Clinical study on intradermal needle therapy in treating urinary retention after cervical cancer surgery
2020-04-21ZhuXuanxuan朱璇璇WuChangzheng吴常征BaoMin包敏
Zhu Xuan-xuan (朱璇璇), Wu Chang-zheng (吴常征), Bao Min (包敏)
1 Xinyi Central Hospital, Jiangsu 221400, China
2 Lianyungang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Jiangsu 222000, China
Abstract Objective: To observe the clinical efficacy of intradermal needle therapy for urinary retention after cervical cancer surgery.Methods: A total of 100 patients with urinary retention after cervical cancer surgery were randomized into a control group and an observation group, with 50 cases in each group. The control group was treated with basic nursing only,and the observation group was treated with additional intradermal needle therapy. Both groups were treated for 2 courses of treatment. The main symptom scores and residual urine volume of the two groups were observed before and after treatment, and the inpatient time, catheter indwelling time and the clinical efficacy were compared between the two groups.Results: The total effective rate was 96.0% in the observation group and 88.0% in the control group, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant (P<0.05). After treatment, the main symptom scores and residual urine volume in both groups decreased significantly (all P<0.05), and the scores and residual urine volume in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group (all P<0.05). The inpatient time and catheter indwelling time in the observation group were significantly shorter than those in the control group (both P<0.05).Conclusion: Intradermal needle therapy has an obvious effect in improving symptoms of urinary retention after cervical cancer surgery, and the effect is significantly more persistent than that of simple basic nursing.
Keywords: Acupuncture Therapy; Embedding Therapy; Intradermal Needle Therapy; Uterine Cervical Neoplasms;Postoperative Complications; Urinary Retention; Women
Worldwide, cervical cancer is the fourth most common malignant tumor in women, with a mortality rate second only to breast cancer. Eight-five percent of cervical cancer occur in developing countries, and it is the first cause of cancer death among women[1]. Its incidence has been increasing year by year in China[2].Surgical treatment is the main way to treat cervical cancer in early stage at present. However, the radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer causes massive trauma,involving multiple organs and tissues and resulting in various postoperative complications, among which,urinary retention is the most common one[3]. In foreign reports, the incidence of urinary retention is 3.8%-21.0%, and in domestic reports, the incidence is 7.5%-44.9%[4]. The routine time of postoperative indwelling catheterization is 7-14 d[5], but long-time indwelling can increase the risk of urinary tract infection. Continuous drainage of urine can make the bladder tension decrease or disappear, and recover the bladder function[6-7]. In recent years, the treatments of urinary retention after cervical cancer surgery have been continuously enriched. According to clinical studies,acupuncture can regulate meridians and unblock collaterals, improve physical function as a whole, and improve symptoms and quality of life[8-9]. In this study,we observed the clinical efficacy of intradermal needle at Qihai (CV 6), Guanyuan (CV 4), Zhongji (CV 3),Yinlingquan (SP 9), Zusanli (ST 36) and Sanyinjiao (SP 6)points for urinary retention after cervical cancer surgery.
1 Clinical Materials
1.1 Diagnostic criteria
1.1.1 Diagnostic criteria of Western medicine
All cases were confirmed by cervical biopsy before operation[10]; patient who was unable to urinate spontaneously 2 weeks after operation, or the patient was able to urinate, but the residual urine volume was≥100 mL[11].
1.1.2 Diagnostic criteria of Chinese medicine
This study referred to the diagnostic criteria of Long Bi (dribbling and retention of urine) in the Guiding Principles for Clinical Study of New Chinese Medicines(2002)[12]: frequent and urgent desire to urinate,repeatedly tried to urinate but had difficulty urinating,with unsmooth dripping or urinary stoppage; lower abdominal distending pain; dysuria without urethral pain; postvoid residual urine in the bladder confirmed by examination.
1.2 Inclusion criteria
Those who were aged 30 to 70 years old; patients with Ⅰb-Ⅱa clinical staging of cervical cancer; who had radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy;operation time within 4 h and anesthesia time within 5 h; whose operation was performed by associate senior physician (or above) as the chief surgeon with at least 50 cases of experiences; patients with clear consciousness, without disturbance of intelligence or hearing impairment; patients with complete data in the register system of medical record department and pathology laboratory; agreed to participate in this clinical trial and signed informed consent.
1.3 Exclusion criteria
Those who had urinary retention caused by other issues such as lower urinary tract obstruction, bladder tumor, urethral injury, calculus, urinary tract infection or spinal cord injury; preoperative urinary retention,preoperative dysuria, preoperative urine incontinence of moderate degree or above; those with severe injuries of ureter and bladder due to operation; with skin lesion,swollen or infection in the acupoint area.
1.4 Elimination and shedding criteria
Those who were not in line with the inclusion criteria or met the exclusion criteria; who did not follow the required treatment protocol; dropped out because of incomplete clinical data or poor compliance that affected the evaluation; those presenting with severe adverse events or complications that were unsuitable to continue the treatment; dropped out during the trial or lost to follow-up.
1.5 Statistical methods
All data were statistically analyzed by the SPSS version 22.0 statistical software. Measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (x ±s).Independent sample t-test was applied to the comparison between groups. Paired sample t-test was applied to the comparison of intra-group data.Chi-square test was applied to the comparison of non-ranked counting data. P<0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference.
1.6 General data
A total of 100 cases were enrolled from the Obstetrics and Gynecology Ward of Lianyungang Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, between January 2017 and January 2019. They were randomly divided into an observation group and a control group, with 50 cases in each group. There were no dropout cases in either group. This study was reviewed and approved by the ethics committee. There were no statistically significant between-group differences in age, operation time and operation methods (all P>0.05), indicating that the two groups were comparable (Table 1).
