A review of phytochemistry and pharmacology perspectives of Gentiana rhodantha Franch.ex Hemsl.
2020-10-14DingdingZhangZhuoyangChengXiaoxiaoHuang
Dingding Zhang,Zhuoyang Cheng,Xiaoxiao Huang*
Key Laboratory of Computational Chemistry-Based Natural Antitum Drug Research &Development,Liaoning Province,School of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica,Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,Shenyang 110016,China
Abstract Gentiana rhodantha Franch.ex Hemsl.(G.rhodantha) is a perennial herb distributed in southwest China,belonging to the Gentiana genus of Gentianaceae family.Previous research indicated that G.rhodantha contains flavonoids,anthraquinones,terpenes and other compounds,which possess the effects of antioxidant,antibacterial,and antitumor.Besides,its dry herb is used as antiphlogistic and antitussive remedy for the treatment of lung,liver,and gallbladder diseases.This review outlines the chemical constituents and biological activities of G.rhodantha,which will be useful for the further research on this plant.
Key words:Gentiana rhodantha Franch.ex Hemsl.; chemical compositions; pharmacological effects
1 Introduction
Gentiana rhodanthaFranch.ex Hemsl.(G.rhodantha) is mainly distributed in southwest China,especially in Yunnan province [1].G.rhodantha,a new Chinese medicine in 2015Pharmacopoeiaof the People’s Republic of China,has the functions of clearing away heat,drying dampness,detoxifying,purging fire,relieving cough and so on,showing great potential in the development and application of single substance drugs and proprietary Chinese medicines [2].The dry herb ofG.rhodanthais a heat-clearing,antiphlogistic and antitussive drug commonly used in Miao,Tujia,and Han nationalities,treating lung,liver,and gallbladder diseases [3].
