基于改进Otsu的电润湿缺陷图像分割
2020-07-05廖钦楷林珊玲林志贤陈哲亮李甜甜
廖钦楷,林珊玲,林志贤*,陈哲亮,李甜甜,唐 彪
基于改进Otsu的电润湿缺陷图像分割
廖钦楷1,2,林珊玲1,2,林志贤1,2*,陈哲亮1,2,李甜甜1,2,唐 彪3
1福州大学平板显示技术国家地方联合工程实验室,福建 福州 350116;2福州大学物理与信息工程学院,福建 福州 350116;3华南师范大学,华南先进光电子研究所,广东省光信息材料与技术重点实验室,广东 广州 510006
针对像素缺陷影响电润湿电子纸的显示效果,本文提出一种基于Otsu的自动阈值检测方法对缺陷进行检测。Otsu是一种常用的自动阈值方法,在图像直方图为双峰时,该方法能给出令人满意的结果。但是电润湿缺陷图像直方图通常为单峰,容易得到错误的结果。电润湿由于不同颜色的填充油墨使得缺陷与背景对比度不同,导致分割更加困难。本文在目标方差前引入加权系数,权值随着缺陷的累积概率的增大而减小。权值在阈值过峰前保持较大的数值,过峰后权值降低,保证了阈值在单峰情况下始终处于峰的左边。实验结果表明:本文提出的方法能够有效分割电润湿缺陷区域,尤其在对比度较低的电润湿缺陷图像中比Otsu、VE、WOV和熵加权方法的ME值更接近0,有更好的分割效果。
电润湿电子纸;图像处理;机器视觉;缺陷分割;最大类间方差法
1 引 言
随着信息产业的快速发展,显示技术已经成为人们获取信息的重要渠道。近些年,电润湿[1]这种新型的显示技术开始崭露头角,它是一种电子纸显示器[2],具有响应速度快、造价低、能量损耗小等优点,有望引领潮流,成为下一代主流显示器。电润湿显示技术目前处在高速发展期,国内外许多机构对其进行了大量的研究[3-10]。由于生产技术等问题,电润湿器件生产过程中可能存在缺陷,缺陷影响显示效果,因此对电润湿器件缺陷的检测必不可少。目前对电润湿显示器件的缺陷检测还未有研究,但存在许多其他相似的显示面板的缺陷检测方法。对于显示器件的缺陷检测,机器视觉技术是代替传统人工检测的常用方法,它是一种无损缺陷的检测方法,能够在不接触产品的情况下对缺陷进行检测。Jin[11]等人提出基于离散余弦变换和双伽马分段指数变换的TFT-LCD缺陷检测方法;何俊杰[12]等人通过区域神经网络对缺陷进行检测。但这些方法计算复杂,较难实现。自动阈值技术是较为常用的缺陷检测方法,与上述方法相比计算简单,速度快,更易于实现,因此被广泛应用于缺陷检测中。
