Practice of Mind Mapping Technology in "Re-flipped Classroom" Teaching Mode: A Case Study of the Course Principles of Residential District Planning
2021-01-27LiwenLIUXiquanCHENXiaoyunLIJianrongZHANG
Liwen LIU, Xiquan CHEN, Xiaoyun LI, Jianrong ZHANG
1. College of City Construction, Jiangxi Normal University, Nanchang 330022, China; 2. Jiangxi College of Applied Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China
Abstract The present study proposed the "re-flipped classroom" teaching mode taking the course Principles of Residential District Planning as an example. Using the Small Private Online Courses (SPOCs) and Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) of the iCourse platform, with the aid of the mind mapping technology, the complex content is visualized to the information that can be easily accepted by the brain, to improve the efficiency of thinking problems and apply theories to practical teaching. The results indicate that the teaching mode combined with mind mapping technology has strong appeal, can improve teacher-student interaction, and effectively improve the teaching effects. Finally, it came up with recommendations including attaching importance to the "re-flipped classroom" teaching mode, integrating teaching methods, and using online platform resources. It is concluded that the research of teaching mode has important theoretical and practical significance for ensuring the teaching quality.
Key words Residential district, Flipped classroom, Min map, Teaching reform
1 Introduction
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs)+Small Private Online Courses (SPOCs), SPOC flipped classroom, SPOC+Presentation-Assimilation-Discussion (PAD) and other online and offline mixed teaching have become the focus of attention in universities[1-2], student-centered and flipped classrooms that first learn and then teach[3], output-oriented, student-centered and continuous improvement Outcome Based Education (OBE) concept[4-5], and teaching modes such as teaching, internalizing and assimilating and discussing the three processes of PAD classrooms have become the mainstream mode of college information-based teaching[6]. Liu Chunyanetal., using a systematic evaluation method, compared and analyzed the teaching effect of SPOC flipped classroom and traditional teaching, and used large sample data to reach scientific conclusions[7]. Li Xiaojie explored the satisfaction of SPOC and flipped classroom in Henan Agricultural University[8]. For teachers starting from scratch, online course construction, video recording, post-processing, online course framework construction, course content maintenance, data processing,etc. are quite difficult and the workload is increased. The focus of improving teaching quality lies in the research of teaching modes and teaching methods. The research experience of the "re-flipped classroom" teaching mode is of great value to improving the teaching quality of other majors in urban and rural planning in the universities of the whole country.
In this study, we proposed the "re-flipped classroom" teaching mode including five teaching processes, namely, pre-class preview, interactive discussion, classroom teaching, internalized assimilation, and problem review. In the process of teaching, we used a variety of teaching methods such as mind maps and Project Based Learning (PBL), aiming to improve the teaching effect in network education in special periods by integrating existing network platform resources and teaching methods and modes, and abandoning the teaching design of "teacher-centered teaching". We explored "student-centered" teaching mode, apply the "re-flipped classroom" mode of mind mapping technology to the practical teaching of the course Principles of Residential District Planning, and strive to improve students’ learning enthusiasm and teaching effect, in the hope of providing certain reference for subsequent research.
2 Mind mapping technology
2.1 FeaturesMind Map, also known as Brain Map, was invented by Tony Buzan. He stated that the human brain’s ability to accept pictures is much higher than that of textual information. Mind mapping is a way of displaying information. It uses graphical methods to display the thinking process and display information, the information is diaplayed from the inside to the outside. With the help of mind maps, it is helpful to form a systematic thinking mode, improve the efficiency of thinking problems, and the brain accepts information more easily. The basic structure of the mind map is illustrated in Fig.1. The mind map includes the root node or "central theme" data indicators. The entire map clearly displays the data indicators, which are helpful for memorizing the hierarchical relationship between each land use. Mind mapping method is to extract "keywords" and apply them in teaching. Then, chapters or important knowledge points can be organized systematically to form visual teaching content. Through art forms such as colors, lines, pictures,etc., it is feasible to enhance the stimulation of the students’ brains and activate the memory associations of the right brain pictures, which is convenient for students to memorize key content and helps to cultivate students’ divergent and comprehensive (holistic) thinking.
