Antimicrobial activities and analysis of the crude extract,fractions and compounds from the Lomatogonium rotatum
2020-10-14RuoningWangQinHeQingdiMuMengyuanTanJingWangChongningLvHangHeJincaiLuLingyunJia
Ruoning Wang,Qin He,Qingdi Mu,Mengyuan Tan,Jing Wang,Chongning Lv,Hang He,Jincai Lu,Lingyun Jia
School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Box 79,Shenyang 110016,Liaoning Province,PR China
Abstract This study was evaluated the antimicrobial activities of the crude extract,different fractions,and compounds from the plant of Lomatogonium carinthiacum.The fractions of chloroform and compounds 5,2 and 6 exhibited stronger antimicrobial activities.Compound 5 was the most active while Staphylococcus aureusand Candida albicans were sensitive to all the tested compounds.The existence of a relationship between the xanthone structures and inhibition of microorganism activity.The antimicrobial activity of this plant was reported here firstly.The results provided evidence that the studied plant extract,fractions as well as some of the isolated compounds might be potential sources of new antimicrobial drug.
Key words:Lomatogonium carinthiacum; fractions; compounds; antimicrobial activities; HPLC-EIS-MS/MS
1 Introduction
Lomatogoniumis a genus of about 18 species in the family Gentianaceae.L.carinthiacumandL.rotatum(L.) have been used as an appetite stimulant and a digestion regulator in Siberian folk medicine [1].Lomatogonium carinthiacum(Wulfen)Rchbs.is not among annuals and grows in areas which are characterized by an altitude 3000-5400 meters above the sea level and a wet and swampy environment,mainly exists in China,Mongolia,Nepal,Bhutan,India,Pakistan,Kashmir,Afghanistan,Japan,Austria,Germany,Helvetica,Italy,Romania and Russia [2].L.carinthiacumis usually recommended as an appetite stimulant and a digestion regulator in Siberian folk medicine,and has been used as remedies for gastritis,intestinal and stomach pain,liver diseases,colitis,and enterocolitis [3].L.carinthiacumis rich in xanthones,flavonols,iridoids,and secoiridoids,and has an immunity-protection effect on liver injury [4],anti-inflammatory [5],anti-tumor efficacy [6].Despite the traditional use of this plant,there is no scientific report focused on the biological activity ofL.carinthiacum.Therefore,we undertook this study to evaluate the antimicrobial potential of the ethanolic extract,fractions of chloroform,n-butanol,water and compounds from the plant ofL.carinthiacum.HPLC-EIS-MS/MS was used for the analysis of the constituents of different fractions ofL.carinthiacum.The crude extract,fractions and compounds fromLomatogonium carinthiacumantimicrobial activityin vitro,and moreover suggest the existence of a relationship between the xanthone structures and inhibition of microorganism activity.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Plant Material
Dried plant ofL.carinthiacumwas collected in Neimeng province in China over the period October 2006.Voucher specimens have been deposited in the School of Pharmacy of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.The plant identification was verified by Professor Qishi Sun,School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica (Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,China).
2.2 Extraction and fractionation
The dried and ground aerial parts ofLomatogonium carinthiacum(3 kg) were extracted with 75% hot ethanol (EtOH),yielding total crude extract of 800 g that was partitioned,in turn,with CHCl3andn-BuOH.And yielded four fractions,namely crude extract,fraction of chloroform,n-butanol,and water.
