Effects of virtual reality balance games combined with muscle strength training on balance function and motor ability of Parkinson's patients
2020-07-10LiChunSunRongChen
Li-Chun Sun, Rong Chen
1. Rehabilitation medicine department
2. Neurology department, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical College, Haikou 570000
Keywords:Parkinson's disease Balance movement Virtual reality balance games Strengthen muscle strength trainin
ABSTRACT Objective To investigate the effects of virtual reality balance games combined with strengthening muscle training on balance function and exercise capacity in patients with Parkinson's disease. Methods Sixty patients with Parkinson's disease were selected from January 2018 to October 2019. The random number table method was divided into the control group (n = 30) and the observation group (n = 30). Both groups were given conventional drugs and For rehabilitation training, the observation group was given a virtual reality balance game combined with strengthening muscle training. The upper limbs, lower limbs, balance function, comprehensive rehabilitation effect and daily living ability were compared before and after training. Results After training, the Brunnstrom score, FMA-UE, FMA-LE score, and cadence score of the two groups of patients increased. The common contraction rate (CR) of the biceps brachii in elbow flexion and the three heads of the brachii in elbow extension Muscle CR, standing walking test, 10m walking test, reduced left and right step difference, and the observation group was better than the control group, which was significant (P <0.05). Conclusion Patients with Parkinson's disease have improved their upper and lower extremity motor capacity and balance function through virtual reality balance games combined with strengthening muscle training, which can improve the overall rehabilitation effect and ability of daily living.
1. Introduction
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease with clinical symptoms such as posture balance disorder, resting tremor, muscle rigidity, and bradykinesia. Patients show reduced balance function, abnormal posture, walking disorder and etc., and most of them have expression, psychological disorders, autonomic dysfunction and dysarthria[1]. Patients with PD worsens as the disease progresses, leading to impaired balance and motor ability and increased risk of falls, reduced stride, slow pace, flustered gait, difficult to stop in time, severe frozen gait[2-3]. At present, the rehabilitation training for patients with PD is mainly based on reducing muscle tone training, but lacks training of the core muscles of the trunk, and is boring, and the patient's compliance is poor. Virtual reality (VR) technology is a virtual realm generated by computer and sensing technology, which stimulates multiple senses, and interacts directly with a computer-simulated environment through multiple sensory feedback, and timely feedback to improve the training effect[4]. Strengthening strength training is mainly to train the core muscle strength to improve balance and motor ability[5]. The study investigated the effects of virtual reality balance games combined with strengthening muscle training on balance function and motor ability in patients with PD. The analysis is as follows.
2.Materials and methods
2.1General data
Sixty Parkinsonian patients from January 2018 to October 2019 were included. They were randomly assigned to the control group (n=30) and the observation group (n=30) according to random trial number table. There were 19 males and 11 females in the observation group. The age ranged from 52 to 72 years, with an average of 61.43±7.34 years. The average disease duration was 6.17±2.39 years, and the length of education was 10.78±4.73 years, and the Hohen-yahr was 2.78±0.93 grades. There were 21 males and 9 females in the control group. The age was 50-71 years, with an average of 62.54±6.98 years. The average disease duration was 6.44±1.97 years, the length of educatio was 9.58±5.10 years, and Hohen-yahr was 2.91±0.84 grades. There was no significant difference between the two groups (P> 0.05).
Inclusion criteria were: ①diagnosis of PD; ②Age≥50 years;
③Hohen-yahr stage 1to 4; ④ sign written informed consent.
Exclusion criteria were: ①balance disorders due to other factors; ②severe organ dysfunction or bone and joint system diseases; ③severe visual, auditory or cognitive dysfunction; ④severe adverse reactions due to drugs ⑤cannot receive rehabilitation training because of lower limb fractures or severe pain.
2.2 Method
2.2.1 Conventional drugs and rehabilitation training
①Drug treatment: dopashydrazide tablets (H10930198, Shanghai Roche Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) were taken from the initial dosage 0.45-1.00g per day, and gradually increase.The average dosage was 0.75mg per day, usually 1-2 weeks to adjust. ②Rehabilitation training: include stretch, muscle, oral and facial muscle, coordinated balance, gait, joint mobility, upper and lower limb function and posture training. They performed 60 min of the training each time, 5 days per week for 1 month.