自动阈值技术将图像分成前景和背景两部分。几十年来,为了更好地使用自动阈值方法对图像进行分割,人们提出了许多方法进行改进。大津法(Otsu)[13]是常用的全局自动阈值分割方法,因其方便、高效、分割效果良好而被广泛应用于图像分割中,但在直方图为单峰或接近单峰时,该方法容易得到错误的阈值。为了更加接近期望阈值,Ng[14]提出了一种改进的Otsu方法,即谷强调法(valley emphasis,VE),它利用目标函数中的谷值信息最大化类间方差,但对于目标与背景方差差距很大的图像,则不能成功地分割。针对这个问题,Fan和Bo[15]提出了一种改进的Otsu方法,称为邻域谷强调(neighborhood valley emphasis,NVE),该方法利用谷点的邻域信息进一步提高分割质量。张博[16]等人结合图像梯度和Otsu方法提取缺陷目标,克服了Otsu方法对噪声敏感的问题。Yuan[17]等人提出了一种改进的Otsu方法。对象方差加权法(weighted object variance,WOV),该方法是将一个参数加权到类间方差的对象方差上,该权重为缺陷发生的累积概率,以确保阈值始终位于两个峰值之间或单个峰值柱状图左下边缘的值。Mai[18]等人使用熵加权(entropy weighting,EW)方法对Otsu进行改进,该方法能够检测非常小的缺陷,但是该方法在处理缺陷与背景对比度较小的图像时难以将缺陷分割出来。
由于填充的油墨不同,电润湿电子纸缺陷图像的缺陷与背景的对比度也不同。当填充浅色油墨时,缺陷与背景的对比度较大,较容易分割。当填充深色油墨时,缺陷与背景的对比度较低,分割比较困难。为了能够在不同油墨下实现缺陷分割,提出一种改进的Otsu阈值分割算法,在目标方差前引入权重,通过权重影响类间方差的数值,最终得到期望的阈值。权值随着缺陷累积概率的增大而减小,使得阈值在单峰时能够处于峰的左侧边缘,确保在不同颜色的油墨中实现缺陷图像的分割。
2 电润湿器件结构
电润湿器件的基本单元是一个个像素格,器件以镀有氧化铟锡(ITO)的透明玻璃板为基底,旋涂疏水绝缘层,以光刻技术将每个像素格分开形成像素墙,然后再填充有色油墨及水。在不加电时,油墨在表面张力的作用下铺满整个界面,此时器件为“关”状态。加电以后,水和绝缘层之间的表面张力发生改变,水将油墨挤到一边,露出底层的基板,此时电润湿为“开”状态。电润湿显示原理示意图如图1所示,图1(a)为未加电时的电润湿器件,此时油墨平铺在像素格中。图1(b)为加点后的电润湿器件,此时电润湿的水和绝缘层之间的表面张力发生改变,油墨收缩在像素格中。图1(c)和1(d)分别为图1(a)和1(b)的测试样品图。
三层叠加式的电润湿电子纸由三基色油墨填充进像素从而实现彩色显示,且不同颜色油墨其油墨回流的程度不同,因而对不同颜色油墨的光电性能的分析是电润湿显示器件的重要研究之一。生产过程中,由于油墨溢出,疏水绝缘层旋涂不均匀,制作过程中外部引入的杂质,不同区域刻蚀程度的差异以及显影过程中残留显影液的不完全蒸发,可能导致缺陷的产生。缺陷与背景油墨的灰度存在差异,降低了显示效果。也正因为如此,由于缺陷与背景灰度的差异性,缺陷灰度和背景灰度被分为两类。对于两类分割,Otsu是决定一般图像阈值最常用的方法。不同的油墨对于缺陷的分割将带来不同的分割难度,当油墨颜色较浅时,缺陷与背景对比度高,分割较容易。当油墨颜色较深时,缺陷与背景对比度较低,缺陷较难从背景中分割出来。
