Design and experiment of the grading device for a potato seed cutting machine
2020-12-25LyuJinqingWenXinyuLiZihuiLiJichengLiuZhongyuan
Lyu Jinqing, Wen Xinyu, Li Zihui, Li Jicheng, Liu Zhongyuan
Design and experiment of the grading device for a potato seed cutting machine
Lyu Jinqing1,2, Wen Xinyu1, Li Zihui1, Li Jicheng1, Liu Zhongyuan1
(1.,,150030,;2.,,163319,)
There is a large land area for potato s in China, the mechanized potato sowing operation is an important part of the entire potato mechanization process. At present, the cultivation mode of potato mechanized sowing is mainly based on cut potatoes, and the uniformity of potato tubers directly affect the quality of sowing. In most areas, manual cutting is still used, and the cutting efficiency is low. In some areas, potato cutting machines are used for potato cutting, which is more efficient, but the traditional potato seed cutting machine cannot get the uniform potato tubers when cutting potatoes, and cannot meet the requirements of mechanized seeding. It would affect the subsequent growth and development of potatoes and has a greater impact on the entire potato mechanization process. Aiming at solving the above-mentioned problem, a grading device that can installed on the potato seed cutting machine was designed. Firstly, the structure of the grading device was introduced, the grading device is mainly composed of grading roller, frame, side baffle, spacing adjustment mechanism, etc. And the working principle of the grading device was explained in the study, the potato seeds inputted in the grading device would be guided and graded with the rotation of the grading rollers, and the small potato seeds would fall from the grading gap of the adjacent grading rollers, while the large potato seeds would continue to move backward with the rotation of the grading rollers until leaving the grading device. Conveyor belts are arranged below and behind the grading device to receive the potatoes outputed by the grading device. Moreover, the cutting process of the potato seeds was explained, potato seeds weighing less than 100 g need to be cut once, and the potato seeds weighing more than 100 g need to be cut twice or more to meet the sowing requirements. The stress state of potato seeds on the grading rollers and the movement state on the grading rollers were analyzed, so as to determine the structural parameters of each part of the grading roller wheel of the grading device and the reasonable grading roller rotation velocity. The number of grading rollers, the rotation velocity of the grading roller, and the feeding amount were selected as the experimental factors, and the grading precision was selected as the evaluation index for the orthogonal test. Kexin 1 was selected as the experimental potato seeds. The software Design-Expert 8.0.6 was used to process and optimize the experimental data and determine the optimum parameter combination. The test results showed the primary and secondary order of influencing factors for the grading precision. The order was the number of grading rollers, the rotation velocity of the grading roller, the feeding amount. And the article performed a verification test on the optimum parameter combination obtained from the test. The verification test was conducted under the optimum parameter combination and the results showed that when the number of grading rollers was 7, the rotation velocity of the grading roller was 110 r/min, and the feeding amount was 40 t/h, the grading precision was 98.7%, which can meet the grading requirements. This research provides a high-efficiency and high-grading precision device for potato seed cutting machine.
design; experiment; potato; cutting machine; grading device; mechanical analysis
0 Introduction
There is a large land area for potato sowing in China. The cultivation mode of potato mechanized sowing is mainly based on cut potatoes, and the uniformity of potato tubers directly affect the quality of sowing[1-3], According to the agronomic requirements of pre-sowing cutting, potato seeds weighing less than 50 g can be sown entirely, 51-100 g potato seeds need to be cut into two pieces, and 101-150 g potato seeds need to be cut into 4 pieces. For potato seeds weighing more than 150 g, they need to be cut into small pieces according to the number of buds, and ensure that each potato tuber has more than one bud[4-5].
Foreign company have studied potato grading machinery earlier, such as the large grading equipment produced by Grimme, Germany, which integrates transportation, cleaning, sorting and packaging[6], but its cost is high and the volume is large, so it cannot be used exclusively for the grading of potato seed. In recent years, domestic scholars have also the research of the potato grading machine, Wang et al[7]designed the potato cleaning and sorting machine, which integrates cleaning and grading, and the spacing between the grading rollers can be adjusted by the telescopic frame. Lv et al[8]designed a roller potato grading machine, a guide was designed to improve the height of the floating guides in the grading process, and then the spacing of the grading rollers was changed to grade. At present, the existing grading machine is too large in volume, the structure is too complicated, and the cost is high. Therefore, it cannot be installed on the cutting machine to carry out the grading operation before cutting the potato seed, which is not conducive to timely mechanized sowing and catching up the right seeding time.