2.2 Basis for the application of mind mapping technology to teachingInstructional design (or teaching design) is a dynamic and non-deterministic process with strong exploratory and creative nature. To present this non-deterministic process concretely, certain technical means are obviously needed. If the instructional design is visualized based on the human brain thinking model, and logical analysis is made for teaching elements through complex instructional design, and the process and results are demonstrated in an intuitive visual form, it will be more conducive to helping students establish a subject knowledge framework and system. Visual instructional design is to use all possible graphical methods to analyze and process all links of instructional design to form a teaching implementation plan. Mind mapping technology is to display key knowledge points level by level through a tree structure with both pictures and texts, and visualize thinking. Therefore, it is evident that mind mapping technology can be used for visual instructional design.
3 Teaching construction of mind mapping technology in the "re-flipped classroom" teaching mode
3.1 Theoretical basisFlipped Classroom is a teaching mode that first appeared in the United States[9-10]. This mode uses modern network technology to build Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) or Small Private Online Courses (SPOCs), and publish learning resources (videos, PPT, discussion content,etc.) on the Internet before class. Students can preview in advance through mobile phones or computers to complete the basic theoretical knowledge that originally needs to be taught in the classroom, and students can independently study courseware or video resources. The flipped classroom has the characteristics of allowing students to study and preview themselves before class, and the teachers answer questions in the class, which can help students to internalize and assimilate knowledge.
The Presentation-Assimilation-Discussion (PAD) was proposed by Professor Zhang Xuexin of Fudan University in 2014. Its core concept is to divide the time, half of the time is used for teacher-guided lectures, and half of the time is used for discussion-style interactive learning, with an interval of time (within a week) for students to internalize and assimilate the knowledge. Its distinct characteristic lies in staggering the lecture presentation and discussion time. Students go through the learning process of independent learning, guided lecture presentation, and internalized assimilation, and interact with questions and insights in the classroom. PAD includes presentation of teacher, student assimilation, and student discussion. The purpose is to give full play to the guiding role of teachers, and emphasize on improving the initiative and enthusiasm of students[11].
In this study, we integrated the two teaching modes of flipped classroom and PAD, made clear the teaching objectives and sort out the curriculum content, organize efficient teaching activities by reconstructing the teaching content and decomposing the learning tasks, and proposed the "re-flipped classroom" teaching mode including five teaching processes: pre-class preview, interactive discussion, classroom teaching, internalized assimilation, and problem review, to realize the teaching objectives.
The basic concept of the "re-flipped classroom" teaching mode is to move the basic knowledge in the traditional classroom to the pre-class, dividing the classroom time, and help students internalize and assimilate the content of the course. Before class, students watch videos and read PPT on the platform SPOC to preview the key content of teaching tasks. During the class, the teaching time is divided half and half. One half is used for question discussion and test in MOOC classroom. The teacher gives the discussion content and test questions in MOOC classroom. Through QQ communication, teacher-student, student-student interaction, the teacher can test the learning effect of preview and live classroom. The other half time (one week later) is used to answer questions and solve questions on DingTalk, re-examine the remaining problems in the classroom and the problems that students are difficult to assimilate. Teachers explain and implement key and difficult points in the form of projects or cases, and analyze how knowledge points are reflected in the project process.
3.2 Teaching objectivesThe course Principles of Residential District Planning, as the main course of urban and rural planning, covers a wide range with strong theory and practice, and has the characteristics of a large amount of learning and high skills[12]. It requires students to master theoretical knowledge proficiently and also have strong practical ability[13]. The course objectives of Principles of Residential District Planning include using a task-driven approach to improve students’ learning initiative, constructing a curriculum project based on residential district planning and design projects, applying theory to practice, and applying what students have learned to enable them to master residential district planning skills, grasp the ability to express plan drawings and language to improve teaching quality, and improve students’ theoretical knowledge system and practical skills.
3.3 Teaching implementation plan for application of mind mapping technology in "re-flipped classroom" teaching mode
Based on the grasp of the characteristics of the course, the teaching objectives and the re-flipped classroom teaching mode, we incorporated the mind mapping method through the teaching mode of Principles of Residential District Planning (Fig.1). Before the class, teachers focus on researching teaching mode, teaching methods and teaching objectives, and subdivide the teaching content into multiple teaching tasks. It constructs a student-centered, teacher-led, project-based teaching system to create conditions for active participation and autonomous collaboration of students, so as to better cultivate students’ self-learning ability and creativity. Through pre-class SPOC online preview, interactive discussion in the classroom, DingTalk live class lecture, internalized assimilation and after-class consolidation of the problem review process, it is expected to inspire students to think about problems, guide them to solve problems, and solidify their theoretical knowledge and improve their practical ability.