如图2中所示,图2(a)中为填充浅色油墨的电润湿器件,其中的缺陷可以很容易被观察到,也较容易分割。图2(b)填充了深色油墨,缺陷难以被观察到,因而分割较为困难。
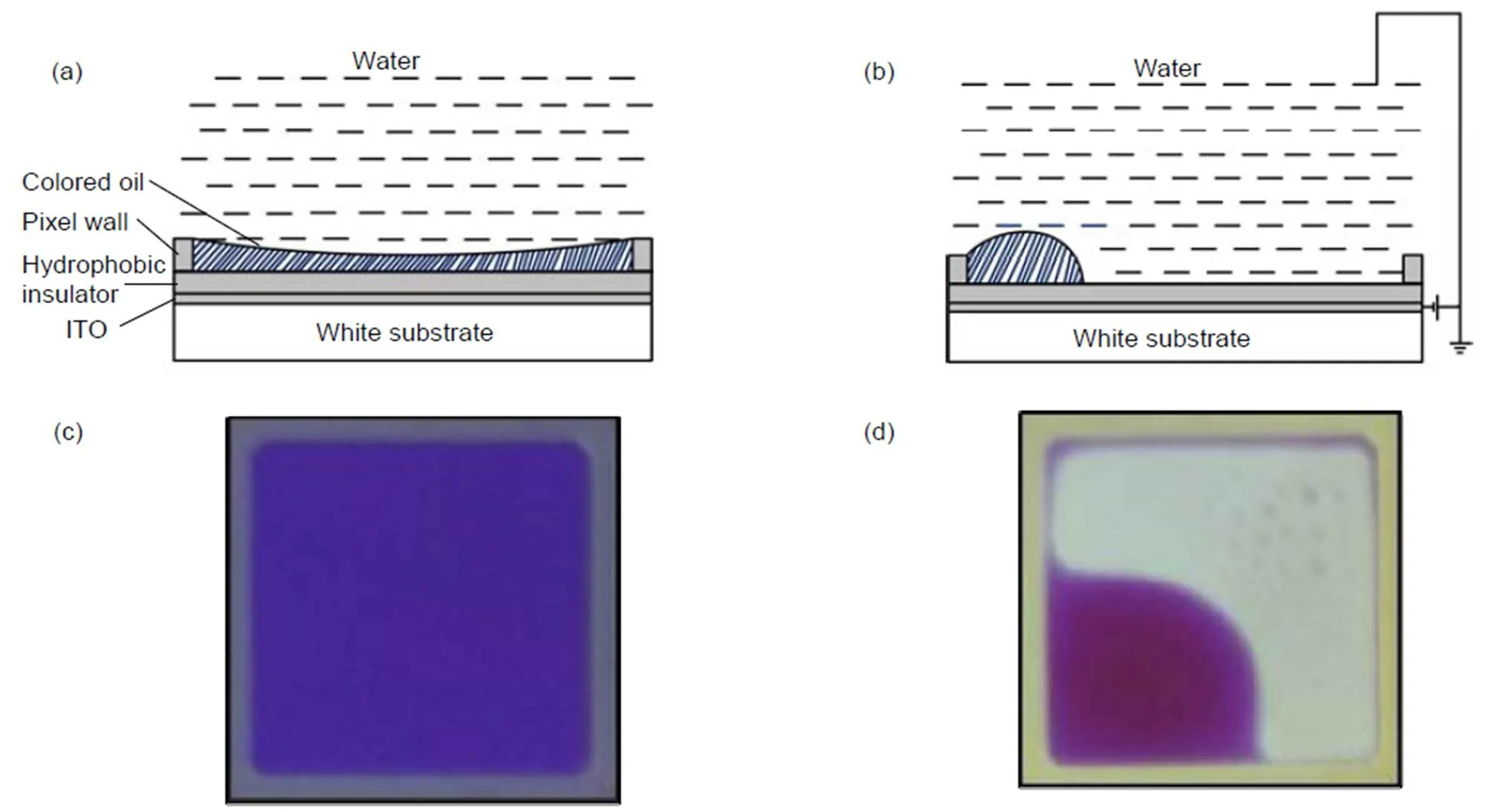
图1 电润湿显示原理示意图及测试样品。(a) 油墨平铺在像素格中;(b) 油墨收缩在像素格中;(c) 图(a)的测试样品图;(d) 图(b)的测试样品图
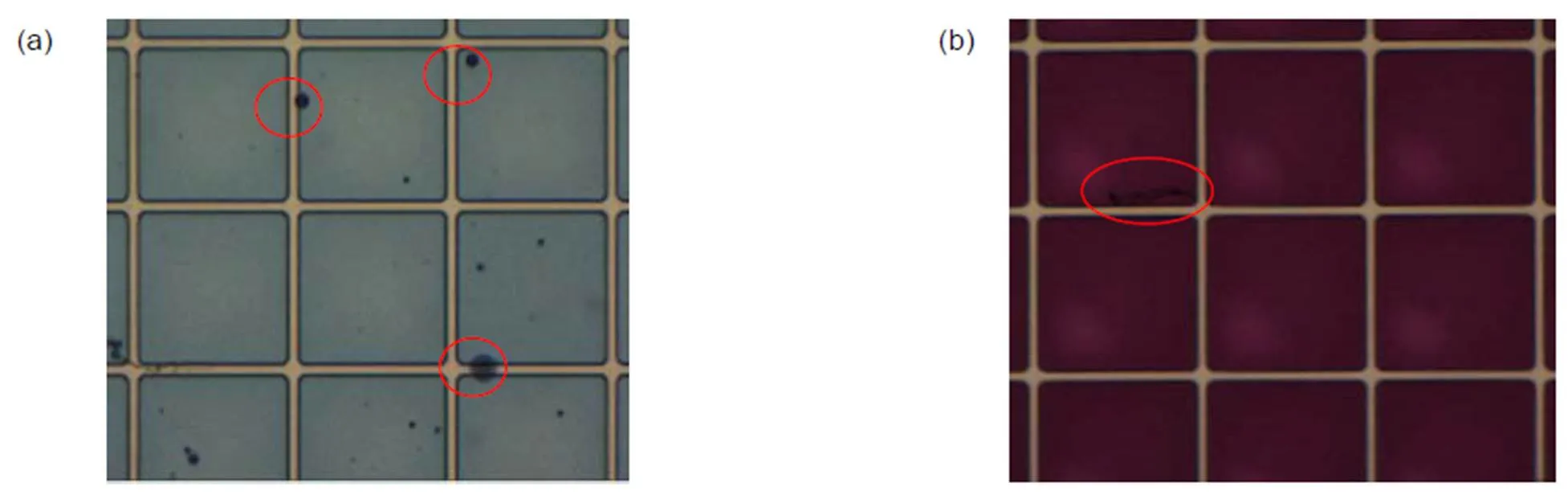
图2 不同填充油墨中的电润湿器件缺陷。(a) 浅色油墨中的电润湿缺陷;(b) 深色油墨中的电润湿缺陷
3 自动阈值方法以及存在的问题
Otsu是一种全局自动阈值技术,常用于图像分割。本章简要介绍Otsu方法,并研究分析其存在问题。
3.1 大津法(Otsu)
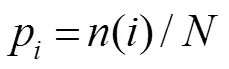
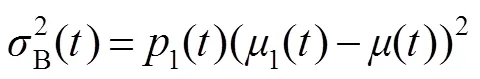
文献[20]给出类间方差的快速算法:
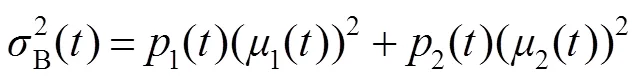
使得类间方差达到最大值时为最佳阈值。令为图像的最佳阈值,则有
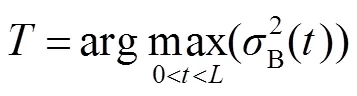
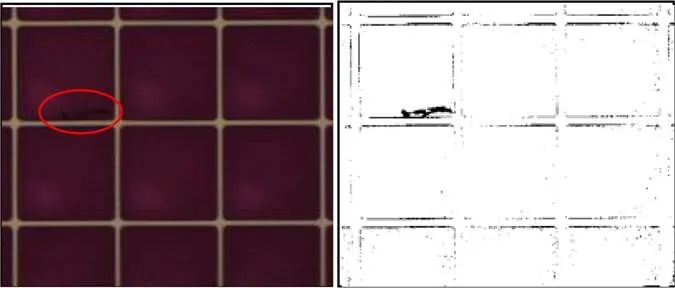
当灰度直方图为双峰且两峰的类间方差差距不大时,Otsu能够取得令人满意的效果;但是当灰度直方图为单峰时,Otsu方法容易得到错误的阈值,如图3所示。图3(a)中红色圈中为缺陷区域,图3(b)为Otsu方法的分割结果,该方法没有将红圈中的缺陷与背景分割开。图3(c)中,右边的黑色直线为Otsu方法得到的阈值,该方法得到的阈值为175,在峰的内部;而期望阈值在102左右,在峰值的左边,两者相差很大。因此Otsu方法在处理缺陷与背景类间方差差距很大的情况时效果不理想。
3.2 改进方法
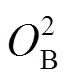
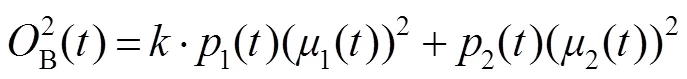
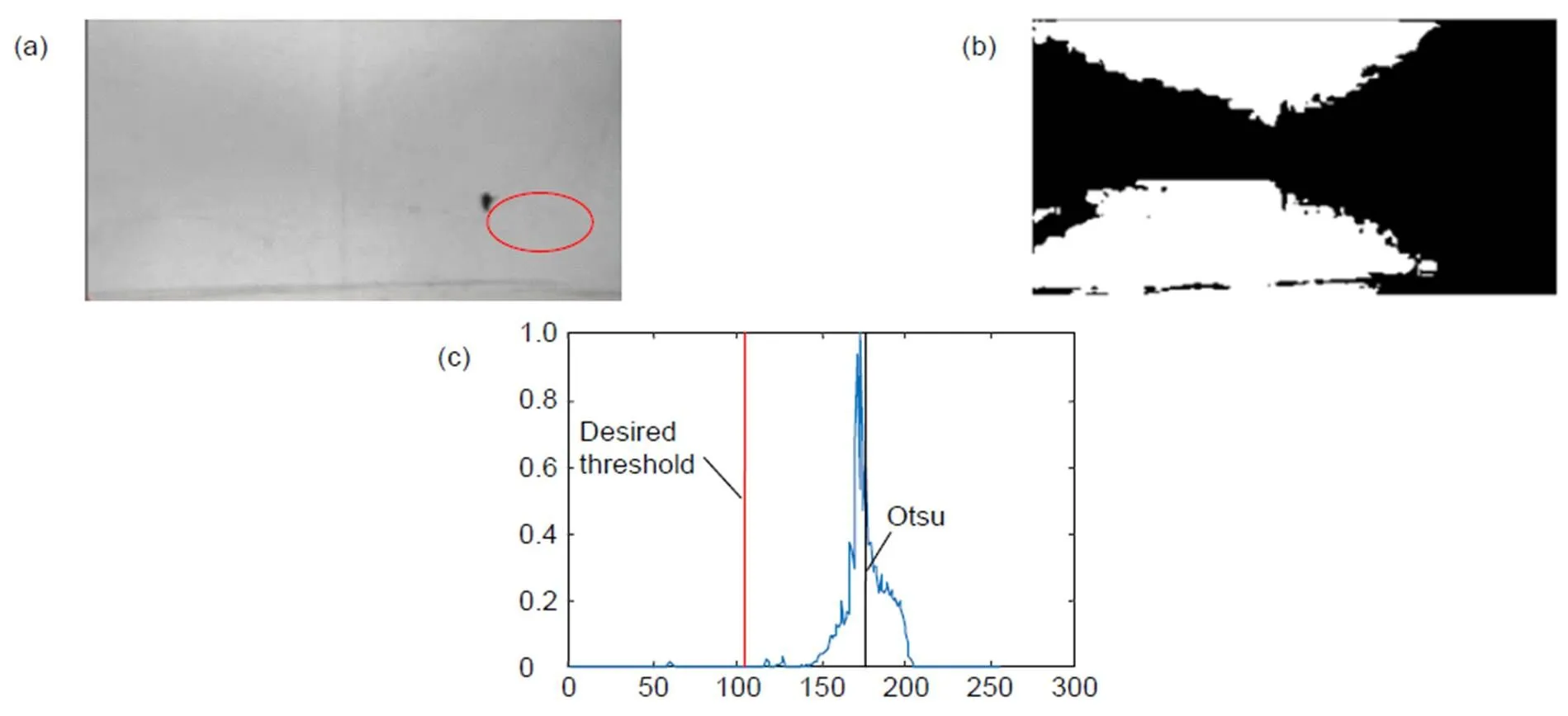
图3 Otsu缺陷图像分割结果。(a) 原始图像;(b) Otsu方法处理结果;(c) 直方图和阈值
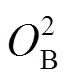
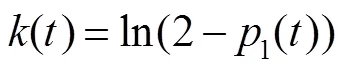
因此式(4)改写成:
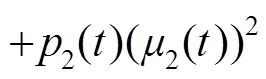
分割结果如图5(b),5(c)所示,图5(b)是Otsu的分割结果,其阈值在峰内,大部分背景被划分为了缺陷,难以区分出实际的缺陷区域。图5(c)改进后阈值位于峰的左边,将缺陷和背景分成两类,从而分割出缺陷。缺陷方差、背景方差以及类间方差的变化规律如图5(d)~5(f)。图5(d)是Otsu缺陷方差和背景方差的变化规律,得到的阈值在缺陷方差和背景方差变化最快的区域,即峰值内部。图5(e)中黑色的粗曲线是加权后的缺陷方差,其在缺陷方差变化最快的区域即过峰时降低了对类间方差的贡献。最终改进后类间方差的结果如图5(f)所示,改进后类间方差的最大值在100左右,较Otsu的结果左移了大约60个灰度值。
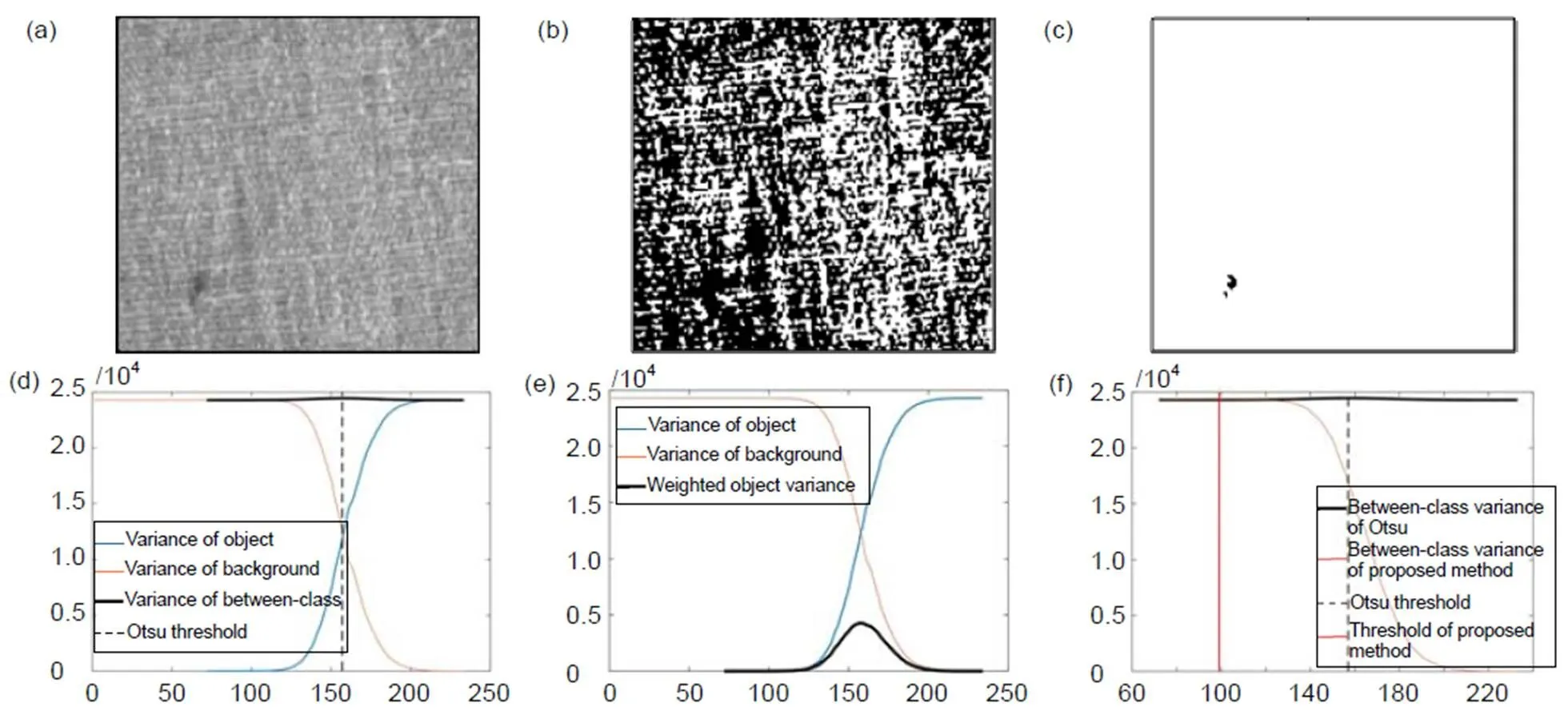
图5 缺陷图像与灰度方差图。(a) 原始图像;(b) Otsu结果;(c) 本文方法分割结果;(d) 灰度方差曲线;(e) 灰度方差曲线与加权后缺陷方差曲线;(f) Otsu类间方差曲线与加权后类间方差曲线
4 实验结果与讨论
本文提出方法主要对电润湿缺陷像素进行分割,实验对象为浅色和深色油墨的电润湿缺陷图像,这两种图像的不同点在于缺陷与背景的对比度不同。实验对这两类图像进行分割,并将Otsu及其他改进方法,如VE、WOV、EW,与本文提出的方法进行对比,再通过ME(misclassification error)值评估这几种方法的性能。实验图像数据来自华南师范大学光信息材料与技术重点实验室测试平台,由Phantom高速摄像机拍摄,图像全分辨率为1280×800。
4.1 电润湿缺陷像素分割结果与讨论
图6到图10为不同油墨下的不同方法的缺陷分割结果。图6和图7中电润湿像素油墨较浅,缺陷和背景油墨对比度高,缺陷较容易被分割。图6中Otsu、VE、WOV和本文方法都能都成功将缺陷与背景分割,但是EW的分割效果不理想,该方法把油墨错误地分割成了缺陷。图7中存在5个缺陷点,Otsu、VE和EW法都将背景错误地分割成了缺陷,没有分割出任何缺陷。WOV法分割出了部分缺陷,本文方法则将5个缺陷点全部从背景中分割出来。图8和图9为填充深色油墨的电润湿缺陷图像,此时缺陷与背景的对比度较低,分割较困难。图8和图9中的红圈内是缺陷区域,Otsu、VE、WOV和EW方法得到的阈值都在峰的右边,把深色的油墨错误地分割成缺陷,没有将图像的缺陷分割出来。本文方法得到的结果在峰的左边,将缺陷从深色的油墨背景中分割出来。图10的实验图像中缺陷与背景的对比度极低,甚至人眼也不易察觉。Otsu、VE、WOV和EW方法在深色油墨中无法分割出缺陷,本文方法则能够在极低的对比度中把缺陷与背景分离。
4.2 ME值对阈值分割结果的评价
为了验证本文方法对电润湿缺陷的分割效果,采用ME[21]值对各自动阈值方法性能进行评估。ME反映的是错误分配给前景或者背景像素的百分比。ME法可以简单表示为
