G试验对侵袭性真菌感染新生儿早期筛查价值分析
2020-11-09何景东陈秀莲庞海明
何景东 陈秀莲 庞海明

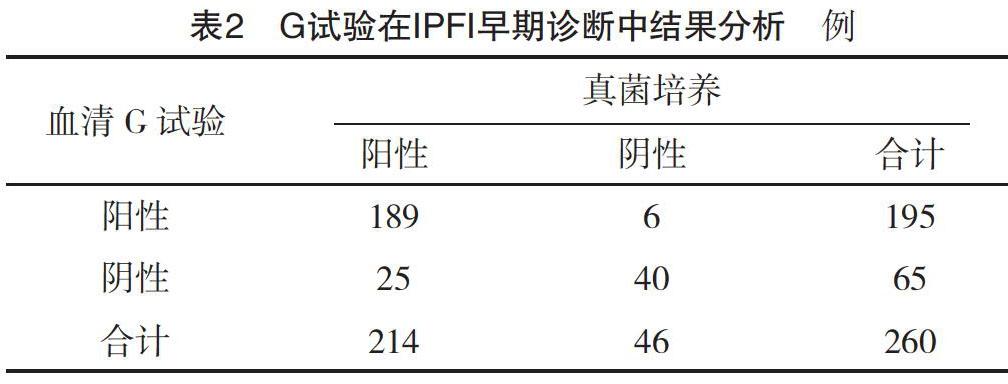
【摘要】 目的:探讨G试验对侵袭性真菌感染(IPFI)新生儿早期筛查价值。方法:选取2016年1月-2019年6月本院收治的疑似IPFI新生儿260例作为真菌感染组,选取同期本院117例细菌感染新生儿作为细菌感染组,另选取本院同期健康新生儿54例作为对照组。三组均进行G试验,比较三组血清1,3-β-D葡聚糖水平。以真菌培养结果为诊断金标准,比较IPFI与非IPFI患儿的血清1,3-β-D葡聚糖水平,分析G试验在IPFI新生儿早期筛查中的价值。结果:真菌感染组血清1,3-β-D葡聚糖水平均高于细菌感染组与对照组(P<0.05)。真菌感染组中,IPFI患儿214例,非IPFI患儿46例。IPFI患儿的血清1,3-β-D葡聚糖水平高于非IPFI患儿(P<0.05)。214例IPFI患儿致病菌均为念珠菌属,其中白色假丝酵母菌与近平滑假丝酵母菌占比较高。G试验对IPFI诊断的敏感度为88.32%、准确度为88.08%、特异度为86.96%。结论:G试验在IPFI新生儿早期筛查中具有较高诊断价值,可作为临床对IPFI的早期预警指标,值得临床推广。
【关键词】 G试验 侵袭性真菌感染 早期筛查
[Abstract] Objective: To explore the value of G test in early screening of invasive pulmonary fungal infection (IPFI) in neonates. Method: A total of 260 suspected IPFI neonates admitted to our hospital from January 2016 to June 2019 were selected as the fungal infection group, 117 bacterial infection neonates in our hospital during the same period were selected as the bacterial infection group, and 54 healthy neonates in our hospital during the same period were selected as the control group. Serum 1,3-β-D glucan levels were compared among the three groups by G test. The serum 1,3-β-D glucan levels were compared between IPFI and non-IPFI neonates with fungal culture results as the gold standard for diagnosis, and the value of G test in early screening of IPFI neonates was analyzed. Result: The serum 1,3-β-D glucan level of the fungal infection group was higher than those of the bacterial infection group and the control group (P<0.05). In the fungal infection group, 214 neonates with IPFI and 46 neonates with non-IPFI. The serum 1,3-β-D glucan level of IPFI neonates was higher than that of non-IPFI neonates (P<0.05). The pathogenic bacteria of 214 IPFI neonates were all Candida, among which Candida albicans and Candida albicans accounted for a high proportion. The sensitivity, accuracy and specificity of G test to IPFI diagnosis were 88.32%, 88.08% and 86.96%. Conclusion: G test has high diagnostic value in early screening of IPFI neonates, it can be used as an early warning indicator of IPFI in clinical practice and is worthy of clinical promotion.
[Key words] G test Invasive pulmonary fungal infection Early screening
First-authors address: Clinical Laboratory of Maoming Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Maoming 525000, China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2020.23.030
侵袭性真菌感染(invasive pulmonary fungal infection,IPFI)指的是一种侵袭人体器官、组织甚至全身的真菌感染,深部组织感染及真菌血症,肺炎、黏膜及皮下组织感染、中枢神经系统感染、败血症、泌尿系统感染是其常见表现形式,严重者可能危及生命安全[1]。近年来,新生儿IPFI发生率逐年升高,病情进展快,且无明显临床特征,与细菌感染及其他常见新生儿疾病表现难以鉴别,常表现为低血压、腹胀、喂养不耐受、低体温、白细胞增多、血小板减少、呼吸困难等症状,严重者会导致骨、眼、脑部受到影响,因此给予早期诊断、治疗是临床研究重点[2-3]。真菌的实验室檢查包括血清学检查、涂片及真菌培养,血培养具有一定的诊断价值,DNA阳性率不高,耗时长,鉴定过程较为复杂,且血培养阴性也无法准确排除真菌感染[4]。有研究提出,血清1,3-β-D葡聚糖检测(即G试验)在真菌中具有一定的检出价值,但在IPFI新生儿中应用较少[5]。本研究以真菌培养为IPFI新生儿诊断金标准,采用G试验对疑似IPFI新生儿进行诊断,分析其在IPFI早期筛查中的诊断价值,现报道如下。
