A Homozygotic Mutation in KDSR may Cause Keratinization Disorders and Thrombocytopenia:A Case Report
2020-10-03ChaoLiuXiaoyanChenWenqiWuXiaofanZhu
Chao Liu,Xiaoyan Chen,Wenqi Wu,Xiaofan Zhu
State Key Laboratory of Experimental Hematology,National Clinical Research Center for Blood Diseases,Institute of Hematology and Blood Diseases Hospital,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences &Peking Union Medical College,300020 Tianjin,China
Key words:3-keto-dihydrosphingosine reductase gene;thrombocytopenia;keratinization disorders;infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma
Abstract Pathogenic mutations in 3-keto-dihydrosphingosine reductase (KDSR) gene are associated with keratinization disorders and impaired platelet function.However,no case with both homozygotic mutation of KDSR and hepatic hemangioendothelioma has ever been reported due to its low prevalence.Here we report a seven months old Chinese boy with a homozygotic missense mutation in KDSR and both of his parents carry a same heterozygous mutation.He was born with thick plate-like scales overlying erythrodermic skin,but the skin symptoms were resolved spontaneously over the first month of his birth.He was also diagnosed with hepatic hemangioendothelioma at birth and accepted a resection surgery at 2 months old.At birth,his platelet count was severely low (10-20×109/L) with recurrent skin and gingival bleeding.Meanwhile,he suffered a mild normocytic,normochromic anemia with normal iron and hematinic levels.The anemia spontaneously recovered over the first 6 months,while the platelet count keeped at a low level (4-20×109/L).Treatment with corticosteroids,immunoglobulin or thrombopoietin was all suboptimal.
KDSR,which encodes 3-keto-dihydrosphingosine reductase,is a fundamental enzyme for de novo sphingolipid synthesis.[1,2]Sphingolipids are essential to membrane trafficking,apoptosis and cell differentiation and proliferation.[3,4]Recent discoveries showed that pathogenic mutations inKDSRcan result in mild to severe skin disorder,mostly severe thrombocytopenia and self-recovery anemia.[5-7]Up to now,all of ten reported cases carry compound heterozygous mutations inKDSRand are born to unrelated parents.[5-7]Besides,to our knowledge hepatic hemangioendothelioma has never been reported in these patients.Here we review a case with thrombocytopenia,anemia,minimal skin involvement and hepatic hemangioendothelioma,which may be associated with a homozygotic mutation inKDSR.
CASE DESCRIPTION
A seven-month boy is the only child of related healthy parents and the only affected individual among his relatives.His mother’s and father’s grandmothers are cousins.He was delivered vaginally following spontaneous onset of labor at 38+2 weeks with a birth weight of 3.35 kg.
He was born with a thick covering of plate-like scales overlying erythrodermic skin,but eclabium and ectropion were not observed.Histopathological examination of the affected skin was not tested because of his parents’ refusal.The skin symptoms were resolved spontaneously over the first month of his life only with intermittent use of urea and vitamin E cream.
At birth,his platelet count was severely low(10×109-20×109/L) accompanied by recurrent skin and gingival bleeding.He also had mild normocytic,normochromic anemia with normal iron and hematinic levels.But the white blood cell count and the mean volume of platelets were normal.The bone marrow morphology test showed increased number of primitive and naive lymphocytes (6.6%).The total number of megakaryocyte was 25 and no apparent morphology dysplasia was found.The bone marrow biopsy and immunohistochemistry were not performed in view of his age.Serum immunoglobulins and peripheral T-lymphocyte subsets were both normal.The whole exome sequencing showed a novel homozygotic missense mutation inKDSRand both of his parents have a same heterozygous mutation [NM-002035.4:exon9:c.869G>A(p.Gly290Glu)].The mutation was not included in Exome Sequencing Project,1000 Genomes Project and Exome Aggregation Consortium.However,it was predicted by multiple computer simulations to be probably damaging.According to the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) guidelines,the clinical significance of this mutation is still unclear.
The anemia had a spontaneous recovery over the first 6 months,while the platelet count keeps low (4-20×109/L).He was once treated with corticosteroids,immunoglobulin and thrombopoietin,but none of them made a significant improvement of platelet count.
The abdominal ultrasound at birth suggested a heterogeneous mass in the right lobe of his liver,whose maximum diameter was 5.3 mm.His liver function tests showed elevated levels of both alanine aminotransferase (112.2 U/L) and aspartate aminotransferase (227.5 U/L).Coagulation test showed a significant decrease in fibrinogen (0.88 g/L) and prolonged thrombin time (21 s).Besides,alpha-fetoprotein was 16 038.0 ng/ml,which was significantly higher than normal.Then abdominal plain scan and enhanced CT were carried out to determine the nature of the mass and infantile hemangioendothelioma was suggested.After transfusion of platelets,his platelet count rose up to 200×109/L and then he accepted a resection surgery successfully at 2 months old.
The patient is currently one year old and has no abnormalities other than thrombocytopenia.He has not received any treatment since he was 2 months old.The platelet count keeps low (4×109-20×109/L) with recurrent skin and gingival bleeding.
