules of the competition are based on the task or content of the job, and the content of the competition is consistent with the needs of the enterprise, so the rules and evaluation criteria of the competition are directly selected as the curriculum standards at the teaching level, and through the interpretation of the competition rules and the analysis of the examination questions, teachers are assisted in the development of teaching materials. Li Yanmei (2012) pointed out that the competition emphasizes that students complete various tasks in real or simulated work situations, and the hosting colleges and participating institutions optimize and expand the training environment, as well as introduce industry enterprises to carry out university and enterprise cooperation, to meet the training requirements of the competition; through the holding of the competition, all kinds of resources of the whole society have been gathered, and a new situation has emerged in the cooperation between university and enterprise. You Jing and Xiong Yanlan (2011) pointed out that the competition has a certain impact on teachers. The training of the teams participating in the skill competition has accelerated the construction of the school’s "double-qualified" teachers. For the development of teachers, no matter in educational concept or professional ability and skill operation, they are gradually realizing the transformation from idea innovation to practical exploration.
2.3 Influence of skill competition on course teaching
Ma Chengronget
al.
studied the significance of the competition to the course teaching and believed that the skill competition can effectively promote the reform of education and teaching. Chen Chunju studied the influence of the competition on the course teaching model. Si Shoujinget
al.
studied the effect of the competition on the teaching content and form of the course, proposed transforming the competition resources into teaching resources (divided into basic resources and expansion resources), and discussed the integration of the two kinds of teaching resources. In addition, there is also the research on the ways and strategies of the curriculum teaching reform in the competition, and Pang Jiweiet
al.
elaborated the basic laws and approaches of the integration of the two from four key points: the path, the construction of teaching staff, the construction of teaching evaluation mechanism and the construction of training time conditions. With the help of the platform of the "combination of work and learning" of the skill competition, taking the skill competition as the project carrier, a competition think tank is established to break the boundaries between majors, realize the full integration of teaching resources of various majors, and improve students’ comprehensive skills. Chen Chunju concluded that based on the skill competition, the teaching methods are innovated, including "cooperation+competition" teaching method, bilingual teaching method,etc.
, the course teaching assessment is changed, in-school examination is combined with competition, application assessment is emphasized, and project assessment, post skills assessment are implemented.3 Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives
When studying the literature on promoting teaching using competition, it is found that Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives can be applied to the construction of the curriculum system by promoting teaching using competition. Based on Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives, classroom teaching before, during and after class can be systematically constructed, which lays a good foundation for the realization of using competition to promote teaching. Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives has gone through two stages of development.
3.1 The old version of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives
Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives is the earliest analytical tool for the evaluation of classroom teaching goals, and behaviorism is the foundation of this analytical tool. Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives originated from a goal classification framework proposed by a research team led by Bloom for college examiners and evaluators. In the course of the research, through the unremitting efforts of Bloom and his team, the first analysis and evaluation framework in the cognitive field was published in 1956—Taxonomy
of
Educational
Objectives
,Educational
Purpose
Taxonomy
,Handbook
1
:Cognitive
Domain
. After the publication of the manual, it has had a great impact all over the world, and has been rated as an educational reality that had a great impact on American education in the 20century. In the 1956 version of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives, the development of cognitive field is divided into six levels, namely, knowledge, understanding, application, analysis, integration and evaluation. These six levels present an one-way dimension increasing step by step, and the secondary categories under the six levels are defined in the manual. However, the old Bloom’s taxonomy theory often assumes that the cognitive process is one-dimensional in the process of application, and the categories of different levels do not overlap in the hierarchical structure, only paying attention to the importance of knowledge in the design of educational goals but ignoring the different degrees of mastery of different knowledge in the teaching process.3.2 The new version of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives
With the development of teaching, Anderson, a student of Bloom, and nearly ten other experts revised the framework of taxonomy of educational objectives on the basis of Bloom, and published the book—A
Taxonomy
for
Learning
,Teaching
and
Assessing
:A
Revision
of
Bloom
’s
Taxonomy
of
Educational
Objectives
(Complete
Edition
).The revised Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives turns the original one-dimensional framework into two-dimensional framework, which are "knowledge" and "cognitive level", respectively. The dimension of "knowledge" includes factual knowledge, conceptual knowledge, procedural knowledge and reflective knowledge, which can help teachers to have a clearer understanding of the teaching content. In the new version of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives, it is divided into six levels, namely remembering, understanding, application, analysis, evaluation and creating. The first three levels are low-level cognition, and the latter three are high-level cognition.
