A label-free immunosensor for electrochemical detection of serum biomarker for early stage hepatocellular carcinoma
2020-11-20YANGJiaoLIYingchun
YANG Jiao,LI Yingchun
(School of Science,Harbin Institute of Technology,Shenzhen,Guangdong 518055,China)
Abstract:Objective Golgi protein 73 (GP73),a resident Golgi glycoprotein,is discovered as a serum marker for early hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) recently.GP73 is strongly up-regulated and expressed in HCC with both high sensitivity and specificity.Methods A label-free immunosensor for electrochemical detection of GP73 was prepared,in which GP73 antibody was immobilized on a gold electrode and GP73 antigen was detected quantitatively by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy.Results Electron transfer resistance (Ret) increased linearly with GP73 concentration in the range of 0.001~0.1 ng·mL-1 with the detection limit of 0.002 1 ng·mL-1 (S/N=3).Conclusion The GP73 immunosensor also showed high sensitivity,specificity and good reproducibility,thereby serving as a useful and reliable platform for early diagnosis of HCC.
Key words: immunosensor;GP73;hepatocellular carcinoma;electrochemical analysis;biomarker
1 Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer worldwide[1-2].Despite the development of many novel therapeutic strategies,the five-year survival rate of HCC remains low because HCC is typically diagnosed in later stages and thus associated with high mortality[3-5].Therefore,it is need to explore a new route to detect HCC in high-risk groups at early stages to effectively improve the survival rate.Ultrasound has a high likelihood of being HCC with a sensitivity of 71% and a specificity of 93%;however,its positive predictive value is only 14%[6-8].Examination with ultrasound every six months for the detection of early HCC is recommended in cirrhotic patients and other specific risk groups[1,3,6,9].HCC also can be diagnosed by the coincident findings in two techniques,computed technology (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)[1,10,11].However,the use of CT and MRI are too expensive and invasive.Also,it requires acquiring the degree of expertise for the diagnostic capabilities of the modern equipment.
HCC has been diagnosed by immunological techniques.Immunoblotting is a widely accepted analytical technique to detect specific proteins in the given sample of tissue homogenate or extract[12-13].Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) has been the most popular biomarker for HCC[14-15];it has a sensitivity of 39~64%,a specificity of 79~91%,and a positive predictive value of 9~32% for early HCC[16-17].AFP is often detected in the absence of serious disease,and thus the marker has limited value as an individual indicator of HCC[18].Given the limitations imposed by AFP,a more appropriate marker should be screened for diagnosing HCC.
Golgi protein-73 (GP73),also known as Golgi phosphorprotein 2 (GOLPH2) or Golgi membrane protein 1 (GOLM1),is a newly identified serum biomarker for HCC[12,19,20].GP73 is widely expressed in normal epithelial cells of numerous tissues[21].A recent study showed that GP73 is a potential biomarker for the early detection of HCC with a higher sensitivity than AFP[16].However,AFP and GP73 in the early detection of HCC were tested by semiquantitative western blot[12].The assay is highly effective at detecting low levels but usually takes long analysis time.
Other related techniques include immunostaining and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to detect proteins in tissues and cells[1,22].Gu et.al.has developed a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for quantifying GP73 in serum[23].In this case,the antibody should be labeled using an enzyme or fluorophore.In order to achieve high sensitivity,the amount of enzyme needs to be sufficiently high.These immunological methods have been successful in HCC diagnosis but involve complicated assay process,long analytical time,and a broad range of detecting.These drawbacks necessitate the development of a novel detection method without labeling.
Immunosensors based on antibody-antigen interaction are one of the most widely used analytical techniques in the quantitative detection of biomarker.Electrochemical immunosensors,which exploit the highly specific immunoreaction between antibody and antigen as a transducer,have mounted even greater interest[24-28].Due to their high sensitivity,low cost,suitable miniaturization,and short analysis time,they have been widely used as bioanalytical devices in recent years[27,29,30].Electrochemical immunosensors determine the target molecule level by detecting changes in current[31],potential[32-33],impedance[34-35],or conductance[36-37],caused by immunoreactions between antibodies and antigens.Impedance immunosensor among the electrochemical immunosensors is an especially powerful tool for direct monitoring of immunoreactions because it is less destructive to the activities of the target biomolecules during detection and also has high sensitivity and low detection limits[27-36].