The grading roller is an important part of the potato grading device, and the shape of the grading roller determines the movement state of the potato on the device. At present, most of the grading rollers used in the grading device are cylindrical rollers[9-12], the movement state of the potatoes on the device is that the long axis of the potato is the same as the axial direction of the grading roller, and the potatoes whose short axis diameter is smaller than the grading gap would be graded[13-16]. The potato seed cutting machine used currently cannot meet the agronomic requirements of the sowing due to the poor uniformity of potato tubers, affecting the seeding quality and the subsequent growth of the potato.
Aiming at the problem of poor tuber uniformity and inconvenience for direct seeding of traditional potato cutters.A grading device applied to the potato seed cutting machine was designed. The potato seed is graded before the cut, and then a reasonable cutting method is selected according to the size of the grading potato seed. The purpose of this article is to design a grading device to solve the above problems, according to the movement analysis of the potato seeds on the grading rollers, the main factors affecting the grading precision are determined, the optimum parameter combination is obtained through orthogonal experiments. And verify whether the grading device can meet the grading requirements.
1 Materials and method
1.1 Structure and working principle of the device
The device is mainly composed of grading device, frame, side baffle, spacing adjustment mechanism, etc. The structure is shown in Fig. 1a, and the left side is the feeding end.
The grading device is equipped with 7 grading rollers, the motor drives the grading device to operate, and the grading roller is driven by the chain. The working principle is shown in Fig. 1b. The motor drives the entire grading device by rotating the grading roller set on the left feeding side. The potato seed need to be graded inputs from the left side of the grading device and falls to the grading roller, the potato seed is graded with the rotation of the grading roller, the side baffles on sides of the grading device prevent the potato seed from moving to the outside of the device during the grading process, the smaller potato seeds would fall from the grading gap of the adjacent grading rolls to the conveyor below the grading device, the conveyor below the device transports the small potato to the cutting knife of the potato seed cutting machine for cutting, similarly, the large potato that has not been dropped will fall from the rear of the grading device to the upper conveyor, and be transported to the potato seed cutting machine for cutting. For the large potato and small potato, different cutting methods are adopted, large potatoes on the upper layer still need to be cut horizontally after vertical cutting, and the small potatoes on the lower layer only need to be cut vertically to ensure the uniformity of the potato tubers.
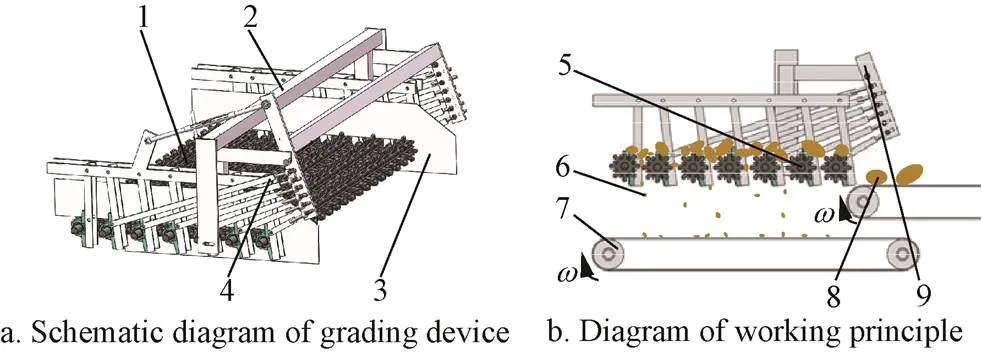
1. Grading roller 2.Frame 3.Side baffle 4.Spacing adjustment mechanism 5.Grading roller 6.Small potato 7.Potato conveyor 8.Large potato 9.Adjustment handle
The grading device can adjust the size of the graded potato seed according to the agronomic requirements,the distance between the grading rollers can be changed by adjusting the adjustment handle on the spacing adjustment mechanism,thereby changing the size of potato seed on the lower layer graded by the grading device,and the potato tubers of corresponding size are obtained after being cut by the cutting machine. It can meet the requirements of different agronomic techniques for sowing potato tubers.
1.2 Process for cutting the potato seed before sowing
The potato seeds should undergo the process of feeding, impurity removal, grading, arranging, and finally cutting. In the whole process, the grading process has a direct impact on the quality of the cut. In the process of cutting the potatoes, the potato seeds are first cut vertically, after the vertical cutting, the large potatoes still need to be cut horizontally to ensure the appropriate quality of the potato tubers. While the small potatoes just need to be cut vertically to meet the requirements. If the potato seeds are not graded, the small potatoes will be cut together with the large potatoes, resulting in the quality of the potato tubers cut by the small potato is too small, it would not meet the sowing requirements, and affects the sowing quality.