2.2.2 Virtual Reality Balance Game
All patients were trained under the guidance of the same physiotherapists. The system, Silverfit 2.5.5.8229 version, was a virtual scene from Silverfit in the Netherlands. There were two types of games, each 10min and 20min in total. ①City walking: Taking a standing position, the patient's feet projected onto the screen,which shows the scene of an urban road. The patient move the body back and forth, left and right to avoid the roadblock to successfully reaches the end point. If obstacle was encountered in the game, there would appeared corresponding sound and icon reminder. The difficulty would be increasing and time decreasing during the game. ②Garden picking: Taking a standing position, the patient was projected as a shovel. The screen was a vegetable garden where vegetables were randomly palced. They controled the movement of the shovel through a small range of body movement. If the shovel was hovering over the vegetable, the vegetable would flashes, and they can harvest the vegetable by squat or bend down. The difficulty wouldl be increasing and time decreasing during the game. 5 day per week for 1 month.
2.2.3 Strengthening muscle training
①trunk training: include trunk forward flexion, back extension, lateral flexion, rotation and other training; ②gluteal muscle training: flexion and extension in the prone position, left and right knees alternately lift the lower limbs; ③abdominal breathing training: the patient flexed his knees in a supine position, the therapist placed both hands on the patient's upper abdomen, inhaling with his nose and exhaling with his mouth. At the end of the exhalation, the hand slightly pressured in the direction of the upper crotch and the patient exhaled again. When practicing alone, they can place 1-2kg sandbags on the abdomen to try to achieve "Qi Chen Dan Tian". After mastering abdominal breathing in the supine position, and they switched to sitting exercises, and the difficulty gradually be increasing. Finally, the step of abdominal exhalation was converted into coughing. The above training was performed alternately, 20 minutes, separated into four 5-minute trials, with an interval of 2min. 5 days per week for 1 month.
2.3 Observation indicators
2.3.1 Upper limb conditions
①Brunnstrom score: the recovery of upper limb function process was divided into 6 stages (1-6 scores) according to motor function using Brunnstrom 6-stage scale. The higher the score suggested the better of motor function; ②FMA -UE score: Included hand speed, hand coordination and other items, a total of 66 scores.The higher the score indicated the lighter of movement disorder;③the surface electromyography analysis system was used to test and calculate the biceps brachii and triceps contraction rate (CR) when perfomed maximum isometric contraction.
2.3.2 Lower limbs