Several phytochemical and bioactivity studies demonstrated thatG.rhodanthawas rich in iridoids and polyphenols,which showed anti-inflammatory,hepatoprotective,and anti-microbial activities [1].In order to contribute to the development of new drugs and the full use of natural medicinal resources,the present study reviews the timely and comprehensive information about chemical constituents of theG.rhodantha,summarizes the pharmacological activities ofG.rhodantha,and provides an insight for further research.
2 Chemical composition
The investigation on chemical constituents ofG.rhodanthashowed that it contained flavonoids,anthraquinones,terpenes,pirones,phenolic acids,lignans,and other compounds.
2.1 Flavonoids
There were seven flavonoids isolated fromG.rhodantha(Fig.1),including simple flavonoids and flavone glycosides.These compounds were naringenin (1) [3],luteolin (2) [3],quercetin (3) [4],lutonarin (4) [3],isoorientin (5) [3],isovitexin(6) [3],and apigenin 7-O-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-glucopyranosyl-(1→3)-glucopyranoside (7) [5].
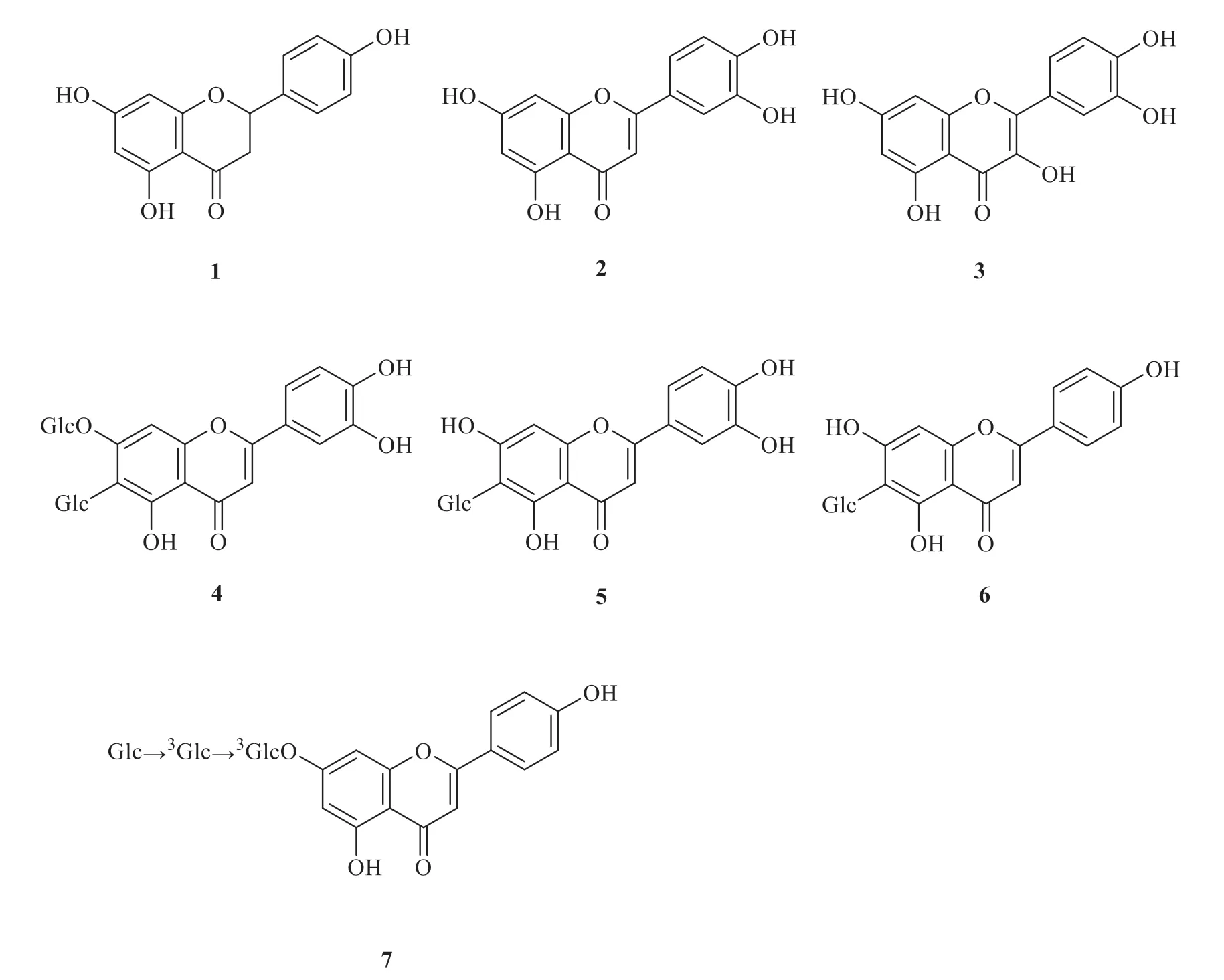
Fig.1 Flavonoids in G.rhodantha
2.2 Anthraquinones
According to previous reports,fourteen anthraquinones have been isolated fromG.rhodantha(Fig.2).These compounds were identified as mangiferin (8) [1],1,3,5,8-tetrahydroxyxanthone(9) [4],1,3,8-trihydroxyxanthone 5-O-β-D-glucoside(10) [4],1,3,7-trihydroxyxanthone 2-C-β-Dglucoside (11),norswertianin (12),triptexanthoside A (13) [3],rhodanthenone D (14),lancerin (15),neomangiferin (16) [5],norswertianin (17),bellidifolin (18) [6],gentinone (19) [7],1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone (20),and 1,3,7-trihydroxy-4,8-dimethoxyxanthone (21) [4].Among these compounds,mangiferin was confirmed as the characteristic one[1].
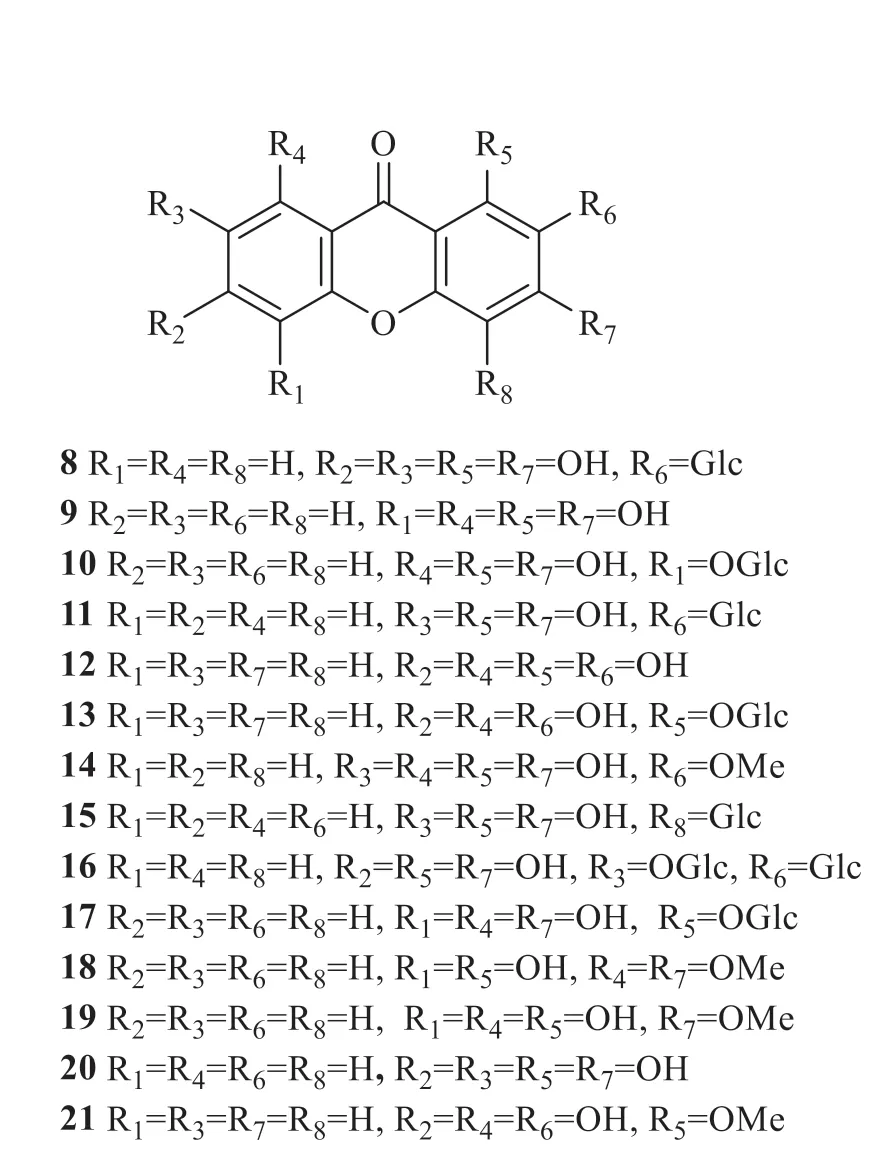
Fig.2 Anthraquinones in G.rhodantha
2.3 Terpenes
Several studies demonstrated thatG.rhodanthawas a rich in iridoids [1].Twenty-three terpenoids,especially iridoids,were extracted fromG.rhodantha(Fig.3),including sweroside (22) [8],loganic acid (23),swertiamarin (24),gentiopicroside(25),secoxyloganin (26),secologanoside (27),2'-(2,3-dihydroxybenzoyl)-sweroside (28),anarogentin (29),macrophyllosides B (30),rindoside(31) [6],rhodenthoside A (32) [9],rhodenthoside B (33),rhodenthoside C (34) [10],2'-O-(3''-hydroxybenzoyl)-8-epikingiside (35),6'-O-pcoumaroyl-8-epikingiside (36),8-epikingiside (37),2'-O-(3''-hydroxybenzoyl)-kingiside (38),kingiside(39),loganic acid 11-O-β-glucopyranosyl ester(40),6'-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl loganic acid (41),6'-O-β-glucopyranosyl secologanoside (42),6'-O-βglucopyranosyl secologanol (43),and alpigenoside(44) [11].Two monoterpenes,namely alangionoside O (45) and 1-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-4-epiamplexine(46) [5],were extracted fromG.rhodantha.In addition,pentacyclic triterpenoids have been isolated fromG.rhodantha,including erythrodiol 3-palmitate(47),ursolic acid (48),and 2α-hydroxyursolic acid(49) [4].
