Epidemiological characteristics of 168 cases of COVID-19 in Hainan Island, tropical China: A descriptive study
2020-07-10XiaoZhenLiWenTingCaoShangBinLiuHaiRongHuang
Xiao-Zhen Li, Wen-Ting Cao, Shang-Bin Liu, Hai-Rong Huang
Department of Epidemiology, School of Public health, Hainan Medical University, Haikou, Hainan 571199, China
Keywords:COVID-19 Epidemiological characteristics Tropical areas
ABSTRACT Objective: To understand the epidemic characters of COVID-19 epidemic in Hainan province of tropical China and provid evidences for the prevention and control of the epidemic.Methods: Data on the COVID-19 epidemic collected from Health Commission of Hainan Province were analyzed by using the methods of retrospective descriptive epidemiology. Results: From January 22nd to February 21st, 2020, COVID-19 was diagnosed in 168 confirmed cases (including 8 severe cases) in Hainan Province with the temporary fatality rate of 2.38% of 4 deaths, and 96 cases discharged from hospital, with the cure rate of 57.14%. The cases were distributed in altogether 15 cities and counties in Hainan Province, among which 121 cases were distributed in Sanya, Haikou, Danzhou and Wanning, accounting for 72.02% of the total number of cases. Cases in Sanya City were mainly found in Tianya district and Jiyang district, accounting for 69.81% of the total number of cases in Sanya. Cases in Haikou City were mainly found in Qiongshan district and Xiuying district, accounting for 72.5% of the total number of cases in Haikou. Among the patients, there were 81 males and 87 females, with a male-to-female ratio of 1.1; the youngest age was 3 months, the oldest was 79 years old, 80% of the patients were in the age group of 30 to 69 years old, and the number of children and adolescents under 20 years old were relatively low. Conclusion: The daily number of new confirmed cases showed a gradual downward trend in Hainan province, and the epidemic situation was in transition from imported to local renewal, mainly in close contact between family members. With the increase of personnel mobility such as the resumption of work by enterprises and the return of migrant workers to the island, there is a risk of agglomeration epidemic. Prevention and control work in urban and rural areas should take a two-pronged approach. Amid preventing imported cases, more proactive measures should be taken to prevent and control the spread of local cases.
1. Introduction
The epidemic of novel coronavirus infection in Wuhan in late 2019 has attracted worldwide attention. The real-time dynamics of the epidemic affects everyone's heart. The pathogen of the novel coronavirus pneumonia is the novel coronavirus. The International Committee on Taxonomy of viruses has named it as "SARSCoV-2". WHO also officially named the disease as "corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19)". Hainan, as the southernmost tropical island in China, is also hard to escape. In order to prevent and control the spread and spread of the epidemic, Hainan has taken active and comprehensive scientific and effective measures, among which the track data of 14 days before the onset of the confirmed cases are more detailed, providing conclusive evidence for tracking the source of infection and close contacts. The epidemiological characteristics of covid-19 patients in Hainan Island were analyzed by using the data published by Health Commission of Hainan Province, to provide reference for preventing and treating the novel coronavirus pneumonia.
2. Data and methods
2.1 Data source
Patient information published on the official website of Health Commission of Hainan Province.
2.2 Methods
Using the methods of retrospective descriptive research. The activity track data of 14 days before the onset of the disease of 168 confirmed cases in February 21st, 2020 were analyzed by SPSS 20.0 software. The time, space and popular characteristics of patients were visualized by charts.
3. Results
3.1 Case overview
Since the first novel coronavirus report in Hainan province in January 22, 2020, as of February 21, 2020 at 24, Hainan has reported 168 cases of new coronavirus pneumonia in one month, including 8 cases of severe cases, 4.76% constituent ratio, 4 cases of cumulative deaths, 2.38% case fatality rate, 96 discharged cases [1], and the cure rate of 57.14%.
3.2 Case time distribution
Since January 22 to mid February 2020, new cases have been reported every day, with the most cases reported on January 27, February 4 to February 7 and February 12; since February 13, there have been 0 new cases reported on 6 days, as shown in Figure 1. The first death case occurred on January 27, and the other three cases occurred on February 6, 9 and 12, respectively; the first case was discharged on January 29, and the cumulative number of discharged patients increased gradually, as shown in Figure 2. As can be seen from table 1, from the perspective of development speed, the cumulative number of confirmed cases generally shows a declining trend.

