Quality Evaluation of Threshing and Redrying Process Based on Analytic Hierarchy Process
2021-01-27XiaohanGUOChaohuaTANGJingTANQiuguoWUBowenXIEZhuangyuCHEN
Xiaohan GUO, Chaohua TANG, Jing TAN, Qiuguo WU, Bowen XIE, Zhuangyu CHEN
Chenzhou Tobacco Redrying Plant, Hunan Tobacco Redrying Co., Ltd., Chenzhou 423000, China
Abstract Improving the stability of the homogenization process to achieve the homogeneity of tobacco products is one of important targets for the redrying industry. According to the specification for threshing and redrying process, a total of 14 indicators in three categories that affect the quality of the threshing and redrying process were selected. Using analytic hierarchy process, combined with expert experiences, a judgment matrix was constructed to conduct consistency test. The weights of indices in production were obtained. This will help in evaluating the actual production quality, finding the weak links of process and adjusting the parameters of the corresponding links in a targeted manner, thereby improving the quality of production process.
Key words Threshing and redrying, Quality evaluation, Analytic hierarchy process, Index weight
1 Introduction
With the continuous enhancement of the cigarette industry’s requirements for the homogenization of tobacco leaves and the fierce market competition, the improvement of the productive process’s stability and the homogeneity of the produced tobacco leaves is the development direction of the technology and product quality of the cigarette industry[1-2]. In 2016, theCigaretteProcessSpecificationsissued by the China National Tobacco Administration included threshing and redrying into the standard documents of flue-cured tobacco process specifications. Therefore, as the "first workshop" of cigarette production, redrying enterprises need to comprehensively consider the productive process and the quality of tobacco leaves and to evaluate the quality of the threshing and redrying process, so as to meet the requirements ofCigaretteProcessSpecifications.
Threshing and redrying includes the beginning input of the raw tobacco to the storage after processing[3]. China’s redrying enterprises and universities have carried out various researches and studies on the tobacco leaf homogenization indices that affect the chemical composition and structure of tobacco leaves in the production process. Through raw material inspection, modular formula threshing,etc., the multi-level inspection and control of the chemical composition of tobacco leaves is realized[4]. Based on the tobacco industry’s threshing concept of "controlling the percentage of large pieces, increasing the percentage of medium pieces, and reducing the percentage of fragments", researchers have achieved good threshing quality from the reasonable matching between frame’s shape and size[5-6], the threshing machine roller speed, the wind divider frequency[7-8]and other equipment parameters. After entering the redrying machine, the aroma of the processed tobacco leaves is maintained, and their moisture content is stabilized by lowering the redrying temperature, controlling the moisture in the cold room,etc[9-10]. Currently, the researches in the redrying industry are focusing on optimizing the processing parameters of threshing and redrying processes to improve the homogeneity level of the tobacco. But for the intermediate parameters throughout the threshing and redrying, complete evaluation criteria are not in place, leading to companies’ one-sided pursuit of homogeneity level of finished tobacco leaves and ignoring of quality control of the intermediate process. Based on experts’ survey, Huang Qiutingetal.[11]proposed a method for evaluating the production capacity of threshing and redrying. It comprehensively considers the three stages of tobacco pretreatment, stalk separation, redrying and packaging. However, some redundant indices were introduced when constructing the evaluation model, which is prone to causing experts to make mistakes in scoring and coordinating, reducing the authenticity of the evaluation results and the applicability in actual production.
In this study, combined withCigaretteProcessSpecifications, a total of 14 indices in three categories of production process moisture content and temperature stability, leaf quality after threshing and homogeneity level were selected. A quality evaluation model was conducted for threshing and redrying process by using the analytic hierarchy process (AHP) to evaluate the production process comprehensively. It can help to find the weak links of the process, and to adjust the parameters of the corresponding links in a targeted manner, thereby improving the quality of the production process.
