lncRNA与胃癌临床特征相关性的meta分析
2020-07-04李璠王玉平陈兆峰郭庆红关泉林周永宁
李璠 王玉平 陈兆峰 郭庆红 关泉林 周永宁


[摘要] 目的 研究胃癌患者長链非编码RNA(lncRNA)表达与胃癌临床特征及预后相关性。 方法 计算机检索PubMed、EMbase、Web of Science数据库,检索时间截至2019年4月。根据检索策略及纳入、排除标准对文献进行筛选,并提取相关资料数据。使用Stata软件进行meta分析。 结果 本研究最终纳入18篇文献。lncRNA高表达组患胃癌风险是低表达组的1.510倍(HR = 1.510,95%CI:1.213~1.878,P = 0.000)。meta分析结果显示文献存在发表偏倚。lncRNA表达水平与胃癌患者的TNM分期(HR = 1.981,95%CI:1.458~2.692,P = 0.000)、肿瘤分化程度(HR = 1.273,95%CI:1.103~1.469,P = 0.001)、浸润深度(HR = 1.862,95%CI:1.565~2.216,P = 0.000)、淋巴结转移(HR=1.570,95%CI:1.086~2.270,P = 0.016)、远处转移(HR = 2.581,95%CI:1.503~4.430,P = 0.001)相关性明显。结论 lncRNA与胃癌患者预后不良以及临床病理特征相关,可能成为胃癌患者预后以及病情监控的重要指标,但其临床应用价值还需在未来更多研究中予以证实。
[关键词] 长链非编码RNA;胃癌;预后;临床特征;meta分析
[中图分类号] R735 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2020)05(b)-0090-05
Meta analysis of the relationship between the lncRNA and clinical features of gastric cancer
LI Fan1,2 WANG Yuping1,2 CHEN Zhaofeng1,2 GUO Qinghong1,2 GUAN Quanlin3 ZHOU Yongning1,2
1.Department of Digestive, the First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730000, China; 2.Lanzhou University Gansu Key Laboratory of Gastroenterology, Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730000, China; 3.Department of Oncology, the First Hospital of Lanzhou University, Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730000, China
[Abstract] Objective To study the correlation between long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) and gastric cancer and prognosis. Methods PubMed, EMbase and Web of Science database were searched, the search ended on April 2019. According to the retrieval strategy and inclusion and exclusion criteria, the literatures were screened and the relevant data were extracted. Stata software was used for meta analysis. Results Eighteen literatures were included in this study. The risk of gastric cancer in the group with high expression of lncRNA was 1.510 times than that of the group with low expression of lncRNA (HR = 1.510, 95%CI: 1.213-1.878, P = 0.000). Meta-analysis showed that there was publication bias in the literature. LncRNA expression level and TNM stage of gastric cancer patients (HR = 1.981, 95%CI: 1.458-2.692, P = 0.000), tumor differentiation degree (HR = 1.273, 95%CI: 1.103-1.469, P = 0.001), invasion depth (HR = 1.862, 95%CI: 1.565-2.216, P = 0.000), lymph node metastasis (HR = 1.570, 95%CI: 1.086-2.270, P = 0.016), and distant metastasis (HR = 2.581, 95%CI: 1.503-4.430, P = 0.001) were significantly correlated. Conclusion lncRNA is associated with poor prognosis and clinicopathological features in patients with gastric cancer, so it may be an important biomarker for gastric cancer patients. However, its clinical application still needs to be verified through more researches in the future.