1.3 Key component design
1.3.1 Grading device
The grading device is mainly composed of U-shaped plate, grading roller and connecting frame, the structure is shown in Fig. 2a, and the left side is the feeding end.
The 7 grading rollers are arranged horizontally, and the two ends of the grading roller are installed to the U-shaped plate of the frame through the fixed bearing seat,The upper end of the U-shaped plate is installed to the connecting frame of the whole frame,the grading roller on the left side is adjacent to the hopper and can take potato seeds.And the grading roller is composed of grading roller shaft, grading roller wheel, locking piece, etc.The grading roller wheels are closely arranged on the grading roller shaft, two half of the grading roller wheels are arranged at two ends of the grading roller, and the smaller diameter end faces the inner side of the grading roller,it can prevent the potato seed from colliding with the sidewall of the grading device during grading.Locking pieces are arranged at both ends of the grading roller to lock the grading roller wheels installed on the shaft, and it can prevent the grading roller wheels from axial movement during the grading process.

1.U-shaped plate 2.Locking piece 3.Grading roller shaft 4.Grading roller wheel 5.Connecting frame 6.Stir piece 7.Reinforcing plate 8.Guide plate
As shown in Fig.2b, the grading roller wheel is mainly composed of stir piece, reinforcing plate and guide plate. The reinforcing plates on sides of the stir piece support it to prevent the stir piece from serious deformation and affecting the grading accuracy during the grading process. And the guide plates can guide and adjust the posture of the potatoes on the grading roller wheels. Each grading roller wheel has 8 stir pieces and 8 guide plates, they are arranged in a circle, and they can continuously stir potato seeds and improve grading efficiency.
1.3.2 Comparison of grading devices
In the existing grading device, the state of the potato seed during the grading process is that the short axis is parallel to the plane, as it’s shown in Fig.3a. The potato seed will be graded in this state as the rotation of the grading rollers group, but this will increase the overall width of the grading device. While the grading device designed in this study is installed on the cutting machine and cooperates with the cutting device to complete the grading and cutting operation before seeding potatoes. Therefore, the size of the grading device would be limited by the size of the cutting machine. And the parallel of the short axis of the potato and the planewill limit the number of potatoes accommodated on the grading roller simultaneously, which affects the grading efficiency.

Note: XOY is a coordinate system established by the radial connection of adjacent grading roller shafts as the X axis.
The innovation of the grading device designed is that it can adjust the posture of the potato seed on the grading device during the grading process, so that the potato seed can be graded in a posture where the long axis is perpendicular to the grading plane, as it’s shown in Fig. 3b. Under the premise of meeting the size of the potato seed cutting machine, it would maximize the number of potatoes simultaneously accommodated on the grading rollers, and the grading efficiency can be improved.
1.4 Key parameter determination
1.4.1 Grading roller wheel size
The grading roller wheel size affects the size of the potato seed that is transported to the cutting machine after grading[17-18]. Therefore, the design of the grading roller wheel should take into account the size requirement of potato tubers for sowing. According to the national standard[19]and the size requirement of potato tubers for sowing, potato seeds weighing less than 100 g need to fall from the grading gap between the grading rollers when grading, and they only need to be cut once. By referring to the reference[20]and the actual measurement of the potato seed, it is found that the average long axis size of the potato seed weight 100 g is 60-75 mm, and the average short axis size is 30-45 mm, and the shape of the potato seed is approximately ellipsoidal. In order to prevent the potato seed from being clamped between adjacent stir pieces and unable to be transported backwards during the grading process, the height difference between the guide plate and the stir piece should not be larger than 1/3 of the diameter of the short axis of the potato seed, and to ensure that the potato seeds move continuously on the grading roller, considering that the height difference between the guide plate and the stir piece is 10 mm, the height of the stir piece is 25 mm, and the height of the guide plate is 15 mm, in order to ensure the strength of the guide plate, the thickness of the guide plate is designed to be 5 mm, the structure of the grading roller wheel is shown in Fig. 4. The length of the grading roller wheel also has a great influence on the grading accuracy, if the length of the grading roller wheel is too large, it would limit the number of grading roller wheels installed on the grading roller, which affects the grading efficiency, while if the length is too small, the potato seed would be clamped on the adjacent guide plate of the grading roller wheel when grading, and cannot be guided and graded smoothly, affecting the grading accuracy. Therefore, considering the overall width of the grading device and the average length of the graded potato seed, design that the length of the single grading roller wheel is 75 mm, the width of the stir piece is 25 mm, the thickness of the stir piece is 10 mm. The slope of the guide plate affects the guiding process of the potato on the guide plate. If the slope of the guide plate is too small, its strength will be reduced, the guide plate will deform during the grading process, affecting the grading precision, If the slope of the guide plate is too large, the shape of the guide plate will tend to be flat, which will affect the guiding quality of the potatoes on the guide plate. Considering comprehensively, design that the slope of the guide plate is 150°.
