Meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy and safety of Urinary Kallidinogenase in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction
2020-11-27YuanQinQianYiHuiHuiShiYaLinQiJingYueHuChongqingMentalHealthCenterGeleshanwardeightwardChongqing400036ChinaMilitaryArmyMedicalUniversityThirdMilitaryMedicalUniversityDapingHospitalNeurologyChongqing40000China
Yuan Qin,Qian Yi,Hui-Hui Shi,Ya-Lin Qi*,Jing-Yue HuChongqing Mental Health Center,Geleshan ward eight ward,Chongqing 400036,China.Military Army Medical University(Third Military Medical University)Daping Hospital Neurology,Chongqing 40000,China.
Abstract Objective: To evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of Urinary Kallidinogenase for Injection in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction.Methods: PubMed,The Cochrane Library,Embase,CNKI,VIP,Wan Fang and bibliographic database of Chinese medicine were searched by computer to collect randomized controlled trials of Urinary Kallidinogenase 's treatment of acute cerebral infarction.The time limit was set up until September 2019.At the same time,the references and grey literature in the literature were manually screened.Two independent researchers were screened,evaluated and extracted according to inclusion and exclusion criteria.Meta-analysis was carried out by RevMan 5.3 software.Results: A total of 17 randomized controlled trials involving 2,066 patients,including 1,033 in the experimental group,and 1,033 in the control group.meta-analysis results showed that compared with the conventional treatment,Urinary Kallidinogenase had better effect in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction [OR=3.26,95%CI (2.56,4.16), P <0.00001];the national institule of Health Stroke Scale of the Urinary Kallidinogenase group was significantly better than that of the control group.Urinary Kallidinogenase group activity of daily living scale was better than the control group[OR=21.33,95%CI(6.64,36.01),P=0.004];a total of 7 articles reported adverse reactions,including 19 cases in the trial group and 21 cases in the control group,the main adverse reactions were blood pressure drop,other symptoms were chest tightness,facial redness,dizziness fever,nausea and vomiting,arrhythmia,and no other serious adverse reactions.It can recover itself.Conclusion:the available evidence shows that Urinary Kallidinogenase can effectively improve the symptoms of neurological deficits and improve the ability of daily living in patients with acute cerebral infarction,and is safe.However,the quality of the study is limited.
Keywords:Human urinary kallikrein,Urinary Kallidinogenase,Acute cerebral infarction,Randomized controlled trial,meta-analysis
Background
At present,stroke has become the first cause of death in China.It is also an important cause of disability.Its main clinical manifestations are disturbance of consciousness,dysfunction and other symptoms.It has a high disability rate and mortality rate [1].Cerebral infarction,also known as ischemic stroke,is caused by local cerebral vascular supply disorders leading to hypoxic degeneration and necrosis of the brain tissue,resulting in a corresponding clinical neurological deficit 80%,which accounts for all stroke types,is used in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction.In addition to recombinant tissue plasminogen activator(rt-PA),an antiplatelet drug aspirin and thrombolytic drugs,has become an international guideline for grade A and grade I recommendation.The evidence for other drugs is not yet sufficient.Therefore,it is of great significance to study new drugs for improving cerebral circulation and protecting brain function.
Urinary Kallidinogenase,also known as the human Urinary Kallidinogenase (trade name,Kai Likang),is a serine proteinase composed of 238 amino acids extracted from the urine of healthy men.It is a new class I drug developed in recent years in China.It has been shown that the drug has a certain dose under certain dose.It can expand the small artery in ischemic area,increase blood flow in ischemic brain tissue,and improve cerebral circulation in 10 years.In October 2005,it was approved by The State Food and Drug Administration and widely used in clinical practice.In recent years,the drug has been more widely used in China,and the corresponding clinical randomized controlled trials (RCT) are also increasing,but the research quality is uneven,so it is necessary to carry out systematic evaluation to provide evidence-based medical evidence for it.
Materials and methods
Search strategy Computer
Search strategy retrieves databases such as PubMe d,The Cochrane Library,Embase,CNKI,VIP,Wa n Fang and Chinese biomedical literature database.Registry from inception to September 2019.“Stro ke” and Chinese search terms such as “Urinary K allidinogenase”,“human urinary kinase” and “cereb ral infarction” were retrieved by combining themati c words and free words.
Inclusion criteria
(1) Study type:RCT,whether or not use blindness.Language is restricted to Chinese and English.
(2) The subjects met the diagnostic criteria of cere bral infarction diagnosed by the Fourth National C onference on cerebrovascular diseases,and confirm ed by cranial computed tomography (CT) and/or magnetic resonance Imaging(MRI)patients with a cute cerebral infarction within 72 hours had no ge nder or age.No strict gravity center,liver or kidn ey insufficiency,no systemic bleeding or bleeding tendency.