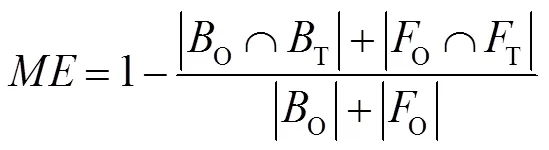
其中:O代表手动阈值化图像背景,T代表不同方法分割的图像背景,O代表手动阈值化图像前景,T代表不同方法分割的图像前景。对于分割完全正确的图像,ME值等于0,ME的值越大,说明分割效果越差。
表1中ME值反映了五种自动阈值法的分割效果。ME值越小,分割效果越好。图6和图7中是浅色的电润湿像素图片,缺陷与背景的对比度较大,Otsu、VE在图6中的ME值很小,但图7中的ME值很大,其分割效果并不稳定。WOV和本文方法都得到了一个接近于0的ME值,说明被错误分类的像素数很少。而EW法得到的ME值很大,该方法将大部分的背景错误分割成缺陷。图8到图10是对比度较低的深色油墨中的电润湿缺陷,只有本文方法的ME值保持在一个很小的数值,而Otsu以及其他自动阈值方法的ME值都在0.85以上,分割的结果远离期望阈值。本文方法在浅色油墨和深色油墨中都能够得到接近0的ME值,能够分割不同油墨中的缺陷,尤其在缺陷与背景对比度较低时有更好的分割效果。
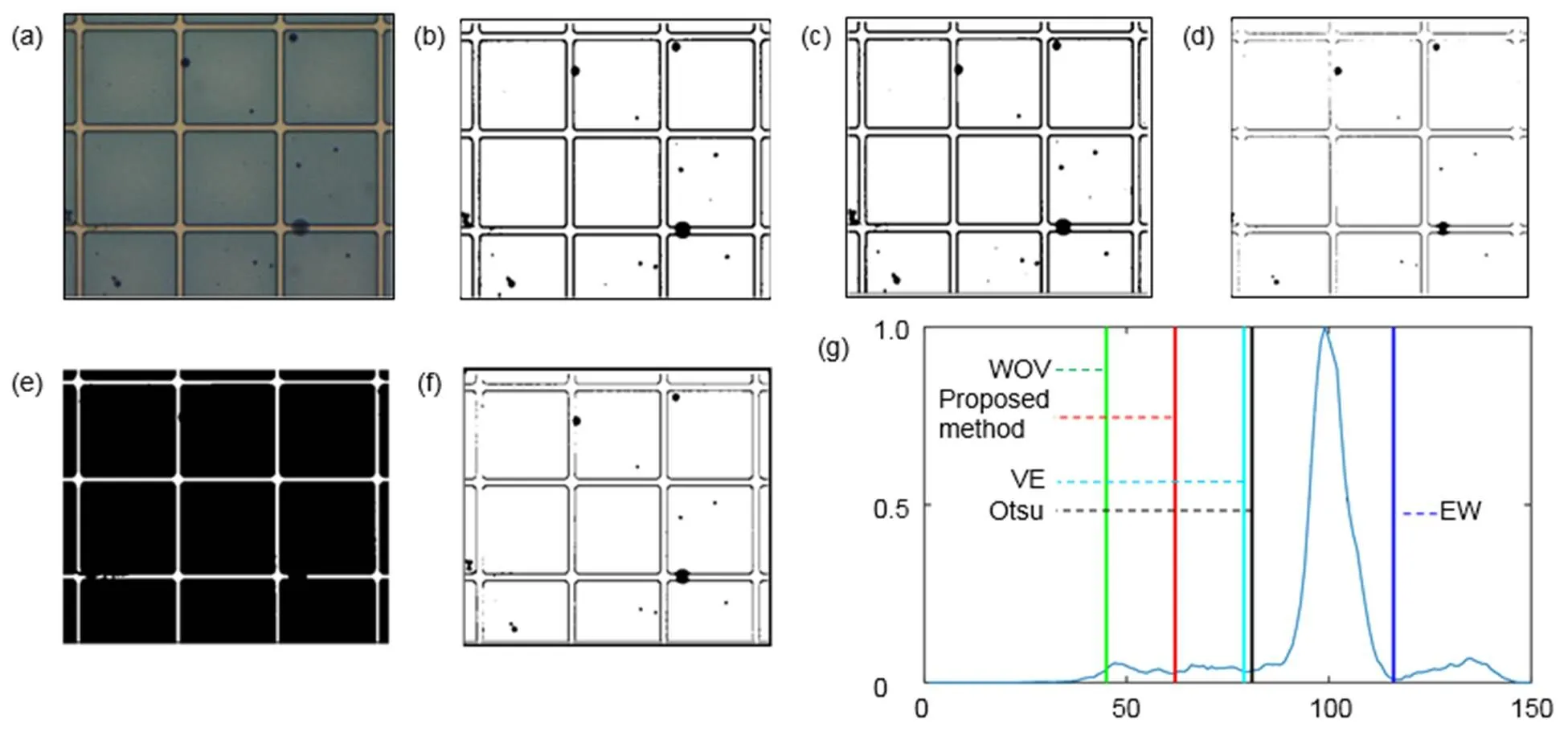
图6 五种自动阈值方法对电润湿图像Ⅰ的分割结果。(a) 原始图像;(b) VE方法;(c) Otsu方法;(d) WOV方法;(e) EW方法;(f) 本文提出方法;(g) 直方图和阈值
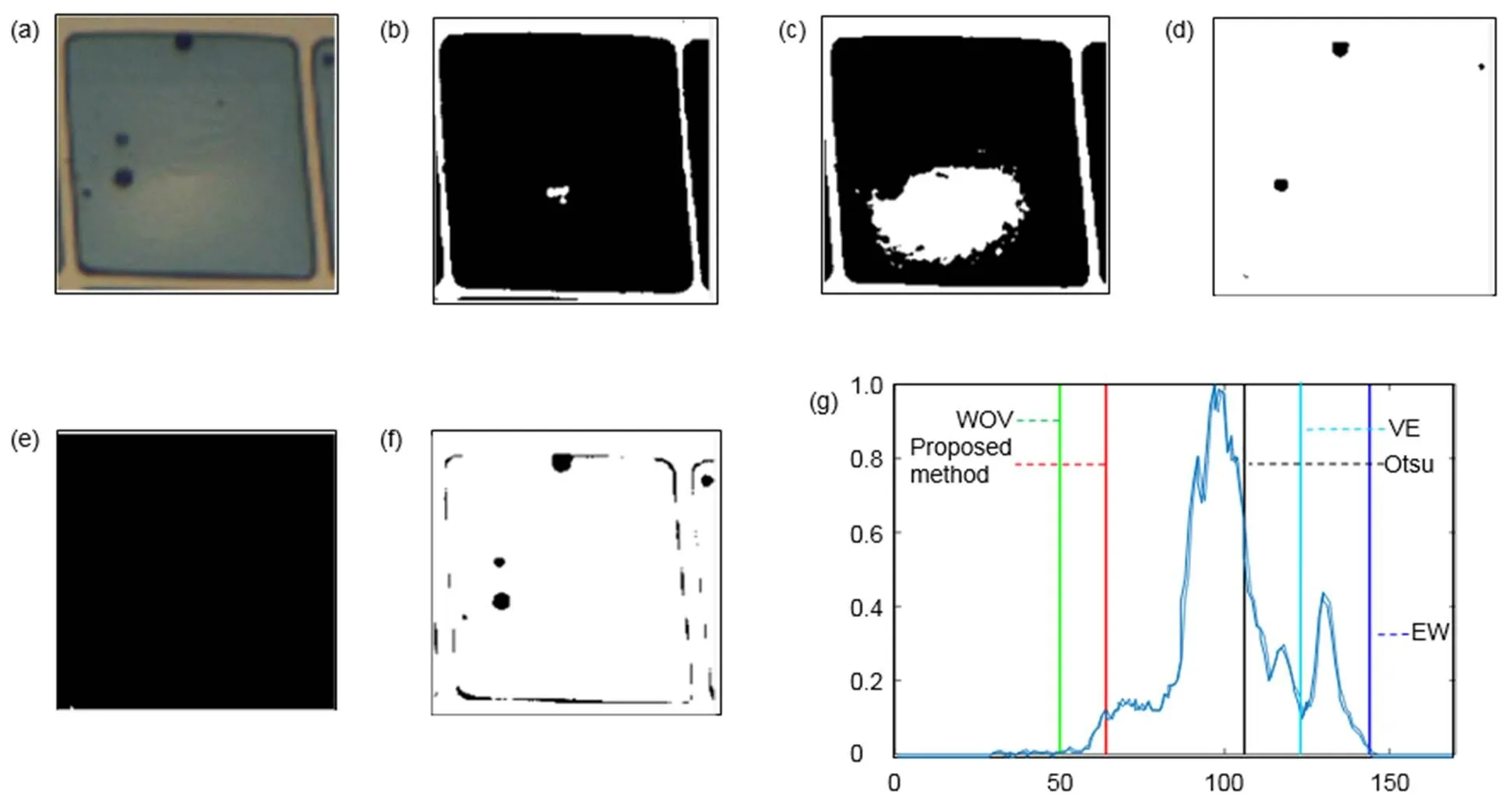
图7 五种自动阈值方法对电润湿图像Ⅱ的分割结果。(a) 原始图像;(b) VE方法;(c) Otsu方法;(d) WOV方法;(e) EW方法;(f) 本文提出方法;(g) 直方图和阈值
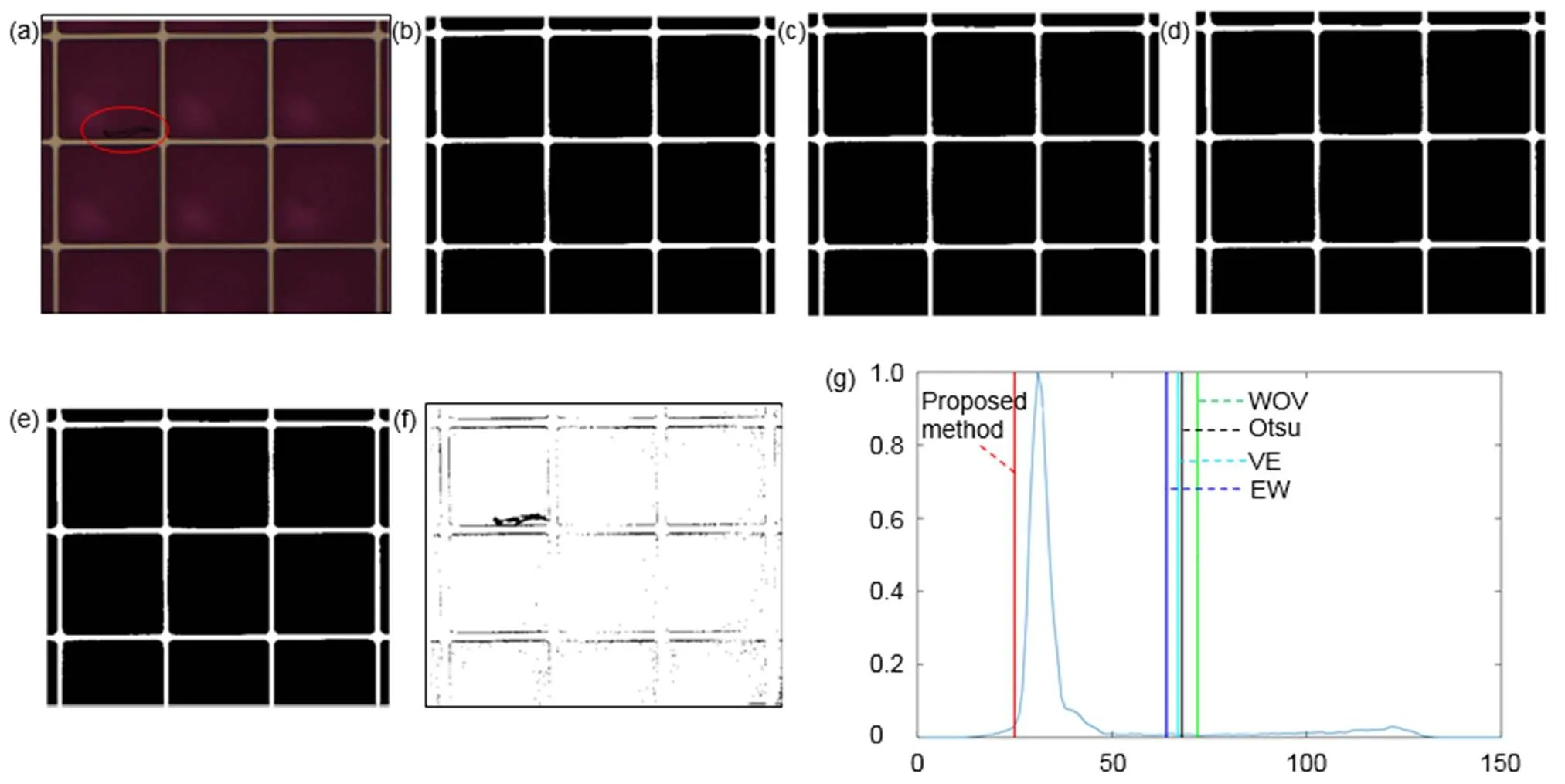
图8 五种自动阈值方法对电润湿图像Ⅲ的分割结果。(a) 原始图像;(b) VE方法;(c) Otsu方法;(d) WOV方法;(e) EW方法;(f) 本文提出方法;(g) 直方图和阈值
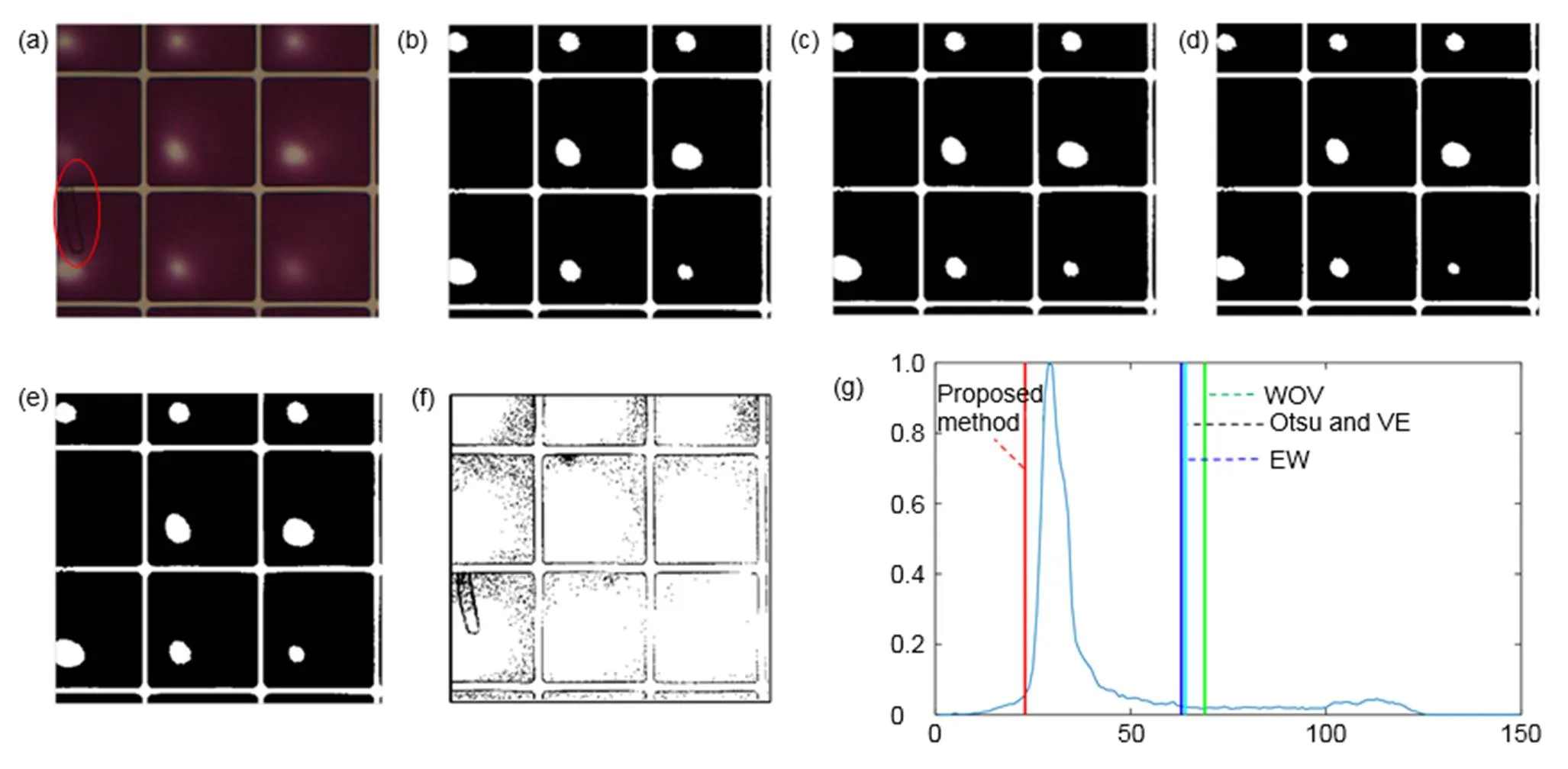
图9 五种自动阈值方法对电润湿图像Ⅳ的分割结果。(a) 原始图像;(b) VE方法;(c) Otsu方法;(d) WOV方法;(e) EW方法;(f) 本文提出方法;(g) 直方图和阈值
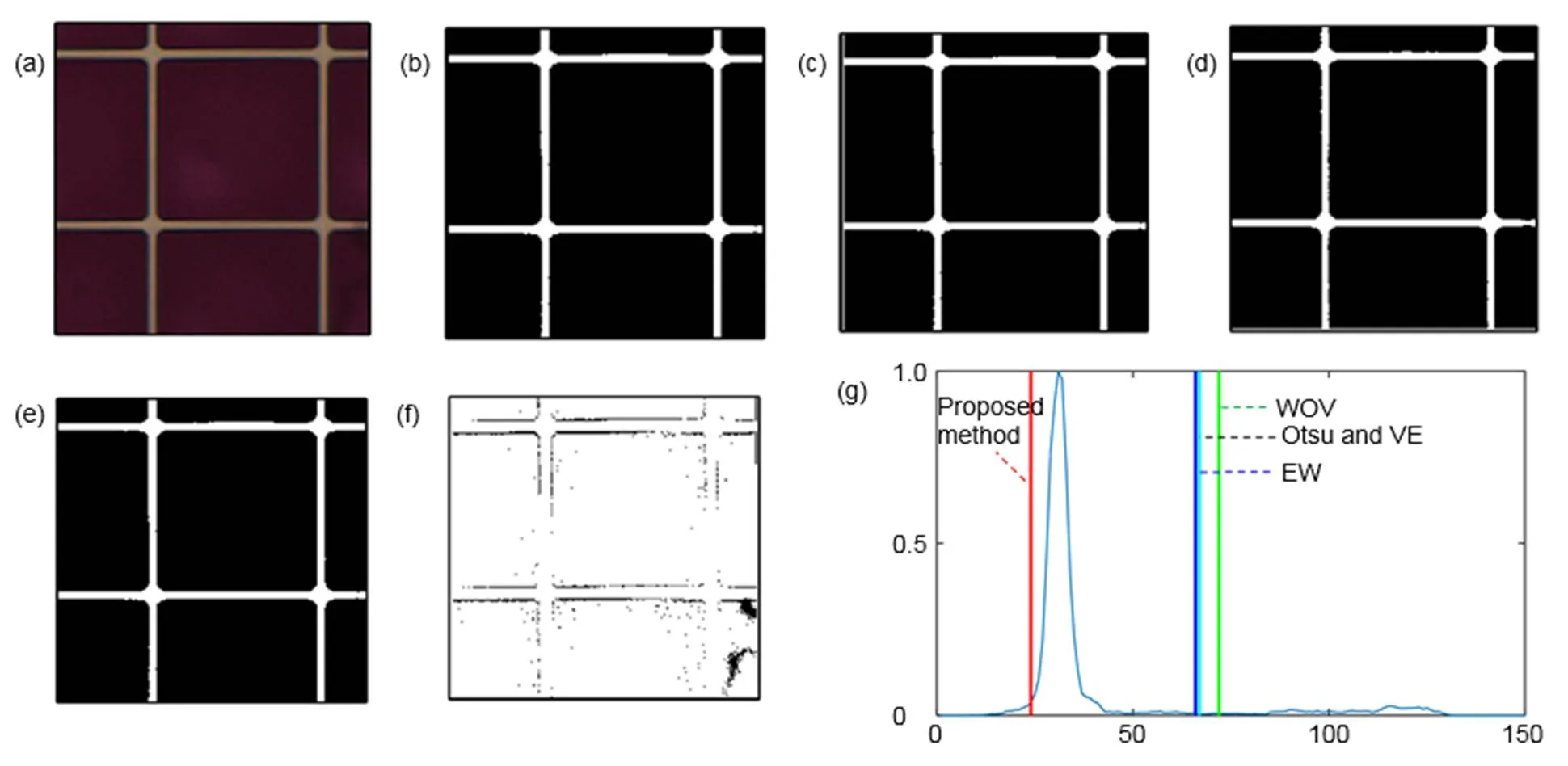
图10 五种自动阈值方法对电润湿图像Ⅴ的分割结果。(a) 原始图像;(b) VE方法;(c) Otsu方法;(d) WOV方法;(e) EW方法;(f) 本文提出方法;(g) 直方图和阈值
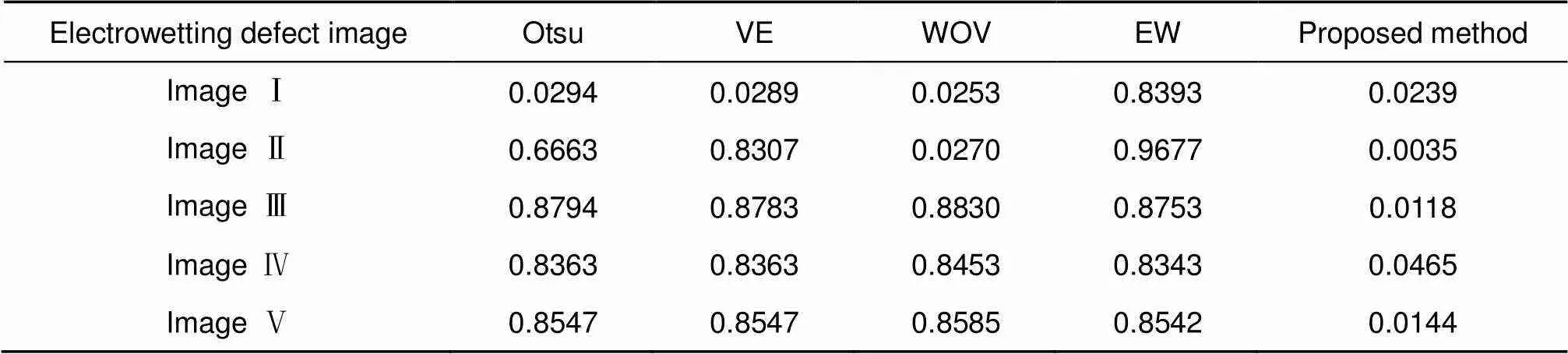
表1 五种方法分割结果的ME值