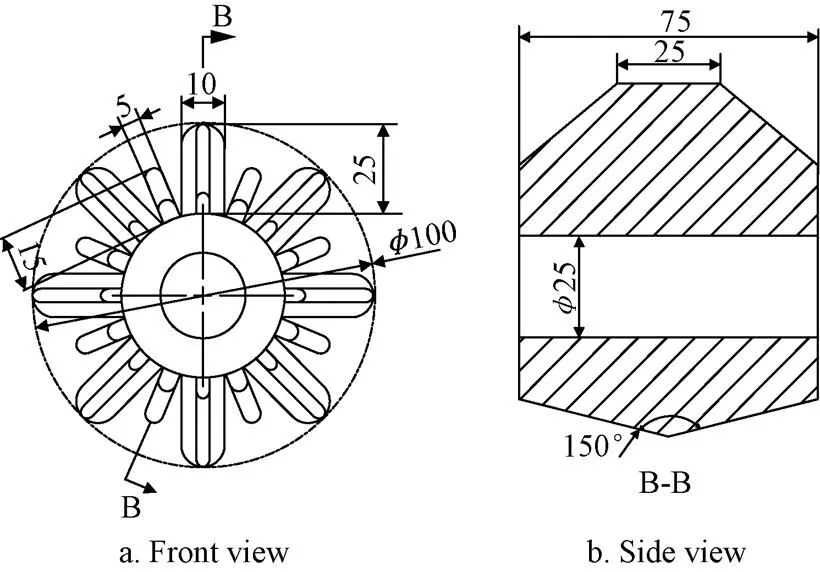
Note: 10 is thickness of the stir piece, mm; 25 is height of the stir piece in Fig.a, mm; 5 is thickness of the guide plate, mm; 15 is height of the guide plate, mm; 100 is diameter of the grading roller, mm; 25 is width of the stir piece in Fig.b, mm; 75 is length of the grading roller wheel, mm; 150° is slope of the guide plate, °; φ25 is diameter of the grading roller hole, mm.
The stir piece is higher than the guide plate, so the stir piece would guide the long axis of the potato seed to the same axial direction as the grading roller in the grading process. The middle of the guide plate is high, and the sides are low, so the potato seed guided by the stir piece moving to the guide plate will dump to both sides.the potato seed falls into the grading gap formed by the adjacent grading roller for grading.
1.4.2 Grading roller rotation velocity
When the potato seeds moves on the grading device during the process, if the rotation velocity of the grading roller is too large, the potato seed will jump on the grading roller, affecting the grading quality, and easily cause surface damage of the potato seed, so it is necessary to determine the appropriate grading roller rotation velocity range to ensure the grading quality of the potato seed[21-23]. Fig.5a shows the position of the potato seed on the grading roller.
The coordinate system is established by connecting the centroid of the potato seed and the axis center of the grading roller as theaxis,As shown in Fig.5b, the component force of the seed potato in the positive direction of the-axis is:

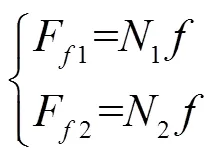
Where,is a coefficient of friction.

Note: ω1is the rotational angular velocity of the grading roller, r·min-1; a is the distance between the grading roller axis and point O, mm.; O is the center of mass of the potato; O1 is the contact point between the potato and the guide plate; O2 is the contact point between the potato and the stir piece; XOY is a coordinate system established by the connection of point O and grading roller axis as the Y axis;mg is the gravity of the potato, N; Ff1, Ff2 are the fricitional forces of the tuber, N; N1, N2 are the support forces of the tuber, N; α is the angel of tuber gravity and Y-axis direction, °; θ is the angel of support force N1 and Y-axis direction, °; β is the angel of support force N2 and X-axis direction, °.