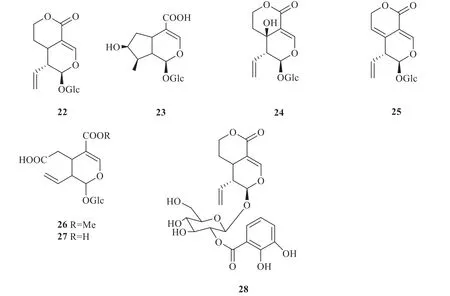
Fig.3 Terpenes in G.rhodanth
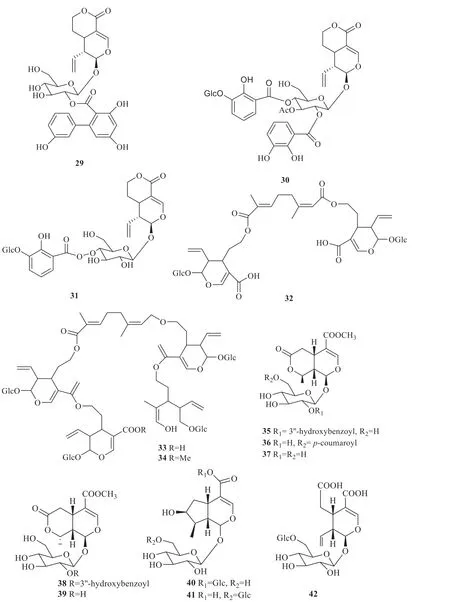
Continued fig.3
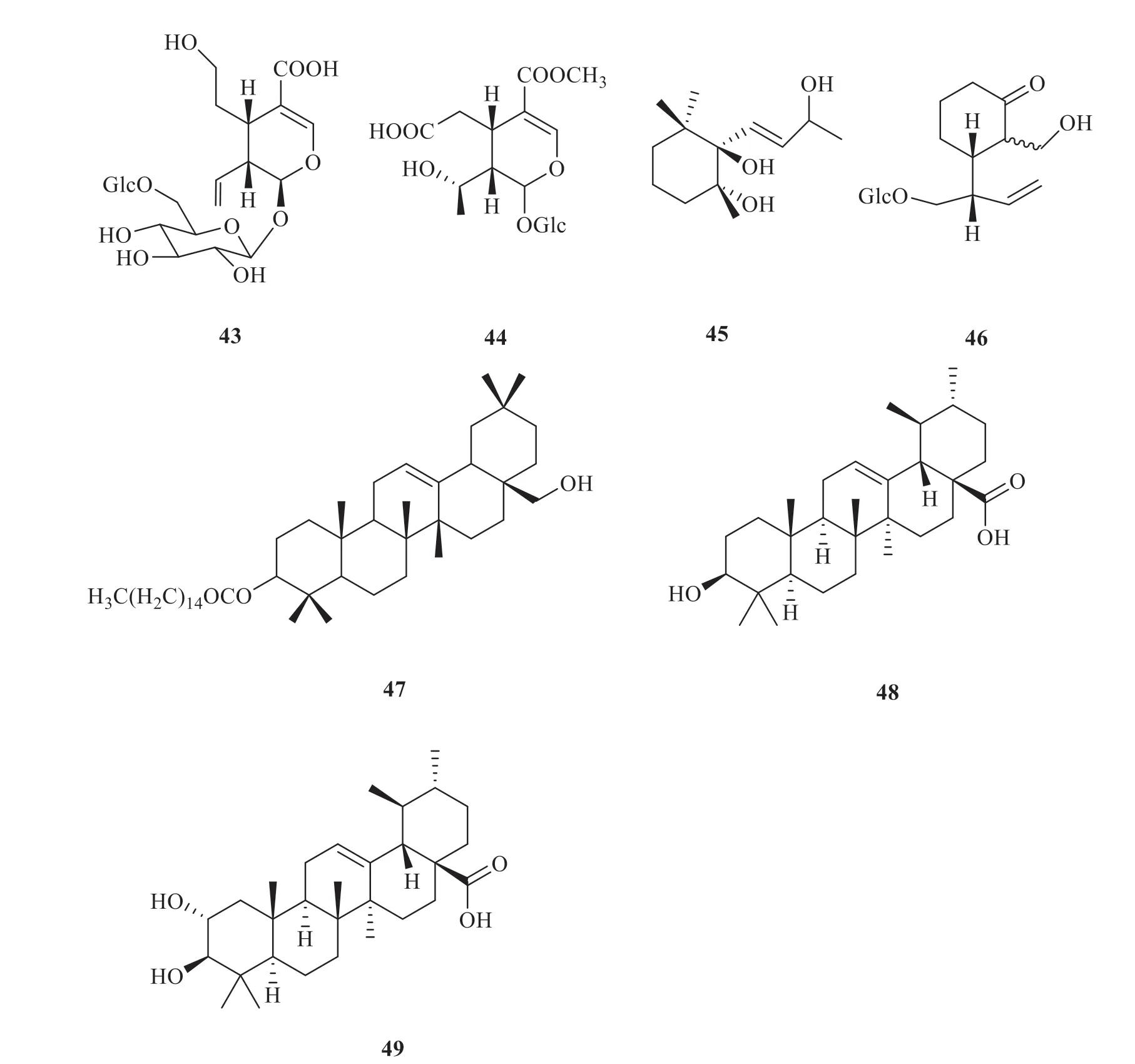
Continued fig.3
2.4 Other compounds
Five new phenolic compounds were firstly identified in 2011,including rhodanthenones B(50),rhodanthenones A (51),rhodanthenones C(52),1,2-dihydroxy-4-methoxybenzene 1-O-α-Lrhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside (53),and 1,2-dihydroxy-4,6-dimethoxybenzene 1-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranoside(54) [5].Gallic acid ethyl ester (55) [4] was identified fromG.rhodanthain 2014.Other three compounds were extracted fromG.rhodantha,including methyl 2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-2,4,6-trihydroxybenzoate (56),rhyncoside D (57) and vanilloloside (58) [5].Four phenolic acids have been isolated fromG.rhodantha,including syringic acid(59),vanillic acid (60),2-(β-D-glucopyranosyloxy)-3-hydroxybenzoic acid (61) and glucosyringic acid (62) [5].Two lignans were isolated fromG.rhodantha,including foliachinenoside C (63)and (-)-syringaresinolO-β-D-glucopyranoside(64) [5].Two rareα-pyrone derivatives,namely rhodanthpyrone A (65) and rhodanthpyrone B(66) [3],were extracted in 2015 fromG.rhodantha.In addition,a phenylpropanoid compound ferulic acid(67) [6] was isolated fromG.rhodantha(Fig.4).