5 结 论
电润湿缺陷与背景的对比度由于填充的油墨不同所以无法确定,当填充深色油墨时缺陷与背景对比度较低,导致分割困难。本文提出一种改进的Otsu方法,在目标方差前引入权重,权值随着缺陷累积概率的增大而减小,提高了类间方差在峰值左边缘时达到最大值的概率。且加权因子简单,易于实现,不用人为设置参数。实验结果表明,本文提出的方法能够分割不同颜色油墨下的缺陷,对比Otsu、VE、WOV和EW等方法,在填充深色油墨的电润湿缺陷像素中ME值更接近0,在对比度较低的深色油墨下有更好的分割效果。
[1] Hayes R A, Feenstra B J. Video-speed electronic paper based on electrowetting[J]., 2003, 425(6956): 383–385.
[2] Overton G. ELECTRONIC PAPER DISPLAYS: Kindles and cuttlefish: Biomimetics informs e-paper displays[J]., 2012, 48(12): 16.
[3] Hayes R A, Feenstra B J, Camps I G J,. 52.1: a high brightness colour 160 PPI reflective display technology based on electrowetting[J]., 2004, 35(1): 1412–1415.
[4] Cheng W Y, Lo K L, Chang Y P,. 37.1: novel development of large-sized electrowetting display[J]., 2008, 39(1): 526–529.
[5] Kuo S W, Chang Y P, Cheng W Y,. 34.3: novel development of multi-color electrowetting display[J]., 2009, 40(1): 483–486.
[6] Schultz A, Heikenfeld J, Kang H S,. 1000:1 contrast ratio transmissive electrowetting displays[J]., 2011, 7(11): 583–585.
[7] Chang R L J, Liu P W, Wu C Y,. 54.2: reliable and high performance transparent electrowetting displays[J]., 2014, 45(1): 785–788.
[8] Zhang X M, Bai P F, Hayes R A,. Novel driving methods for