Previously we reported impedance immunosensors using aptamer immobilization on Au electrode for lipopolysaccharide determination,where the sensor showed a wide linear detection range and high sensitivity[38-39].Here we demonstrate a novel immunosensor based on GP73 antibody using direct electrical communication between the antibody and the electrode without any label.We develop the immunosensor with high sensitivity,specificity and stability for GP73 determination to diagnose HCC.The GP73 electrochemical immunosensor is designed to show linear response range that covers at least 100-fold lower than the known median serum level of GP73.Our results suggest that the designed GP73 electrochemical immunosensor could be applicable as an immunosensor for the early diagnosis of HCC.
2 Materials and method
2.1 Reagents
Recombinant non-glycosylated GP73 antigen was purchased from Sino Biologic,Inc.(Beijing,China).GP73 polyclonal antibody produced in rabbit,glucose,ascorbic acid (AA),and glycine,N-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-N′-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC),N-hydroxysuccinimide(NHS),3-mercaptopropionic acid (MPA),bovine serum albumin (BSA) and IgG obtained from human serum were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (US).All other chemicals were analytical grade ones.Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (50 mmol·L-1with 50 mmol·L-1NaCl,pH 7.4) was used as an electrolyte for all electrochemical measurements.All solutions were prepared with deionized water (DI,18.2 MΩ).
2.2 Modification and immobilization of gold electrode
A disk type Au electrode (2 mm in diameter) was polished and sonicated in acetone,alcohol and water each for 15 min,and then treated by piranha solution (a mixture of 3∶1 98% H2SO4and 30% H2O2) for another 15 min.Subsequently,the electrode was electrochemically activated by CV with a range from -0.3 to 1.6 V in 0.5 M H2SO4until reproducible gold oxide stripping peaks were obtained.A 2 mmol·L-1MPA solution was prepared by dissolving 70 μL MPA in 40 mL H2O/ethanol (1∶3 v/v) mixed solvent.The electrode was soaked in this solution overnight to obtain the SAM and then rinsed with ethanol and water[40].After the carboxyl group of SAM was activated by EDC and NHS,the GP73 antibody was immobilized through amine coupling by dropping 10 μL anti-GP73 solution (10 μg·mL-1) onto the electrode surface and incubating for 2 h at 4 ℃.The electrode was then immersed in 1% BSA solution for 1 h to block non-specific binding sites[41].The electrode was then incubated in different concentrations of GP73 solution and washed with PBS solution.The prepared immunosensor was stored at 4 ℃ when not in use.
2.3 Characterization of immunosensor
All electrochemical measurements were performed with a VSP potentiostat (Princeton Applied Research,US) at room temperature.A three-electrode system was employed with the antibody-modified electrode as a working electrode,a platinum plate as a counter electrode,and an Ag/AgCl in saturated KCl solution as a reference electrode.For the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) studies,we applied a 5 mV alternating current (AC) amplitude potential superimposed on the appropriate direct current (DC) potential,and a wide frequency range from 10 kHz to 100 mHz was scanned.Analysis of the EIS data was performed by selecting the appropriate models using ZSimpWin©.
3 Result and Discussion
The GP73 immunosensor was prepared by immobilizing GP73 antibody by amine coupling on gold electrode coated with self-assembled monolayer of MPA and further modified with BSA in order to block non-specific binding sites.The fabricated procedure was shown in Scheme 1.The electrochemical behavior of each modification process was monitored by EIS and cyclic voltammetry (CV),respectively.For GP73 detection,EIS was used to quantify the response signal of antibody-antigen immunoreactions in the presence of [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-as a redox probe.

Scheme 1 The synthesis process of the immunosensor
In EIS,the impedance plot is semicircular in the high-frequency region related to electron transfer-limited process;in the low frequency region,a Warburg line corresponds to the diffusion step of the overall process.The diameter of the semicircle is equal to the electron transfer resistance (Ret).TheRetvalue increased rapidly during the first 5 min and then reached at asymptotic value.So,all the electrodes were immersed in the sample solution for 5 min,and the impedance data were obtained.Retvalue of a bare Au electrode is 146 Ω (Figure 1 A curve a).Upon SAM formation of MPA,theRetincreased to 3093 Ω (Figure 1 A curve b).After anti-GP73 was covalently immobilized on the electrode surface through amine coupling,theRetalso increased to 6369 Ω (Figure 1 A curve c) since it acts as an insulating layer which inhibits electron transfer and hampers the [Fe(CN)6]3-/4-redox probe close to the electrode surface.TheRetfurther increased to 8092 Ω after BSA blocking layer formation for the non-specific binding sites (Figure 1 A curve d).EIS represents a powerful method for probing the interfacial reaction at electrode surfaces[24-25],providing a rapid approach for monitoring the dynamics of biomolecular interactions.