Fig 1 Daily confirmed cases of COVID - 19 in Hainan in 2020 ( updated at 21st Feb 2020 )

Fig 2 The cumulative number of COVID - 19 cases in Hainan in 2020 ( updated at 21st Feb 2020 )

Tab 1 Dynamic changes of COVID - 19 cases in Hainan in 2020
3.3 Regional distribution of cases
January 31st, 57 novel coronavirus pneumonia cases were diagnosed as imported cases in Hubei, 53 cases, accounting for 92.98%. Except for Sansha City, Wuzhishan City, Tunchang County and Baisha Li Autonomous County, there are no confirmed cases reported in other regions, as shown in Table 2. Cases were mainly distributed in Sanya, Haikou, Danzhou, Wanning and other places, a total of 121 cases, accounting for 72.02% of the total. In Sanya, 53 cases were reported, accounting for 31.55% of the total cases in the province. The cases in Sanya City are mainly in Tianya districtand Jiyang district. 25 cases and 12 cases were reported respectively, accounting for 69.81% of the total cases in Sanya. In Haikou, 40 cases were reported, accounting for 23.81% of the total cases in the province. The cases in Haikou are mainly concentrated in Qiongshan district and Xiuying District, 16 cases and 13 cases were reported respectively, accounting for 72.50% of the total cases in Haikou. The activity track of 168 cases involved 286 districts or places in the province, including 88 in Sanya and 83 in Haikou.
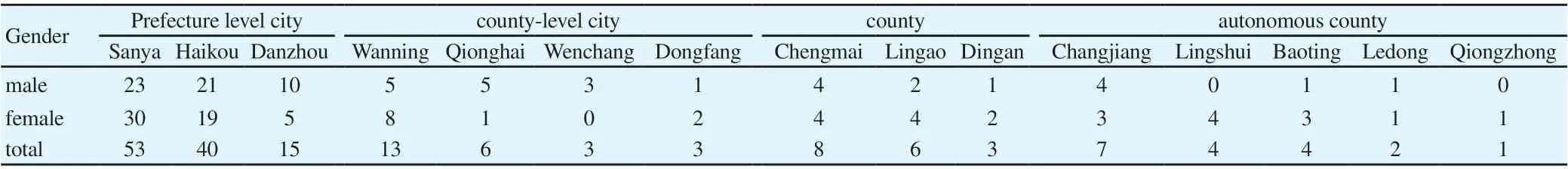
Tab 2 Distribution of confirmed cases of COVID - 19 in Hainan
3.4 Epidemic aggregation
The number of local cases has been increasing since February 1. For example, 7 of the 10 cases confirmed on February 9 were local cases, accounting for 70% of the cases on that day, while 5 cases confirmed on February 19 were all local cases. As of February 21, there were 48 local cases. According to the novel coronavirus pneumonia Epidemiological Investigation Technical Guide (trial version 1) [2] (excluding aircraft, train, motor vehicle, ship), 44 cases of epidemic have occurred in the province, including 21 close family contacts, 9 relatives and family meals, 6 friends' dinner contact, 4 District transmission, 2 Thailand tour group, 1 Haikou passengers and drivers. 1 contact between colleagues, see Table 3.

Tab 3 Distribution of regional aggregation of COVID - 19 in Hainan
3.5 Population distribution of cases
Among the 168 cases, 81 were male and 87 were female. The ratio of male to female was 1:1.1. There were 18 couples. The minimum age of onset was 3 months, the maximum age was 79 years, and the median age was 51.0 years. The patients aged 30-69 accounted for 79.76%, of which the patients aged 50-69 were the most, while the patients under 20 were relatively few, as shown in Figure 3.