The chloroform-soluble fraction (100 g) was subjected to silica gel column chromatography(CC) (200-300,500 g) and eluted with petroleum ether-ethyl acetate (100:1 to 0:100,20 L) to yield 9 fractions (C1-C9).1,8-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyxanthone C15H12O6[2,18 mg,[7]] and 1-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetramethoxyxanthone C17H16O7[4,26 mg,[8]] were crystallized from C2 and C3 in ethyl acetate,respectively.C5 was chromatographed over a silica gel (160 g) column with a petroleum ether-ethyl acetate solvent system (100:1 to 50:1),to afford 1-hydroxy-3,5,8-trimethoxyxanthone C16H14O6[1,12 mg,[9]].C7 was chromatographed over a silica gel (200 g) column with petroleum ether-ethyl acetate (50:1 to 25:1) to yield 1,4,8-trihydroxy-5,6-dimethoxyxanthone C15H12O7[6,11 mg,[10]] and 1,7-dihydroxy-3,8-dimethoxyxanthone C15H12O6[5,8 mg,[11]].1-hydroxy-3,5-trimethoxyxanthone C15H12O5[3,7 mg,[12]] was yielded by Sephadex-LH 20 (60 g)column chromatography with methanol.The chemical structures of the isolated compounds are presented in Fig.1 and the corresponding spectral data (1H-NMR) of isolated compounds provided in Table 1.
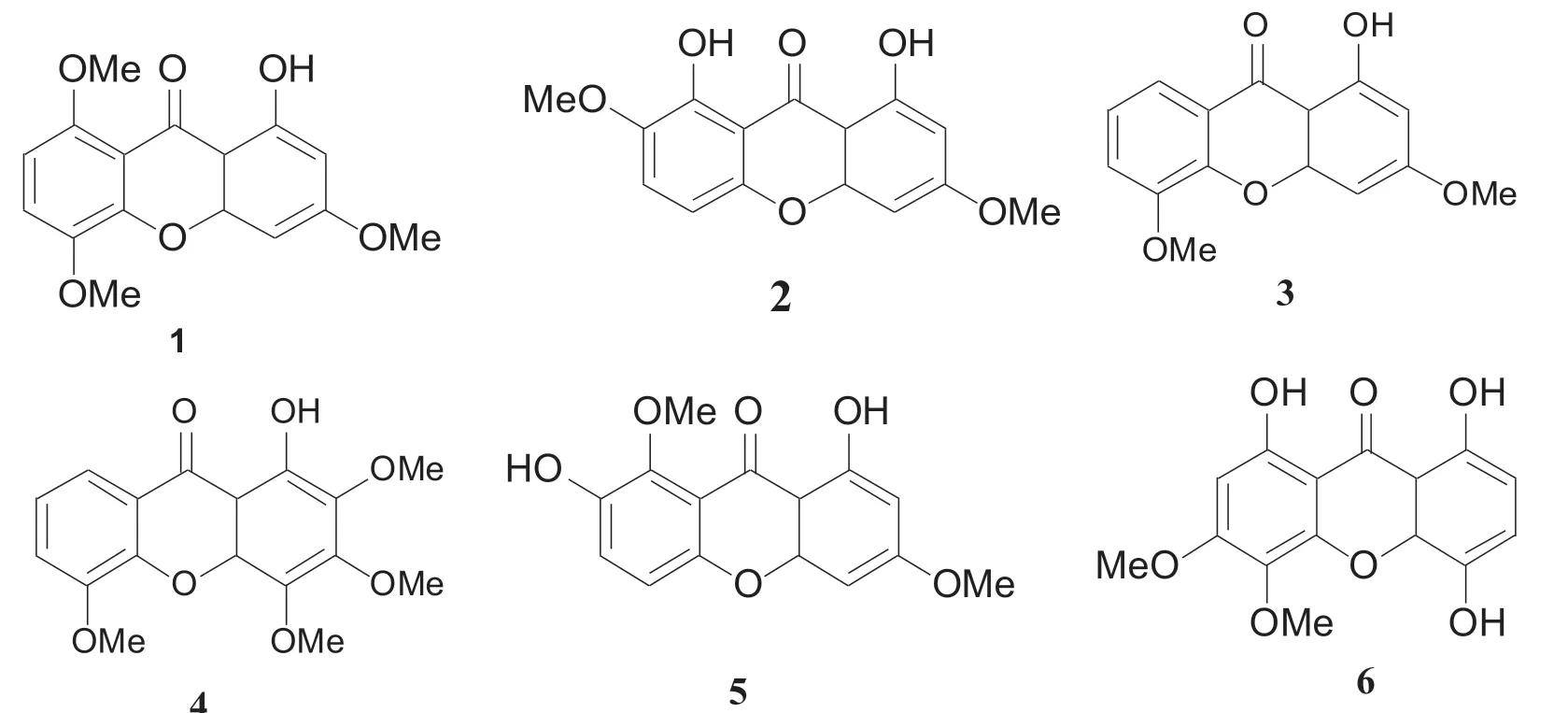