[Key words] Long non-coding RNA; Gastric cancer; Prognosis; Clinical features; Meta-analysis
胃癌作为全球范围内高发的恶性肿瘤,严重威胁人类的健康生存状态。据统计,胃癌的发病率及病死率分别位居全球恶性肿瘤的第四位和第二位[1]。现阶段临床诊断胃癌的金标准仍为活组织病理检查,但其为有创检查且费用昂贵,难以在临床上推广。多种肿瘤标志物在临床应用于胃癌的诊断,但其诊断效能仍较局限[2],因此寻找一种诊断效能较高且易在临床推广的肿瘤标志物有十分重要的意义。长链非编码RNA(lncRNA)是一类长度超过200 nt,无蛋白编码功能的RNA,与肿瘤的发生发展密切相关[3-5],lncRNA与胃癌患者的临床病理特征、生存情况以及肿瘤细胞的生物学行为有着十分密切的联系[6],但是目前尚缺乏有效的循证医学证据证实。因此本研究对纳入的文章进行meta分析,探讨lncRNA与胃癌患者临床病理特征以及预后之间的关系。
1 资料与方法
1.1 检索策略
计算机检索PubMed、EMbase、Web of Science数据库,检索时间截至2019年4月。主题词与自由词相结合的方式制订检索策略,根据纳入与排除标准纳入本次meta分析文献。检索词:Stomach Cancer,Gastric Cancer,Stomach Neoplasms,Cancer of Stomach,LNCRNA,long noncoding RNA,survival,prognostic
1.2 纳入及排除标准
纳入标准:①经组织病理学确诊为胃癌;②组织标本中验证lncRNA的差异表达;③对组织标本来源进行临床病理分析以及预后相关性分析;④纳入文献为公开发表的文献;⑤可获得全文;⑥研究资料齐全,可提取HR、95%CI以及观察指标的文献。排除标准:①重复文献、综述类文章、会议报道等;②文献研究内容为非原发性胃癌。
1.3 文献质量评价
仔细阅读纳入文献,根据纽卡斯尔-渥太华量表(NOS)对纳入文献进行质量评价[7]。<6分为低质量文章,≥6分为高质量文章。
1.4 文献筛选与资料提取
根据已制订的文献纳入与排除标准对文献进行筛选,并提取相关资料数据。文献提取的数据包括:研究题目、第一作者、发表年份与地区;研究纳入样本类型与数量;lncRNA名称、表达水平、对预后的影响、检测方法;预后指标,如总生存期;临床病理资料,包括年龄、性别、肿瘤分化程度、肿瘤直径、肿瘤浸润深度、淋巴结转移、远处转移、TNM分期。
1.5 统计学方法
使用Stata 12.0软件评价纳入文献的异质性程度。若I2 < 50%,P > 0.1,提示纳入文献无明显异质性,采用固定效应模型;若I2 > 50%,P < 0.1,提示纳入文献存在明显异质性,采用随机效应模型。对存在明显异质性的文献进行敏感性分析。绘制漏斗图评价发表偏倚。
2 结果
2.1 文献检索结果
本研究最终纳入18篇[8-25]文献,发表年限为2014年~2019年,共纳入病例2291例。本研究纳入文献均≥6分,属于高质量文章。见图1、表1。
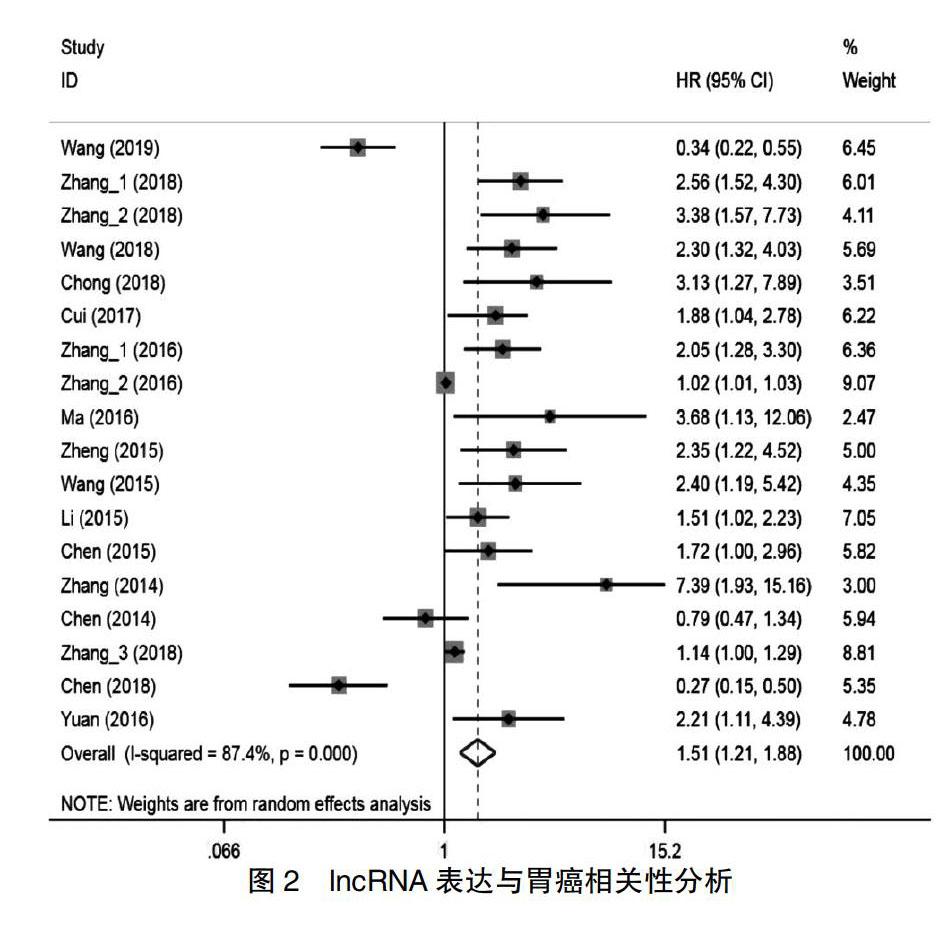
2.2 lncRNA表达与胃癌相关性分析
I2=87.4%,P = 0.000,提示文献异质性较高,采用随机效应模型进行分析。研究显示,lncRNA高表达组患胃癌风险是低表达组的1.510倍[HR = 1.510,95%CI:1.213~1.878,P = 0.000]。见图2。
2.3 发表偏倚结果
18篇文献观察指标不在一个漏斗内,且左右不对称,存在明显的发表偏倚。见图3。
2.4 敏感性分析
5篇文献[8,14,20,24-25]对研究结果存在较大影响,其他纳入文献研究结果基本稳定。见图4。
2.5 lncRNA表达与临床病理特征的相关性分析
lncRNA的表达水平与胃癌患者临床病理特征中的TNM分期[HR = 1.981,95%CI:1.458~2.692,P = 0.000]、肿瘤分化程度[HR = 1.273,95%CI:1.103~1.469,P = 0.001]、浸润深度[HR = 1.862,95%CI:1.565~2.216,P = 0.000]、淋巴结转移[HR = 1.570,95%CI:1.086~2.270,P = 0.016]、远处转移[HR = 2.581,95%CI:1.503~4.430,P = 0.001]相关性明显。见表2。
3 讨论
