Research progress of micro(nano)plastics in marine survey in China
2020-08-12GAOYanDAIYuanyuanSUNXueliangLIWangcanHEQingLIUZeping
GAO Yan,DAIYuanyuan*,SUN Xueliang,LIWangcan,HE Qing,LIU Zeping
1.Fisheries Research Institute of Tianjin,Tianjin 300221,China;
2.Tianjin Agricultural College,Tianjin 300384,China;
3.Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria of Nankai University,Tianjin 300350,China
Abstract:The extensive existence of microplastics in the marine environment and the various definite and indefinite harm to the living creatures have been paid much attention.In this paper,the definition,source and pollution of micro(Nano)plastics in marine environment are reviewed.The related literatures are retrieved by using big data platform,the distribution characteristics of micro(Nano)plastics in the marine environment,control measures and so on,and the characteristics of key words making,resource distribution and contribution rate of research institutions are comprehensively analyzed.It provides the technical support for the scientific management of micro(Nano)plastics in the future.
Keywords:micro-nano plastics,oceanographic survey,research progress
In the environment,plastic waste may persist and physically break down into plastic particles,or microplastics.Microplastics are plastic particles with a diameter of less than 5 mm,which are usually broken up from plastic wastes of a larger size by ultraviolet light,atmospheric oxidation and microbial activity.In addition,microplastics may also be directly produced and used as raw materials,such as facial cleanser and other daily care products.The plastic grit is also an important source of environmental microplastics[1].In 1972,researchers detected polystyrene particles in seawater off the southern coast of New England.Because most micro-plastics are not easy to degrade,they will accumulate in the real environment and make the pollution more and more serious.In recent years,there are more and more research reports on microplastics in the world and in China.For example,surveys have shown that concentrations of microplastics in seawater and sediments from the coast of Hong Kong can be as high as 35 642 per 100 m3and 458 per kg.Zhang detected 0.55×105-342×105per km2and 80-342 per m2in water and sediment of the Xiangxi River,Three Gorges Reservoir in China.In 2015,microplastics were detected for the first time in sediments off the coast of China by Qiu et al.,and the major components were identified as high-density polyethylene,polyethylene terephthalate,polyethylene terephthalate and polystyrene,with total concentrations ranging from 5 020 to 8 720 per kg.In addition,Shi Huahong’s team detected the presence of microplastic particles in edible sea salt,with polyethylene terephthalate plastic having the highest content[2].
1 Overviews
1.1 The concept of micro(Nano)plastics
In general,microplastics are defined as having a size in the range of 0.1-5 000 M.In the natural environment,micro-scale plastic particles can be further degraded into nano-scale,also known as nano-plastic.
1.2 Sources of micro(nano)plastics
In recent years,the proportion of plastic products in daily life is getting higher and higher,and its production is also increasing year by year.In recent years,the output value of plastic products in China has been increasing year by year,and has a large proportion in the global total output of plastic products.As an artificial product,micro-and nano-plastics mostly come from the degradation of domestic garbage and the discharge of domestic sewage.Its main components are polyethylene PE,polypropylene PP,polystyrene PS,polyvinyl chloride,PLA,Polyethylene terephthalate and other polymers[3].
The sources of micro-and nano-plastics in marine environment include land input,coastal tourism,marine transportation,marine aquaculture and fishing,and atmospheric deposition.Land based sources are the main source of micro(nano)plastics in the marine environment,and current estimates of the global sources of plastic waste in the oceans suggest that Terrigenous sediment accounts for about 80%.Due to the small size of micro-nano plastic particles,it is difficult to filter and remove the micro-nano plastic in daily chemical products,industrial production and the shedding of textile fibers from different sources entering the sewage treatment system.As a result,large quantities of microplastic particles are released into the marine environment.Another source of land-based inputs is soil containing micro-and nano-plastics that enters the marine environment through erosion.Coastal tourism and shipping industry lead to a large number of plastic products and waste into the beach or the sea,which is also a major reason for the increase in marine plastic pollution.The United Nations Environment Programme estimated in 2005 that about 5 million tons of plastic waste was shipped to the oceans worldwide[4].
1.3 Toxic effects of micro(nano)plastics on marine organisms
1.3.1 Toxic effects of micro plastics on marine organisms
Microplastics are easy to be absorbed by organisms and accumulated in organisms because of their small size and non-degradability.Studies have shown that many species of algae,shellfish,fish,seabirds and marine mammals can directly or indirectly ingest microplastics.However,at present,most studies on the toxic effects of microplastics on marine organisms are based on short-term exposure experiments,and the measured concentrations of microplastics exposure are yet to be quantified accurately.Therefore,the sublethal level of feeding rate,growth rate,oxidative damage,enzyme activity and abnormal behavior were the only evaluation indexes.
1.3.2 Toxic effects of nano-plastics on marine organisms
The toxic effects of nano-plastics on marine organisms are mainly related to the size,shape,composition and characterization of the particles.At present,due to its small size,the detection of nano-plastic in biological tissues are not yet set.The research on the composition,distribution and impact on environment and living things of nano-plastics is still in the stage of exploration,and many conclusions of nano-plastics in marine living things need to be further explored[5].
2 The sources of data
2.1 Document overview
The literature is derived from the search results of the CNKI database.The search time is from 1995 to 2020 and the search date is April 8,2020.In the relevant literature,the microplastics in marine studies are retrieved as comprehensively as possible with the search theme of"microplastics"and then obtained 482 papers.The present study makes statistical analysis in terms of published annual distribution,research level distribution and keywords,research institutions,funding sources,subject distribution,source distribution,etc.At the same time,the subject of"micro-nano Plastic"was searched.However,there are only 4 papers on"micro-nano Plastics".The keywords"marine environment"and"micro-nano plastics"were searched simultaneously,and 71 related literatures were obtained,among which the investigation and research on micro-plastics was the main research direction.Use Data analysis software to obtain the annual volume of statistical results(Fig.1)in CNKIdatabase.
As can be seen from Fig.1,the number of articles published has shown a trend of gradually increasing since 2015.By 2018,the number of articles published has increased fourfold to 125,accounting for 18.5%of the total and 251 articles are expected to be published in 2020.