Fig.1 Chemical structures of compounds isolated from the plant of Lomatogonium carinthiacum:1-hydroxy-3,5,8-trimethoxyxanthone (1),1,8-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyxanthone (2),1-hydroxy-3,5-trimethoxyxanthone (3),1-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetramethoxyxanthone (4),1,7-dihydroxy-3,8-dimethoxyxanthone (5),and 1,4,8-trihydroxy-5,6-dimethoxyxanthone (6)
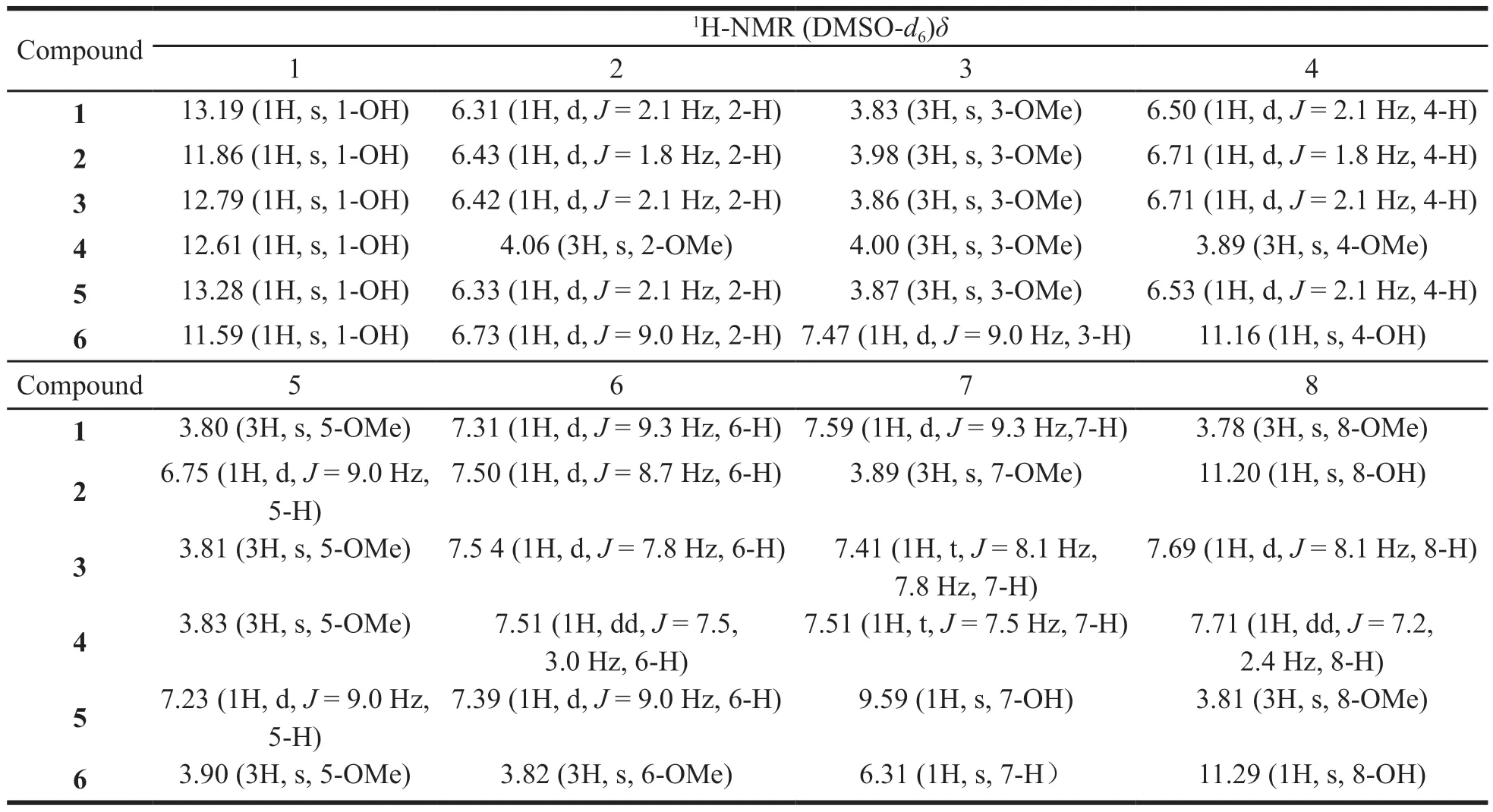
Table 1 The 1H-NMR data of compounds 1-6 in DMSO-d6
2.3 General procedure
1H-NMR,13C-NMR were performed on a Bruker ARX instrument and TMS as internal standard.Mass spectra were recorded on a micro-API instrument.Precoated silica gel plates (Merck,Kiesel gel 60 F254) were used for TLC.Spots were visualized at 254 and 365 nm,and by spraying with 20% H2SO4followed by heating at 120 °C.All melting points were determined on a micro-melting point apparatus and are uncorrected.The structures of the compounds were confirmed by comparing with reference data from available literature.
2.4 Microorganisms
The organisms testedStaphylococcus aureusCMMCC26001,Bacillus subtilisSYCDC63501(Gram-positive bacteria),two Gram-negative bacteria namelyEscherichia coliATCC25923 andPseudomonas aeruginosaATCC27853,and two fungi namelyCandidaalbicansATCC9002,Saccharomyces cerevisiaeATT560.The microbial species were provided by the laboratory microbiology of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.They were maintained on agar slant at 4 °C and sub-cultured on a fresh appropriate agar plate 24 or 48 h.
2.5 Antimicrobial assay
The MICs of the methanolic extract,fractions,compounds and Brewis-Peptore Agar (bacteria) or Peptore-Glucose Agar (fungi) were determined as follows:the test sample was first of all dissolved in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO).The solution obtained was then added to reciprocal liquid nutrient medium to give a final concentration of 640μg/mL.This was serially diluted twofold to obtain concentration ranges of 1.25-640μg/mL.100μL of each concentration was added in a well(96-well microplate) containing 95μL of MH and 5μL of inoculum (standardized at 5×105CFU/mL by adjusting the optical density to 0.1 at 600 nm SHIMADZU UV-120-01 spectrophotometer).The final concentration of DMSO in the well was less than 1% [preliminary analyses with 1% (v/v)DMSO do not the growth of the test organisms].The negative control well consisted of 195μL of liquid nutrient medium and 5μL of the standard inoculum.The plates were covered with a sterile plate sealer,then agitated to mix the contents of the wells using a plate shaker and incubated at 35 °C for 24 h(bacteria) or 35 °C for 48 h (fungi).The assay was repeated three times.MIC was defined as the lowest sample concentration that prevented this change and exhibited complete inhibition of bacterial growth.The results are shown in Table 2.