①FMA-LE score: using the FMA lower limb function scale, 2 scores can be completely completed, 1 score can be partially completed, 0 score cannot be completed, a total of 34 scores. ②Tied "standing-walking" test: the patient stood independently on a chair with a height of 45 cm and a height of 20 cm and walkedfor 3 meters in usual gait, then turned back and sat down. The time was counted based on whether the spine touched the chair, and the average was taken twice.③10m walking test: the patient walked 10m with relaxed steps and recorded the time.④Three-dimensional gait analysis: The Vicon system (UK) was used to collect the movement trajectories of the marked points on the body surface during walking, and analyze the frequency and lengh differences of left and right step.
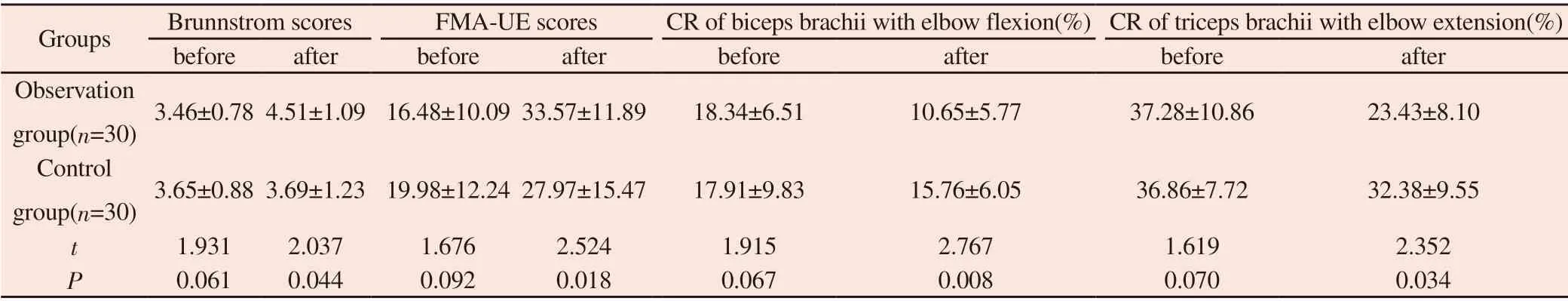
Table 1 Comparison of upper limbs before and after training
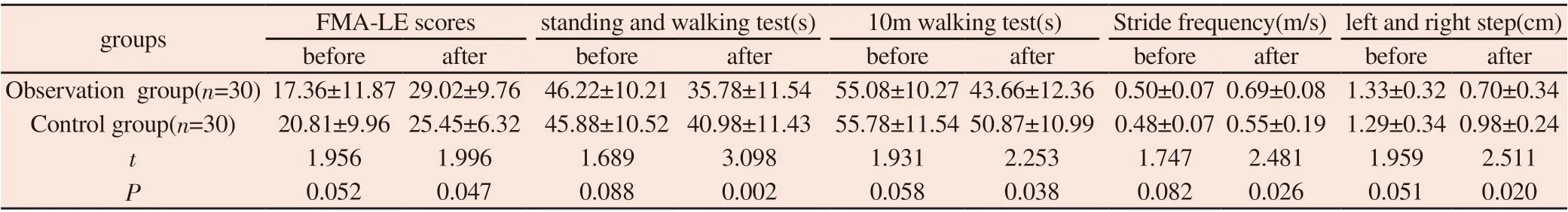
Table 2 Comparison of lower limbs before and after training

Table 3 Comparison of balance function before and after training
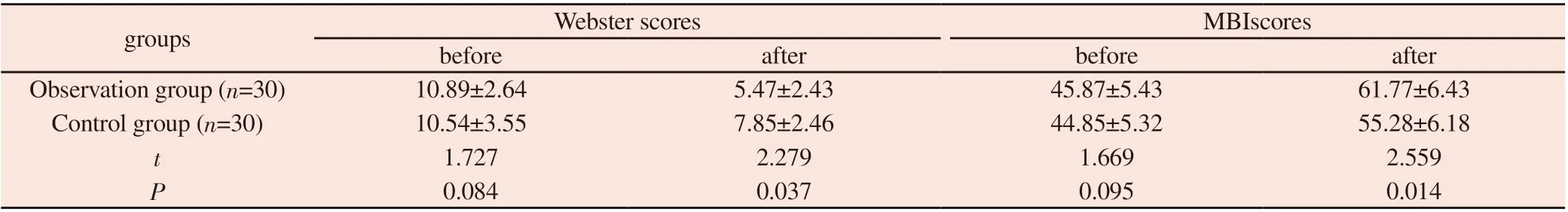
Table 4 Improved rehabilitation and daily activities before and after training
2.3.3 Balance function
①Using the Berg Balance Scale (BBS), including 14 activities such as sitting, unsupported sitting, with a total of 56 scores, and a score <40 was the risk of falling. The higher the score suggest the better the balance function. ②Posture stability test: compare standard deviation of the distance in four standing positions, standing with eyes open and closed on two feet, open and closed on heels and heel.
2.3.4 Rehabilitation effect and ability of daily living activities
①Webster score: the scale included 10 items such as upper limb movement posture, muscle rigidity, posture, and sit-up disorder, and adopted Likert-3 grade. The higher the score indicated the better the rehabilitation. ②MBI score: the modified Basel Index (MBI) scale included 11 items, grooming, bathing, eating, and toileting. The total score was 100 scores.
2.4 Statistical methods
SPSS 22.0 software was used for statistical analysis, and t-test was used for enumeration data. P <0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
3.1Comparison of the upper limbs before and after training
There were no significant differences in Brunnstrom, FMA-UE score, CR of biceps brachii with elbow flexion and triceps brachii with elbow extension between the two groups before training (P> 0.05). The upper limb indexes of the two groups were improved after training, and they were better in the observation group than that in control group, which was significant (P<0.05). It can be seen in Table 1.
3.2 Comparison of lower limbs before and after training
There were no significant differences in FMA-LE scores, standing and walking test, 10m walking test, stride frequency, left and right step between the two groups before training (P> 0.05). All indicators after training were improved, and they were better in the observation group than that in control group, which was significant (P<0.05). It can be seen in Table 2.
3.3 Comparison of balance functions before and after training
There were no significant differences in BBS scores, EO1, EO2, EOTS, and EC2 between the two groups before training (P> 0.05). BBS scores and EOTS were improved after training, and they were better in the observation group than that in control group, which was significant (P<0.05). It can be seen in Table 4.