Fig.1 Annual growth of papers included in CNKIdatabase
2.2 Keyword analysis
The keywords in the literature can reflect the content,method and object of the research.From the distribution of high-frequency keywords,we can see the key research direction.In this paper,482 research papers were searched for key words,in which microplastics digestion,plastic garbage,plastic pollution,marine garbage and plastic particles have high frequency of keywords.According to the 6 highest frequency keywords in the related research of micro-nano plastics,a comprehensive analysis is carried out and Fig.2 is obtained.As shown in Fig.2,micro-nano plastics are mainly concentrated in the study of marine organisms,toxic effects,combined toxicity of organic pollutants,combined toxicity of heavy metals,ecological risks assessment,ecological effects and so on.
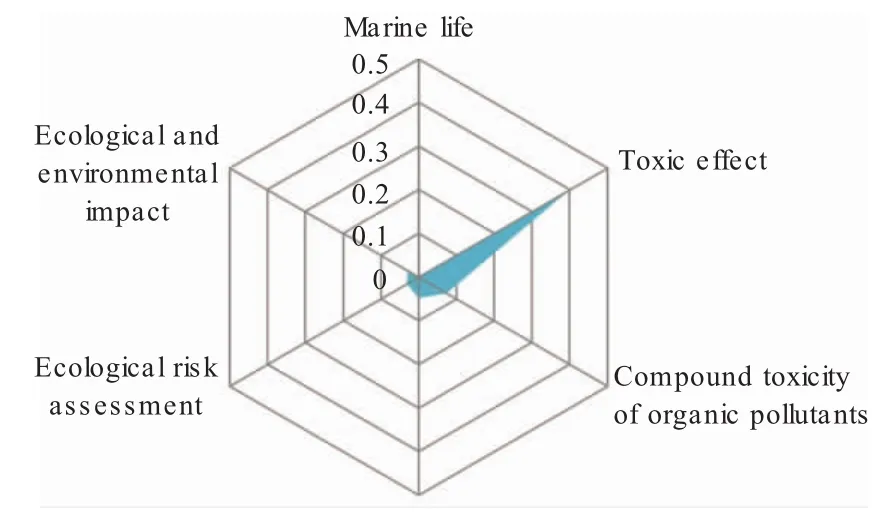
Fig.2 The proportion of high-frequency keywords and the main research direction