Combine Eqs. (1) and (2) and simplify:
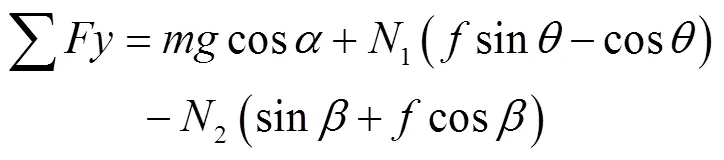
The direction of the centrifugal force of the potato seed is along the negative-axis direction:

Where,is the weight of the potato, g.
If the rotation velocity of the grading roller is too large, that’s means, when the centrifugal force of the potato seed1is greater than the combined force of the potato seed along the positive-axis direction, the seed potato will undergo centrifugal movement and the potato seed would be thrown up, so in the grading process it needs to guarantee that:

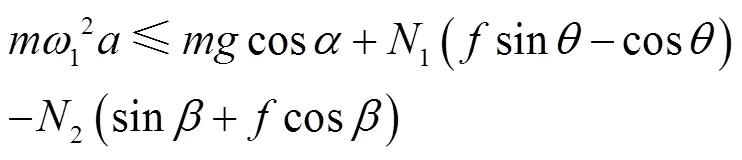
And simplify:

It can be seen from the Eq. (6) that the rotation velocity of the grading roller cannot exceed a maximum value, or the potato seed will be thrown up on the grading roller during the grading process, affecting the grading effect, and if the throwing height is too large, it would cause drop damage[24-26]. Referring to the refs.[27-29], it is found that the static friction coefficient between the potato tubers and the rubber plate is about 0.6.
According to the actual measurement of the potato seeds, it is found that the average short axis size of the potato seed weight 100 g is 30-45 mm, according to the design part, it is found that the height of the stir piece is 25 mm, the height of the guide plate is 15 mm, and the diameter of the grading roller is 100 mm. It is necessary to consider that the potato seed would rotate along its own axis when moving on the grading roller[30], it is determined that the grading roller rotation velocity is 90-120 r/min.
1.5 Mechanical properties analysis of grading process
The position the potato seed on the adjacent two grading rollers is shown in Fig. 6a.

Fig.6 Schematic diagram of the potato seed on the grading roller
The force analysis of the potato seed is shown in Fig.6b, the frictional force can be defined as following equation:

Where,is a coefficient of friction.
Ignoring the centrifugal force of the potato seed caused by the rotation of the grading roller, the torque to point3of the resultant force acting on the potato is:

The necessary condition that the potato seed can be moved by the grading roller and conveyed to the next grading roller smoothly is that the combined torque to the point3is greater than or equal to zero. Combine Eqs. (7) and (8) and simplify:
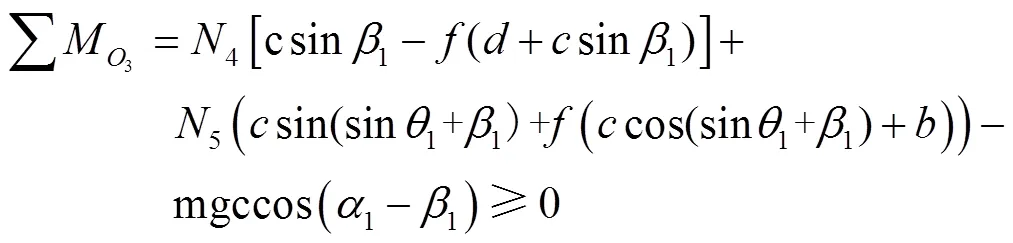
And it should be fulfilled that the combined force of the potato along the positive-axis direction is greater than or equal to zero:
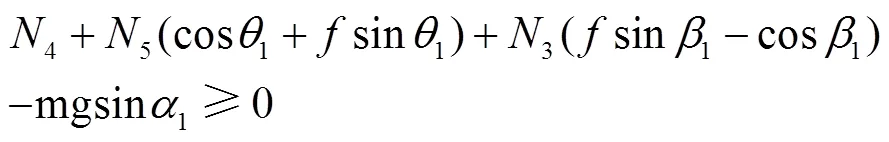
It can be seen from the above mechanical property analysis that the force of potato seed on the grading roller would affect the movement state of the potato seed on the grading device in the grading process, and the rotation velocity of the grading roller has an influence on the force condition of the potato seed. The number of the grading roller will affect the movement time of the potato seed on the grading roller, the larger the number of grading rollers, the longer the movement time of the potato on the grading device, the potato can be fully graded, and higher grading precision can be achieved, but the increase of the number will increase the length of the entire grading device, since the grading device is installed on the cutting machine to cooperate with the cutting device, reasonable number of grading rollers needs to be determined to ensure the high grading precision while meeting the size of the cutting machine. Feeding amount is also a factor that affects the grading precision. If the feeding amount is too large, it will cause the potatoes to accumulate on the grading rollers, so that the potatoes cannot fully contact the grading rollers for grading, which will affect the grading precision.