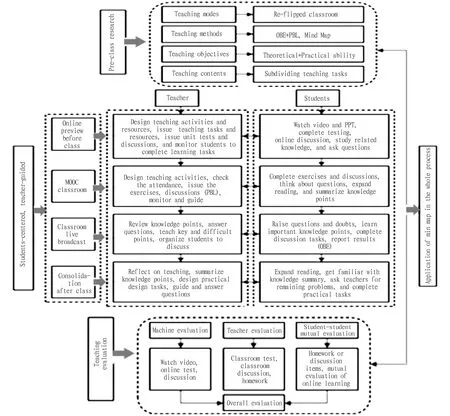
Fig.1 Implementation scheme for application of mind mapping technology in "re-flipped classroom" teaching mode
3.4 Assessment and evaluationThe urban and rural planning discipline is highly practical, and rote memorization of concepts or formulas cannot demonstrate students’ actual output and operational ability. In this study, we divided the course evaluation into two parts, online and offline, namely machine statistics, teacher statistics data evaluation and student-student mutual evaluation (Fig.1). (i) Machine statistics mainly include data such as online watching videos (duration), unit tests and speeches in the discussion section before class, and data during the MOOC classroom, such as exercises, discussions, and attendance. In the discussion session, we included the number and effectiveness of students’ speeches in the MOOC discussion section in the evaluation. For example, the MOOC discussion section can set up excellent speeches according to the students’ answers. (ii) Teacher evaluation is based on the performance of students in the live classroom, submitting multiple data such as homework accuracy, actual project completion, and student mutual evaluation. Finally, the performance evaluation items and ratios are set so that each student can get fair results. (iii) Student-student mutual evaluation. For the completion of each assignment or discussion, students will score and evaluate each other to achieve fairness.
4 Cases of teaching practice
4.1 Online self-learning of students before classTeachers deliver classroom teaching tasks and teaching resources before each class. According to teacher requirements, students log in to the platform and watch animations, videos, documents and other materials on the iCourse platform supplemented by other books, complete tests and discussions, and students can make online record of the problems and doubts they find. In the pre-class study stage, students should record study notes, organize and summarize the knowledge points they have learned, and improve their self-reflection and autonomous learning ability.
4.2 MOOC classroom discussions and tests during classIn the MOOC classroom, focusing on the teaching tasks, teachers adopt teaching methods such as call-out, discussion, testing (PBL problem-oriented), announcements,etc., to allow students to actively participate in classroom testing activities. In this way, it is able to find the remaining problems during students’ self-study before class and live classroom. For example, the teacher guides the students to analyze the difference between residential area land and residential land and calculate the plot ratio of residential area land (Fig.2). Through guiding and observing students’ participation in teaching activities, the teacher can cultivate students’ ability to discover, think about, and solve problems. At the same time, in response to students’ problems, they can use QQ chat tools, language or video analysis, and then prepare targeted lessons to help students solve the problems.
