CT和MR对小儿脑性瘫痪诊断中的效果研究
2020-05-25张洪涛
张洪涛
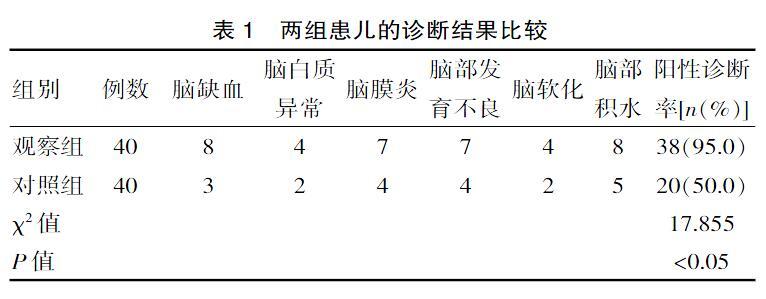
[摘要] 目的 对CT和MR在小儿脑性瘫痪诊断中的临床应用价值进行分析和探究。方法 方便选择该院在2016年6月—2018年12月期间收治的80例小儿脑性瘫痪患者作为该次研究纳入的对象,回顾性分析其临床资料,将该次研究的患儿按照病历单双号将其随机划分为对照组和观察组,每组各有40例。采用CT检查的方式检查对照组患儿,采用MR检查的方式检查观察组患儿,对两组患儿的诊断准确率进行分析和比较。结果 对照组患儿检查出3例脑缺血,2例脑白质异常,4例脑膜炎,4例脑部发育不良,2例脑软化以及5例脑部积水,共计达到了50.0%的阳性诊断率;观察组患儿检查出8例脑缺血,4例脑白质异常,7例脑膜炎,7例脑部发育不良,4例脑软化以及8例脑部积水,共计达到了95.0%的阳性诊断率。观察组的阳性率明显高于对照组患儿,两组相比差异有统计学意义(χ2=17.855,P<0.05) 。两组患儿的致病原因为产伤、缺血缺氧、脑先天发育不良;在检查阳性的58例患儿的影像中,致病原因為产伤的患儿共计11例,在CT和MR影像中具有脑膜炎(4例)和脑炎(7例)的影像特征;致病原因为缺血缺氧的患儿共计33例,在CT和MR影像中具有脑积水(11例)、脑灰白质萎缩(1例)、脑白质变性(3例)、脑缺血灶(11例)、脑软化灶(5例)、双侧额部硬膜下积液(2例)的影像特征;致病原因为脑先天发育不良的患儿共计14例在CT和MR影像中具有脑灰白质移位(2例)、脑裂畸形(1例)、无脑汇(2例)、巨脑汇畸形(2例)、胼胝体发育不良(3例)、脑贯通性畸形(1例)、脑软化灶(1例)和脑多发钙化斑(2例)的影像特征。结论 与CT相比,MR在小儿脑性瘫痪的临床诊断中具有更高的阳性诊断率,应用价值更高。
[关键词] CT;MR;小儿脑性瘫痪;临床诊断;阳性诊断率;效果
[中图分类号] R730.41 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1674-0742(2020)02(a)-0186-03
Effect of CT and MR on the Diagnosis of Cerebral Palsy in Children
ZHANG Hong-tao
Department of Imaging, Liangshan County People's Hospital, Liangshan, Shandong Province, 272600 China
[Abstract] Objective To analyze and explore the clinical application value of CT and MR in the diagnosis of cerebral palsy in children. Methods Convenient selection of eighty children with cerebral palsy admitted to the hospital from June 2016 to December 2018 were enrolled as the subjects of this study. The clinical data were retrospectively analyzed. The children in this study were selected according to their medical records. The number was randomly divided into a control group and an observation group, with 40 cases in each group. The children in the control group were examined by CT examination. The children in the observation group were examined by MR examination. The diagnostic accuracy of the two groups was analyzed and compared. Results In the control group, 3 cases of cerebral ischemia, 2 cases of abnormal white matter, 4 cases of meningitis, 4 cases of brain dysplasia, 2 cases of encephalomalacia and 5 cases of hydrocephalus were detected, with a positive diagnosis rate of 50.0%. In the observation group, there were 8 cases of cerebral ischemia, 4 cases of abnormal white matter, 7 cases of meningitis, 7 cases of brain dysplasia, 4 cases of cerebral softening and 8 cases of hydrocephalus, which reached a positive diagnosis rate of 95.0%. The positive rate in the observation group was significantly higher than that in the control group, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(χ2=17.855, P<0.05) . The pathogenic causes of the two groups of children were birth injury, ischemia and hypoxia, and brain congenital dysplasia. Among the 58 positive cases, a total of 11 cases were caused by birth injury. The CT and MR images showed the imaging characteristics of meningitis (4 cases) and encephalitis (7 cases). A total of 33 children were diagnosed with hypoxia and ischemia, and the CT and MR images showed hydrocephalus (11 cases), atrophy of gray matter (1 case), degeneration of white matter (3 cases), cerebral ischemia (11 cases), cerebral softening (5 cases) and bilateral subdural effusion (2 cases). Causes of congenital dysplasia with a total of 14 cases in CT and MR imaging of brain gray matter translocation (2 cases), split brain malformation (1 case), no brain (2 cases), giant brain malformation (2 cases), corpus callosum dysplasia (3 cases) and brain malformation (1 case), encephalomalacia foci (1 case) and brain imaging features of multiple calcified plaque (2 cases). Conclusion Compared with CT, MR has a higher positive diagnosis rate in the clinical diagnosis of cerebral palsy in children, and its application value is higher.