DISCUSSION
KDSR is one of the most essential enzymes in the pathway of de novo sphingolipid synthesis.[1,2]It catalyzes the conversion of 3-keto-dihydrosphingosine to dihydrosphingosine on the cytosolic leaflet of the endoplasmic reticulum.Sphingolipids are essential to apoptosis,cell differentiation,proliferation and membrane trafficking.[3,4]Boydenet al.[5]reported compound heterozygous damaging mutations inKDSRof four unrelated probands in 2017 (Table 1).All of them exhibited recessive progressive symmetric erythrokeratoderma,a skin disorder with symmetric scaling,erythema,and palmoplantar keratoderma.In the report,both of probands who received systemic isotretinoin therapy have achieved nearly complete resolution and it is consistent with the effects of retinoic acid on alternative pathways for ceramide generation.But later studies showed that mutations inKDSRmay not cause progressive symmetric erythrokeratoderma.[6,7]Takeichiet al.[6]reported four cases in June 2017 (Table 1):Patient 1 and 2 developed diffuse hyperkeratosis and had anogenital hyperkeratosis and erythema.Light microscopy of the affected skin showed psoriasiform acanthosis,parakeratosis,and focal hypergranulosis but no epidermolytic changes.Patient 3 and 4 were both covered in thick plate-like scales at birth and had severe ectropion and eclabium.Skin biopsy of Patient 4 showed marked hyperkeratosis with parakeratosis,which was consistent with Harlequin ichthyosis.However,the thick scales desquamated gradually over the first 2 months of his life without any special treatment and resulted in generalized erythroderma and small scaling.Three of the four patients once received oral acitretin,two of them had no improvement in skin,one showed some reduction in adherent scaling.In the report of Barianaet al.(Table 1),[7]one patient’s possible skin involvement was a slow-to-heal perianal wound following rectal manometry,the other had mild ichthyosis in her left axilla,but the skin symptoms resolved spontaneously over her first month.Our patient was born with thick plate-like scales overlying erythrodermic skin,but eclabium and ectropion were not observed.The skin symptoms were resolved spontaneously over the first month of his life without any special treatment.
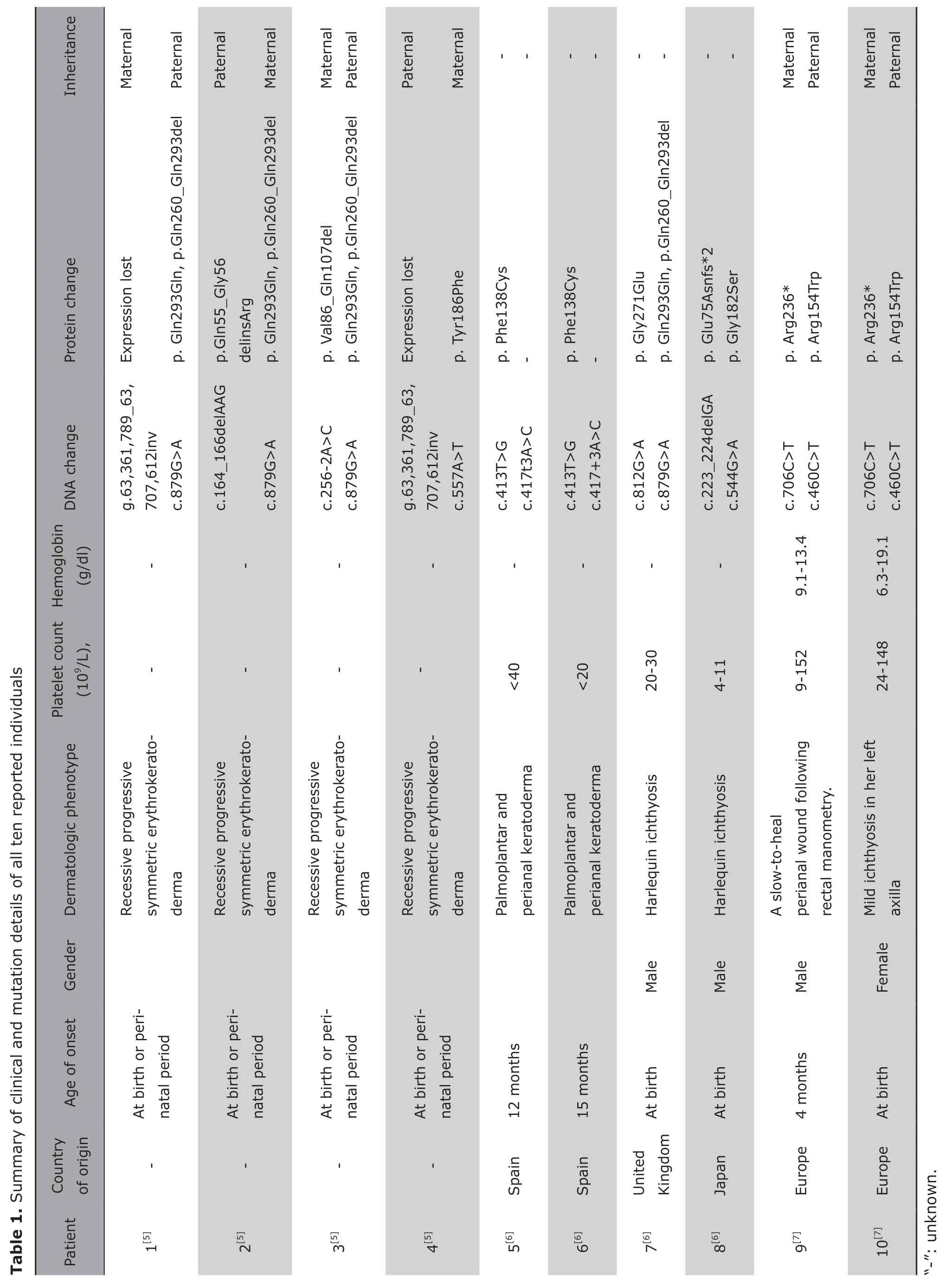
Boydenet al.[5]did not mentioned the decrease of platelet count,but further studies showed that mutations inKDSRare implicated in an extended spectrum of disorders,not only including keratinization disorders but also impaired platelet function.In the report of Takeichiet al.,[6]all of four patients had a severe isolated thrombocytopenia and the platelet counts were mostly less than 30×109/L.One of the four patients accepted oral corticosteroids and splenectomy,both of the treatments were suboptimal.Bone marrow studies of one patient showed normal hematologic morphology.Detailed analysis of platelets performed in two patients revealed no morphologic abnormalities except for slightly increased platelet volume.The adhesive surface glycoproteins levels of the two patients were both normal,but in terms of basal annexin V binding positive percentages,the level of phosphatidylserine exposure was low and thromboplastin expression in unstimulated washed platelets was reduced.Besides,the platelet function of granule release and the conformational change of αⅡβ3 integrin with different platelet agonists were also impaired.Barianaet al.[7]later reported two related patients and both of them had thrombocytopenia and normocytic,normochromic anemia.The mean volumes of the platelets are both within the normal ranges,which is contrary to the report of Takeichiet al.