2 Quality evaluation indices for threshing and redrying process
The process flow of threshing and redrying is shown in Fig.1. It includes raw material preparation, vacuum moisture regain, leaf spreading, leaf conditioning, leaf threshing and wind separation, redrying and packaging[12]. Among them, the vacuum moisture regain is an optional process which can be selectively performed according to the input quality of tobacco leaves. This paper comprehensively considers the operation stability of the equipment in the production and the evaluation indices of tobacco leaf processing quality.
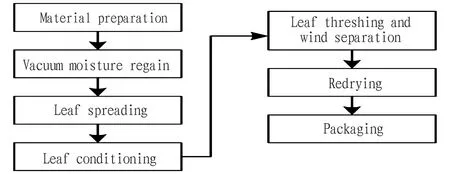
Fig.1 Threshing and redrying process
2.1 Moisture content and temperature stabilityIn threshing and redrying, moisture and temperature are the key factors in affecting the quality of tobacco leaves[13]. Among the links of the process, leaf conditioning and redrying mainly affect the moisture and temperature of tobacco leaves. Leaf conditioning is the process of increasing the temperature and humidity of the tobacco leaves to reach the required standards for threshing and wind separation. The moisture and temperature after conditioning directly affect the structural quality of the threshed tobacco leaves. The main purpose of redrying is to adjust the moisture of tobacco leaves, kill insects and sterilize them,etc. It affects the retention of the aroma components and the moisture stability of tobacco leaves when packaged and put into storage. Therefore, this paper chooses the unilateral process capability indexCPKof the temperature and moisture content at the outlet of the second conditioning and the redry machine during the production process to reflect the stability of the moisture and temperature of the leaf conditioning and redrying based on customer needs. The process capability indexCPKwas calculated according to the following formula:
(1)
whereUslis the upper limit of customer satisfaction, andμandσare the average value and variance of the moisture or temperature of the batch. The stability of the moisture content of the tobacco leaves is reflected by the range mean of the moisture content of the cold room (left and right) and the moisture content of the left, middle and right sides of the machine tail. The corresponding moisture content and temperature stability evaluation indices and scoring criteria are shown in Table 1.
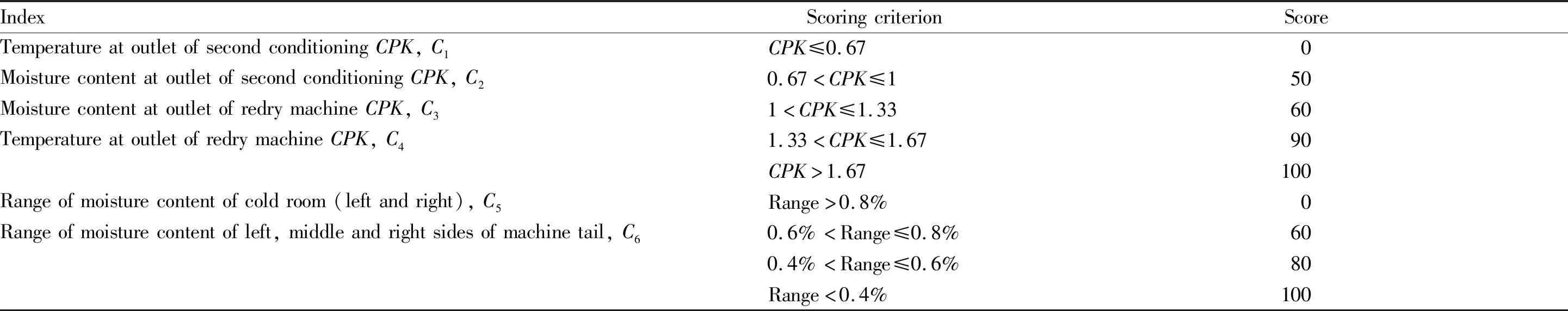
Table 1 Moisture content and temperature stability indices and scoring criteria
2.2 Structural quality of tobacco leaves after threshingLeaf structure quality refers to the sheet structure of tobacco leaves after threshing and redrying, including large piece percentage, medium piece percentage, small piece percentage, fragment percentage,etc[14]. Structural quality of tobacco leaves is the basis for stabilizing shredded tobacco products, which determines the length of tobacco strips cut[15-16]. In this paper, according to theTechnologicalRulesforThreshingandRedryingofLeafTobacco(YC/T 146-2017), the percentage of large and medium pieces (>12.7 mm×12.7 mm), the percentage of medium pieces (6.35-12.7 mm), the percentage of fragments (<2.36 mm×2.36 mm) and the rate of stalks in leaves are used as the main evaluation indices. Considering the current production process of threshing and redrying, the concept of "threshing to control the large piece percentage, increase the medium piece percentage, and reduce the fragment percentage" has increasingly become the consensus of re-drying companies. The ratio of medium piece percentage to large-medium piece percentage is used to reflect the ratio of medium pieces. The quality indices and scoring criteria of tobacco leaves after threshing are shown in Table 2.
