葫芦素B抑制STAT3/Bcl-2表达诱导非小细胞肺癌H1975细胞凋亡
2020-06-01何臣王菊辉丘韶校徐羽中李元广
何臣 王菊辉 丘韶校 徐羽中 李元广
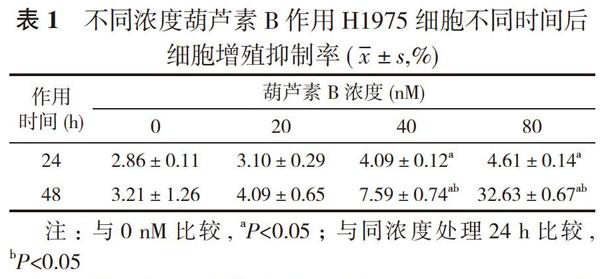
【摘要】 目的 探討葫芦素B对非小细胞肺癌H1975细胞凋亡的影响及可能的机制。方法 应用不同浓度葫芦素B作用H1975细胞不同时间, 分别使用Annexin/7-AAD双染法检测细胞凋亡, Western blot法测定信号转导与转录活化因子3(STAT3)、B淋巴细胞瘤-2(Bcl-2)蛋白表达。结果 0 nM的葫芦素B处理后24、48 h的细胞增殖抑制率分别为(2.86±0.11)、(3.21±1.26)%, 20 nM的分别为(3.10±0.29)、(4.09±0.65)%, 40 nM的分别为(4.09±0.12)、(7.59±0.74)%, 80 nM的分别为(4.61±0.14)、(32.63±0.67)%。0、20 nM葫芦素B处理后24、48 h对H1975细胞增殖抑制率无明显影响;40、80 nM葫芦素B处理后24、48 h, 对H1975细胞增殖抑制率均高于0 nM与20 nM, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。葫芦素B处理后24 h的细胞增殖抑制率均低于处理后48 h, 呈时间-剂量依赖性增加, 80 nM葫芦素B作用48 h对H1975细胞的细胞凋亡诱导作用最为明显, 差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。40 nM以上浓度葫芦素B作用H1975细胞48 h后p-STAT3、STAT3、Bcl-2明显降低。结论 葫芦素B通过抑制STAT3信号活化下调Bcl-2蛋白表达诱导H1975细胞凋亡的发生。
【关键词】 非小细胞肺癌;葫芦素B;信号转导与转录活化因子3;B淋巴细胞瘤-2
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2020.13.086
Inhibition of STAT3 / Bcl-2 expression by cucurbitacin B on apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer H1975 cells HE Chen, WANG Ju-hui, QIU Shao-xiao, et al. Department of Respiratory Medicine, Baoan Peoples Hospital, Shenzhen 518101, China
【Abstract】 Objective To discuss the effect of cucurbitacin B on the apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer cell line h1975 and its possible mechanism. Methods The H1975 cells were treated with different concentrations of cucurbitacin B at different times, the cell apoptosis were detected by Annexin / 7-AAD double staining, and the expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and B-cell lymphoma-2 (Bcl-2) protein expression were detected by Western blot method. and STAT3 / BCL2 expression were analyzed by the and respectively. Results The cell proliferation inhibition rates of 0 nM cucurbitacin B at 24 and 48 h were (2.86±0.11), (3.21±1.26)%, respectively, 20 nM were (3.10±0.29) and (4.09±0.65)%, respectively, 40 nM were (4.09±0.12) and (7.59±0.74)%, respectively, and 80 nM were (4.61±0.14) and (32.63±0.67)%, respectively. After 0 and 20 nM cucurbitacin B treatment for 24 and 48 h, there was no significant effect on the proliferation inhibition rate of H1975 cells. After 40 and 80 nm cucurbitacin B treatment for 24 and 48 h, the proliferation inhibition rate of H1975 cells was higher than that of 0 nM and 20 nM, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The inhibition rate of cell proliferation at 24 h after treatment with cucurbitacin B was lower than that at 48 h after treatment, showing a time-concentration-dependent manner. The cell apoptosis of H1975 cells induced by 80 nM cucurbitacin B for 48 h was the most obvious, and the difference was statistically significant (32.63±0.67)%. H1975 cell was treated by Cucurbitacin B above 40 nM for 48 h, p-STAT3, STAT3 and Bcl-2 were significantly decreased. Conclusion Cucurbitacin B can induce apoptosis of H1975 cells by inhibiting STAT3 signal activation and down regulating Bcl-2 protein expression.