containing 2 mmol·L-1 Fe(CN)63-/4-:(curve a) bare Au;(curve b) MPA/Au;(curve c) anti-GP73/MPA/Au;(curve d) BSA/anti-GP73/MPA/Au.Inset:Equivalent circuit
Each modification step (BSA/anti-GP73/MPA/Au) was also confirmed by CV (Figure 1B).The redox probe exhibited reversible CV curve at the bare Au electrode (curve a);after the MPA monolayer was assembled (curve b) the peak current decreased very little.These results indicated that the MPA was thin enough to be favorable for electron tunneling current.The data shows that the peak current (Ip) decreased and the peak potential separation (ΔEp) increased in each step.A clear decrease ofIpand an increase of ΔEpwere observed when anti-GP73 was immobilized on the MPA modified electrode surface (curve c),which indicated that the large antibody molecules hindered the electron transfer process of the redox probe in solution[30].
After BSA was introduced in order to block non-specific binding sites,a further decrease ofIpwas observed,and ΔEpreached 412 mV (curve d).This value corresponds to a slow electron transfer process.The CV data was in good agreement with the EIS data (see in Figure 1 A),but the EIS method showed a much higher sensitivity to the surface assembly.

a:20、b:50、c:100、d:300、e:500、f:700、g:1 000 mV/s
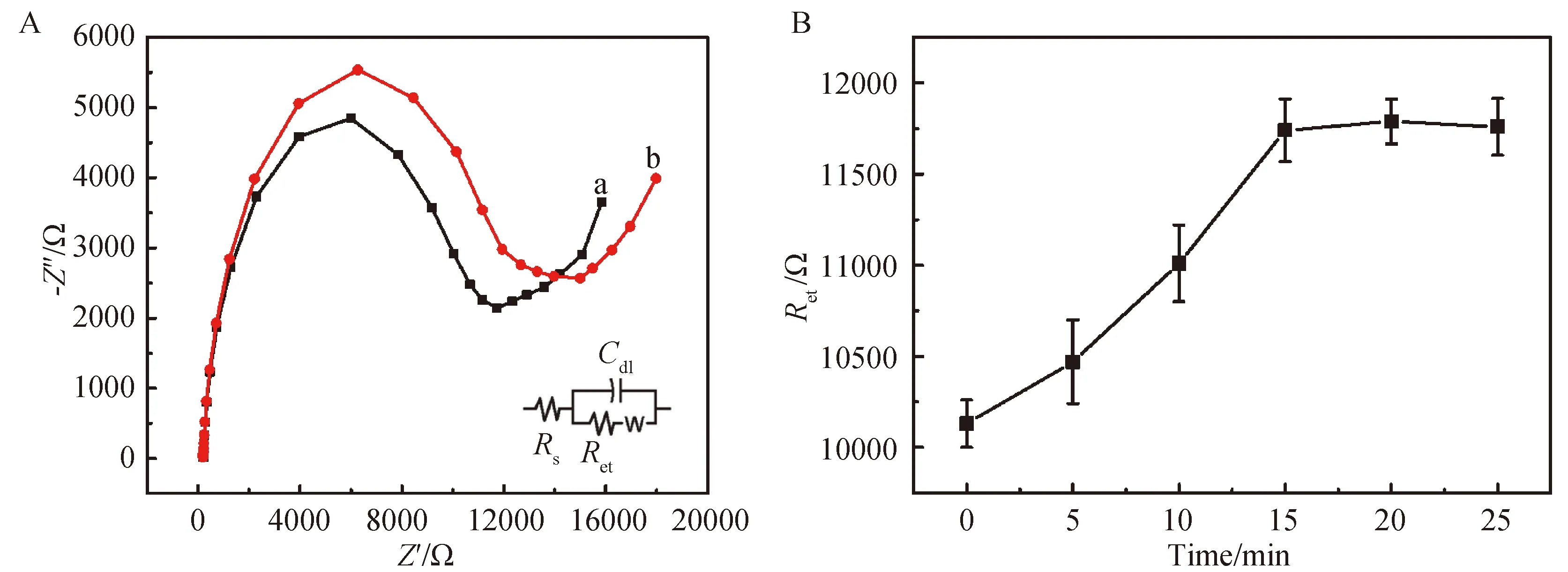
Figure 3 A—Nyquist diagrams of BSA/ anti-GP73/MPA/Au before a and after b incubated in GP73 solution for 15 min B—The effect of incubation time on the Ret response of the immunosensor (n=3)
CV curves of modified immunosensors at various scan rates are shown in Figure 2A.Both anodic and cathodic peak currents exhibited a linear relationship with the square root of the scan rate in the range of 20~1 000 mV/s (in Figure 2B),indicating a diffusion-controlled redox process[42].The peak potential was slightly changed with increasing scan rate.Our data suggest that the BSA/anti-GP73/MPA/Au electrode was well prepared.