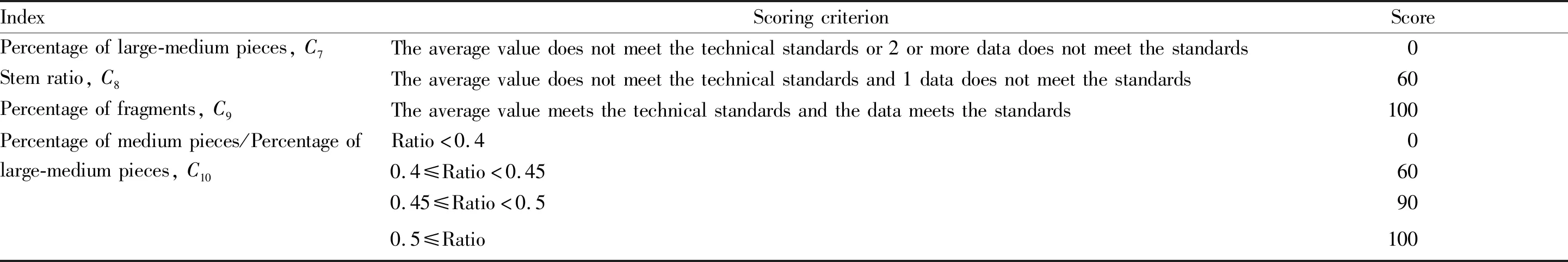
Table 2 Post-threshing leaf structural quality indices and scoring criteria
2.3 Homogeneity levelHomogenization of tobacco leaves includes moisture content, chemical composition and packaging indices after flue-curing. It will directly affect the quality of subsequent shredded cigarettes. The homogeneity level proposed by the specification for threshing and redrying process was selected. The set indices and scoring criteria are shown in Table 3.