Table 1 Classification of objectives in Bloom’s cognitive domain
4 Curriculum construction based on Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives
The tourism management major of Taishan University implements the teaching reform of "promoting teaching using competition". The biggest highlight is to make the competition "routine and common", integrate the content of competition into daily teaching, and all students can participate every day. The most critical step is to design the curriculum system of "promoting teaching through competition and integrating competition and teaching", connecting the curriculum standards with professional standards, and effectively linking the teaching content with the content of the competition. Professional skills courses are mostly regarded as core courses in the curriculum system, and efforts should be made to make skills courses the most popular courses for students in the teaching reform.
4.1 Present situation of the construction of the curriculum system by promoting teaching using competition
In recent years, Taishan University has set the goal of building a high-level applied university in the near future. However, at present, many courses of tourism management major can not well meet the requirements of school development and the social demand for tourism management talents, and the problem of "passive learning and lack of practice" is prominent. As the person in charge of the school-level course construction project of "Tourism Reception Industry", we take the course construction of "Tourism Reception Industry" as an opportunity to lead the course team to actively participate in the teaching reform by deeply integrating curriculum knowledge theory and practice in the tourism reception industry, to finally achieve the goal of promoting teaching through competition.4.2 The goal of curriculum construction by promoting teaching using competition
In view of the development goals of high-level applied universities and the characteristics of many levels of students majoring in tourism management in Taishan University, the teaching content is reconstructed on the basis of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives. With the help of the characteristics of large scale, rich media, diversified interaction, massive online resources and innovative assessment and evaluation system on MOOC platform, the students majoring in tourism management in Taishan University can be provided with the opportunities for self-improvement and lifelong learning. According to the educational goal of cognitive field, we establish the course resource database of "Tourism Reception Industry", and release the MOOC video, to promote meaningful learning and the development of "community of practice", increase students’ participation and enhance learning experience, so as to realize the construction of mixed teaching curriculum and train students who can use the concepts, ideas and methods of tourism reception industry management to analyze and solve practical problems in the development of tourism industry, and lay a good foundation for the follow-up courses.4.3 Practice and planning of curriculum construction by promoting teaching using competition
According to the six levels of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives in cognitive domain: remembering, understanding, application, analysis, evaluation and creating, this paper constructs a mixed teaching model based on the MOOC teaching platform of "Tourism Reception Industry". Classroom teaching activities are divided into three stages, namely, pre-class, in-class and after-class stages. Teachers’ activities and students’ activities interact in both directions to form a closed loop that iterates and optimizes the whole teaching process, as shown in Table 2.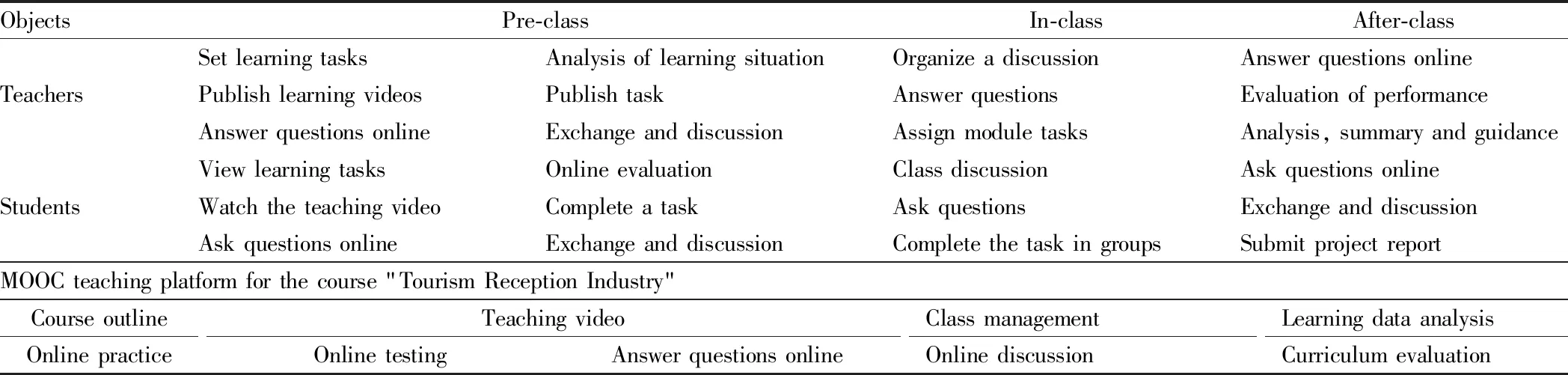