Therefore, number of grading rollers, rotation velocity of grading rollers, feeding amount were selected as the test factors in this article. The test object was the Kexin 1 potato seeds of specific quality. The size of the potatoes was similar. Therefore, the distance between adjacent grading rollers was set to a fixed value according to the size of the potatoes before the test, in order to verify the grading accuracy of potatoes of equal quality, the distance between adjacent grading rollers was no longer adjusted during the test. If the test object is potatoes of other varieties or levels, the distance between adjacent grading rollers is need to be adjusted to a suitable distance according to the size of the potatoes before the test. Therefore, the article does not list the distance between adjacent grading rollers as the main test factor.
1.6 Working performance test
In May 2019, a working performance test of the grading device was conducted at the agricultural machinery laboratory (outdoor) of Northeast Agricultural University, and potato variety Kexin 1 was selected as the material for the grading test. according to the agronomic requirements of pre-sowing cutting, potato seeds weighing less than 100 g need to be cut into two pieces, 101-150 g potato seeds need to be cut into four pieces, potato seeds weighing more than 151 g need to be cut into multiple pieces, that is, 100 g and 150 g are the quality points of different cutting methods for potatoes. Therefore, the grading of potato seeds also needs to be based on the quality point to grade the potato seeds that need to be cut in different ways. The Kexin 1 used in this testis is widely planted locally, and most of its potato seeds do not exceed 150 g in quality. In order to ensure the accuracy of the test results, the potato seeds with the mass equal to 100 g were selected for the test. By calculating the number of potato seeds falling from the distance between the grading rollers to verify the grading precision of the grading device, the distance between the grading rollers was determined to be 120 mm by a single factor test and remained constant before the orthogonal test. The test process is shown in Fig.7.

Fig.7 Experimental process
As mensioned above, the number of grading rollers, the rotation velocity of grading roller and the feeding amount were selected as the experimental factors. The evaluation index was the grading precision1. The calculated equations is:

Where1is the weight of the potato seed graded to the lower layer, g;1is total weight of potato seed fed into the grading device, g.
According to the orthogonal test design method[31-32], the experiment was arranged. The grading precision was selected as the evaluation index. Considering the overall length of the device, the size of the mating cutting machine and the convenience of the transmission, the test selected that the number of the grading rollers is 4-7, the rotation velocity of the grading rollers is 90-120 r/min. According to the previous observation and statistics, the time required for the grading device to complete a single potato grading is 1-3 s, and the number of potatoes that can be graded at the same time is 108. Combining the existing reference and the actual operating conditions of the grading device, selected the feeding amount to be 20-50 t/h. The orthogonal table L16(45) was used to arrange the experiments. Each of the three factors accounted for a column. Two blank columns, marked as “error”, were added to estimate the test error. Thus the test data can be analyzed by ANOVA. The experimental factors and levels are shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Experimental factors and levels
2 Results and discussion
The test procedure and results of grading test are shown in Table 2, and the results of ANOVA and range analysis are shown in Table 3. Table 3 shows that the effect intensity of factors on grading precision is in turn,,. And the number of the grading rollersand the rotation velocity of rollersindicate highly significance to the grading precision (<0.01), and the feeding amountindicates significance to the grading precision (<0.05).

Table 2 Test plan and range analysis of experimental data
With the increase of the number of the grading rollers, the grading precision rose. The main reason was that the more the number of the grading rollers, the longer the potato seed moves on the grading rollers, and it can get the higher grading precision, so the highest grading precision was in4position, when the number of the grading rollers was 7.
With the increase of the rotation velocity of the grading rollers, the grading precision increased firstly and then fell, and reached the maximum value under the3condition, when the rotation velocity of grading rollers was 110 r/min. The main reason was that with the increase of the rotation velocity of grading rollers, the movement of the potato seed on the grading roller was also accelerated, and the guiding and grading process can be completed quickly on the grading roller, and can obtain the higher grading precision. Whilewith the further increase of the rotation velocity, the centrifugal force of the potato seed was too large, and the potato seed were thrown up and unable to fully contact with the grading device and the grading process cannot be completed smoothly, the grading precision was decreased, so the grading precision showed a trend of rising first and then falling.