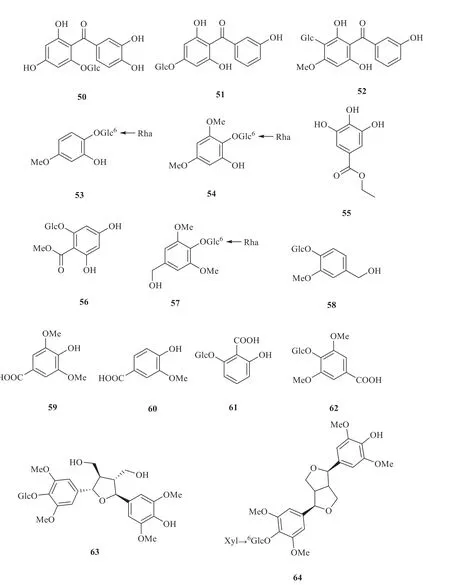
Fig.4 Other compounds in G.rhodantha
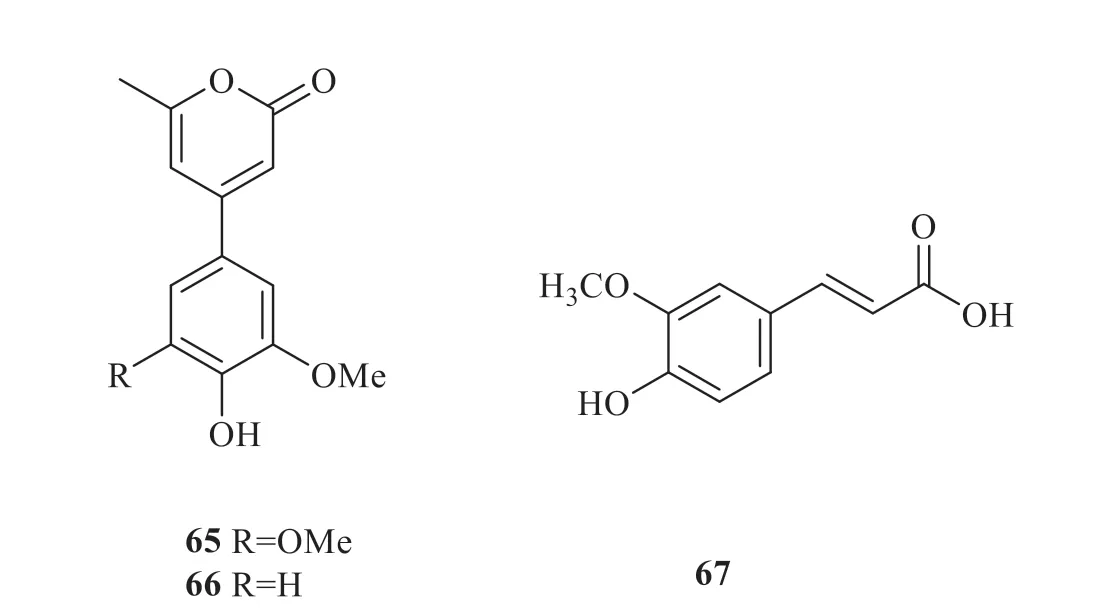
Continued fig.4
3 Pharmacological activities
3.1 Antibacterial activity
In 2017,Liao et al.studied the antibacterial activities ofG.rhodantha,Gentiana cephalanthaFranch.ex Hemsl.andGentiana pterocalyxFranchet extracts againstE.coli,Pseudomonas aeruginosaandStaphylococcus aureus[12].These extracts were obtained by ultrasonic extraction,leaching extraction and reflux extraction.They used filter paper diffusion method to test the antibacterial activity with the size of bacteriostatic circle as the evaluation index.The results showed that the ultrasonic extraction ofG.rhodanthahad the strongest bacteriostatic activity againstPseudomonas aeruginosa,the leaching extraction had the strongest bacteriostatic effect onStaphylococcus aureus,and the reflux extraction had the strongest bacteriostatic effect onPseudomonas aeruginosa.The diameter of bacteriostatic circle ofG.rhodanthaextracts obtained by the above three methods was about 14.14 mm,14.66 mm and 13.54 mm respectively.