有效降低癌症发病率和死亡率是目前全球癌症防控工作亟待解决的问题[26]。胃癌作为肿瘤领域难以攻克的关卡,一直被研究者们所关注,而胃癌的早期诊断也是胃癌相关研究领域的难点所在,因此寻找一种能够对胃癌患者进行有效诊断以及预后的肿瘤标志物有着十分重要的意義。
lncRNA作为一种与肿瘤发生有着密切关系的非编码RNA,与胃癌的发生发展同样有着密不可分的关系[27-28],例如:H19通过结合p53抑制Bax通路实现对胃癌细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[29];HOTAIR通过降低miR-331-3p水平,促进胃癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭[30]。
本研究结果显示,胃癌患者TNM分期、肿瘤分化程度、浸润深度、淋巴结转移、远处转移与lncRNA的表达有着明显相关性,且lncRNA高表达组胃癌的患病风险是低表达组的1.510倍。提示lncRNA作为早期胃癌诊断的标志物有着十分重要的临床应用价值,lncRNA表达量上升可能是重要的致癌因素,提示lncRNA有作为胃癌患者检测指标的潜力。本研究纳入文献存在明显异质性及发表偏倚,不同样本量、基因表达水平以及分析方法可能是纳入文献异质性的主要来源;敏感性分析结果显示,5篇文献[8,14,20,24-25]对研究结果存在较大影响,提示其可能是纳入文献发表偏倚的主要来源。明显的异质性是影响meta分析结果可靠性的一个重要因素,对于meta分析纳入文献的异质性需要在今后的研究中通过提高文章检索的全面性与精确性来降低。
本研究的不足之處在于①本研究所纳入文献均为中国地区的研究,不能很好地描述不同地域及不同人群等条件下lncRNA的表达水平对胃癌患者的预后;②纳入研究均为回顾性研究,可能导致研究结果存在偏倚风险;③不同研究的质量不同,可能是发表偏倚的主要来源。
以本研究结果为基础,结合生物信息学、样本分析、实验研究找出对于胃癌早期诊断具有较高特异性与敏感性的lncRNA作为诊断标志物,为临床工作中胃癌的早诊、早治提供新的有效诊断依据。
[参考文献]
[1] Siegel RL,Miller KD,Jemal A. Cancer Statistics,2017 [J]. CA-Cancer J Clin,2017,67(1):7-30.
[2] Zoalfaghari A,Aletaha N,Roushan N,et al. Accuracy of pepsinogens for early diagnosis of atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer in Iranian population [J]. Med J Islam Repub Iran,2014,28:150.
[3] Wang X. Down-regulation of lncRNA-NEAT1 alleviated the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway [J]. J Cell Biochem,2018,119(2):1567-1574.
[4] Huang GW,Xue YJ,Wu ZY,et al. A three-lncRNA signature predicts overall survival and disease-free survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [J]. BMC Cancer,2018,18(1):147.
[5] Mathy NW,Chen XM. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and their transcriptional control of inflammatory responses [J]. J Biol Chem,2017,292(30):12375-12382.
[6] Iguchi T,Uchi R,Nambara S,et al. A long noncoding RNA,lncRNA-ATB,is involved in the progression and prognosis of colorectal cancer [J]. Anticancer Res,2015,35(3):1385-1388.
