乳腺浸润性导管癌超声微钙化征象与PR ER HER-2 P53 TOPIIa ck5/6 KI67表达的相关性
2021-01-10吴昊冯佩明张可新吴文瑛
吴昊 冯佩明 张可新 吴文瑛


摘要:目的:探索乳腺浸润性导管癌超声内部微钙化征象的出现与雌激素受体ER,孕激素受体PR,人类表皮生长因子2HER-2,p53,DNA拓扑异构酶IIaTOPIIa,细胞角蛋白ck5/6,细胞核抗体KI67等免疫组化因子表达的相关性。方法:收集承德医学院附属医院2020年1月至2021年7月手术治疗的乳腺浸润性导管癌患者350例,术前进行超声检查并留存有标准的超声声像图,并运用χ²、Spearman与二元logistic回归依次分析超声微钙化征象与各个免疫组化因子表达的相关性。结果:浸润性导管癌微钙化征象的出现与HER-2、P53、KI67、TOPIIa、CK5/6的表达具有统计学意义(P<0.05),与ER、PR的表达无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论:乳腺浸润性导管癌超声微钙化征象的出现与HER-2、P53、KI67、topIIa、CK5/6的表達有统计学意义,超声微钙化征象的出现对判断乳腺癌的预后有预测价值。
关键词:超声;乳腺癌;微钙化;免疫组化
【中图分类号】R737 【文献标识码】A 【文章编号】1673-9026(2021)15--03
Abstract:Objective: To explore the correlation between the appearance of ultrasonic microcalcification signs and the expression of estrogen receptor ER, progesterone receptor PR, human epidermal growth factor 2HER-2, p53,DNA topoisomerase IIaTOPIIa, cytokeratin CK5/6, nuclear antibody KI67 and other immunohistochemical factors in invasive ductal carcinoma of breast.Methods: 350 patients with invasive ductal carcinoma of breast who received surgical treatment from The Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical College from January 2020 to July 2021 were collected. Preoperative ultrasound examination was performed and standard ultrasound images were retained. χ² Spearman and binary logistic regression were used to analyze the correlation between ultrasonic microcalcification signs and the expression of various immunohistochemical factors.Results: The microcalcification signs of invasive ductal carcinoma were statistically significant with the expression of HER-2, P53, KI67, TOPIIa and CK5/6 (P<0.05), and had no statistical significance with the