Sliding Mode Control for Nonlinear Markovian Jump SystemsUnder Denial-of-Service Attacks
2020-11-05LeiLiuLifengMaJieZhangandYumingBo
Lei Liu,Lifeng Ma,Jie Zhang,and Yuming Bo
Abstract—This paper investigates the sliding mode control(SMC) problem for a class of discrete-time nonlinear networked M arkovian jump systems(M JSs) in the presence of probabilistic denial-of-service(DoS)attacks. The communication network via which the data is propagated is unsafe and the malicious adversary can attack the system during state feedback. By considering random Denial-of-Serviceattacks,a new sliding mode variable is designed, which takes into account the distribution information of the probabilistic attacks. Then, by resorting to Lyapunov theory and stochastic analysis methods,sufficient conditions are established for the existence of the desired sliding mode controller, guaranteeing both reachability of the designed sliding surface and stability of the resulting sliding motion.Finally,a simulation example is given to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed sliding mode control algorithm.
I.In t roduction
M ARKOVIAN jump systems(M JSs)are one typical type of hybrid systems,which are usually utilized to model plants subject to abrupt structure variations resulting from various situations such as sensor failures,environment changes and so forth,see[1]–[5]for instance.During the past few decades,control of Markovian jump systems has been garnering extensive research interest and several classical algorithms have been exploited,see e.g.,[6]–[11].Among these developed techniques, the sliding mode control(SMC)strategy has stirred particular interests w ithin the areas of systems science and control engineering due to its strong robustnessagainst externaldisturbance,modeluncertainty and parameter variations.For example,a sliding mode controller has been devised in[7]for nonlinear uncertain Markovian jump systems,where themerits of SMC have been exploited to deal w ith the system’s nonlinear and uncertain dynam ics.By constructing a state observer,the estimation-based SMC problem has been solved for a class of stochastic Markovian jump system[8] to achieve the pre-specified performance indices in anH∞sense.
On another research front,as network technology has nowadays been utilized in a w ide range of industrial applications, networked control systems(NCSs) have been gradually becoming a research hotspot and a large amountof research findingshave been available in the literature,seee.g.,[12]–[14].One of the main features of an NCS is that the system modules (e.g.,sensors, controllers and actuators)are connected and communicating via networks.Consequently,in comparison to traditional control systems, NCSs possessmany merits such as easy expansion,low cost,and flexible installation.However,the implementation of communication networks in a control system would probably induce new complexities and bring extra difficulties in the corresponding analysis and synthesis.These network-induced complexities include but are not limited to communication delays[15]–[17], data packet dropouts [13], [18]and data quantization[19]–[21], which could deteriorate system performance and pose additional challenges in the controller design.For the purpose of handling network-induced phenomena, the SMC scheme has been applied for networked control systems and some research results have been published[22]–[24].For example,in[23], by employing the stochastic analysis technique and Lyapunov theory,the authors have designed a sliding mode controller for a class of discrete-time system subject to packet dropouts.Considering the effect of signal quantization,the sliding mode control problem has been investigated in[24], where sufficient conditions have been obtained w ith the guarantee of both reachability and stability.Nevertheless, to date,the study on the SMC problem for stochastic networked control systems has been still far from adequate,especially when the system is sw itching among several sub-systemsaccording to a Markov chain.
Aside from network-induced phenomena,the data transm itted in a networked control system is easily attacked by adversaries[25]ow ing to the sharing nature of the communication network.The popular cyber attack strategies include denial-of-service(DoS)attacks and deception attacks.In DoS attacks, which work by occupying the network bandw idth, the adversary prevents data packets from reaching their destinations.When a deception attack strategy is adopted,the adversary can intercept data packets and inject false data into the packets.If not coped w ith properly,the cyber attacks can degrade the target’s performances or even cause huge losses.So far,some initial results concerning NCSs subject to cyber attacks have appeared,see.e.g.,[26]−[37].For example,in[32],the variance-constrained distributed filtering problem has been solved for a class of time-varying systems subject to deception attacks.W ith the help of a random sequence obeying the Bernoullidistribution,the DoS attack has been described and the optimal state feedback controller has been designed accordingly[33].In[34],in order to deal w ith random DoS attacks, the authors have proposed a prediction compensation strategy,and have researched the distributed fusion estimation problem subject to DoS attacks and bandw idth constraints.A comprehensive cyber attack model containing random DoS attacks and deception attacks has been proposed in[29]and the eventbased security control problem has been addressed.In[36],considering a fading communication channel and powerconstrained DoS attacks,the secure control problem of cyberphysical systems has been investigated.For the security issue of remote state estimation, the optimal attack power schedule of constrained DoS attacks has been obtained in[37].However,when the DoS attack is taken into account,existing SMC research has been lacking,especially for discrete-time Markovian jump system.The challenges may lie in how to design an appropriate slidingmode variableaccounting for the DoS attacks and,subsequently,how to analyze the reachability and stability problems under the selected sw itching surface subject to DoS attacks.Motivated by the above discussion,in this study,such a gap w ill be shortened by conducting current research on the SMC problem for discrete-time Markovian jump systemsunder DoSattacks.
The contributions of this paper can be highlighted as follows:1)a comprehensive system model is researched,which includes the uncertainties of system parameters,the matched and unmatched nonlinearities;2) the DoS attack is considered in the sliding mode control problem for discretetime stochastic nonlinear Markovian jump systems;3)a new sliding mode variable is constructed,which contains the message of DoSattacksoccurred inmulti-channelsand 4)the SMC algorithm is obtained for the proposed systems subject to the DoS attacks.The rest of the paper is arranged as follows.The SMC problem for discrete-time nonlinear Markovian jump system subject to DoS attacks is formulated in Section II.Section III analyzes the reachability of the sliding surface and the stability of the sliding motion.Furthermore,the sliding mode controller can be acquired by solving a m inim ization problem.A simulation is provided in Section Ⅳ.Finally,the conclusion isgiven in Section V.