Table 2 Construction of mixed teaching courses based on Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives in cognitive domain
4.3.1
Completing the primary level at the pre-class stage—remembering and understanding. In the planning stage of the MOOC system, according to the primary level of Bloom’s taxonomy of educational objectives in cognitive field, the knowledge points of MOOC are divided into two categories: task knowledge and extended legend, and analysis, in which the task knowledge video is mainly used for the study of the knowledge, and the educational goal is set to "remembering", clearly defining the key and difficult contents, and requiring students to memorize, describe and list basic concepts through learning; the purpose of extended case and analysis video are to further understand the knowledge points on the premise of mastering the task knowledge, requiring students to understand the practical problems in the development of the tourism reception industry by means of reading and discussion.The online mode is used in the pre-class stage. According to the cognitive goal of the unit task, the teacher publishes the unit MOOC video and unit learning resources to the MOOC teaching platform. Students accept the unit learning task, watch the MOOC video under the guidance of clear learning goals, and learn to master the knowledge points of the unit.
4.3.2
Reaching the intermediate level at in-class stage—application and analysis. The in-class stage of the course "Tourism Reception Industry" uses the form of offline "group discussion+field research". According to the students’ mastery of the unit knowledge, the teacher analyzes the key and difficult knowledge in class, and then puts forward the field research task, which is generally a practical problem customized for the knowledge point. After receiving the task, the students are divided into groups, to discuss and analyze problems within and between groups, cooperate within the group with the basic knowledge mastered before class, solve practical problems, and report the progress of the task after completing the unit task.4.3.3
Following the advanced level at after-class stage—evaluation and creating. The stage of after-class knowledge consolidation uses the online form. The teacher publishes the final results of the tasks of each unit in the class on the MOOC platform to expand the learning tasks and unit test questions. First of all, students obtain the task results of other groups on the MOOC platform for comparison, scoring and evaluation of different groups, and mutual evaluation of students. Then the extended learning task is completed independently. The selection of extended tasks is based on the principles of semi-proposition, openness and innovation, to expand students’ thinking and emphasize uniqueness and innovation.4.3.4
Evaluation of teaching effect. The teaching effect evaluation method adopts the combination of diagnostic evaluation, process evaluation and comprehensive evaluation, as shown in Table 3.
Table 3 Evaluation method of teaching effect of mixed teaching course by promoting teaching using competition
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Research and Application Progress of Silk Fibroin Membranes
- Application Potential of Quinoa as Forage
- The Agriculture-Tourism Integration to Promote the Rural Revitalization: Taking Tea Industry-Agriculture-Tourism in Lishui City as an Example
- Delimitation of Grain Production Functional Zones: An Empirical Analysis of Fangzi District in Weifang City
- Effects of Fermented Nano Chinese Herbal Medicines Replacing Antibiotics on Production Performance and Carcass Quality of Growing-Finishing Pigs
- Screening of New High Quality and High Yield Sweet Potato Varieties in Zaozhuang of Shandong Province