With the increase of the feeding amount, the grading precision increased firstly and then decreased, and reached the maximum value under the3condition, when the feeding amount was 40 t/h. The main reason was thatwith the increase of the feeding amount, more potato seed entered the grading device and completed the grading process, the grading precision gradually increased, but when the feeding amount was too large, the potato seed accumulated on the grading rollers, which resulted that the potato seed unable to fully contact with the grading device, cannot be guided and graded sufficiently on the grading rollers, the grading precision decreased, so the grading precision showed a trend of rising first and then falling.

Table 3 Analysis of variance for experiment result
Note: ** indicates significance, (<0.05); *** indicates highly significance, (<0.01).
According to the results of ANOVA and range analysis, the optimum operating parameters were obtained as: the number of the grading rollers 7, the rotation velocity of the grading rollers 110 r/min, the feeding amount 40 t/h (433). Using the optimum operating parameters, the potato seed with the mass less than or equal to 100 g was selected for the verification test. The verification test was conducted under optimum operating parameters and the results showed that the grading precision of the potato seed was 98.7%, which could meet the grading requirements.
3 Conclusions
1) The grading device for potato seed cutting machine was achieved by using the grading rollers consisted by the grading roller wheels. The grading roller wheels can realize the guiding and grading of the potato seed, and it can accommodate enough seed potatoes and get the high grading precision under the premise of satisfying the size of the cutting machine. And the distance between the grading rollers can be adjusted according to different grading requirements to ensure the uniformity of the potato seeds outputed from the cutting machine.
2) The grading test was carried out by the orthogonal test, and the test results are analyzed by the range and variance analysis. The analysis results show that the order of the factors affecting the grading precision is the number of rollers, the rotation velocity of rollers, and the feeding amount. The the optimum operating parameters were that the number of rollers is 7, the rotation velocity of rollers is 110 r/min, the feeding amount is 40 t/h. Under the conditions, the grading precision is 98.7%, and it can meet the grading requirements.
This research provides solutions for the poor uniformity of the potato seeds outputed from the cutting machine, and provides a high efficiency and grading precision grading device installed on the potato seed cutting machine to grade the potato seed before cut.
[1] Li Z H, Wen X Y, Lv J Q, et al. Analysis and prospect of research progress on key technologies and equipments of mechanization of potato planting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(3): 1-16.
[2] Yang R B, Zhang X, Li J D, et al. Parameter optimization and experiment on cone canvas belt type seed-metering device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of CSAE), 2016, 32(3): 6-13.
[3] Lv J Q, Yang X H, Li Z H, et al. Design and test of seed potato cutting device with vertical and horizontal knife group[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2020, 51(8): 89-97.
[4] Yu Z G, Rao W H, Ao L L, et al. The main problems of potato seed cutting should pay attention to[J]. Practical Technology, 2018(4): 53.
[5] Ren P. Application of potato seed cutting cultivation technology[J]. Agricultural Technology Service, 2017, 34(3): 45-45, 201.
[6] Kang W Q, Fan M S, Ma Z, et al. Luxury absorption of potassium by potato plants[J]. American Journal of Potato Research, 2014, 91(05): 573-578.
[7] Wang X Y, Sun J B, Xu Y C, et al. Design and experiment of potato cleaning and sorting machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(10): 316-322.
[8] Lv J Q, Yu J Y, Feng X, et al. Design and experiment of roller potato grading machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2019, 50(2): 323-332.
[9] Du H W, Deng L M, Han Z Z, et al. Study on mechanical device of carrot intelligent grading machine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015, 37(10): 124-127.
[10] Shen C J, Jia S X, Zheng X, et al. Actuality and development of jujube grader[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2013, 34(01): 26-30.
[11] Xiong P Y, Yuan J P, Xiao J W, et al. Structural design of the grader of winter planting potato in south China[J]. Journal of Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Engineering, 2011, 24(2): 61-63.
[12] Liu H Y, Zhu X M, Tan H L, et al. The design of potato grading production line and its key equipment[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2010, 32(4): 84-86.
[13] Xiao W Z, Gao Y C, Chen H X, et al. Design and test of a small potato pickup and grading machine[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2019, 41(12): 130-134.
[14] Zhou X R. Experiment Research and Mechanism Analyse on Factors Affecting the 5BF-3-sized Fruit Grading Rate[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2006.
[15] ShenTu L F, Wei Q, Gong Z G, et al. Design of potato sorter[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2014, 36(8): 114-117.