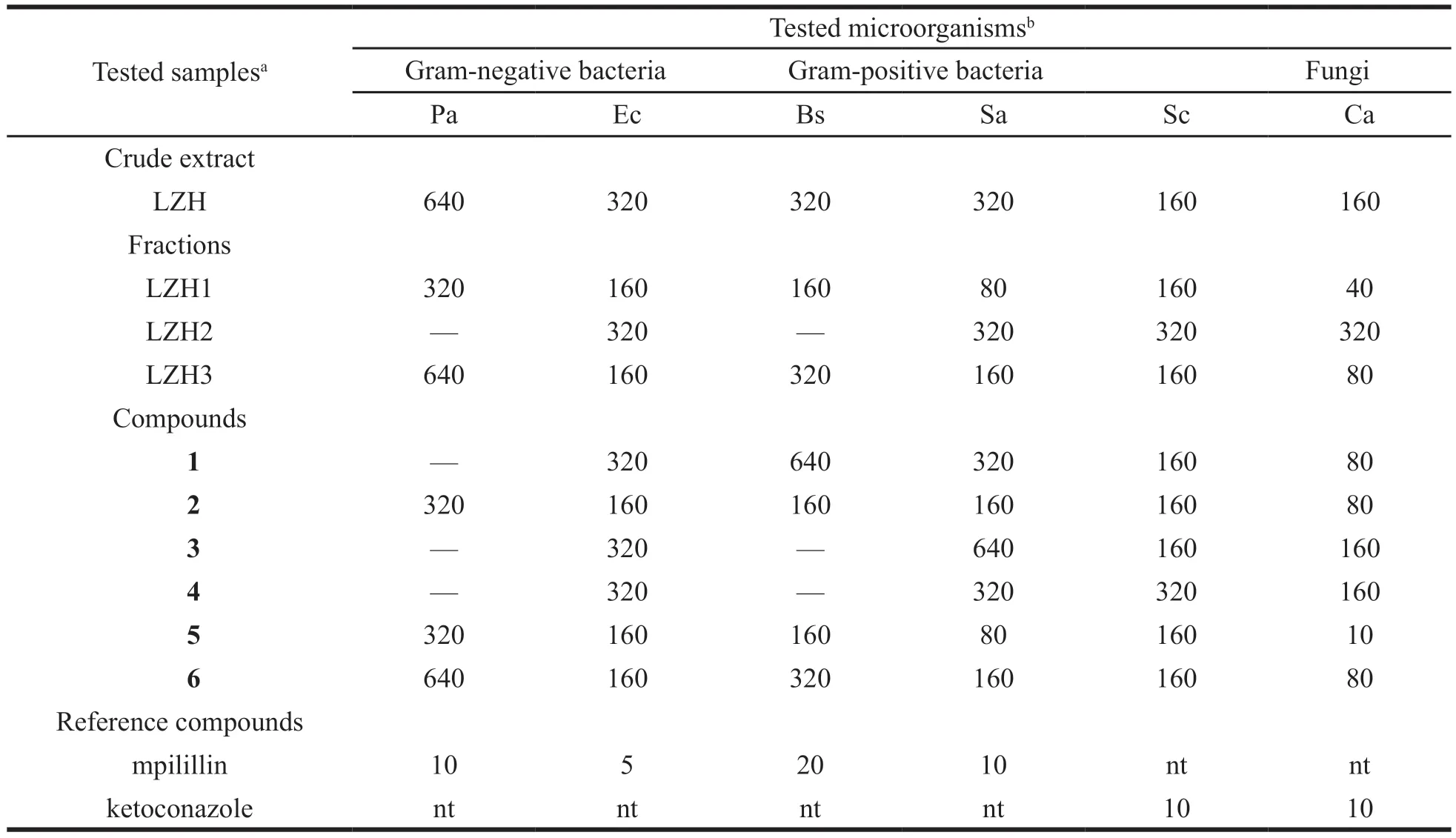
Table 2 Minimal inhibition concentration (μg/mL) of the Ethanolic extract,fractions and compounds isolated from Lomatogonium carinthiacum and reference antibiotics
2.6 HPLC-ESI-MS/MS Experimental
2.6.1 ESI-MS/MS conditions
The ESI-MS/MS system consisted of a Highperformance liquid chromatograph and a mass spectrometer (Bruker Company,USA).Dry Gas Heater=350 °C; Dry Gas Flow=10 L/min;Nebulizer Pressure=45 psi; VCap=± 4000 V;Collision Energy=30 Unit.