Figure 3 A showed the EIS curve after the immunosensor incubated GP73 for 15 min,theRetclearly increased due to the formation of immunocomplex which blocking the tunnel for mass and electron transfer.The influence of incubation time on immunosensor performance is investigated.Figure 3B showed theRetchange as a function of incubation time.It’s obviously found that theRetvalue increase rapidly at first 15 min and then tend flat.Thus,we chose 15 min as optimal incubation time for antigen determination.

The linear relationship between Ret and logarithm of GP73 concentration (n=3)
The impedance responses of the immunosensor in PBS containing different concentrations of antigens are shown in Figure 4 A.The calibration curve between antigen concentration andRetshowed thatRetincreased with increasing concentrations of GP73,andRetleveled off until the concentration reached 0.1 ng·mL-1.The linear relationship ofRetas a function of GP73 concentration in a log scale was obtained as shown in Figure 4B.The linear range was from 0.001 to 0.1 ng·mL-1with a correction coefficient of 0.9940 and a detection limit of 0.0021 ng·mL-1(signal to noise ratio of 3).Ozkan and his coworkers[43]reported the diagnostic and prognostic validity of GP73 in HCC.They determined the serum levels of GP73 in patients with HCC and compared them with AFP levels.The median serum GP73 levels were 0.21 ng·mL-1in those with HCC.The developed immunosensor shows much wide range and lower detection limit.It is suggested that the designed sensor may be used as an immunosensor for the early diagnosis of HCC.
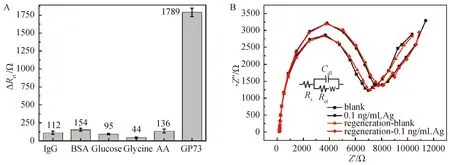
Figure 5 A—Ret response of the immunosensor to 50 μg·mL-1 IgG,500 μg·mL-1 BSA,1 mg·mL-1 glucose,1 mg·mL-1 glycine,1 mg·mL-1 ascorbic acid (AA) and 0.1 ng·mL-1 GP73,respectively (n=3) B—The regeneration measurements of the developed immunosensors
Selectivity plays an important role in sensor performance.In this study,the selectivity of the immunosensor was investigated in the presence of potential interferents,such as glucose,glycine,ascorbic acid (AA),BSA,and IgG.These interferents are typically selected for the testing of immunosensor selectivity[29-30].Based on the literature,the concentration of interferents was chosen as follows:1 mg·mL-1for glucose,glycine and AA,500 μg·mL-1for BSA and 50 μg·mL-1for IgG.The concentration of GP73 was 0.1 ng·mL-1.The DRetchange after immunosensor incubation with different species is shown in Figure 5 A.The result showed that interferent species at relatively high concentrations did not produce any significant effects in sensor response;the maximum DRetinterferent vibration observed with BSA was less than 9%.This result indicated that the selectivity of the designed immunosensor was acceptable.
The regeneration of the immunosensor was performed by immersing the electrode in 0.2 M glycine-HCl solution for 5 min,then rinsing it three times with DI water.In these conditions,the protein molecules become partly unfolded and positively charged,which causes the protein binding sites to repel each other[44].In our case,the antibodies released the bound antigen after the electrode was treated with glycine-HCl solution and the sensor was regenerated.The immunosensor was regenerated acceptably,with about 95% regeneration (3 regenerations and measurements) (Figure 5B).The immunosensors stored in PBS at 4 ℃ for 3 weeks and retained 85.2% of their initial response.The signal decrease could be due to the loss of antibody activity.Study on real sample of patients with HCC is now underway,and we will demonstrate the possibility for medical application in future research.
4 Conclusions
We prepared an impedance immunosensor for detection of the GP73,which is an early HCC serum marker.The GP73 antibody was successfully immobilized on a MPA self-assembled gold electrode.The impedance signal of the antibody-antigen reaction increased linearly with anti GP73-concentrations.The sensor showed a good performance for GP73 determination with a wide range of 0.001~0.1 ng·mL-1.The immunosensor provided high sensitivity,specificity,good reproducibility,and facile synthesis.The GP73 immunosensor is the first electrochemical immunosensor based on GP73 antibody immobilized on gold electrode and would be applicable for early diagnosis of HCC.