【Key words】 Non-small cell lung cancer; Cucurbitacin B; Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; B-cell lymphoma-2
肺癌是最常见的恶性肿瘤之一, 2013年我国肺癌新发病例和死亡病例人数在所有肿瘤登记数据排序中均高居首位, 且其发病率和死亡率仍在逐年上升[1]。随着对肺癌发病机制的研究深入, 新技术、药物不断研发和应用, 新的治疗方案也不断提出、推广, 肺癌的综合诊治水平较前有了明显提高, 但总体生存获益改善仍不理想, 5年相对存活率仅为23%[2]。因此, 探寻包含肺癌在内的恶性肿瘤治疗新药物成为临床面临的巨大挑战。我国中医药文化源远流长, 以植物为主要来源的中草药是传统中医药的重要组成和瑰宝之一, 在长期的临床抗肿瘤治疗实践中已取得一定的成就。借助于现代生物技术和新药筛选技术, 从包含植物在内的各种天然产物中通过活性追踪分离, 筛选、寻找抑制恶性肿瘤的活性成分成为发掘新颖抗癌药物的重要来源[3]。葫芦素是从葫芦科植物中分离得到的一组四环三萜类化合物, 具有抗肿瘤、护肝、抗炎、抗微生物等多种生物学特性[4]。葫蘆素B(cucurbitacin B)是其中疗效最明确和应用最广泛的单体之一。越来越多的证据表明葫芦素B能诱导大肠癌、肝癌、胃癌、卵巢癌等多种肿瘤细胞凋亡并抑制生长[5-9]。本文观察了葫芦素B对人肺癌H1975细胞的细胞凋亡诱导作用, 并通过葫芦素B对细胞增殖和凋亡途径相关蛋白STAT3和Bcl-2表达的影响, 探讨了葫芦素B非小细胞肺癌细胞凋亡的可能机制。
1 材料与方法
1. 1 材料 RPMI1640 培养基、胎牛血清、胰蛋白酶(美国Gibco公司);葫芦素B(美国Sigma公司); Annexin V: FITC 细胞凋亡检测试剂盒(美国BDPharmingen公司);BCA蛋白定量试剂盒(美国Pierce公司);抗人磷酸化及总STAT3、Bcl-2抗体及化学发光检测试剂盒(美国Cell Signaling公司);垂直电泳仪(美国Biorad公司);凝胶成像系统KODAK2000R(美国Kodak公司)。
1. 2 细胞培养 人肺癌细胞系H1975细胞在含有10%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640中在37℃和5%二氧化碳中培养, 每天更换培养基, 用0.25%胰蛋白酶分离细胞。
1. 2 方法
1. 2. 1 细胞凋亡的流式细胞术分析 采用Annexin/7-AAD双染法分析检测葫芦素B对H1975细胞凋亡的影响。在六孔板中每孔接种1×106个细胞, 观察细胞贴壁后加入不同浓度的葫芦素B(终浓度分别为0、20、40、80 nM)。分别处理24 h和48 h。收获细胞, 冷PBS重悬, 并根据说明书用Annexin V/7-AAD 凋亡检测试剂盒染色, 用流式细胞仪分析细胞凋亡情况, 实验至少进行3次重复。
1. 2. 2 Western blot分析 对数生长期H1975细胞, 胰蛋白酶消化、离心, 制成细胞悬液, 以5×105/ml的细胞浓度取接种10 ml细胞悬液至10 cm培养皿中, 待细胞贴壁后加入不同浓度(40、80nM)的葫芦素B分别作用24 h和48 h, 提取总蛋白, 用BCA蛋白检测试剂盒进行蛋白定量, -70℃冰箱冻存备用蛋白质经SDS-PAGE分离后转移到PVDF膜, 含5%脱脂奶粉的TBST中室温封闭60 min, 加入抗磷酸化和总STAT3、Bcl-2和β-肌动蛋白抗体(1∶1000), 4℃孵育过夜, TBST充分漂洗后加入二抗(1∶1000), 室温作用1 h, TBsT充分漂洗后将膜置于5 ml 1×LumiGLO(0.25 ml 20×LumiGLO, 0.25 ml 20×过氧化氢, 9.0 ml水)轻摇孵育1 min;凝胶成像系统成像分析。
1. 3 观察指标 观察不同浓度(0、20、40、80 nM)葫芦素B作用H1975细胞不同时间(24、48 h)后细胞增殖抑制率、葫芦素B下调STAT3和Bcl-2蛋白表达。
1. 4 统计学方法 采用SPSS13.0统计学软件处理数据。计量资料以均数±标准差( x-±s)表示, 采用t检验;通过方差分析和NK(Student-Newnan-Keuls)检验检验数据的统计相关性, P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2. 1 不同浓度葫芦素B作用H1975细胞不同时间后细胞增殖抑制率 0 nM的葫芦素B处理后24、48 h的细胞增殖抑制率分别为(2.86±0.11)、(3.21±1.26)%, 20 nM的分别为(3.10±0.29)、(4.09±0.65)%, 40 nM的分别为(4.09±0.12)、(7.59±0.74)%, 80 nM的分别为(4.61±0.14)、(32.63±0.67)%。0、20 nM葫芦素B处理后24、48 h对H1975细胞增殖抑制率无明显影响;40、