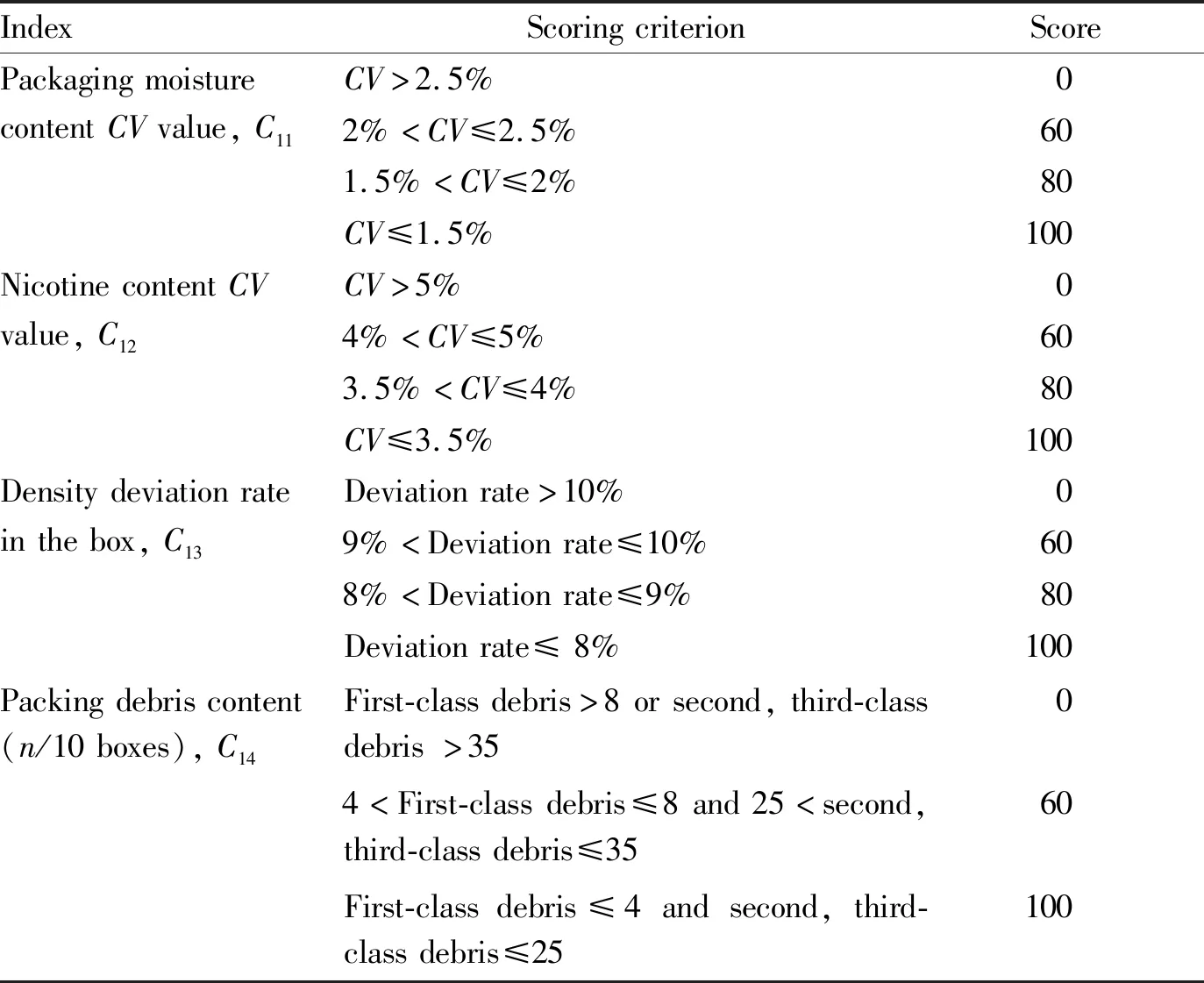
Table 3 Homogeneity level indices and scoring criteria
3 Analytic hierarchy process and production process quality evaluation model
3.1 Introduction to analytic hierarchy processAHP is a systematic and hierarchical analysis method that combines qualitative and quantitative analysis. It was formally proposed by the American researcher T. L. Saaty in the mid-1970s[17]. According to the characteristics and purpose of the problem, starting from a decision problem, different influencing indices are extracted. According to the relationship between indices (association or subordination), the indices are divided into different levels (target level, criterion level, plan level). By constructing a judgment matrix, the single-level ranking of each level of index was calculated from bottom to top, related to the corresponding index of the previous level. Then, the total ranking of the indices was estimated. This analysis method makes complex problems organized and easier to analyze, and it is suitable for solving multi-index decision-making problems.
3.2 Evaluation modeling and consistency test of judgment matrix(i) The indices that affect the quality of threshing and redrying are divided into target level A, criterion level B and plan level C. Among them, the indices in the target level and the criterion level, the criterion level and the plan level are all subordinate. The hierarchical structure of the quality evaluation model for threshing and redrying process constructed based on the 14 indices is shown in Fig.2.