expression of ER and PR (P<0.05).Conclusion: The appearance of ultrasonic microcalcification signs in invasive ductal carcinoma of breast has statistical significance with the expression of HER-2, P53, KI67, topIIa and CK5/6, and the appearance of ultrasonic microcalcification signs has predictive value for the prognosis of breast cancer.
Key words:ultrasound; Breast cancer; Microcalcification; immunohistochemical
乳腺癌是全世界女性中发病率最高的癌症【1】。早期诊断乳腺癌目前主要依靠彩色多普勒超声,钼靶,核磁等,而超声由于其无电离辐射,可显示血流信号等优势被广泛应用于乳腺疾病的早期筛查。随着分子生物学的发展,人们认识到乳腺癌的发生发展与其基因表达等因素关系密切。乳腺癌中浸润性导管癌占80%以上,本研究主要探究超声微钙化征象与PR、ER、HER-2、P53、ck5/6、KI67和TOPIIa表达的相关性。
一、资料与研究方法
1.1资料
选择2020年1月至2021年7月在我院手术病理证实的乳腺浸润性导管癌患者350例,年龄32-84岁,所有患者均为女性,超声检查、病理及免疫组化结果完整,术前未经任何治疗。
1.2研究方法
采用多普勒EPIQ7G、EPIQ5多普勒彩色超声诊断仪高频线阵探头,探头频率5-12MHZ。被检查者平卧位,暴露双侧乳房及腋窝,初步了解病灶的整体情况,而后观察肿块内部微钙化情况。为提高图像识别的准确性,每个病例的微钙化征象的识别均由两个高年资医师共同讨论完成,并去除图像差异较大的病例,得出结果后根据患者所作免疫组化表达的分子类别进行分组,暨分为ER组、PR组、HER-2组、ki67组、TOPIIa组、P53组、ck5/6组7组,并在组内区分出微钙化征象。
1.3病理及免疫组化检测方法
ER、PR、KI67、HER-2、TOPIIa、CK5/6、P53表达的免疫组织化学检测和判定:均采用手术切除标本,肿块标本检测采用迈新公司全自动免疫组化仪。PR与ER细胞核染色数目>1%者视为阳性,350例患者中,PR阳性者231例,阴性119例,ER阳性258例,阴性92例。KI67阳性细胞数<14%为(-),15%-25%为弱阳性(+),25%-50%为中阳性(++),>50%为强阳性(+++),后三者均为阳性,350例患者中阳性308例,阴性42例。HER-2表达3+记为阳性,2+者需要经过FISH技术双探针检测,FISH(+)者HER-2表达2+者记为阳性,FISH(-)者HER-2表达2+者记为阴性,HER-2表达1+及0者记为阴性,阴性者224例,阳性者124例。TOPIIa、P53均以在细胞核内出现棕黄色颗粒为阳性染色,在高倍镜下计数阳性细胞数,并计算其占肿瘤细胞的百分比,以阳性细胞数>10%为阳性,P53阳性者137例,阴性者213例,TOPIIa阳性者260例,阴性者90例。CK5/6的阳性表达于细胞质,抗体染色标注评定标准采用半定量方法,阳性细胞≥5%为阳性,<5%为阴性,CK5/6阳性者104例,阴性者246例。如表1-1。
1.4统计学处理
将得到的病理结果,免疫组化结果以及高回声晕超声特征进行总结和对比分析。实用统计学软件IBM spss22.0,用χ²进行数据分析,并用Spearman和二元Logistic回归进行统计学分析,得出其相关系数与回归系数后根据回归系数正负确定其正负相关性,P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