(3) The intervention group adopted the same routine treatment,including lowering blood fat,anti-platelet aggregation,nourishing brain cells and improving the cerebral circulation.The experimental group was additionally given Urinary Kallidinogenase,while the control group was given placebo,inactive or active drugs on the routine treatment.Two groups were given the same treatment.
(4) Outcome measures:effective rate:the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) was used to evaluate the improvement of neurological deficits at the end of treatment.The following criteria were adopted to improve the degree of improvement:the basic cure was:the neurological deficit score was reduced by 90%-100%,the disability degree was 0 grade;significant progress was achieved:the neurological impairment score was reduced by 46%-89%,and the disability degree was 1-3;progress:neurological deficit score decreased by 18%-45%;no change:neurological impairment score decreased or increased by 18%;deterioration:neurological impairment score increased 18%.Improved conversion to classification variable effective and invalid,which will be effectively defined as basic cure,significant progress and progress,Total Efficiency=(Basic Cure+Significant Progress +Progression/Total Number)×100%;NIHSS score;3 activity of daily living scale(ADL)score.
(5) Adverse reactions were defined as intracranial hemorrhage,extracranial blood,allergies,and unexplained organ dysfunction.
Exclusion criteria
(1)Non randomized controlled trials.
(2)There is no clear diagnosis,inclusion and exclusion criteria.
(3) The course of treatment is inconsistent and there is no definite criteria for evaluating the therapeuticeffect.
(4)Repeated published studies.
Data extraction
Extraction were carried out separately by two researchers,and the data were screened and extracted.If there were differences,reference was made to third people's opinions.The relevant documents were retrieved into the literature management software NoteExpress to read the titles and abstracts,and the articles that did not meet the inclusion criteria were carefully read out and screened again.Finally,the data included the first author or information provider,date of publication,age,time of entry,sample size,intervention measures,course of treatment,and outcome criteria.
Quality evaluation
According to the bias risk assessment method recommended in the Cochrane Systematic Review Manual 5.1.0,bias risk assessment method included bias risk assessment for RCT.The main items were:1)randomization scheme;2) group concealment;3) blind method;4) incomplete data report;5) selective outcome report;6) other bias sources.Each item was evaluated by “low bias risk”,“high bias risk” or“inability to judge”.
Statistical analysis
Meta-analysis was performed using RevMan 5.3 software.Mantel-Haenszel method was used for statistical analysis.Heterogeneity between the studies was explored by Q test andI2test,ifP>0.1 orI2<50%,which is considered to be of low heterogeneity and analyzed by fixed effect model,ifP≤0.1 orI2≥50%,it is considered that heterogeneity is significant.The causes of heterogeneity were also analyzed.The test standard wasP< 0.05.In this paper,two categories of variables are selected.Odds ratio (OR)and 95%confidence interval(CI)are used as statistical analysis variables to draw funnel plots for publication bias detection.
Statistical analysis
The sensitivity analysis of meta-analysis was mainly used to judge whether the statistical effect size was stable and whether it had an impact on the combined results,including the shear and complement method,the removal of single study method,the loss of safety number method,and the replacement model analysis method.It mainly includes the method of scissor compensation,single research method,loss of safety number method and replacement model analysis method.In this paper,the replacement mode analysis method is applied,namely,the meta effect of the combined effect volume of the included literatures is analyzed by the fixed effect model.Then the random effect model is used to calculate the point estimates and interval estimates of the combined values of the effects,and then the changes of the final effect of the two models are observed.If the results are not significant,the results of the meta-analysis are stable and reliable.