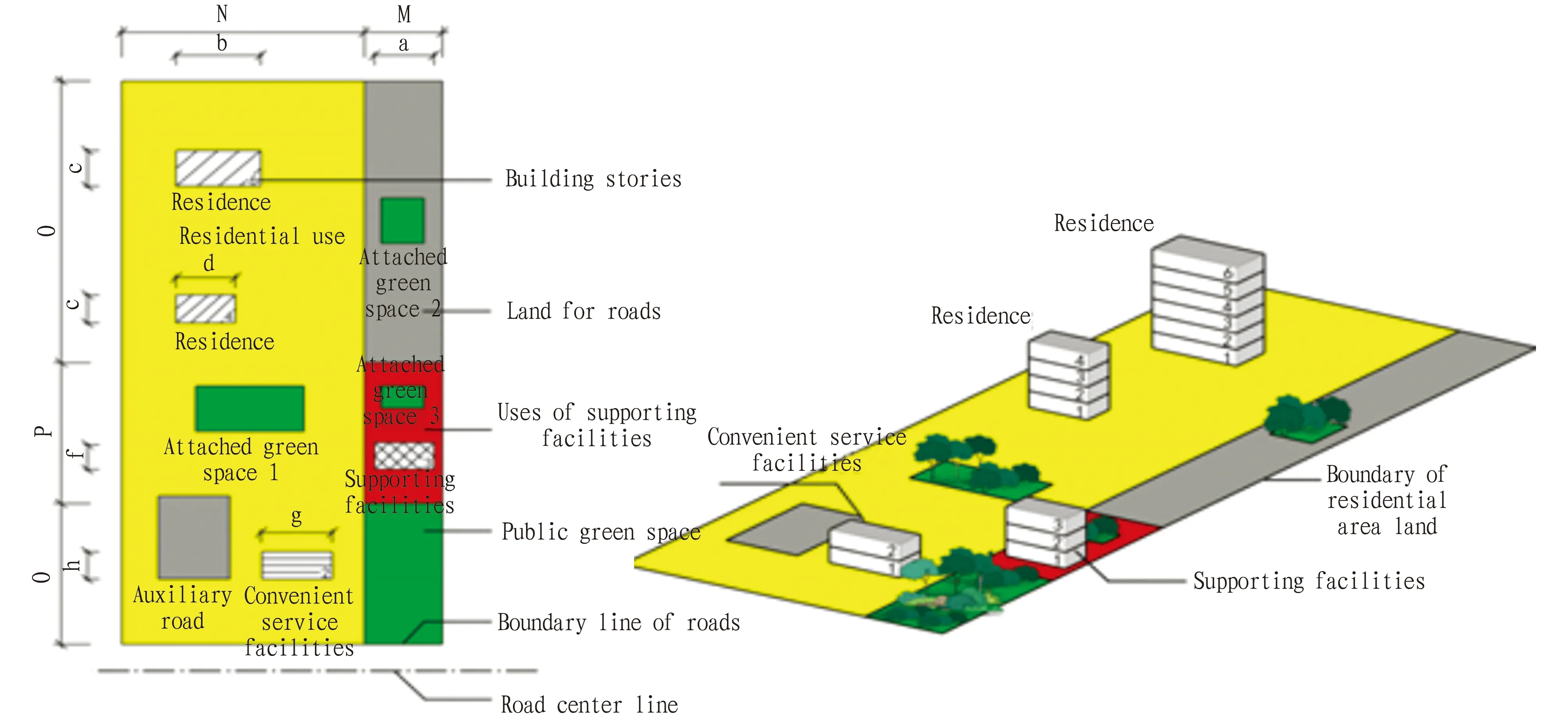
Fig.2 Diagram of building density, green space rate, and plot ratio
4.3 Teachers teach key and difficult points during classThe teacher first answers questions in the discussion area, and explains the key and difficult knowledge of the course tasks. The main task of the "data indicator" is to calculate based on the understanding of the basic concepts. In view of the students’ confusion about the concepts of residential area land plot ratio and residential land plot ratio, the teacher should sort out the following relationships and concepts again: the relationship between supporting facilities and convenient service facilities; the relationship between residential area land, residential land and residential neighborhood land; the concept of plot ratio. After visualizing with a mind map, it is necessary to clarify the various land use relationships, and carefully understand the conceptual difference between residential area land plot ratio and residential land plot ratio.
After sorting out the problems, the teacher once again should guide the students to complete the calculation of residential land plot ratio, building density and green space rate. In theStandardforUrbanResidentialAreaPlanningandDesign, the building density and green space rate are only for residential neighborhoods. The building density is the ratio of (d×e+b×c+g×h)/N × (O+P+Q), and the green space rate is the ratio of the attached green space 1 to the area of residential neighborhood land. In class, students reply the answers via QQ or WeChat. Teachers should discover problems in time, and provide timely feedback and explanation.
4.4 Consolidation after classThe consolidation stage is the process of internalizing, assimilating, solidifying and upgrading the teaching content, and it is an extension after classroom learning. The teacher can condense the teaching content into a mind map (Fig.3), which can visually and intuitively reflect the teaching tasks. After class, the teacher should summarize the teaching experience, increase the students’ after-class exercises to increase the degree of challenge, lead the students’ awareness of practical design, stimulate students’ enthusiasm, introduce a residential area design assignment, introduce the tasks of this course, and guide students to complete calculation of the green space rate, building density, plot ratio and other related economic and technical indicators, to lay a solid foundation for teaching and practical tasks in residential areas.