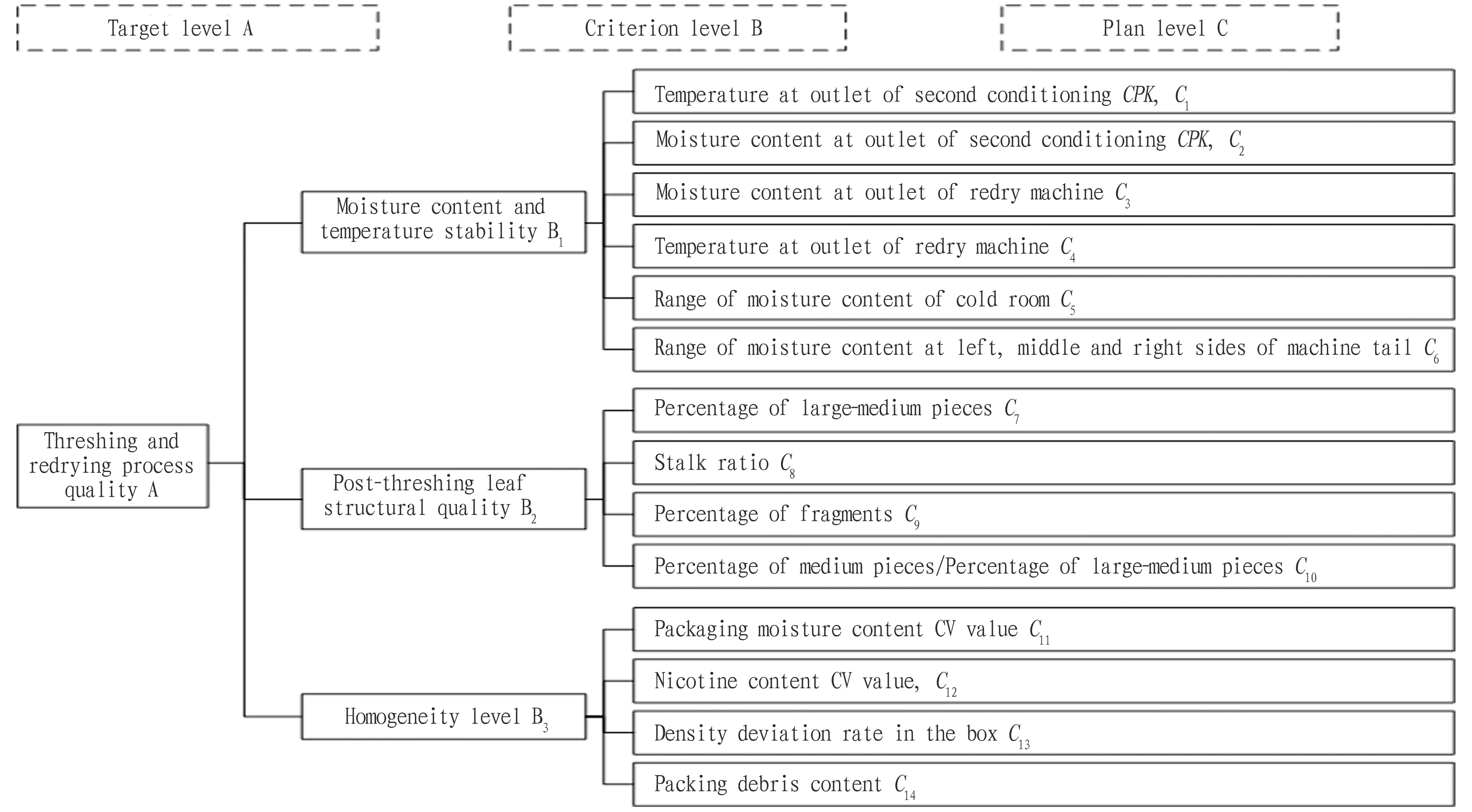
Fig.2 Hierarchy diagram of process quality evaluation
(ii) According to the affiliation in the hierarchy, experts were invited to compare the importance of indices at the same level. That is, the 1-9 scale method was used to assign the importance of each level of indices. The judgment matrix was constructed. The meaning represented by the scale of the judgment matrix is shown in Table 4.