[16] Zhang H. Design and Cleaning Test of Dry and Low Damage Sorting Machine for Potato[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2018.
[17] Yang R B, Yang H G, Shang S Q, et al. Design and test of poking roller shoving type potato harvester[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(7): 119-126.
[18] Wei Z C, Li X Q, Sun C Z, et al. Analysis of potato mechanical damage in harvesting and cleaning and sorting storage[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2017, 19(8): 63-70.
[19] The ministry of agriculture of the People's Republic of China. NY/T1066-2006, Potato grade specification[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006.
[20] Jiang Y W, Wei H A, Lu X H, et al. Design of potato tuber sorter[J]. Journal of GanSu Agricultural University, 2017, 52(01): 139-143.
[21] Cheng P F, Yu W Q, Li X Q, et al. The analysis between dynamic pile angle and transportation speed on the transportation equipment of potatoes[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2016, 38(7): 95-99.
[22] Lv J Q, Wei G J, Fan Z A, et al. Design of 4U-2B potato harvester[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2007, 29(9): 87-88.
[23] Sang Y Y, Zhang D X, Zhang M M. Study on bruising damage experiment of potato and finite element analysis[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2008, 13(1): 81-84.
[24] Liu S D, Li Z Z, C X L, et al. A mechanics analysis of south potatoes classification device[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015, 37(4): 48-50.
[25] Liu Q L, Zhao S X, Zhuang W D, et al. Development of integrated potato sorting machine[J]. Journal of Chinese Agricultural Mechanization, 2019, 41(7): 52-57.
[26] Wang C H, Ding Q Y, Li G M. Design of potato classification machines parameters[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2008, 30(9): 103-104.
[27] Feng B. Study on Physical Characteristics and Damage of Potato Tubers at Harvesting Stage[D]. Lanzhou: GanSu Agricultural University, 2018.
[28] Bentini M, Caprara C, Martellir. Harvesting damage to potato tubers by analysis of impacts recorded with an instrumented sphere[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2006, 94(1): 75-85.
[29] Shi L R, Sun W, Zhao W Y, et al. Parameter determination and validation of discrete element model of seed potato mechanical seeding[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(6): 35-42.
[30] Sun J, Yu W Q, Li X Q, et al. Analysis and calculation method of potato sorting conveyor line statics[J]. Food & Machinery, 2015, 31(5): 89-92.
[31] Pan L J, Chen J Q. Experiment Design and Data Processing[M]. Nanjing: Southeast University Press, 2008.
[32] Ge Y Y. Test Design Methods and Design-expert Software Application[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2014.
马铃薯种薯切块机分级装置的设计与试验
吕金庆1,2,温信宇1,李紫辉1,李季成1,刘中原1
(1. 东北农业大学工程学院,哈尔滨 150030;2. 黑龙江八一农垦大学工程学院,大庆 163319)
针对传统马铃薯种薯切块机存在的切块均匀性差、不便于直接进行播种的问题,设计了一种安装在马铃薯种薯切块机上的分级装置。对分级装置的结构和工作原理进行了阐述,通过力学分析和运动分析确定了分级装置分级辊拨轮各部分的结构参数。选取分级辊组组数、分级辊组转速、上料量为试验因素,分级精度为试验指标进行正交试验,并用Design-Expert 8.0.6软件对试验结果进行分析,确定较优参数组合为分级辊组组数为7,分级辊组转速为110 r/min,上料量为40 t/h,并对较优参数组合进行了验证试验,验证试验结果表明在较优参数组合下的分级精度为98.7%,能够满足分级要求,该研究提供了一种用于马铃薯种薯切块机上的高效率、高分级精度的分级装置。
设计;试验;马铃薯;切块机;分级装置;力学分析
Lyu Jinqing, Wen Xinyu, Li Zihui, et al. Design and experiment of the grading device for a potato seed cutting machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2020, 36(20): 76-83.doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.20.010 http://www.tcsae.org
吕金庆,温信宇,李紫辉,等. 马铃薯种薯切块机分级装置的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(20):76-83. (in English with Chinese abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.20.010 http://www.tcsae.org
date:2019-11-27
date:2020-10-09
National Key Research and Development Plan (2016YFD0701600, 2017YFD0700705); China Agriculture Research System Special Foundation (CARS-09-P23); Heilongjiang Province Potato Industry Technology Collaborative Innovation and Promotion System.
Lyu Jinqing, professor, mainly engaged in potato mechanization technology and equipment research. Email:ljq8888866666@163.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2020.20.010
S226.8
A
1002-6819(2020)-20-0076-08