5 Recommendations
In the context of the ongoing pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), teachers should conscientiously fulfill the historical mission of "stopping classes without stopping teaching, and closing classes without stopping learning". In the face of emergency event, teachers should effectively use existing high-quality network resources, devote themselves to thinking about teaching methods and teaching modes, study the characteristics of majors and courses, determine teaching objectives, guide students to ask questions, think about and solve problems, mobilize and give play to the enthusiasm and initiative of students in learning.
5.1 Attaching importance to the "re-flipped classroom" teaching modeUsing this teaching mode in the coursePrinciplesofResidentialDistrictPlanning, it is found that the characteristic is outstanding, allows teachers and students to participate wholeheartedly in the whole teaching process, and it obtains strong appeal, obvious teaching effects and higher teaching quality. Through the "re-flipped classroom" teaching mode, teachers carefully prepare questions at multiple levels. After the discussion in MOOC classroom, teachers can clearly understand the students’ mastery of knowledge points, understand students’ doubts, and pay attention to students’ learning effectiveness. Teachers actively take the problem as the starting point, analyze and explain the important and difficult points in the live classroom, stimulate students’ cognitive conflicts, mobilize students to participate in activities, and enable students to learn with an active and eager mentality to solve the problems encountered during learning. For the consolidation after class, teachers can raise the difficulty of the problem, carry out the problem review, and check the gaps, which will help to solidify and upgrade the students’ knowledge, improve the students’ independent learning ability, independent thinking, and the ability to explore and seek knowledge, and cultivate their lifelong learning ability.
5.2 Integrating the teaching methods to enhance learning motivationTeaching method is the means by which teachers and students complete the content of teaching activities together in order to realize the teaching objectives and tasks. In this study, we sorted out and applied three important teaching methods: PBL (problem-oriented), OBE (outcome-oriented) and mind mapping method. For the PBL method, the teacher points out the students’ possible or unresolved problems through the discussion method, and attracts students to participate in the classroom. In terms of the outcome-oriented method (OBE), it is to activate the theoretical knowledge of books and enhance students’ practical ability. We stressed the application of the mind mapping method. The coursePrinciplesofResidentialDistrictPlanningis highly practical and standard, combining pictures for knowledge transfer and explanation will make the boring and abstract teaching content more vivid and intuitive. In practice, students stated that the mind mapping method is concise and clear, and abstract concepts are easier to understand and remember. Therefore, it is recommended to stimulate students’ brains through mind maps, and cultivate students’ divergent and comprehensive thinking ability.
5.3 Making full use of online network resourcesTeachers should not blindly "transplant" regular classrooms to online recorded or live broadcast classrooms, but should make full use of existing resources to maximize the value of high-quality network resources. It is recommended to increase the content of the source course, expand the capacity of classroom knowledge, and increase the live classes and interesting homework recorded by some students. "Classmates work, classmates study" easily attract students’ attention and stimulate their interest in learning.
5.4 Integrating the teaching of theories and practiceThe coursePrinciplesofResidentialDistrictPlanningis highly theoretical and practical, it is recommended to take OBE output-oriented idea as the guide to combine course tasks with residential area projects. Taking a certain residential area planning project as the assignment, under the premise of ensuring the integrity of the teaching content, the teaching content is gradually decomposed from simple to difficult, and gradually divided into parts, so as to make it convenient for students to subtly internalize and assimilate knowledge and improve their flexible application ability. In all, it is recommended to really apply theory to practice step by step, enhance students’ enthusiasm and initiative in learning, and improve their practical ability and sense of learning achievement.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- A New Record of Orchidaceae from Guangxi: Galeola nudifolia Lour.
- Quality Evaluation of Threshing and Redrying Process Based on Analytic Hierarchy Process
- Development Strategy of Soundscape in Rural Tourism Based on Tourist Perception: A Case Study of Some Villages in Jiangxi Province
- Sustainable Utilization of Agricultural Land in Chengdu Metropolitan Area Based on Emergy Analysis
- Effect of Different Processing Methods on Storage Quality of Strawberries
- Genome-wide Association Analysis of Maize Flowering Traits