二、结果
2.1.超声微钙化征象与免疫组化分子表达的相关性见表2-1,显示乳腺癌超声内部微钙化征象的出现与HER-2、ki67、P53、CK5/6、TOPIIa的表达均具有相关性(P<0.05),与ER、PR的表达无相关性(P>0.05),如表2-1。
2.2分别对差异具有统计学意义的组别进行Spearman相关分析,从结果可知,微钙化征象的表达与HER-2、KI67、TOPIIa、P53、CK5/6的阳性表达呈正相关,结果如表2-2。
2.3再次分别对差异具有统计学意义的组别进行二元Logistic回归分析见表2-3,根据回归系数正负显示内部微钙化征象的出现与HER-2、KI67、P53、TOPIIa、CK5/6的表达呈正相关(OR=4.072,,2305,1.786,1.803,2.213),结果见表2-4。
三、讨论
肿瘤不同的病理学基础决定其不同的生物学行为及形态学变化,而各个免疫组化因子的表达与乳腺癌的生物学行为存在密切关系已成为现如今人们的共识。其表达也影响着临床上对于乳腺癌的治疗。
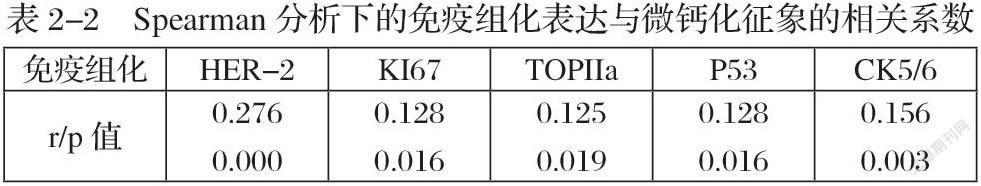
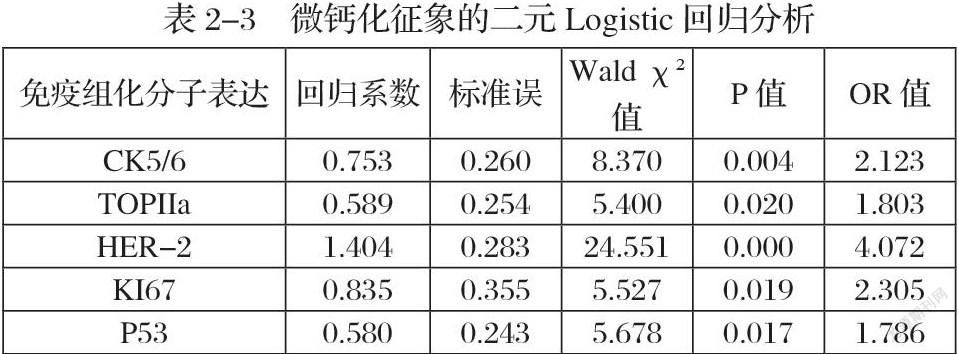
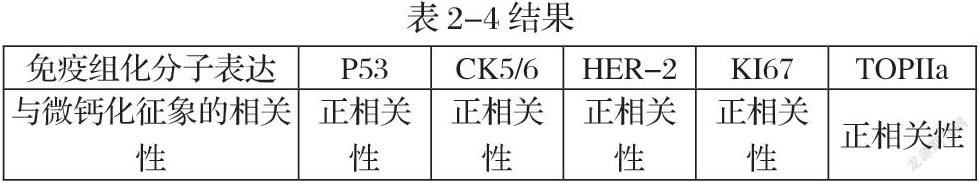
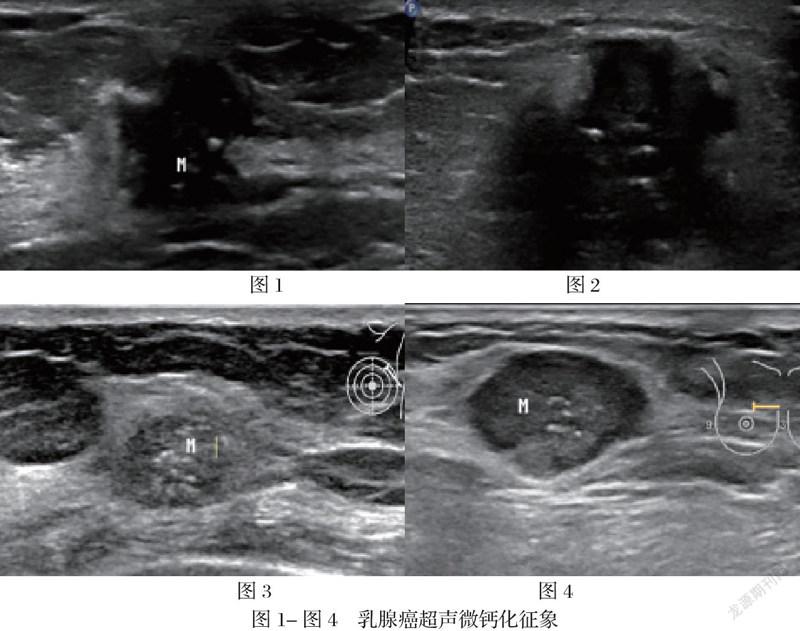
根据现有研究表明,乳腺癌超声检查下的微钙化征象(图1-4)其在病理学层面是由于乳腺癌癌灶快速生长导致局部局部营养不良,进而细胞缺血坏死,释放出硝酸根与钙离子结合成磷酸钙沉积并在超声影像学中表现为微钙化征象【2-3】。其化学成分主要为磷酸盐、碳酸钙、磷酸镁、水及蛋白质【4】。乳腺癌微钙化在声像图上表现为多样化,除数量,直径,分布,回声强弱等有一定区别外,形态表现方面多为点状。超声扫查下乳腺癌的微钙化征象由于其直径较小故通常不伴声影。因为超声对钙化的敏感性较钼靶差,所以超声显示钙化阳性的诊断价值要高于阴性的诊断价值【5】。
ER、PR的表达可反映不同的生物学行为,其在乳腺癌的发生发展中均可对细胞的生长发育,内分泌细胞等进行调节,阳性表达表达提示着较好的预后【6】,其结果也被广泛的指导用于临床的内分泌治疗和评价乳腺癌的预后【7-9】。在本项研究中,ER、PR的表达与微钙化征象并无相关性。
HER-2,即人类表皮生长因子2,是细胞增殖、分化和存活的重要调节因子,根据现有研究,HER-2直接影响着乳腺癌的预后及治疗,针对HER-2的曲妥珠单克隆抗体目前在新辅助性、辅助性和转移性浸润性癌患者中与化疗药物一起使用。HER-2高表达预示着肿瘤对周围组织侵袭能力强,容易远处转移【10,12,13】。在本项研究中,HER-2的阳性表达与微钙化征象的出现呈正相关性,与之前研究结果相符【11】。
P53基因是人类研究最为广泛的抑癌基因,而肿瘤中大部分可有P53基因的突变。当其突变后,即失去对细胞生长的控制作用,进而促进肿瘤的形成。其阳性表达可反映肿瘤的恶性转化和增殖,也可以反映乳腺癌较差的预后,暨KI67越表达,肿瘤越恶性【14】。在本项研究中,P53的阳性表达与超声微钙化征象的出现呈正相关性。
KI67在临床上可根据其表达与其他免疫组化分子的表达对乳腺癌进行分子分型并可以独立预测乳腺癌的预后,在临床上可根据其表达高达预测肿瘤转移,肿瘤的增殖活性及分化高低,KI67指数越高乳腺癌预后越差【15-19】。在本项研究中,KI67的阳性表达与超声微钙化征象的出现呈正相关性。
TOPIIa是近来才开始被研究的一种免疫组化分子,其表达与肿瘤的分化与预后相关【20-21】,表达越高,预后越差【22-24】。在临床上多作为一种药物治疗的靶点而被广泛研究【25-26】。在本项研究中,TOPIIa阳性表达与超声微钙化征象的出现呈正相关性。
CK5/6是乳腺基底细胞所特异性表达的细胞角蛋白,其表达与ER、PR的表达呈负相关,且其阳性表达与肿瘤的远处转移及预后较差具有正相关性【27】。在本项研究中,CK5/6的阳性表达与超声微钙化征象的出现具有正相关性。