2.6.2 Chromatograph conditions
The LC separation was performed on a Kromasil-C18column (5μm,250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d.) from Tianjin Pharmacokinetic Technology Co.,Ltd.(Tianjin,China) for the analysis.The column temperature was maintained at room temperature.The standards and extracts were chromatographed by HPLC using a gradient mobile phase consisting of MeOH as solvent A and water as solvent B.The water extract of the mobile phase were:0 min 12%(v/v) A,15.0 min 25% (v/v) A,35.0 min 40% (v/v)A,40.0 min 65% (v/v) A.Then-BuOH extract of the mobile phase were:0 min 25% (v/v) A,15.0 min 30% (v/v) A,25.0 min 40% (v/v) A,35.0 min 50%(v/v) A,40.0 min 75% (v/v) A.The CHCl3extract of the mobile phase were:0 min 65% (v/v) A,15.0 min 75% (v/v) A,35.0 min 85% (v/v) A,40.0 min 100% (v/v) A.The flow rate was 1.0 mL/min and the injection volume was 10μL.The detection wavelength for the analysis was 254 nm.
2.6.3 Sample extraction
The extracts as Section 2.2 were combined and made up to a volume of 10 mL with the extraction solvent.The herbal extract was passed through a syringe filter of 0.45μm and then the filtrate was injected into the HPLC-ESI-MS/MS for analysis.

Fig.2-1 HPLC-MS/MS of water extracts of Lomatogonium carinthiacum
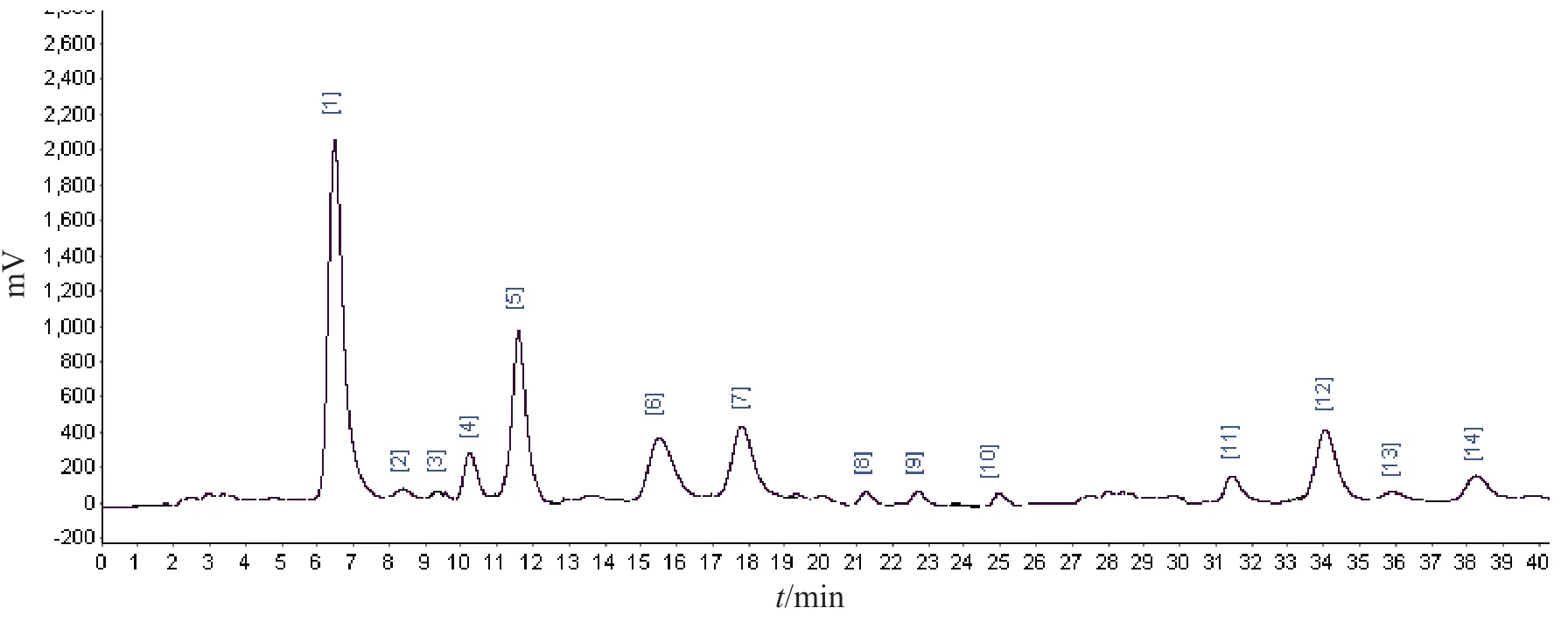
Fig.2-2 HPLC-MS/MS of n-BuOH extracts of Lomatogonium carinthiacumFig.2 HPLC-MS/MS of the fractions from Lomatogonium carinthiacum
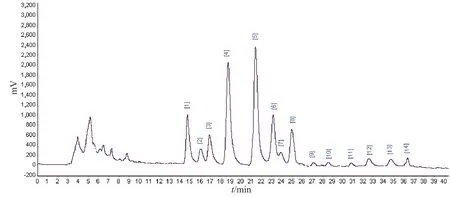
Fig.2-3 HPLC-MS/MS of CHCl3 extracts of Lomatogonium carinthiacum Continued fig.2
3 Results and discussion
The structures of the isolated compounds were established on the basis of spectroscopic data(IR,1H,13C-NMR),and direct comparison with published information and with authentic specimens obtained by our research group for some cases.The compounds isolated from the plant ofLomatogonium carinthiacum(Fig.1) were xanthones namely 1-hydroxy-3,5,8-trimethoxyxanthone (1),1,8-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyxanthone (2),1-hydroxy-3,5-trimethoxyxanthone (3),1-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetramethoxyxanthone (4),1,7-dihydroxy-3,8-dimethoxyxanthone (5),1,4,8-trihydroxy-5,6-dimethoxyxanthone (6),compounds 1,3,5,and 6 were first isolated from theL.carinthiacum.