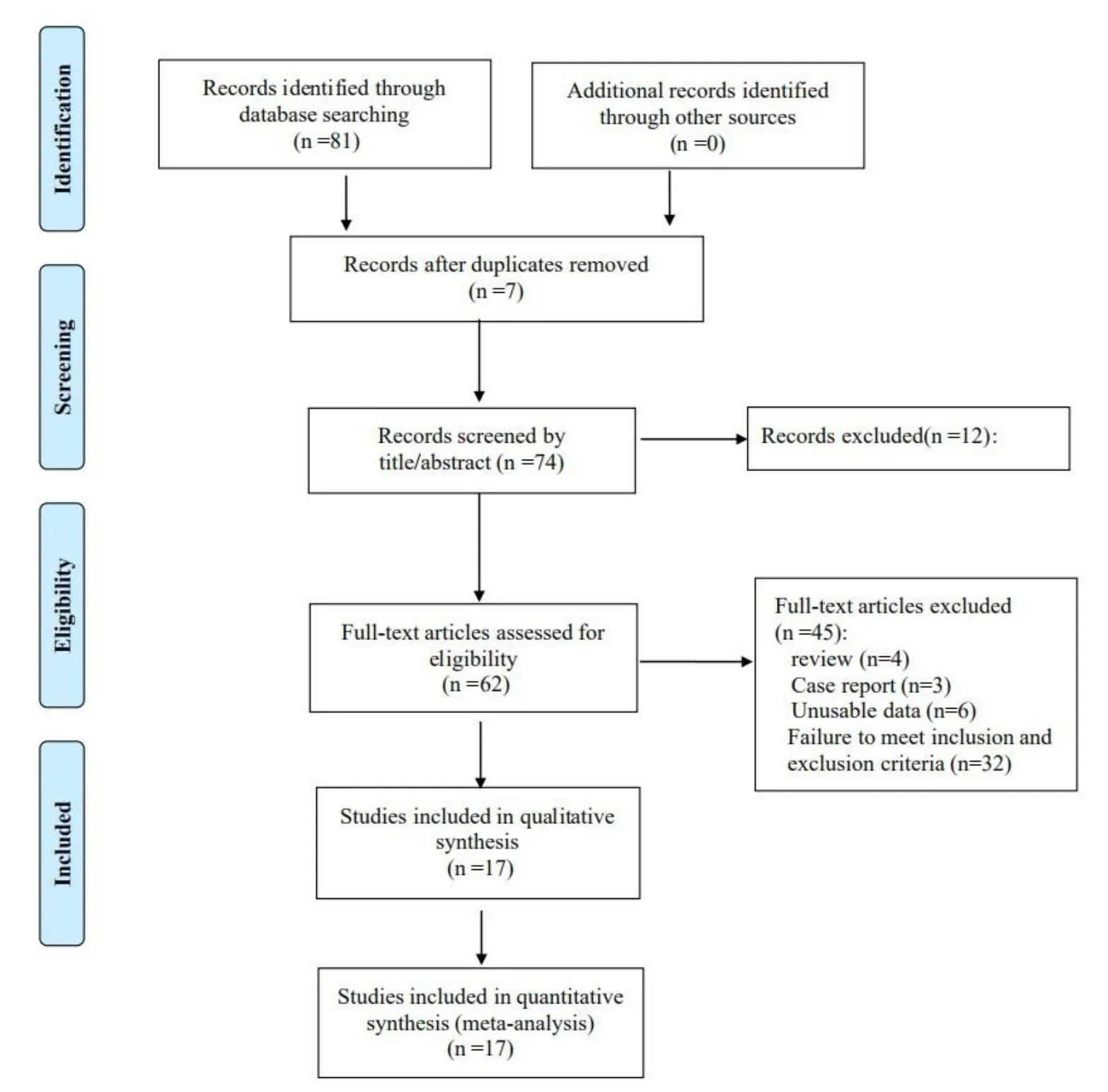
Figure 1 Flow chart of literature screening
Results
Document search results
A total of 81 related articles were retrieved from Chinese and English databases,excluding repetitive reading topics and abstracts.62 articles were obtained,and the full text was screened and screened.4 articles were excluded,3 cases were reported,6 articles were not available,32 articles did not meet the inclusion criteria,and 17 papers [2-17]were finally included in the meta-analysis.All of them were Chinese literatures.(Figure 1).
Basic characteristics of literature
17 articles included [2-18].There were 1,033 cases in the trial group and 1,033 cases in the control group.All the studies were conducted in China,including 2 trials[5,8].7 patients were included in the onset of 24 hours[2,10-12,15-17].8 patients were included in the onset of 48 hours [3,4,6,7,9,13,14,18].All the.17 studies included in the onset of 72 hours were all nonplacebo controlled trials.They all explained the basic medication regimen,including lowering blood fat,antiplatelet aggregation,nourishing brain cells and improving cerebral circulation.All the experimental groups were injected with Urinary Kallidinogenase 0.15 pentose nucleic acid (PNA)+0.9% sodium chloride solution 100ml intravenous drip on the basis of the control group,once a day,and 14 days as a course of 16 study,respectively.All patients in the 17 group were given intravenous drip [2-14,16-18].The NIHSS was used to evaluate the improvement of neurological deficit at the end of treatment.The improvement degree was converted into categorical variable effective and invalid,Total Efficiency=(Basic Cure+Significant Progress+Progression/Total Number) × 100%.Fourteen studies reported detailed NIHSS score values [2-10,12-15,18].The detailed ADL score is reported for 4 studies [8,13,14,17].Three of the 17 studies reported no adverse reactions[11,17,18].No adverse reactions were reported in 8 studies [3,5,7,8,12-14].Adverse reactions were reported,including 3 cases of chest tightness,4 cases of facial redness,6 cases of blood pressure drop,2 cases of dizziness and fever,2 cases of nausea and vomiting,3 cases of arrhythmia,and no other serious adverse reactions.Baseline information on age,sex,onset time and degree of neurological impairment were all comparable in all studies(P>0.05)(Table 1).