综上所述,乳腺微钙化征象的表达与HER-2、CK5/6、P53、TOPIIa、KI67的表达均呈正相关性。乳腺癌癌灶快速生长导致局部局部营养不良,进而细胞缺血坏死形成钙化,而在本项研究中,免疫组化表达反映预后较差的分子类型其与乳腺癌微钙化均具有相关性,暨可从分子的角度證明乳腺癌超声下微钙化征象预示着较差的预后,是否可以作为预测乳腺癌预后的一项独立预测因素尚待进一步研究。
參考文献:
[1]Zujewski JA;Dvaladze AL;Ilbawi A;Anderson BO;Luciani S;Stevens L;Torode J.Knowledge Summaries for Comprehensive Breast Cancer Control.[J].Journal Of Global Oncology.2018,Vol.4(No.4):1-7.
[2]Cha, Hwajin;Chang, Yun-Woo;Lee, Eun Ji;Hwang, Ji Young;Kim, Hyun Joo;Lee, Eun Hye;Ryu, Jung Kyu.Ultrasonographic features of pure ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast: correlations with pathologic features and biological markers.[J].Ultrasonography (Seoul, Korea).2018,Vol.37(No.4):307-314.
[3]Pang, Jia-Min B;Byrne, David J;Takano, Elena A;Jene, Nicholas;Petelin, Lara;McKinley, Joanne;Poliness, Catherine;Saunders, Christobel;Taylor, Donna;Mitchell, Gillian;Fox, Stephen B.Breast Tissue Composition and Immunophenotype and Its Relationship with Mammographic Density in Women at High Risk of Breast Cancer[J].PloS one.2015,Vol.10(No.6):e0128861.
[4]R. W. POWELL;MARJORIE B. McSWEENEY;CATHERINE E. WILSON;.X-ray calcifications as the only basis for breast biopsy.[J].Ann Surg.1983,Vol.197(No.5):555-559.
[5](美)A.Thomas Stavros著;王知力译.乳腺超声经典诊断学 中文翻译版[M].北京:科学出版社.2017.
[6]Tang J1;Cui Q1;Zhang D2;Liao X1;Zhu J1;Wu G1..An estrogen receptor (ER)-related signature in predicting prognosis of ER-positive breast cancer following endocrine treatment(Article)[J].Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine.2019,Vol.23(No.8):4980-4990.
[7]毛羡仪1,2,梁伟翔3,蒋殿虎2,陆培明2.乳腺癌高回声晕超声特征与ER、PR表达水平的相关性分析[J].医学影像学杂志.2020,30(6):1001-1004,1013.