Fig 3 Distribution of COVID - 19 cases by sex and age in 2020 in Hainan ( updated at 21st Feb 2020 )
Among the cases, 111 were from Hubei (48 males and 63 females), 33 from Hainan (17 males and 16 females), 7 from Heilongjiang (3 males and 4 females), 4 from Henan (2 males and 2 females), 3 from Xinjiang and Jiangxi (5 males and 1 female), 2 from Zhejiang, Hunan and Chongqing (5 males and 1 female), and 1 from Shanghai (male). In Hubei, there are 94 cases in Wuhan, 5 in Xiaogan, 4 in Jingzhou, 2 in Xiangyang and Shiyan, 1 in Huanggang, Jingmen, Guangshui and Songzi; in Hainan, there are 15 cases in Haikou, 6 in Danzhou, 5 in Changjiang, 2 in Sanya and Qiongzhong, 1 in Baoting, 1 in Chengmai and 1 in Ledong. The four deaths were 3 Wuhan residents (37, 77, 79 years old respectively) and 1 Thai tourist of Heilongjiang nationality (78 years old).
110 patients came to Hainan from Hubei or had a history of going to Wuhan (101 of them came to Hainan from Wuhan), 9 patients had a history of traveling to Thailand, 16 patients had close contact with people from Hubei (1 local case of Wuhan nationality), 15 patients had a history of close contact with local cases, 7 patients were likely to have community-based infection (3 local cases of Wuhan nationality), 11 patients had no clear exposure history (1 Wuhan native case).
4. Discussion
Novel coronavirus pneumonia cases in Hainan increased from less to more to less than normal in January 22, 2020 to February 21, 2020. The number of newly diagnosed cases increased gradually and the number of newly diagnosed cases decreased gradually compared with the cumulative diagnosis cases, which accords with the epidemic characteristics of the outbreak. At the same time, the results also show that the epidemic prevention and control work of the whole province is relatively solid, and all prevention and control measures have been effectively implemented. In particular, after the government of Hainan Province launched the level I response to public health emergencies, temperature detection points were set up at all airports, stations, ports and other transport hubs in the province to carry out temperature detection and test registration for all personnel entering the island; case trajectory data were collected and analyzed, close contacts were tracked, suspected symptoms were found, isolation and check-up were carried out in a timely manner, and local health and health lines were promptly informed Government departments and disease prevention and control institutions report; the municipal and county governments give full play to the role of grass-roots organizations, mobilize all forces to do a good job in collecting and reporting epidemic information, decentralizing and isolating personnel, and implementing public health measures. These measures novel coronavirus pneumonia played an important role in preventing and controlling the new crown pneumonia.
The novel coronavirus pneumonia epidemic is mainly imported in January. The cumulative number of confirmed cases has exceeded 100 cases in 15 days from January 22nd to February 5th. The possible reason is that Hainan is a tropical region with a pleasant winter climate. Every year, the elder in the whole country come to Hainan for winter after the national day. It increases the risk of infection with various infectious diseases. However, serving of individual dishes has been changing from the local to the local since February. The number of local cases reported in the province has been increasing gradually, and the spread of the district and the spread of the epidemic have increased. The main reason is that the locals in Hainan love to live in concentrated areas and concentrate on food. They should reduce the aggregation and strictly enforce the separate meal system. It is suggested that for the prevention and control of infectious diseases, we should move forward, improve the sensitivity of information, enhance the awareness of active prevention, and strengthen the grass-roots work to prevent the local spread and clustered spread of the epidemic while preventing the imported cases.
80% of the patients are 30-69 years old, among which there are more middle-aged and elderly people, and there are relatively few teenagers, children and infants under 20 years old, which is consistent with the overall incidence of disease in the country [3]. Some studies have confirmed that the population is generally susceptible [3], however, the number of children and infants is small, which may be due to the low risk of exposure, or the symptoms are light and not detected in time [4].
As of March 4, there have been no new cases in the province for 14 consecutive days, but zero new cases are not equal to zero risk, the epidemic has not been fully controlled, and the epidemic prevention work cannot be relaxed, so we should still be vigilant. At the same time, there has not been a large-scale population return in Hainan. With the continuous increase of the turnover of enterprises returning to work, returning to the island to study and other personnel, the risk of imported epidemic and clustered epidemic outside the province has increased, and at this time, we should not take it lightly. Therefore, several prevention and control suggestions are put forward:
1) In combination with the actual situation of Hainan, strictly implement the prevention and control measures of division and classification, and strengthen the grid management of urban and rural communities. The prevention and control departments at all levels should strengthen the management of personnel flow, do a good job in the registration of personnel flow and the screening of fever personnel and external personnel, especially strengthen the management of rework personnel and rental personnel in different places, and timely report the personnel with abnormal temperature or suspected respiratory infection symptoms.
2) We will vigorously carry out patriotic health campaigns, improve environmental health, and manage the excrement of good people and livestock. Pay attention to the hygiene of food and drinking water. Strengthen the publicity and education of prevention and control knowledge, guide the masses to develop good personal hygiene habits, wear masks when going out, wash hands frequently, avoid personnel gathering, and improve the public awareness of prevention and control.
3) All kinds of return to work units in the whole province must assign special personnel to carry out 14 days of health service management for returned employees in the province, monitor their body temperature in the morning and afternoon every day, and guide them to the fever clinic for medical treatment and troubleshooting in case of fever or other physical discomfort. All units try to be wrong in front of the work, flexible scheduling, banning parties and meals, serving of individual dishes, cleaning and living environment, and ventilation.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Effect of aripiprazole and olanzapine on the cognitive function in patients with schizophrenia
- Evaluation of hepatic fibrosis parameter model and elastic modulus of liver and spleen for the diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis b
- Mid-term follow-up of one-stage posterior debridement, intertransverse process bone grafting and screw-rod system fixation for Brucella spondylitis of the lumbar spine
- Effects of virtual reality balance games combined with muscle strength training on balance function and motor ability of Parkinson's patients
- Analysis of treatment strategies of traditional Chinese medicine for COVID-19 in tropical regions based on the pathogens of dampness and heat
- Survey and analysis of anxiety of 804 residents in Hainan during the COVID-19 epidemic