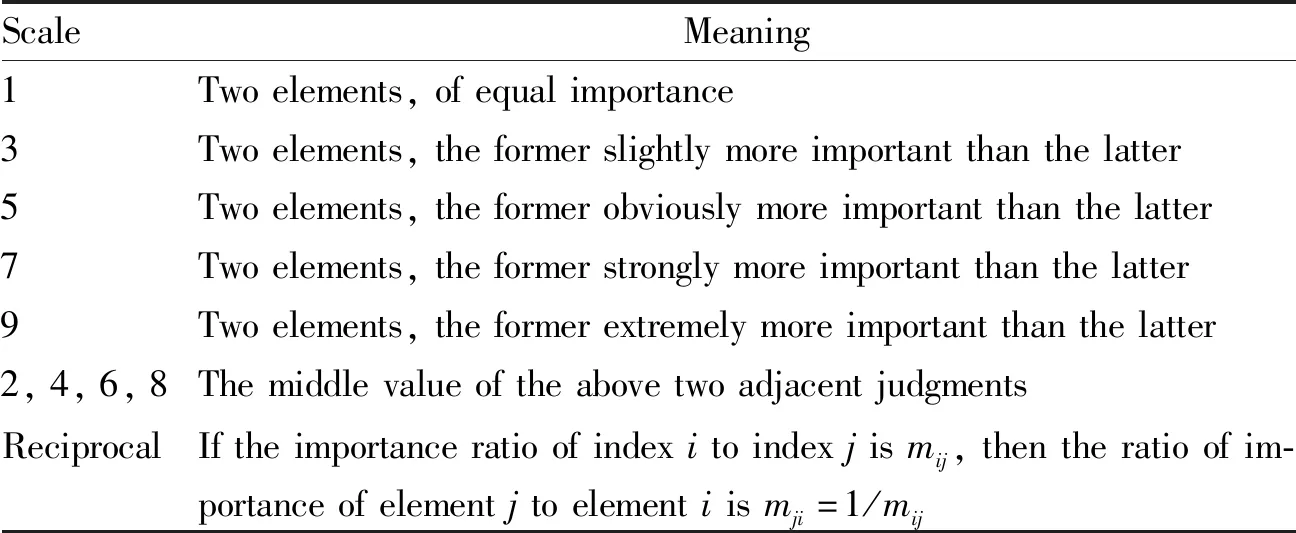
Table 4 Judgement matrix scale
(iii) The weight vectors and the maximum eigenvalue of the indices are calculated through the judgment matrix. Since the score of the judgment matrix is obtained based on the subjective experience of experts, inevitably, there would be decision-making errors or one-sided results. Therefore, it is necessary to check the consistency of the judgment matrix to prove that the evaluation result is correct. The specific test and verification method is as follows:
(2)
CR=CI/RI
(3)
whereCIis the consistency index;λmaxis the maximum eigenvalue of the judgment matrix;nis the order of the judgment matrix;RIis the average random consistency index, obtained by looking up the table;CRis the random consistency ratio. WhenCR<0.1, the consistency of the judgment matrix is considered acceptable. Otherwise, the judgment matrix needs to be revised.
3.3 Quality evaluation of threshing and redrying process
The scoring results of the indices by the 8 experts from Chenzhou Tobacco Redrying Plant were collected. According to the scoring results, the indices were compared in pairs. The judgment matrix of each level and the consistency test results are shown in Table 5-9.
TheCRvalues of the judgment matrices A, B1, B2and B3modeled by the analytic hierarchy process are 0.046 2, 0, 0.005 3 and 0.005 3, all less than 0.1, with reasonable consistency, reflecting the scoring information of the experts well. By solving the eigenvector corresponding to the maximum eigenvalue of the judgment matrix, the index weights obtained after normalization are shown in Table 5-9.