Document quality evaluation results
According to the bias risk assessment tool of Cochrane collaboration,the bias risk was assessed in the literature.The bias was as follows (Figure 2).Among them,4 were articles [8,12-14].Describe the allocation of 1 papers using random number method[2].Using the envelope method,the rest of the literature only represents random grouping,and the specific allocation method is not described in the 17 literature [2-18].There was no clear description of whether allocation concealment and blindness were applied,the outcome data was complete and there was no selective report result.In conclusion,the risk of most literature bias in the meta-analysis was notclear.
Meta-analysis results
Comparison of clinical efficacybetweenthe Urinary Kallidinogenase group and the control group.The 16 articles were included [2-14,16-18].The NIHSS score was improved.Conversion to categorical variables was effective and invalid,Total Efficiency=(Basic Cure+Significant Progress +Progression/Total Number) × 100%.Extracted data for heterogeneity test,P=0.71,I²=0%,and heterogeneity was small,and fixed effect model was used for metaanalysis.Results showed that the effective rate of Urinary Kallidinogenase group (87.70%) was significantly higher than that of control group at the end of treatment (70.44%):combined effect OR=3.26,95%CI [2.56,4.16],P< 0.00001.The difference between the two groups was statistically significant(Figure 3).
Comparison of NIHSS scores between Yuri Clin group and control group.A total of 14 articles were included [2-10,12-15,18].Including 1,538 patients,770 in the experimental group and 768 in the control group.The meta-analysis of the random effect model showed that the NIHSS score in the Urinary Kallidinogenase group was significantly better than that in the control group [OR=-2.56,95%CI(-4.13,-0.99),P=0.001].The difference was statistically significant(Figure 4).
Comparison of ADL scores between Urinary Kallidinogenase group and control group.A total of 4 articles were included [8,13,14,17].Including 384 patients,192 in the experimental group and 192 in the control group.The meta-analysis of the random effect model showed that the ADL score in the Urinary Kallidinogenase group was better than that in the control group[OR=21.33,95%CI(6.64,36.01),P=0.004],the difference was statistically significant(Figure 5).
Comparison of adverse reactions between Urinary Kallidinogenase group and control group.17 studies included[2-18].There are 3 studies[11,17,18].No adverse reactions were reported.7 studies [3,5,7,8,12-14].The adverse reactions were reported.The data were extracted from Urinary Kallidinogenase group(19 cases) and control group (21 cases).The adverse reactions of the two groups were compared,and the results of heterogeneity test showed that:P=0.89,I2=0%,the heterogeneity was small,and the fixed effect model was used for meta-analysis.The results of metaanalysis showed that:OR=0.90,95%CI [0.48,1.69],P=0.75.It was suggested that the incidence ofadverse reactions in the two groups was not statistically significant.Considering the length of time involved in the onset of the disease,the results of adverse reactions were affected.Considering the difference in the onset time of the patients included,the results of adverse reactions were affected.Therefore,the subgroup analysis was conducted according to the onset time of the patients ≤24 hours and ≤ 72 hours,and no significant change was observed(Figure 6).