80 nM葫芦素B处理后24、48 h, 对H1975细胞增殖抑制率均高于0 nM与20 nM, 差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。葫芦素B处理后24 h的细胞增殖抑制率均低于处理后48 h, 呈时间-剂量依赖性增加, 80 nM葫芦素B作用48 h对H1975细胞的细胞凋亡诱导作用最为明显, 差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表1。
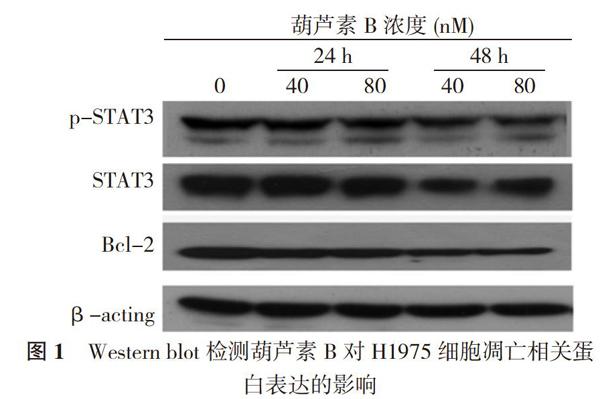
2. 2 葫芦素B下调STAT3和Bcl-2蛋白表达 检测葫芦素B作用H1975细胞后STAT3及其下游与生长和凋亡密切相关的Bcl-2蛋白表达变化。结果显示, 40 nM以上浓度葫芦素B作用H1975细胞48 h后p-STAT3、STAT3、Bcl-2明显降低。见图1。
3 讨论
葫芦素B是从葫芦科植物中分离得到的一种天然产物单体, 具有保肝的生物學特性, 以葫芦素B为主要成分的药品葫芦素片亦在急慢性肝炎与肝硬化的临床治疗实践中取得较好的疗效。近年来, 随着对葫芦素B的研究不断加强, 葫芦素B的药理学机制逐渐阐明, 葫芦素B能够诱导多种人肿瘤细胞的细胞凋亡和增殖抑制[5-10], 展现出广阔的抗肿瘤潜在应用前景。本研究显示葫芦素B可呈剂量和时间依赖性诱导肺癌H1975细胞凋亡, 进一步的作用机制研究表明, 葫芦素B通过抑制STAT3的活化, 降低Bcl-2的表达水平, 进而诱导H1975细胞的凋亡。
细胞凋亡诱导是从药用植物中提取的抗癌药物常见作用机制之一。本研究首先探讨了葫芦素B对H1975细胞凋亡的影响, 流式细胞术检测表明, 中剂量以上葫芦素B治疗可诱导H1975细胞凋亡, 且呈时间-剂量依赖性增加, 与既往葫芦素B可诱导肺癌A549细胞凋亡的研究结果一致[11, 12]。接下来通过观察葫芦素B对一组与细胞增殖和凋亡途径相关蛋白表达的影响研究了葫芦素B诱导细胞凋亡的潜在机制。既往研究表明葫芦素B能够抑制STAT3信号通路的激活, 调节STAT3下游基因表达, 从而抑制肿瘤的生长[10-13]。本研究中中剂量(40 nM)以上葫芦素作用H1975细胞48 h后磷酸化及总STAT3表达水平明显下降, 进一步提示葫芦素B通过抑制STAT3信号活化诱导肺癌细胞凋亡。线粒体功能障碍已被证明参与了细胞凋亡的诱导, 并被认为是凋亡途径的中心环节。对线粒体功能的进一步分析显示, 线粒体功能障碍主要表现在线粒体跨膜电位破坏和细胞色素c
释放, 伴随caspase-3和caspase-9活性水平升高和抗凋亡Bcl-2蛋白表达下调。Bcl-2蛋白位于线粒体外壁, 是STAT3信号转导的下游靶基因之一, 通过控制线粒体通透性和抑制细胞色素c的释放调节细胞凋亡[14]。细胞色素c从线粒体释放后与凋亡蛋白酶激活因子1结合后, 与caspase-9形成激活复合物[15], 进而通过蛋白水解裂解激活Caspase-3促进凋亡的发生[16]。West blot检测结果发现中剂量以上葫芦素作用H1975细胞48 h后Bcl-2蛋白表达显著下降。基于以上结果, 认为葫芦素B可能通过抑制STAT3信号活化下调Bcl-2蛋白表达来激活细胞凋亡级联反应介导细胞凋亡的发生。
综上所述, 葫芦素B具有抑制STAT3途径下调Bcl-2蛋白诱导肺癌细胞凋亡的作用, 可作为肺癌患者潜在有效的治疗策略。
参考文献
[1] 陈万青, 左婷婷, 郑荣寿, 等. 2013年中国肺癌发病与死亡分析. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2017, 39(10):795-800.
[2] Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 2019, 69(5):398.
[3] Luo H, Vong CT, Chen H, et al. Naturally occurring anti-cancer compounds: shining from Chinese herbal medicine. Chin Med, 2019, 14(1):48.
[4] Cai Y, Fang X, He C, et al. Cucurbitacins: A Systematic Review of the Phytochemistry and Anticancer Activity. Am J Chin Med, 2015, 43(7):1331-1350.
[5] Mao D, Liu AH, Wang ZP, et al. Cucurbitacin B inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis in colorectal cancer by modulating methylation status of BTG3. Neoplasma, 2019, 66(4):593-602.