[6]The hemoglobin level of the elder patient was spontaneously improved in the absence of identifiable environmental,therapeutic,or dietary interventions.His bone marrow examinations showed increased numbers of dysplastic megakaryocyte and progressive severe myelofibrosis.Megakaryocyte obtained by differentiation of patients’ hematopoietic stem cells or programming of induced pluripotent stem cells derived from their fibroblasts was abnormal in size and proplatelet formation.They found that downstream metabolites in the sphingolipid pathway were not reduced in plasma.This suggests that hypofunction of KDSR in de novo sphingolipid synthesis is compensated by an alternative pathway and the way may be recycling of relatively abundant sphingomyelins.They also knocked downKDSRin a zebrafish model and found that it is associated with impaired thrombocyte formation.
Our patient had a homozygotic missense mutation inKDSR.Though the mutation was not included in Exome Sequencing Project,1000 Genomes Project and Exome Aggregation Consortium,it was predicted by multiple computer simulations to be probably damaging.The patient not only had keratinization disorders,but also had severe thrombocytopenia and transient anemia.All together we consider the mutation probably is the pathogenic cause of the patient.Since it has not ever been reported,further studies of more cases are essential to determine whether pathogenic mutations inKDSRis the cause of infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma.But a recent study showed that KDSR dysfunction can induce hepatic injury phenotype in both homozygousKDSRmutant larvae and heterozygousKDSRmutant adult zebrafish.[8]The researchers suggest that genetic mutations causing decrease of KDSR activity could be an underlying risk factor for development of liver disease and patients who carry these mutations might be highly susceptible to liver diseases such as steatohepatitis,fibrosis or hepatocellular carcinoma.
In conclusion,our data add a pathogenic mutation inKDSR,which associated with skin disorder,mostly severe thrombocytopenia and self-recovery anemia.Besides,it is probably responsible for infantile hepatic hemangioendothelioma.Further studies of more individuals affected by pathogenic KDSR variants are essential to determine whether systemic retinoid or sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-targeting drugs are effective or not.Because two patients had spontaneous improvement of platelet count and anemia,[7]a careful watch-and-wait approach may be more appropriate than early intervention for patients without severe clinical bleeding symptoms.
Conflict of Interests Statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
杂志排行
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Enhancing Quality of Patients Care and Improving Patient Experience in China with Assistance of Artificial Intelligence
- Advance in Functional Restoration of Injured Nerve with Low Level Laser and its Utilization in the Dental and Maxillofacial Region
- Treatment of Retroperitoneal Cavernous Lymphangioma:A Case Report
- Value of Preoperative Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting Prognosis of Surgically Resectable Urinary Cancers:Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Similarities and Differences of Early Pulmonary CT Features of Pneumonia Caused by SARS-CoV-2,SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV:Comparison Based on a Systemic Review
- Effect of MR Field Strength on the Texture Features of Cerebral T2-FLAIR Images:A Pilot Study