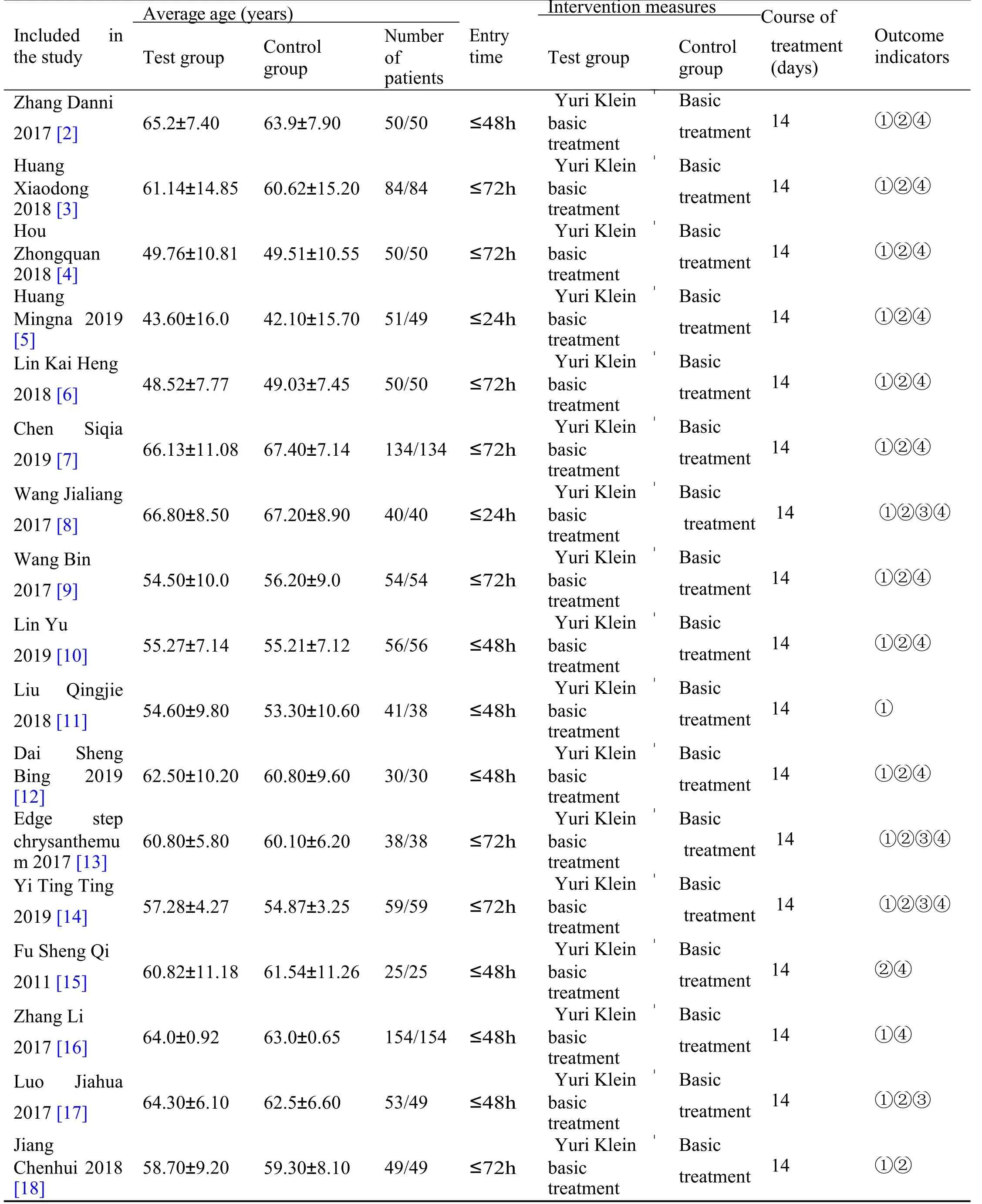
Table 1 Basic information of literature
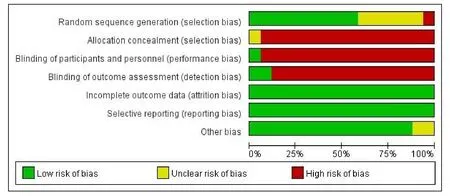
Figure 2 Document quality evaluation form
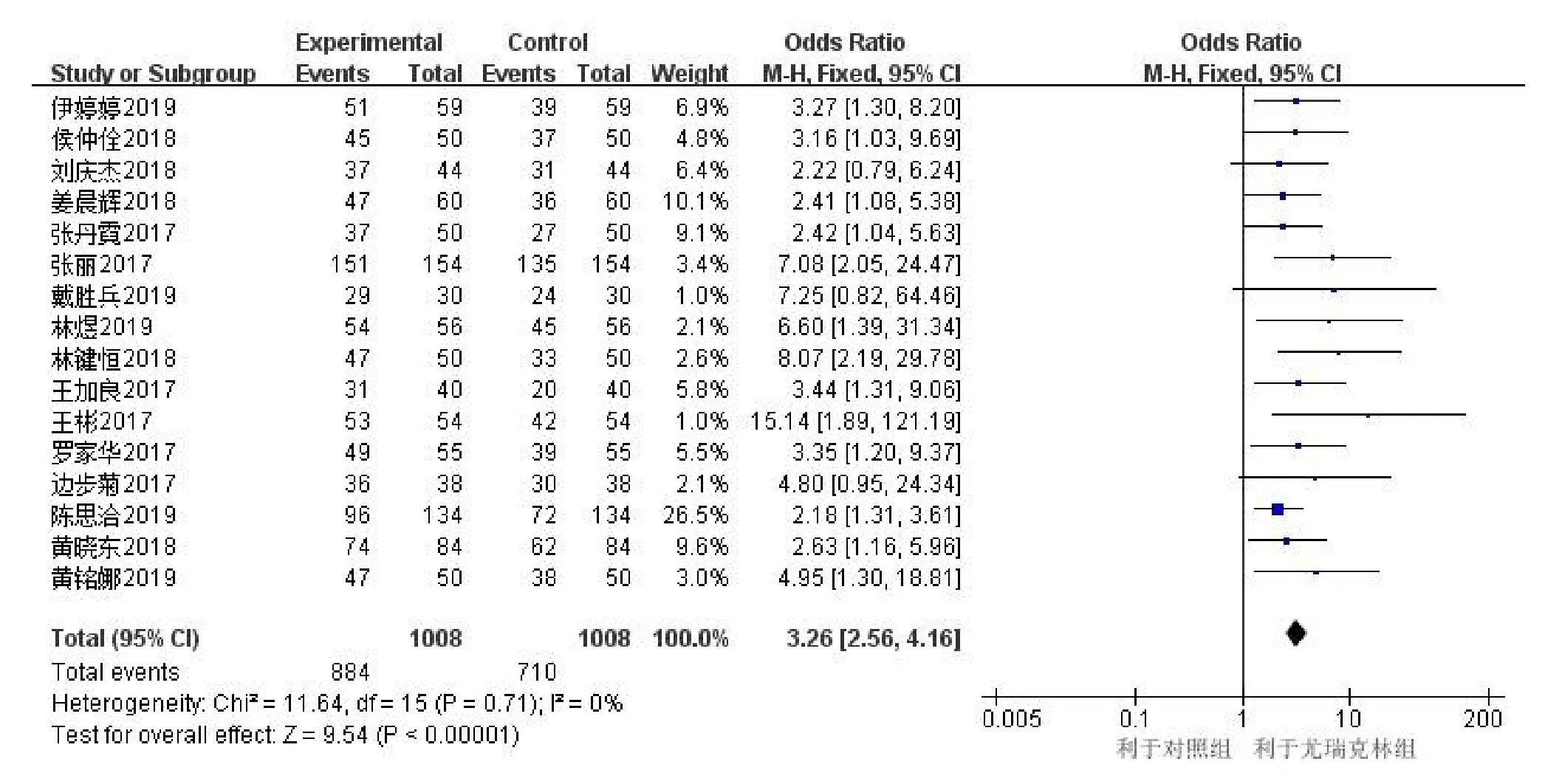
Figure 3 Urinary Kallidinogenase’s clinical analysis of acute cerebral infarction
Publication bias
Funnel plots were drawn for publication bias based on the outcome indicator of efficiency.The funnel plots showed a notch in the lower left corner,indicating the possibility of publication bias (Figure 7).It was considered that the included studies were too few,the sample size was small,and the quality of the included literatures was low.
Sensitivity analysis
After the fixed effect model was changed to a random effect model,the effect volume was recombined.The results showed that there was no significant change in the effective rate,the combined effect volume or value,95%ci and forest map of the two groups,indicating that the combined effect was more stable.
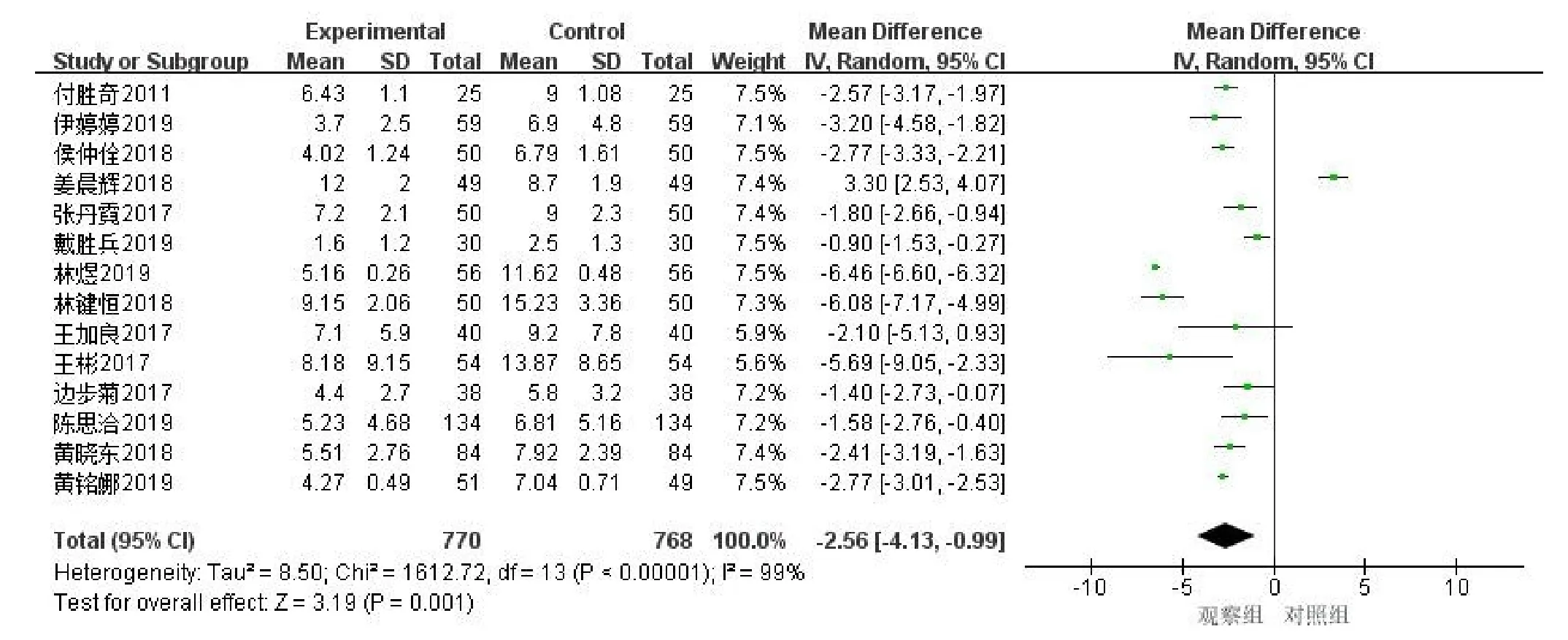
Figure 4 Urinary Kallidinogenase’s national institutes of health stroke scale of acute cerebral infarction