In 2018,Wang et al.studied the effect ofG.rhodanthaon the prevention and treatment ofStreptococcus pneumoniaein mice [13].Thirty mice were randomly divided into control group,model group andG.rhodanthagroup.The results indicated that CRP,PCT,IL-6 and IL-8 of theG.rhodanthagroup were lower than that of the model group.It was also reported thatStreptococcus pneumoniaecould increase the levels of CRP,PCT,IL-6 and IL-8 in mice,leading to the pathological damage of lung.Therefore,G.rhodanthacould prevent lung inflammation caused byStreptococcus pneumoniaein mice.
3.2 Hepatoprotective activity
CCl4can increase the levels of ALT and AST in the serum of mice liver,and reduce the activity of GSH Px.These changes can cause acute liver injury [14].Liu et al.studied the protective effect of gentiopicroside (25) on acute liver injury [15].They used CCl4to establish acute liver injury model,and measured the serum ALT,AST and glutathione peroxidase content in the livers of mice.They found that the compound 25 could significantly reduce serum ALT and AST levels and increase liver glutathione peroxidase activity in mice with acute liver injury caused by CCl4.This showed that the compound 25 had hepatoprotective effect.
3.3 Effect on gastrointestinal system
Gentiopicroside (25) can significantly reduce the content of somatostatin and gastrin in plasma,promote the expression of plasma motilin receptor in gastric antrum,duodenum,jejunum and ileum,and inhibit the expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor in duodenum,to promote gastric emptying and intestinal peristalsis [16].Other studies showed the compound 25 could improve constipation,dyspepsia,abdominal distention and reflux esophagitis,accelerate gastric emptying,promote gastrointestinal peristalsis,increase gastric acid secretion [17],and improve gastrointestinal peristalsis of rats and mice inhibited by atropine [18].
3.4 Analgesic effect
In 2008,analgesic pharmacological effects of gentiopicroside (25) were observed in mice by the acetic acid writhing method and hot plate method [19].This experiment showed that compound 25 had obvious analgesic effect on the pain caused by heat and chemical stimulation.Further research showed that the analgesic mechanism of gentiopicrin was related to the inhibition of Glu N2B expression in the anterior cingulate cortex of mice.Compound 25 could significantly reverse the levels of biogenic amines,cysteine proteases,and N-methyl-Daspartate receptors in the amygdala of mice [20].
3.5 Other pharmacological activity
Gentiopicroside (25) can kill human hepatoma cells and inhibit the proliferation of human hepatoma cells.In addition,compound 25 has the functions of relaxing smooth muscle,benefiting gall,strengthening stomach and antioxidation [15].
4 Conclusion
Among traditional folk medicines,G.rhodanthais generally considered as an important resource with potential therapeutic effects.At present,67 compounds have been isolated fromG.rhodantha,including flavonoids,anthraquinones,terpenes,and other compounds.This review highlights the important pharmacological activities ofG.rhodantha,including antioxidant,antibacterial,antitumor,and other pharmacological activities.The review on the major chemical constituents and pharmacological effects provides the reference for further investigation on phytochemistry and pharmacological effects of theG.rhodantha.
杂志排行
Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines的其它文章
- Contribution Regulations for Asian Journal of Traditional Medicines
- A review of research on coumarins from Radix Glehniae
- Phenolic compounds from Peanut testa
- Study on chemical composition of Viscum coloratum and its HPLC fingerprint in different harvest periods
- Impact of polyherbal formulations MEF-4 and MEF-8 on high fat diet induced obesity in SD rats
- Flavonoids with cytotoxicities from the seeds of Pongamia pinnata (L.) Pierre