[8]Liu, CG (Liu, Caigang)2;Zhang, H (Zhang, Hao)2;Shuang, C (Shuang, Chen)3;Lu, Y (Lu, Yang)2;Jin, F (Jin, Feng)2;Xu, HM (Xu, Huimian)2;Lu, P (Lu, Ping)1,2.Alterations of ER, PR, HER-2/neu, and P53 protein expression in ductal breast carcinomas and clinical implications.[J].Medical Oncology.2010,Vol.27(No.3):747-752
[9]Carol A Parise;Katrina R Bauer;Monica M Brown;Vincent Caggiano.Breast cancer subtypes as defined by the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) among women with invasive breast cancer in California, 1999-2004[J].Breast Journal.2009,Vol.15(No.6):593-602.
[10]Seyed Abbas Mirmalek;Maryam Hajilou;Seyed Alireza Salimi Tabatabaee;Yekta Parsa;Soheila Yadollah-Damavandi;Tina Parsa.Prevalence of HER-2 and Hormone Receptors and P53 Mutations in the Pathologic Specimens of Breast Cancer Patients[J].International Journal of Breast Cancer.2014:564308
[11]Liu, Y (Liu, Y.)1;Xiong, W (Xiong, W.)2;Xu, JM (Xu, J-M)1;Liu, YX (Liu, Y-X)1;Zhang, J (Zhang, J.)3.Correlations between the expression of C-erB-2, CD34 and ER in breast cancer patients and the signs of conventional ultrasonography and ultrasound elastography.[J].European review for medical and pharmacological sciences.2018,Vol.22(No.17):5539-5545.
[12]Liu, CG (Liu, Caigang)2;Zhang, H (Zhang, Hao)2;Shuang, C (Shuang, Chen)3;Lu, Y (Lu, Yang)2;Jin, F (Jin, Feng)2;Xu, HM (Xu, Huimian)2;Lu, P (Lu, Ping)1,2.Alterations of ER, PR, HER-2/neu, and P53 protein expression in ductal breast carcinomas and clinical implications.[J].Medical Oncology.2010,Vol.27(No.3):747-752.
[13]Bansal C1, Sharma A2, Pujani M3, Pujani M4, Sharma KL2, Srivastava AN5, Singh US6..Correlation of Hormone Receptor and Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-2/neu Expression in Breast Cancer with Various Clinicopathologic Factors.[J].Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol.2017,Vol.38(No.4):483-489.
[14]Mitsuchika Hosoda;Mitsugu Yamamoto;Kiichiroh Nakano;Kanako C Hatanaka;Emi Takakuwa;Yutaka Hatanaka;Yoshihiro Matsuno;Hiroko Yamashita.Differential expression of progesterone receptor, FOXA1, GATA3, and p53 between pre- and postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer[J].Breast cancer research and treatment.2014,Vol.144(No.2):249-261.
[15]Tao, MM (Tao, Miaomiao)1;Chen, S (Chen, Shu)2;Zhang, XQ (Zhang, Xianquan)3;Zhou, Q (Zhou, Qi)1.Ki-67 labeling index is a predictive marker for a pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer: A meta-analysis(Review)[J].Medicine (United States).2017,Vol.96(No.51):e9384.
[16]Penault-Llorca, F.a,b,c;Radosevic-Robin, N.a,b.Ki67 assessment in breast cancer: an update(Article)[J].Pathology.2017,Vol.49(No.2):166-171.
[17]Nishimukai, A (Nishimukai, Arisa)1;Yagi, T (Yagi, Tomoko)1;Yanai, A (Yanai, Ayako)1;Miyagawa, Y (Miyagawa, Yoshimasa)1;Enomoto, Y (Enomoto, Yukie)1;Murase, K (Murase, Keiko)1;Imamura, M (Imamura, Michiko)1;Takatsuka, Y (Takatsuka, Yuichi)1;Sakita, I (Sakita, Isao)2;Hatada, T (Hatada, Takuya)3;Miyoshi, Y (Miyoshi, Yasuo)1.High Ki-67 expression and low progesterone receptor expression could independently lead to a worse prognosis for postmenopausal patients with estrogen receptor-positive and HER2-negative breast cancer[J].Clinical Breast Cancer.2015,Vol.15(No.3):204-211.
