蓝芩口服液联合西药治疗反流性咽喉炎的临床疗效
2020-06-23廖俊丰
廖俊丰

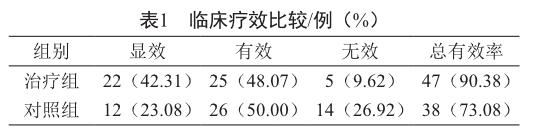

摘 要 目的:探讨蓝芩口服液联合西药治疗反流性咽喉炎(LPRD)的临床效果。方法:選取LPRD患者104例,随机分为对照组和治疗组各52例,对照组给予兰索拉唑和多潘立酮治疗,治疗组在对照组的基础上给予蓝芩口服液治疗,疗程4周。对临床疗效进行评价。结果:治疗前,两组的RSI评分和RFS评分比较无显著性差异。治疗后,治疗组的RSI评分和RFS评分明显低于对照组;临床总有效率明显优于对照组(P<0.05)。结论:采用蓝芩口服液联合兰索拉唑、多潘立酮治疗LPRD,可明显改善患者反流症状和反流体征,提高临床疗效。
关键词 蓝芩口服液 兰索拉唑 多潘立酮 反流性咽喉炎 临床效果
中图分类号:R286; R766.12 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1006-1533(2020)11-0035-03
Clinical effect of Lanqin oral liquid combined with western medicine in the treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux disease
LIAO Junfeng
(Department of Otolaryngology, the Peoples Hospital of Qingxin District, Guangdong Qingyuan 511800, China)
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the clinical effect of Lanqin oral liquid combined with western medicine in the treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux disease (LPRD). Methods: One hundred and four patients with LPRD were randomly divided into a control group and a treatment group with 52 cases each. Both groups were treated with lansoprazole and domperidone and the treatment group was additionally treated with Lanqin oral liquid, which were lasted for 4 weeks, and their clinical effects were evaluated. Results: There were no significant differences between the two groups in the RSI score and RFs score before treatment. However, the RSI score and RFs score were significantly lower and the total clinical effective rates were significantly higher in the treatment group than the control group after treatment (P<0.05). Conclusion: Lanqin oral liquid combined with lansoprazole and domperidone for the treatment of LPRD can significantly improve the symptoms and signs of reflux and the clinical efficacy.
KEy WORDS Lanqin oral liquid; lansoprazole; domperidone; laryngopharyngeal reflux disease; clinical effect
反流性咽喉炎(laryngopharyngeal reflux disease, LPRD)是临床上常见的一种疾病,普遍认为其病因与饮食有较大关系。经常性的过饥过饱、进食辛辣刺激性食物、睡前2 h进食或宵夜等习惯,均是本病的常见诱因。本病的损伤病机主要有两个方面:其一是返流的胃酸直接引起咽喉黏膜的损伤和不适;其二是胃和十二指肠的内容物返流刺激远端食管,引起迷走反射,导致咳嗽、清嗓以及食道上括约肌舒张,而使胃内容物反流并导致咽喉损伤。其症状为:咽异物感或癔球感、声嘶及发音困难、慢性干咳等。体征为:咽喉黏膜劈裂、溃疡或肉芽肿,后联合、声带充血水肿,严重的会出现刺激性咳嗽、呕吐等[1]。而胃食管反流病患者其胃酸经过食管反流到咽喉位置后对咽喉黏膜产生刺激,可导致慢性咽炎发生。相关研究显示,胃食管反流病和慢性咽炎存在一定的联系,并且二者会相互影响,从而导致LPRD[2]。
1 临床资料
1.1 一般资料
选取2016年5月—2019年3月在清远市清新区人民医院治疗的LPRD患者104例,所有患者经电子喉镜和胃镜检查确诊为LPRD,诊断标准参考《咽喉反流性疾病诊断与专家共识》及其解读中的标准[3]:反流症状指数量表评分(RSI)>13分和/或反流体征评分量表评分(RFS)>7分。将患者按随机数字表法分为治疗组和对照组,每组52例。其中治疗组男21例,女31例;年龄24~65岁,平均年龄(45.7±10.3)岁;病程6个月~ 7年,平均病程(2.3±1.0)年。对照组男21例,女31例;年龄20~64岁,平均年龄(42.5±11.6)岁;病程7个月~6年,平均病程(2.2±1.1)年。两组患者一般资料比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),具可比性。