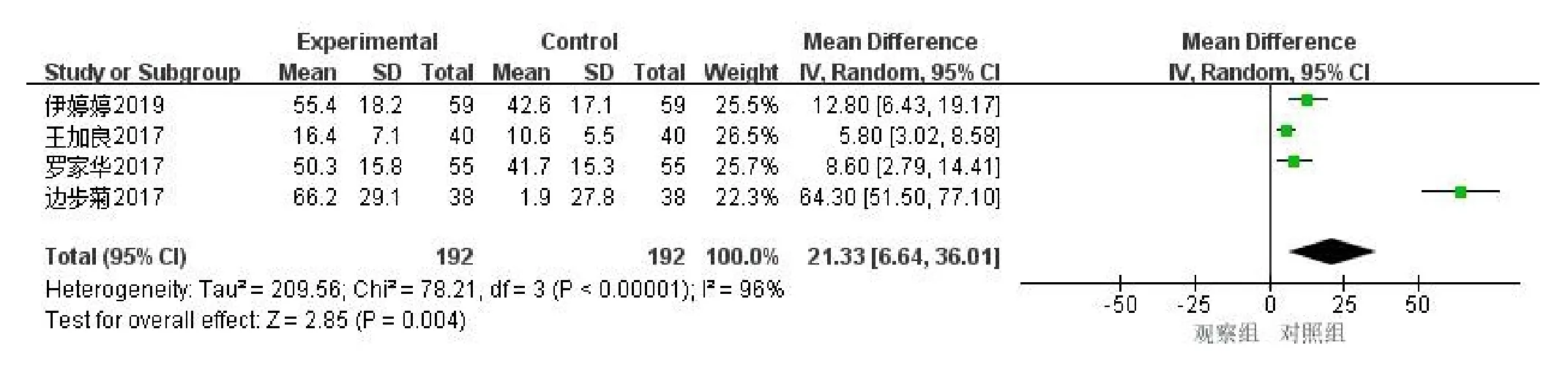
Figure 5 Urinary Kallidinogenase forest’s activity of daily living score of acute cerebral infarction
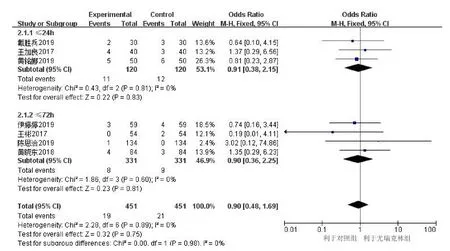
Figure 6 Forest diagram of adverse effects of Yuri Klein on acute cerebral infarction
Discussion
Acute ischemic stroke is the most common stroke type,which seriously affects the life and quality of life of patients.In recent years,the incidence of acute cerebral infarction has been increasing year by year and younger.Although the mortality rate of patients with acute cerebral infarction has decreased with the progress of medicine,most of them have left neurological deficits and affect their quality of life in the future.It brings great pain to patients and families[19].After acute cerebral infarction,there are a series of physiological changes in the body,including aggravation of brain edema,thrombocytopenia and platelet activating inducer activity.The formation of micro thrombus will further aggravate cerebral ischemia and hypoxia [20].At present,the early treatment of acute cerebral infarction is the first choice for thrombolysis,followed by interventional therapy,including mechanical thrombectomy,carotid endarterectomy and stent implantation.Although these therapies can make vascular recanalization,there are strict time windows.At present,the treatment schemes that exceed the time window mainly include defibrillator,anti-platelet agglutination,nutritive nerve,traditional Chinese medicine,rehabilitation treatment,etc.,but there are no other effective treatment schemes at present.In recent years,the concept of collateral circulation has been widely applied to the treatment of acute cerebral infarction.Even after carotid artery ischemia,compensatory compensation can be made to different degrees of ischemic brain tissue.The establishment of collateral circulation can effectively reduce the death rate of cerebral infarction and improve the prognosis [21].Therefore,in the acute stage of cerebral infarction,how to save the ischemic penumbra and promote the establishment of collateral circulation is of great significance for improving the prognosis of patients and improving the quality of life of patients.
