二级预检分诊管理模式在改进门诊质量管理中的应用效果
2020-07-04黎惠贞
黎惠贞
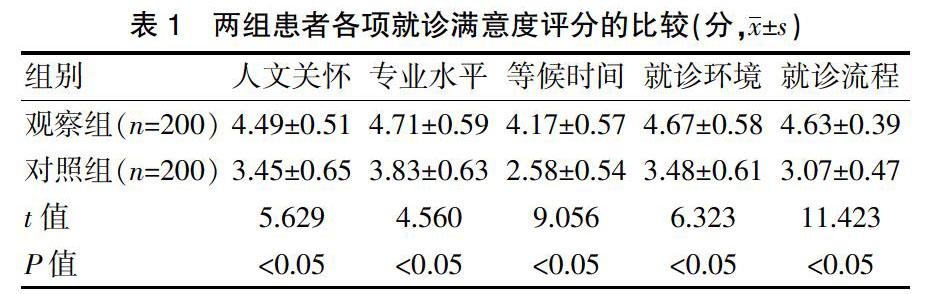
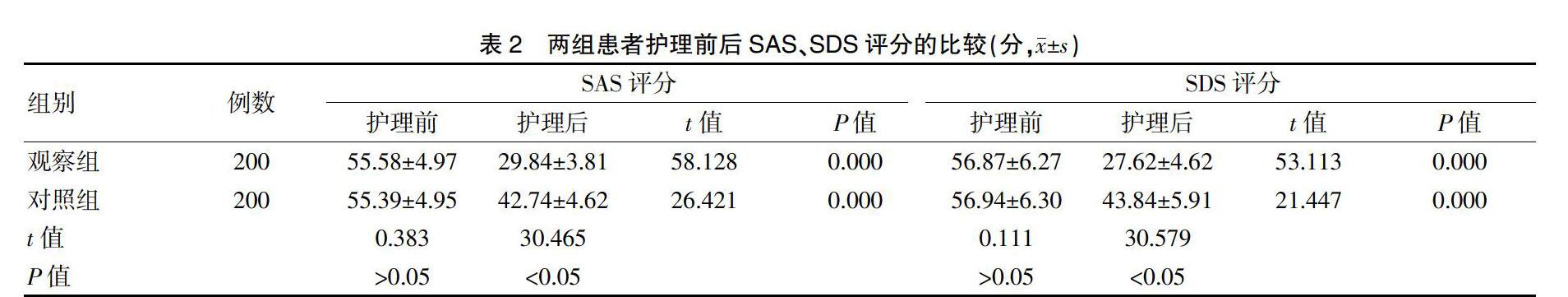
[摘要]目的 探討二级预检分诊管理模式在改进门诊质量管理中的应用效果。方法 选取2018年6月~2019年1月到我院接受治疗的400例门诊患者作为研究对象,将其随机分为对照组(采用常规分诊管理模式)与观察组(采用二级预检分诊管理模式),每组各200例。比较两组患者的人文关怀评分、专业水平评分、等候时间评分、就诊环境评分、就诊流程评分、分诊准确率、医疗纠纷率、护理工作质量评分、情绪评分[焦虑自评量表(SAS)、抑郁自评量表(SDS)]。结果 观察组的人文关怀评分、专业水平评分、等候时间评分、就诊环境评分、就诊流程评分、护理工作质量评分均高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);护理后,观察组患者的SAS、SDS评分低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组患者的分诊准确率(97.5%)高于对照组(73.0%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);观察组患者的医疗纠纷率(1.00%)低于对照组(8.50%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 二级预检分诊管理模式方法可有效提高门诊患者的就诊满意度,提升门诊分诊质量,值得推广使用。
[关键词]管理;质量管理;门诊;预检分诊
[中图分类号] R473 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-4721(2020)5(b)-0178-04
Application effect of secondary pre-examination and triage management mode in improving outpatient quality management
LI Hui-zhen
The Fourth People′s Hospital of Nanhai District of Foshan City, Guangdong Province, Foshan 528211, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the application effect of the secondary pre-examination and triage management mode in improving the outpatient quality management. Methods A total of 400 outpatients who were treated in our hospital from June 2018 to January 2019 were randomly divided into the control group (using the conventional triage management mode) and the observation group (using the secondary pre-examination and triage management mode), 200 cases in each group. The humanistic care scores, professional level scores, waiting time scores, medical environment scores, visit procedure scores, triage accuracy, medical dispute rates, nursing quality scores, and emotional scores (self-rating anxiety scale [SAS], self-rating depression scale [SDS]) were compared between the two groups. Results The humanistic care score, professional level score, waiting time score, medical environment score, visit procedure score, and nursing quality score in the observation group were all higher than those in the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). After nursing, the SAS and SDS scores in the observation group were lower than those in the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The triage accuracy in the observation group (97.5%) was higher than that in the control group (73.0%), the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The medical dispute rate in the observation group (1.00%) was lower than that in the control group (8.50%), the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion The secondary pre-examination and triage management mode can effectively improve the satisfaction of outpatients and improve the quality of outpatient triages, which is worth promoting.