In this study,we evaluated the antibacterial and antifungal activities of the crude extract,fractions and the isolated compounds fromL.carinthiacum.The results summarized in Table 2 showed that the crude extract prevented the growth of all tested microorganisms.The activities of the isolated compounds were found to be comparable to those of the reference drugs (ampicillin and ketoconazole).These results demonstrated that the same xanthones basic skeleton could effectively inhibit the differentiation of antifungal and antibacterial activities.Compounds 2,5 and 6 were more active than compounds 1,3,and 4.This could be due to the number and position of hydroxyl groups in the compounds (Fig.1).Notably,all of the six xanthones showing potent activity have a hydroxy group at the 1 position,but Compound 5 also includes another hydroxy group at the 7 position,Compounds 2 and 6 include another hydroxy group at the 8 position,and compounds 1,3,and 4 with a disaccharide substituted at another position.Although more information is necessary to define the relationship between structure and activity,our results suggest both that the hydroxyl group at the 7 position in the xanthone structure might play a role in the inhibition of microorganism differentiation,and that the hydroxy group at the 8 position might reduce such inhibitory activity.
The fractions of chloroform and water showed more active than crude EtOH extract andn-BuOH.This could be due to a fraction of chloroform and water including main constituents of xanthones and iridoids and secoiridoids.This supports the traditional use of this plant in the treatment for gastritis,intestinal and stomach diseases.Therefore,it is not surprising since some individual xanthones have shown this type of biological activity [13-16].