3.4 The comprehensive rehabilitation effect and the improvement of daily living activity ability
There was no significant difference between the Webster and MBI score of the two groups before training (P> 0.05). The Webster score decreased and the MBI score increased in the two groups after training. And the sores in the obervation group was better than that in the control group, which was significant (P<0.05). It was seen in Table 4
4. Discussion
It is impossible to cure PD completely at present. Drug intervention is the main ways in clinic, in addition to physical rehabilitation, acupuncture, surgery and other interventions. However, drug treatment has resistance and toxic side effects. Physical rehabilitation, acupuncture, surgery and other treatments not only need certain requirements on technician but also cause longterm economic burden on patients[6]. Game training can increase repetitive and high-intensity training, which is fun and inexpensive, and has certain advantages in rehabilitation [7]. And the core muscles of the body can stabilize joints and counteract gravity to ensure the stability of various postures. It is responsible for transmitting the energy of joints in the training to the trunk. The body balance ability and the extension of the trunk range have a better effect [8].Therefore, strengthening the core muscles is beneficial for improve body control , enhance balance, and expand the range of torso activity.
The body constantly changes the weight to complete walking, so good posture control and balance are crucial to completing walking. So walking stability is affected by pelvic stability which are mainly supported by the superficial core muscles and motor coordination. Wang et al.[10] used intensive muscle strength training in the rehabilitation of elderly patients with PD, and the results showed that it can change the patient's gait and promote the recovery of walking ability. In this study, the patients in the observation group who used intensive muscle training to improve the strength of the core muscle group. Intensive muscle training can stimulate the muscle cells of the corresponding muscle group, promote the synthesis of protein, and produce more myosin and action that improves and repairs contractile units. It can also stimulate muscle excitation-contraction coupling during training, thereby improving exercise coordination. Therefore, the strength of the core muscle group in the observation group was improved, the stability was enhanced, the weight control ability was strengthened, which provided support for the lower limb alternation and eventually promoted functional brain reconstruction[11]. Bao et al.[12] found that stroke patients given virtual reality therapy, the primary sensor motor cortex on the contra lateral side of the lesion was activated, and the function of upper limb could be effectively improved. In this study, patients in the observation group underwent rehabilitation training through virtual reality game. It provided various ways of feedback for proprioception, hearing, and vision. The patients observe the projection of the body in the screen through "urban walking", and can perceive his own movement direction and position in the space, combining sensory and physical information to improve anti-interference ability, selecting reliable information to reconstruct sensory and motor connection to improve balance ability. In "garden picking", patients need to complete the tasks of standing up and squatting many times and switch at any time, which distract their attention. It can improve the ability of integration of the vestibular information, central organization and posture control so that adapt to various situations better in daily life. The study showed that patients in the observation group have significantly improved their ability of upper limb or lower limb motor and balance function, and comprehensive rehabilitation effects and daily activities have also effectively improved. It may be related to patients who were given a virtual reality balance game combined with strengthened muscle training in the observation group, in addition to conventional training. On the one hand, the goals positive feedback were given in the virtual reality game to promote the brain to process all kinds of feedback to help patients adjust posture, maintain movement, promote optimization of exercise patterns, and improve learning and performance of exercise [13-14]. On the other hand, the training of core muscle groups through intensive muscle training provided strong muscle support for patients' various movements[15].The combination of the two kinds of rehabilitation training can complement each other and jointly promote the stability, postural control and balance of the patients in the completion of various movements, so as to better adapt to daily life activities. However, there were few research objects selected and geographical restrictions in this research, which may affect the results. It should be further explored in the future.
In summary, patients with PD had improved their upper and lower extremity exercise capabilities and balance functions through virtual reality balancing games combined with intensive muscle training, which can improve the overall rehabilitation effect and ability of daily life activities.
杂志排行
Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Analysis of treatment strategies of traditional Chinese medicine for COVID-19 in tropical regions based on the pathogens of dampness and heat
- The prevalence of depression among students in Chinese universities over the past decade: A meta-analysis
- Epidemiological characteristics of 168 cases of COVID-19 in Hainan Island, tropical China: A descriptive study
- Survey and analysis of anxiety of 804 residents in Hainan during the COVID-19 epidemic
- Evaluation of hepatic fibrosis parameter model and elastic modulus of liver and spleen for the diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis b
- Effect of aripiprazole and olanzapine on the cognitive function in patients with schizophrenia