Urinary Kallidinogenase,namely human urine excitation peptide enzyme (commodity called Kai LiKang),is developed in recent years,China’s independent I class of new drugs.It is recommended“Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke in China 2014”.Urinary Kallidinogenase is a tissue type kininase,a glycoprotein extracted from healthy male urine and is a positive regulator in kininase kinin system.It can convert kinin to kallikrein and vasodilation,and kinin and its corresponding receptors bind to nitric oxide cyclic guanosine,prostacyclin cyclic guanosine and other signal pathways,and play a variety of physiological functions,such as dilating blood vessels,improving cerebral oxygen supply,blood supply and energy metabolism.It can effectively improve blood supply in ischemic penumbra area and save ischemic brain cells.A large number of clinical studies have confirmed that Yuri Colin has a good effect in opening collateral circulation,improving neurological symptoms and daily living ability.
The results of this study showed that in the clin ical treatment effect,the total effective rate of Uri nary Kallidinogenase test group in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction was higher than that in t he control group without the application of Urinar y Kallidinogenase(OR=3.26,95%CI [2.56,4.16],P<0.00001),the difference was statistically sign ificant.It suggested that Urinary Kallidinogenase c ould significantly improve the degree of neurologic al deficit.Compared with the incidence of adverse reactions in the two groups,the difference was n ot statistically significant (OR=0.90,95%CI [0.4 8,1.69],P=0.75 >0.05),indicating that in the t reatment of acute cerebral infarction,the adverse r eactions caused by Urinary Kallidinogenase were s imilar to those in the neurology department.The s afety of clinical application is guaranteed.Through the summary of the adverse reactions included in the literature,we can see that the most common adverse reaction of Urinary Kallidinogenase is mil d blood pressure drop,which may be related to th e synergistic effect of the drug and some antihype rtensive drugs.According to the research,ACEI dr ugs can enhance the concentration of hk1 and pro kinin in the blood circulation,and enhance the ant ihypertensive effect.Therefore,during the treatment of acute cerebral infarction,Urinary Kallidinogena se should avoid using ACEI drugs.In the two gro ups,a small number of patients had chest tightnes s,nausea and vomiting,flushing,dizziness,fever a nd so on,most of them were mild,and they coul d relieve themselves without special treatment.
According to the results of the meta-analysis,we did not search for a randomized controlled clinical study of Urinary Kallidinogenase in the treatment of acute cerebral infarction.Most of the research designs in China are not of high quality and lack of rigor.The main findings are as follows:even though all studies are described as randomized controlled trials,only a few have mentioned specific random allocation methods.The distribution of concealment and blindness is not mentioned.The limited number of samples in the literature has a certain effect on the strength of argumentation in this paper.
Conclusion
To sum up,the current evidence shows that Urinary Kallidinogenase can significantly improve the neurological deficit degree and safety of patients with acute cerebral infarction compared with conventional treatment.It is safe and has great significance for improving the quality of life of patients.However,due to the limited quality and quantity of existing research,large sample and high quality randomized controlled trials are needed to provide corresponding evidencebased medical evidence.
杂志排行
Clinical Research Communications的其它文章
- Candidate genes associated with cold-coagulation or heataccumulation blood stasis syndrome in hypertension
- Acute uterine inversion at cesarean section:an emergency condition in obstetrics
- The prognostic value of baseline circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic breast cancer:a meta-analysis
- Research on the aetiology and treatment of premature ovarian insufficiency