Table 5 Judgement matrix of criterion level

Table 6 Judgement matrix 1 of plan level
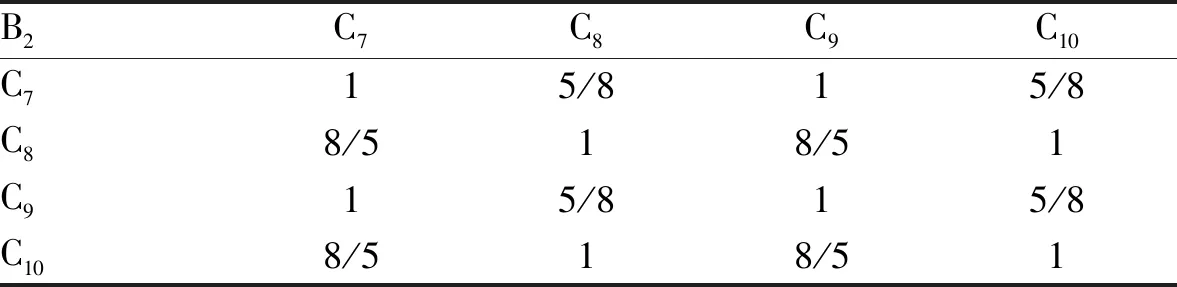
Table 7 Judgement matrix 2 of plan level
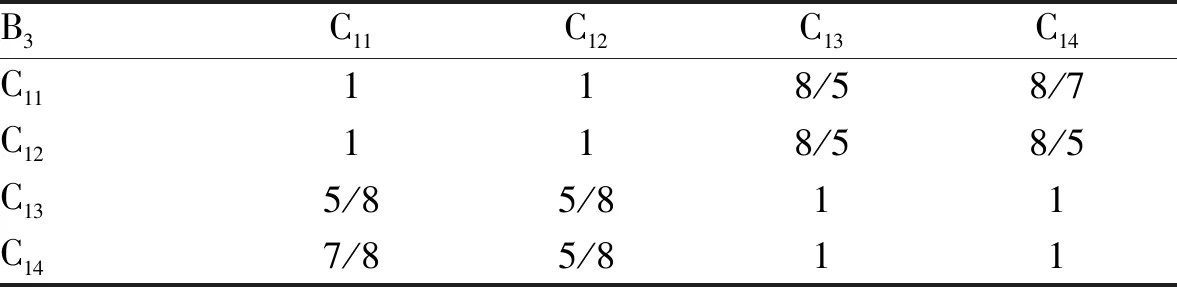
Table 8 Judgement matrix 3 of plan level
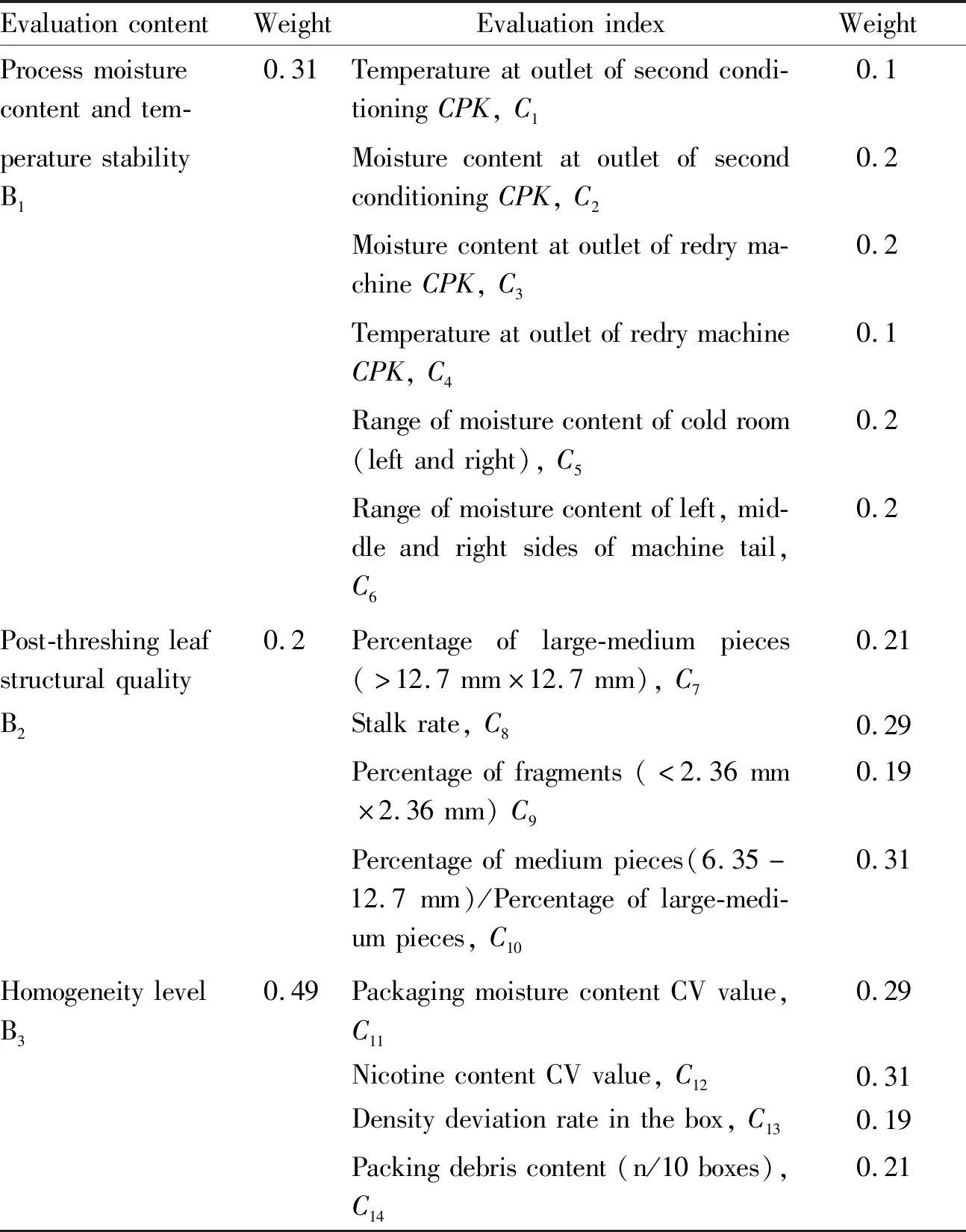
Table 9 Weight distribution of quality indices of threshing and redrying process
4 Conclusions
In this paper, 14 indices that affect the stability of equipment operation and the quality of tobacco leaves were selected to represent the performance of the threshing and redrying process. By using AHP, the weights of the indices were determined. From the weight analysis, it can be seen that the level of homogenization processing is still the focus of processing in the redrying industry in the face of specification "modularization, homogenization, purification and fragrance preservation". Introducing temperature and moisture stability and structural quality of tobacco leaves after threshing, the shortcomings in the tobacco processing process of redrying enterprises can be analyzed, and the weak links in the production process can be adjusted in time.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- A New Record of Orchidaceae from Guangxi: Galeola nudifolia Lour.
- Sustainable Utilization of Agricultural Land in Chengdu Metropolitan Area Based on Emergy Analysis
- Development Strategy of Soundscape in Rural Tourism Based on Tourist Perception: A Case Study of Some Villages in Jiangxi Province
- Practice of Mind Mapping Technology in "Re-flipped Classroom" Teaching Mode: A Case Study of the Course Principles of Residential District Planning
- Genome-wide Association Analysis of Maize Flowering Traits
- Construction of Evaluation System for High-quality Development of Characteristic Towns from the Perspective of Production-Living-Ecology Integration