Fig.1.The sliding mode control problem in the presence of DoSattacks.

Remark 3:It is worth pointing out that,on account of the complicated network environment,when perform ing the attacks,the adversary w ill confront certain problems such as transmission latency and data packet dropout thatoften occur in a probabilisticmanner.Accordingly,in the proposed attack model,the Bernoulli sequence is adopted to describe the situation that the DoS attacks could only be performed successfully at certain random time instants due to the aforementioned network-induced random complexities.In comparison to the traditional consecutive attack models,the proposed modelplaces theemphasison the characterization of the engineering reality in a networked environment w ith unanticipated stochasticity.
III.Design of SMC

A. Performance Analysis of the Sliding Motion




B. Reachability Analysis




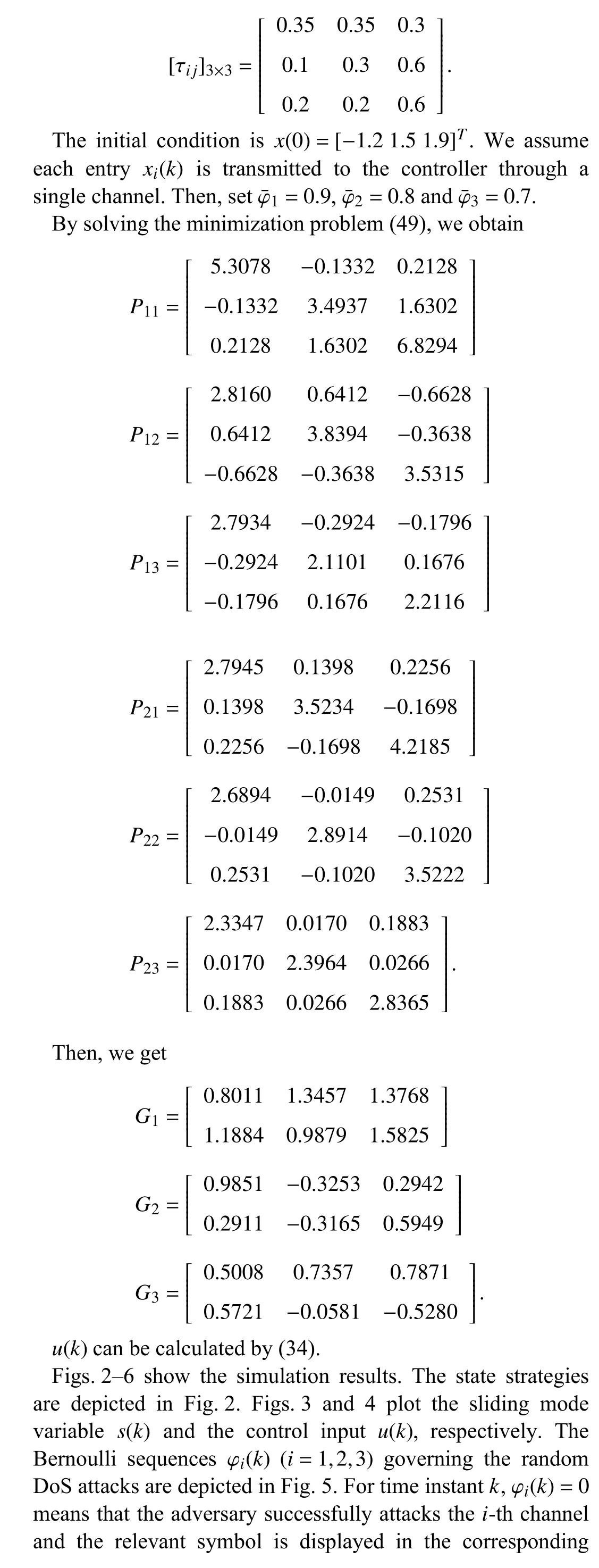

Fig.2.The trajectoriesof x(k).

Fig.3.The sliding mode variable .

Fig.4.The control input .


Fig.5.The random DoSattacks to channel

Fig.6.The realization of Markov chain .
the sliding surface.Thus,the simulation results confirm the effectivenessof the algorithm.
V.Conc lusions
In this paper,we have discussed the sliding mode control problem for a class of discrete-time nonlinear networked Markovian jump system subject to DoS attacks to the communication networks.Considering the DoS attacks at multiple communication channels,a new sliding mode variable has been constructed, which makes use of the statistical information of DoS attacks.The sufficient conditions guaranteeing the reachability of sliding surface and stability of slidingmotion have been derived in terms of a set of linear matrix inequalities.Moreover,a m inim ization algorithm has been set up to obtain the desired sliding mode controller parameters.Finally,a simulation example has been given to illustrate the effectiveness of the SMC problem.It is worthmentioning that,aside from the random model studied in this paper,the DoS attack behavior can be illustrated by othermodels.In future studies,we are interested in studying the slidingmode control problem under different typesof DoS attack modelssuch asdeterministic consecutive attacks.
杂志排行
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica的其它文章
- Parallel Control for Optimal Tracking via Adaptive Dynamic Programming
- A Novel Radius Adaptive Based on Center-Optim ized Hybrid Detector Generation Algorithm
- Neural-Network-Based Nonlinear Model Predictive Tracking Controlof a Pneumatic Muscle Actuator-Driven Exoskeleton
- Single Image Enhancement in Sandstorm Weather via Tensor Least Square
- Understanding Nonverbal Communication Cues of Human Personality Traits in Human-Robot Interaction
- A Behavioral Authentication Method for Mobile Based on Browsing Behaviors
