前列地尔治疗高龄糖尿病并慢性肾脏病患者疗效研究
2020-09-26范新钊田珂
范新钊 田珂
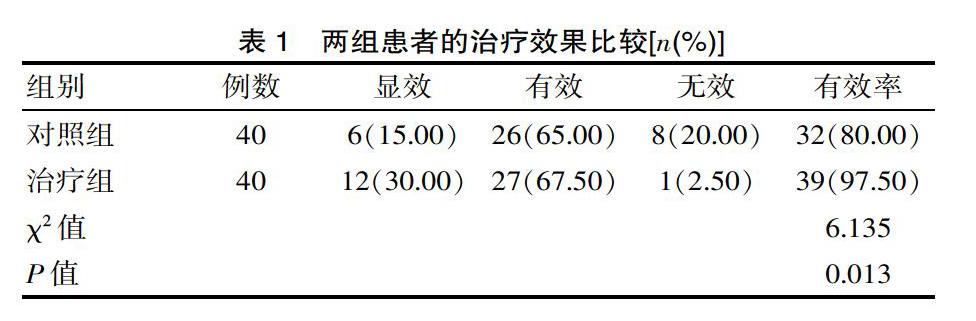


[摘要] 目的 研究高龄糖尿病并慢性肾脏病患者采用前列地尔药物进行治疗,分析患者的治疗效果。 方法 研究对象为80例高龄糖尿病并慢性肾脏病患者,研究时间为2018年4月—2019年4月期间,在该院治疗的患者中抽取且平均分为两组,常规药物治疗组(对照组,40例)和前列地尔药物治疗组(治疗组,40例)。将两组患者的治疗效果、血糖指标和肾功能和肾功能指标予以对比分析。 结果 治疗后,治疗组患者临床症状改善明显,较之对照组显著(P<0.05);治疗后,治疗组患者肾功能指标明显改善,较之对照组显著(P<0.05);治疗后,治疗组患者空腹血糖、甘油三酯、低密度脂蛋白等指标较低,较之对照组显著(P<0.05)。 结论 针对高龄糖尿病并慢性肾脏病患者采用前列地尔药物进行治疗,患者的治疗效果显著,大大地改善了患者的临床症状,同时改善患者的肾功能指标,促进患者恢复。
[关键词] 前列地尔;高龄糖尿病;慢性肾脏病;治疗效果
[中图分类号] R587.2;R692.9 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1672-4062(2020)06(b)-0174-02
[Abstract] Objective To study the treatment of elderly patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease using alprostadil, and analyze the therapeutic effect of the patients. Methods The study object was 80 elderly patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease. The study period was from April 2018 to April 2019. Conventional drug treatment group (control group, 40 cases) and alprostadil drug treatment group (treatment group, 40 cases). The treatment effects, blood glucose indexes, renal function and renal function indexes of the two groups of patients were compared and analyzed. Results After treatment, the clinical symptoms of the treatment group were significantly improved, compared with the control group(P<0.05); after treatment, the renal function index of the treatment group was significantly improved, compared with the control group (P<0.05); after treatment, the fasting blood glucose, Triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein and other indicators were lower, compared with the control group was significantly(P<0.05). Conclusion For the elderly patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease, Alprostadil is used for treatment. The treatment effect of the patient is significant, which greatly improves the clinical symptoms of the patient, at the same time improves the patient's renal function indicators and promotes the patient's recovery.
[Key words] Alprostadil; Advanced diabetes; Chronic kidney disease; Treatment effect
由于老年患者的机能衰退,其极易患有慢性疾病。糖尿病合并慢性肾脏疾病是老年群体常见疾病,对患者生活影响较大,秉持着早发现早治疗的原则,要加强对糖尿病合并慢性肾脏疾病患者进行治疗,提升患者的治疗效果[1-2]。糖尿病患病周期长,患者的血糖水平始终保持在较高的水平上,这对于患者体内的各个脏器器官的功能性有着较大的损害。随着人口老龄化的发展,患有糖尿病的人數越来越高,由糖尿病所引发的慢性肾脏疾病的发病率越来越高。因此该文2018年4月—2019年4月选取80例高龄糖尿病合并慢性肾脏疾病患者,针对不同药物的治疗效果进行对比分析,报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
研究对象为80例高龄糖尿病并慢性肾脏病患者,在该院治疗的患者中抽取且平均分为两组,常规药物治疗组(对照组,40例),其中男性和女性各26例、14例;病程为5~10年,平均病程为(8.52±1.21)年;年龄最小为74岁,年龄最大为85岁,平均年龄(78.59±2.12)岁。前列地尔药物治疗组(治疗组,40例),其中男性和女性各28例、12例;病程为6~11年,平均病程为(8.69±1.23)年;年龄最小为75岁,年龄最大为87岁,平均年龄(78.58±2.32)岁。两组样本数据经统计学分析,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。