[6] Ge W, Chen X, Han F, et al. Synthesis of Cucurbitacin B Derivatives as Potential Anti-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Agents. Molecules, 2018, 23(12):e3345.
[7] Klungsaeng S, Kukongviriyapan V, Prawan A, et al. Cucurbitacin B induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis pathway in cholangiocarcinoma cells via suppressing focal adhesion kinase signaling. Arch Pharmacol, 2019, 392(3):271-278.
[8] Lin Y, Li J, Ye S, et al. LncRNA GACAT3 acts as a competing endogenous RNA of HMGA1 and alleviates cucurbitacin B-induced apoptosis of gastric cancer cells. Gene, 2018(678):164-171.
[9] Qu Y, Cong P, Lin C, et al. Inhibition of paclitaxel resistance and apoptosis induction by cucurbitacin B in ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett, 2017, 14(1):145-152.
[10] Zhang ZR, Gao MX, Yang K. Cucurbitacin B inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells via modulation of the JAK2/STAT3 and MAPK pathways. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 14(1):805-812.
[11] Silva IT, Geller FC, Persich L, et al. Cytotoxic effects of natural and semisynthetic cucurbitacins on lung cancer cell line A549. Invest New Drugs, 2016, 34(2):139-148.
[12] Zhang M, Bian ZG, Zhang Y, et al. Cucurbitacin B inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis via STAT3 pathway inhibition in A549 lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep, 2014, 10(6):2905-2911.
[13] Wiart C. The definition and significance of Cucurbitacin B a STAT3 inhibitors. Cancer Lett, 2013, 328(1):188.
[14] Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, et al. Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene, 2002, 21(13):2000-2008.
[15] Malladi S, Challa-Malladi M, Fearnhead HO, et al. The Apaf-1*procaspase-9 apoptosome complex functions as a proteolytic-based molecular timer. EMBO J, 2009, 28(13):1916-1925.
[16] Inoue S, Browne G, Melino G, et al. Ordering of caspases in cells undergoing apoptosis by the intrinsic pathway. Cell Death Differ, 2009, 16(7):1053-1061.
[收稿日期:2020-01-07]