manipulating oil motion in electrofluidic display pixels[J]., 2016, 12(2): 200–205.
[9] Zhao R, Tian Z Q, Liu Q C,. Electrowetting-based liquid prism[J]., 2014, 34(12): 1223003.
赵瑞, 田志强, 刘启超, 等. 介电润湿液体光学棱镜[J]. 光学学报, 2014, 34(12): 1223003.
[10] Qian M Y, Lin S L, Zeng S Y,. Real-time dynamic driving system implementation of electrowetting display[J]., 2019, 46(6): 180623.
钱明勇, 林珊玲, 曾素云, 等. 电润湿电子纸的实时动态显示驱动系统实现[J]. 光电工程, 2019, 46(6): 180623.
[11] Jin S Q, Ji C, Yan C C,. TFT-LCD mura defect detection using DCT and the dual-γ piecewise exponential transform[J]., 2018, 54: 371–378.
[12] He J J, Xiao K, Liu C,. TFT-LCD circuit defects detection based on faster R-CNN[J]., 2018(7): 33–38.
何俊杰, 肖可, 刘畅, 等. 基于区域神经网络的TFT-LCD电路缺陷检测方法[J]. 计算机与现代化, 2018(7): 33–38.
[13] Otsu N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms[J]., 1979, 9(1): 62–66.
[14] Ng H F. Automatic thresholding for defect detection[J]., 2006, 27(14): 1644–1649.
[15] Fan J L, Lei B. A modified valley-emphasis method for automatic thresholding[J]., 2012, 33(6): 703–708.
[16] Zhang B, Ni K Z, Wang L J,. New algorithm of detecting optical surface imperfection based on background correction and image segmentation[J]., 2016, 36(9): 0911004.