Fig.3 The distribution of subjects in discipline
2.3 Research field and periodicaldistribution
Based on the papers published in the main subject areas,field and periodical publications of the core statistical search in Chinese were carried out,and statistical analysis was conducted.Then the publication of important source journals was collected and analyzed.The data show that the research papers involve multiple disciplines,with five of the most published being the Engineering Technology I,and have received more attention in the fundamental science.
The authors selected 71 papers with high correlation to make a comprehensive analysis.Among them,68 on Engineering Technology I were published,accounting for 44.7%of the analysis papers;59 are on Fundamental Science,accounting for 38.8%of the literature;and 8 are on Agricultural Technology,accounting for 5.3%.
2.4 Resource type distribution
A comprehensive analysis of the relevant literature shows that 77.5%of the articles mainly published in the form of periodicals,with a total of 55 articles published,followed by master's theses(15.5%)and 11 articles published,2 articles published in Newspaper(2.8%)and 2 doctoral theses(2.8%),and only 1 articles from international conferences,accounting for 1.4%.

Fig.4 The distribution of subjects in publication source

Fig.5 The distribution of literature sources
2.5 Distribution of research institutions
The statistical data of the literature publishing institutions show that,the East China Normal University,the Environmental Monitoring,the Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences,the Qingdao National Marine Science and Technology Laboratory,the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,the Ocean University of China,and the State Oceanic Administration contributed to this publication.Among them,19 were published by the East China Normal University,accounting for 17.8%;9 were published by Environmental Monitoring,accounting for 8.4%;and 7 were published by the Huanghai Fishery Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Fisheries.In view of the attention of researchers on the basic research of micro-plastics is still at the initial stage,scholars from different research institutions have published relevant literature,accounting for 36.4%of the total,so the contribution rate is the largest.

Fig.6 The distribution of project fund sources
2.6 The Analysis of project fund sources
As shown in Fig.6 the source of fund is mainly from the support of national science foundation.There are 14 articles from the National Natural Science Foundation,totaling 18.2%;the second is supported by state key basic research and development plan(Program 973),accounting for 6.5%;National Social Science Foundation,Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation contribution rate were 3.9%and 2.6%.Besidesa number of important foundations have provided funds and carried out work in this field,with a proportion as high as 63.6%,which may be due to the fact that micro(nano)plastics study is still in the development stage,and that some basic research is still in the exploratory stage.Overall,the relevant research institutes at the East China Normal University,Environmental Monitoring and Qingdao National Laboratory of Marine Science and Technology have done a lot of preliminary work in model application.
3 Expectation
Bibliometric studies for a subject may be influenced by the type of database,the key words,the time of retrieval,and the tools of statistical analysis.
This article uses the literature metrology method for the analysis of micro(nano)plastics related literature to improve comprehensive understanding of the marine ecological environment for researchers,marine fisheries producers and marine environmental monitoring departments.The results may provide reference to the competent agencies and plastics enterprises to understand and grasp the domestic micro(Nano)plastics research progress,and problems to be solved,thus to strengthen academic exchanges,to promote effective research cooperation and to stimulate innovative ideas.
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the Opening Foundation of Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Pollution Processes and Environmental Criteria(2019-04)and the Science and Technology Innovation Project for Youth of Tianjin Agricultural Development Service Center(19KY11).
杂志排行
Marine Science Bulletin的其它文章
- Bibliometric analysis of Ecopath model in different ecosystem in China
- The benthic diatom community of Xiangshan Bay
- An overview of studies on marine macrobenthic community structure and biodiversity in the Bohai Sea
- Introduction to marine emergency forecasting and early-warning system(MEFES)
- Effect of mangrove forest on coastal hazards reduction
- Estimating shoreline response to sea level rise:the equilibrium model