In order to identify the components which are responsible for the anti-microorganism activity ofL.carinthiacum.HPLC-EIS-MS/MS was used for the analysis of the constituents of different extracts ofL.carinthiacum.Full peaks were detected within 40 min in the MS chromatogram of every extract in positive ion modes (Fig.2).More than 30 peaks were detected in all of the extracts,and the chemical structures of 21 constituents were deduced based on their MS spectra.The possible structures of 21 constituents were deduced by careful studies on their MS spectra and by comparison with literature data[10-12,17-25].
The 4 constituents were a fraction of water,as swertiamarine,swertiside,swertiamarin and gentiopicroside,mainly with iridoids and secoiridoids.The 8 constituents fromn-BuOH were flavonols,as luteolin-7-O-glucoside,diosmetin-7-O-glucoside,apigenin-7-O-glucoside,orientoside,isoorientoside,apigenin,luteolin,quercetin.The 9 constituents from CHCl3,as 1,3,8-trihydroxy-4,7-dimethoxyxanthone,1,4,8-trihydroxy-5,6-dimethoxyxanthone,1,8-dihydroxy-3,4,5-trimethoxyxanthone,1,8-dihydroxy-3,7-dimethoxyxanthon e,1-hydroxy-3,7,8-trimethoxyxanthone,1-hydroxy-3,4,5-trimethoxyxanthone,1-hydroxy-3,5,8-trimethoxyxanthone,1-hydrox y-3,5-dimethoxyxanthone,8-hydroxy-1,3,5-trimethoxyxanthone,and mainly with xanthones.In order to identify different xanthones,six reference compounds of 1,3,8-trihydroxy-4,7-dimethoxyxanthone,1,4,8-trihydroxy-5,6-dimethoxyxanthone,8-hydroxy-1,3,5-trimethoxyxanthone,1-hydroxy-3,4,5-trimethoxyxanthone,1-hydrox y-3,5,8-trimethoxyxanthone,1-hydroxy-3,7,8-trimethoxyxanthone were isolated and identified in our laboratory,and purities were confirmed by HPLC and1H and13C-NMR.The retention time of six constituents and xanthones of HPLC-EIS-MS/MS was consistent.From the inhibition date,it was showed xanthones were the strongest.According to the result,the antimicrobial order to these extracts were fraction of CHCl3> water >n-BuOH,namely xanthones > iridoids and secoiridoids > flavonols.
Previous activity studies on constituents fromL.carinthiacumlargely relied on water extract.Such as swertiamarine [5,26],gentiopicroside [4],isoorientin,and anti-tumor activity was only on swertiamarine.The results of the present study provide an important basis for the use of the EtOH extract from the plant ofL.carinthiacumfor the treatment of diseases.The crude extract,fractions as well as the isolated compounds found to be active in this study could be useful for the development of new antimicrobial drugs.However,further pharmacological and toxicity studies currently going on in our laboratory will be necessary to establish if they could be safely used as topical antimicrobial agents.
4 Conclusion
This study establishes,for the first time,the crude extract,fractions,and compounds fromLomatogonium carinthiacumantimicrobial activityin vitro,and moreover suggests the existence of a relationship between the xanthone structures and inhibition of microorganism activity.
Acknowledgements
We thank the fourth national survey of traditional Chinese medicine resources (2018016)for funding this research.
杂志排行
Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines的其它文章
- Flavonoids with cytotoxicities from the seeds of Pongamia pinnata (L.) Pierre
- Impact of polyherbal formulations MEF-4 and MEF-8 on high fat diet induced obesity in SD rats
- Study on chemical composition of Viscum coloratum and its HPLC fingerprint in different harvest periods
- Phenolic compounds from Peanut testa
- A review of research on coumarins from Radix Glehniae
- A review of phytochemistry and pharmacology perspectives of Gentiana rhodantha Franch.ex Hemsl.