[18]Sana Wajid? 1,?Fauzia A Samad? 1,?Abdus S Syed? 2,?Faiza Kazi? 3.Ki-67 and Its Relation With Complete Pathological Response in Patients With Breast Cancer[J].Cureus.2021,Vol.13(No.7):e16788.
[19]Pérez-López ME;Department of Oncology, University Hospital of Ourense, University of Vigo, C/Ramón Puga 52-54, 32005, Ourense, Spain. maria.eva.perez.lopez@sergas.es.;García-Gómez J;Department of Oncology, University Hospital of Ourense, University of Vigo, C/Ramón Puga 52-54, 32005, Ourense, Spain.;Alves MT;Research Unit, University Hospital of Ourense, University of Vigo, Ourense, Spain.;Paradela A;Department of Pathology, University Hospital of Ourense, University of Vigo, Ourense, Spain.;García-Mata J;Department of Oncology, University Hospital of Ourense, University of Vigo, C/Ramón Puga 52-54, 32005, Ourense, Spain.;García-Caballero T;Department of Morphological Sciences, School of Medicine-University Clinical Hospital, University of Santiago de Compostela, Ourense, Spain..Ki-67 is a prognostic marker for hormone receptor positive tumors.[J].CLINICAL & TRANSLATIONAL ONCOLOGY.2016,Vol.18(No.10):996-1002.
[20]Rudolph P;Olsson H;Bonatz G;Ratjen V;Bolte H;Baldetorp B;Ferno M;Parwaresch R;Alm P.Correlation between p53, c-erbB-2, and topoisomerase II alpha expression, DNA ploidy, hormonal receptor status and proliferation in 356 node-negative breast carcinomas: prognostic implications.[J].Journal of Pathology: Journal of the Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland.1999,Vol.187(No.2):207-216
[22]L Nakopoulou;A C Lazaris;N Kavantzas;P Alexandrou;P Athanassiadou;A Keramopoulos;P Davaris.DNA topoisomerase II-alpha immunoreactivity as a marker of tumor aggressiveness in invasive breast cancer[J].Pathobiology.2001,Vol.68(No.3):137-143。
[22]Yegor S. Vassetzky, Gian‐Carlo Alghisi & Susan M. Gasser.DNA topoisomerase II mutations and resistance to anti‐tumor drugs[J].Bioessays.1995,Vol.17(No.9):767-774.
[23]Engelstaedter V.;Schiffers J.;Kahlert S.;Mainka P.;Engel J.;Kirchner T.;Diebold J.;Mayr D..Her-2/neu and topoisomerase IIα in advanced breast cancer: A comprehensive FISH analysis of 245 cases[J].Diagnostic Molecular Pathology.2012,Vol.21(No.2):77-83.
[24]Ping, S..Expressions of HER2 and Topo IIα in breast cancer and its clinical significance(Article)[J].Journal of Central South University (Medical Sciences).2016,Vol.41(No.11):1143-1147.
[25]B J Lynch;D G Guinee;J A Holden.Human DNA topoisomerase II-alpha: a new marker of cell proliferation in invasive breast cancer.[J].Human pathology.1997,Vol.28(No.10):1180-1188.
[26]Delgado, JL (Delgado, Justine L.)1;Hsieh, CM (Hsieh, Chao-Ming)2;Chan, NL (Chan, Nei-Li)2;Hiasa, H (Hiasa, Hiroshi)3.Topoisomerases as anticancer targets.[J].Biochemical Journal.2018,Vol.475(No.2):373-398.
[27]Lisa M Sutton;Jeong S Han;Kyle H Molberg;Venetia R Sarode;Dengfeng Cao;Dinesh Rakheja;Joseph Sailors;Yan Peng.Intratumoral Expression Level of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and Cytokeratin 5/6 Is Significantly Associated With Nodal and Distant Metastases in Patients With Basal-like Triple-Negative Breast Carcinoma[J].American journal of clinical pathology.2010,Vol.134(No.5):782-787.
作者簡介:吴昊,硕士研究生在读。
通讯作者:吴文瑛,副主任医师,硕士,研究方向:超声诊断。