张博, 倪开灶, 王林军, 等. 基于背景校正和图像分割定量分析光学元件表面疵病的新算法[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(9): 0911004.
[17] Yuan X C, Lu W S, Peng Q J. An improved Otsu method using the weighted object variance for defect detection[J]., 2015, 349: 472–484.
[18] Truong M T N, Kim S. Automatic image thresholding using Otsu’s method and entropy weighting scheme for surface defect detection[J]., 2018, 22(13): 4197–4203.
[19] Liao P S, Chen T S, Chung P C. A fast algorithm for multilevel thresholding[J]., 2001, 17(5): 713–727.
[20] Yasnoff W A, Mui J K, Bacus J W. Error measures for scene segmentation[J]., 1977, 9(4): 217–231.
Electrowetting defect image segmentation based on improved Otsu method
Liao Qinkai1,2, Lin Shanling1,2, Lin Zhixian1,2*, Chen Zheliang1,2, Li Tiantian1,2, Tang Biao3
1Institute of Optlelectronic Display, National & Local United Engineering Lab of Flat Panel Display Technology, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian 350116, China;2College of Physics and Information Engineering, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian 350116, China;3Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Information Materials and Technology, South China Academy of Advanced Optoelectronics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510006, China
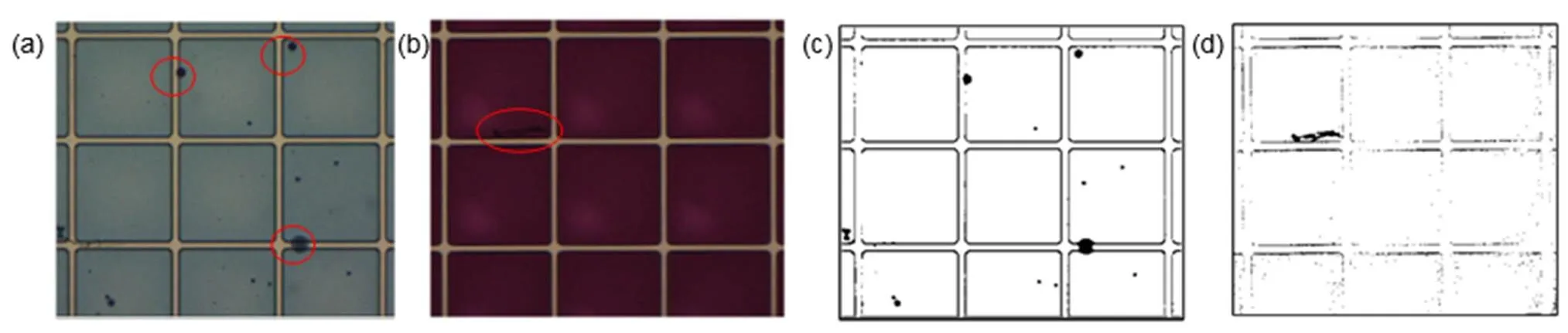
Defects of electrowetting devices in different filling inks. (a) Electrowetting defects in light ink; (b) Electrowetting defects in dark ink; (c) Segmentation results of Fig. (a); (d) Segmentation results of Fig. (b)
Overview:Electrowetting is an electronic paper display with the advantages of fast response, low cost, and low energy loss. Electrowetting display technology is currently in a high-speed development period. Electrowetting devices may have defects in the production process, due to ink spillage, the uneven spin coating of the hydrophobic insulating layer, and externally introduced impurities. Defects affect the display of electrowetting devices, so the detection of defects is indispensable. Aiming at the effect of pixel defects on the display of electrowetting electronic paper, an automatic threshold detection method based on Otsu is proposed to detect defects. Otsu is a commonly used automatic threshold method that gives satisfactory results when the image histogram is bimodal. However, since the electrowetting defect image histogram is usually unimodal, it is easy to get incorrect results. Moreover, the electrowetting electronic paper is filled with pixels by three primary inks to realize color display, so the contrast between the defect and the background is different, and the difficulty of segmentation is also different. In order to separate the electrowetting defects in different shades of ink, an improved Otsu threshold segmentation algorithm is proposed. The basic principle of the method is to introduce a weighting factor before the target variance and affect the value of the variance between-class by the weighting factor, which affects the final threshold selection. The weight decreases with the increase of the probability of accumulation of defects, and the weight is always at a higher value when the threshold is at the left edge of the peak. Specifically, the weights have different change rules before and after the peak to change the contribution of the defect variance. When the threshold passes through the peak, the contribution of the defect variance is reduced, and the value of the between-class variance is affected by the weight, which can make the threshold on the left side of the peak. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively segment the electrowetting defect area. In the electrowetting defect image in the dark ink with low contrast, the ME value of this method is small. Otsu and other automatic threshold methods have ME values above 0.87, and the segmentation results are far from the desired threshold. The proposed method can segment defects in different inks and have better segmentation effects especially when the contrast of defects and background is low.
Citation: Liao Q K, Lin S L, Lin Z X,Electrowetting defect image segmentation based on improved Otsu method[J]., 2020, 47(6): 190388
Electrowetting defect image segmentation based on improved Otsu method
Liao Qinkai1,2, Lin Shanling1,2, Lin Zhixian1,2*, Chen Zheliang1,2, Li Tiantian1,2, Tang Biao3
1Institute of Optlelectronic Display, National & Local United Engineering Lab of Flat Panel Display Technology, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian 350116, China;2College of Physics and Information Engineering, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian 350116, China;3Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Information Materials and Technology, South China Academy of Advanced Optoelectronics, South China Normal University, Guangzhou, Guangdong 510006, China
Aiming at the effect of pixel defects on the display of electrowetting electronic paper, an automatic threshold detection method based on Otsu is proposed to detect defects. Otsu is a commonly used automatic threshold method that gives satisfactory results when the image histogram is bimodal. However, the electrowetting defect image histogram is usually a single peak, and Otsu method fails. Electrowetting differs from the background contrast due to the filling inks of different colors, making segmentation more difficult. In this paper, the weighting coefficient is introduced before the target variance, and the weight decreases as the cumulative probability of defects increases. The weight keeps a large value before the threshold crosses the peak, and the weight decreases after the peak, ensuring that the threshold is always to the left of the peak in the case of a single peak. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively segment the electrowetting defect region, especially in the electrowetting defect image with lower contrast ratio. The method is closer to 0 compared to the ME value of Otsu, VE, WOV and entropy weighting methods. The proposed method has a better segmentation effect.
electrowetting display; image processing; machine vision; defect segmentation; Otsu method
TP391.4
A
10.12086/oee.2020.190388
: Liao Q K, Lin S L, Lin Z X,. Electrowetting defect image segmentation based on improved Otsu method[J]., 2020,47(6): 190388
廖钦楷,林珊玲,林志贤,等. 基于改进Otsu的电润湿缺陷图像分割[J]. 光电工程,2020,47(6): 190388
Supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFB0401503), Science and Technology Major Program of Fujian Province (2014HZ0003-1), Science and Technology Major Program of Guangdong Province (2016B090906001) and the Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Information Materials and Technology (2017B030301007)
* E-mail: lzx2005000@163.com
2019-07-06;
2019-11-08
国家重点研发计划资助项目(2016YFB0401503);福建省科技重大专项资助项目(2014HZ0003-1);广东省科技重大专项资助项目(2016B090906001);广东省光信息材料与技术重点实验室开放基金资助项目(2017B030301007)
廖钦楷(1995-),男,硕士研究生,主要从事电润湿电子纸驱动系统及图像处理的研究。E-mail:610402018@qq.com
林志贤(1975-),男,博士,教授,博士生导师,主要从事信息显示技术与平板显示器件驱动方面的研究。E-mail:lzx2005000@163.com