[7] Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses [J]. Eur J Epidemiol,2010:25(9):603-695.
[8] Chen X,Sun J,Song Y,et al. The novel long noncoding RNA AC138128.1 may be a predictive biomarker in gastric cancer [J]. Med Oncol,2014,31(11):262.
[9] Zhang EB,Han L,Yin DD,et al. c-Myc-induced,long,noncoding H19 affects cell proliferation and predicts a poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer [J]. Med Oncol,2014,31(5):914.
[10] Zheng Q,Wu F,Dai WY,et al. Aberrant expression of UCA1 in gastric cancer and its clinical significance [J]. Clin Transl Oncol,2015,17(8):640-646.
[11] Wang CY,Hua L,Yao KH,et al. Long non-coding RNA CCAT2 is up-regulated in gastric cancer and associated with poor prognosis [J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol,2015,8(1):779-785.
[12] Li L,Zhang L,Zhang Y,et al. Increased expression of LncRNA BANCR is associated with clinical progression and poor prognosis in gastric cancer [J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2015,72:109-112.
[13] Chen WM,Huang MD,Kong R,et al. Antisense Long Noncoding RNA HIF1A-AS2 Is Upregulated in Gastric Cancer and Associated with Poor Prognosis [J]. Dig Dis Sci,2015,60(6):1655-1662.
[14] Zhang Y,Yang R,Lian J,et al. LncRNA Sox2ot overexpression serves as a poor prognostic biomarker in gastric cancer [J]. Am J Transl Res,2016,8(11):5035-5043.
[15] Zhang E,Yin D,Han L,et al. E2F1-induced upregulation of long noncoding RNA LINC00668 predicts a poor prognosis of gastric cancer and promotes cell proliferation through epigenetically silencing of CKIs [J]. Oncotarget,2016,7(17):23212-23226.
[16] Ma P,Xu T,Huang M,et al. Increased expression of LncRNA PANDAR predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer [J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2016,78:172-176.
[17] Yuan CL,Li H,Zhu L,et al. Aberrant expression of long noncoding RNA PVT1 and its diagnostic and prognostic significance in patients with gastric cancer [J]. Neoplasma,2016,63(3):442-449.
[18] Cui WC,Wu YF,Qu HM. Up-regulation of long non-coding RNA PCAT-1 correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in gastric cancer [J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2017,21(13):3021-3027.
[19] Zhang W,Song Y. LINC00473 predicts poor prognosis and regulates cell migration and invasion in gastric cancer [J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2018,107:1-6.
[20] Zhang MH,Yang Y,Zhao Y,et al. LncRNA DQ786243 expression as a biomarker for assessing prognosis in patients with gastric cancer [J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2018,22(8):2304-2309.
[21] Wang Z,Qin B. Prognostic and clinicopathological significance of long noncoding RNA CTD-2510F5.4 in gastric cancer [J]. Gastric Cancer,2019,22(4):692-704.
[22] Chong DQ,Shan JL,Yang CS,et al. Clinical prognostic value of A FOXM1 related long non-coding RNA expression in gastric cancer [J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2018,22(2):417-421.
[23] Zhang JF,Jiang W,Zhang QF,et al. Long noncoding RNA STCAT16 suppresses cell growth and its downregulation is significantly associated with poor survival in gastric cancer patients [J]. Mol Med Rep,2019,19(6):4613-4622.
[24] Chen CL,Ke Q,Luo M,et al. Loss of LINC01939 expression predicts progression and poor survival in gastric cancer [J]. Pathol Res Pract,2018,214(10):1539-1543.
[25] Wang W,Song ZJ,Wang Y,et al. Elevated long non-coding RNA LINC00958 was associated with metastasis and unfavorable prognosis in gastric cancer [J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci,2019,23(2):598-603.
[26] 曹毛毛,陳万青.中国恶性肿瘤流行情况及防控现状[J].中国肿瘤临床,2019,46(3):145-149.
[27] UA ?覫,Shiekhattar R. Long non-coding RNAs and enhancers [J]. Curr Opin Genet Dev,2011,21(2):194-198.
[28] 郑斌,王宇.长链非编码RNA UCA1在消化系统肿瘤中的研究进展[J].中国肿瘤,2018,27(3):209-213.
[29] Yang F,Bi J,Xue X,et al. Up-regulated long non-coding RNA H19 contributes to proliferation of gastric cancer cells [J]. FEBS J,2012,279(17):3159-3165.
[30] Liu XH,Sun M,Nie FQ,et al. Lnc RNA HOTAIR functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate HER2 expression by sponging miR-331-3p in gastric cancer [J]. Mol Cancer,2014,13:92.
(收稿日期:2019-10-10 本文编辑:刘明玉)