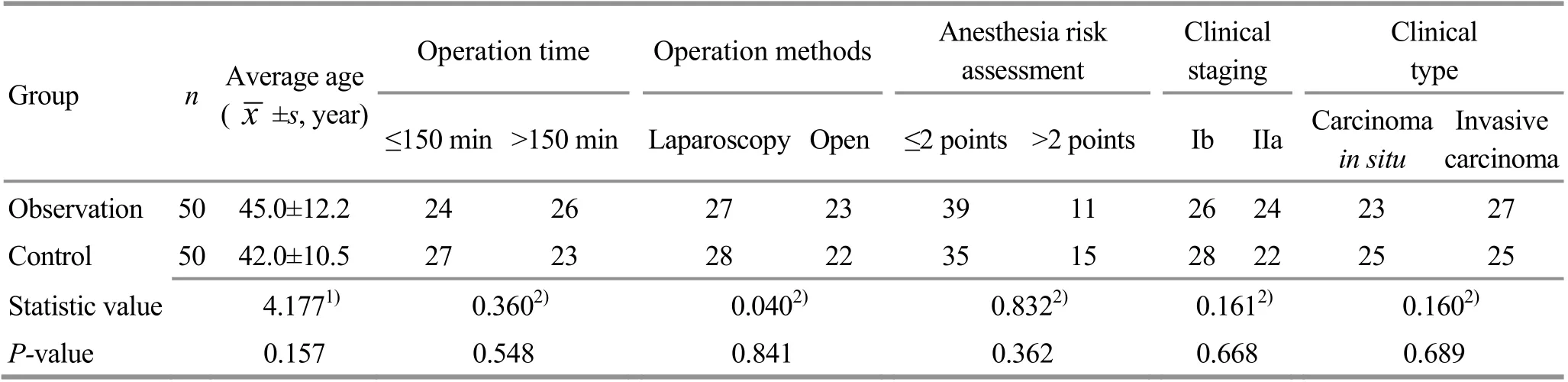
Table 1. Comparison of general data between the two groups
2 Treatment Methods
2.1 Control group
Only basic nursing was applied in the control group.The vulva and urethral orifice were scrubbed with 0.3%iodophor twice a day, and perineal care was applied after urination timely to keep vulva clean. During the indwelling catheterization period, the urethral catheter was well fixed, and the urine collection bag was changed once every day from the first day after operation. The volume, color and feature of urine were observed. After removal of the urethral catheter,urination-promoting measures such as listening to the sound of running water or flushing the vulva with warm water could be used to induce urination[13]. Hot compress therapy with hot towel or rolling massage with towel-wrapped hot water bag at lower abdomen was applied for 20-30 min to reduce urethral edema and reflexively stimulate the bladder to contract,thereby promoting urination. The patient was guided to start pelvic floor muscle training, i.e. anal sphincter contraction exercise, from the first day after operation,in order to improve the function of pelvic floor muscle and improve the recovery of bladder function. The patient took a supine position, with abdomen, hip and lower limb muscle relaxed. Then, the patient was asked to contract and lift the levator ani muscle ≥3 s, then relax, and then repeat the contraction and relaxation.Continued the training for 15-30 min as one set, and performed 2-3 sets of training every day[14], 7 d as a course of treatment, for 2 courses in total.
2.2 Observation group
The observation group was treated with additional intradermal needle therapy.
Acupoints: Qihai (CV 6), Guanyuan (CV 4), Zhongji(CV 3), Yinlingquan (SP 9), Zusanli (ST 36) and Sanyinjiao(SP 6).
Methods: The treatment was carried out by trained and qualified professionals. After the skin around the acupoint was fully exposed and twice routine disinfection, the physician held the adhesive tape attached to the intradermal needle handle (Wujiang Cloud & Dragon Medical Device Co., Ltd., China,0.22 mm in diameter and 1.3 mm in length) with a pair of tweezers, aimed at the acupoint, and inserted perpendicularly and stabilized the adhesive tape to the local area, and pressed properly within the patient's tolerance. The superficial blood vessels should be avoided, and the needles should not cause pain.Instructed the patient to press the intradermal needle appropriately to enhance the effect of unblocking meridians and improve the efficacy. Observed the position of needle embedding, and asked the patient if there was discomfort. If the patient felt a stabbing pain,the needle should be removed: the skin on both sides of the needle should be stabilized with one hand, and the tapes should be peeled off with the other hand;then, the physician pinched the tape on both sides,removed the needle perpendicularly, and re-embedded the needle. The needle should remain for 12 h, and the treatment was conducted once a day, 7 d as a course of treatment, for 2 courses in total.
3 Observation of Curative Efficacy
3.1 Observation items
The main symptoms scores and residual urine volume were observed before and after treatment in the two groups. The indwelling catheterization time and hospital duration were recorded.
3.1.1 Main symptom score
Accordingtotherelated standardsintheGuiding Prin ciples forClinicalStudy ofNewChineseMedicines[12],the criteria of scoring in this study were established.The main symptoms of urinary retention, such as difficulty voiding urine, lower abdominal distending pain, soreness and weakness of low back and knees,and lassitude were scored according to the severity:0 point (none), 1 point (mild), 2 points (moderate),3 points (severe).
3.1.2 Residual urine volume
The residual urine after micturition was considered postvoid residual urine. The most commonly used and well accepted B-ultrasonic method was used, and the results were highly reliable, which could be used as a standard to evaluate bladder micturition function[15].
3.1.3 Urethral catheter removing time and inpatient time
The longer the indwelling catheter was placed, the greater the chance of urinary tract infections would be.Meanwhile, the length of hospital stay was directly proportional to the cost of hospitalization. Therefore,the catheter indwelling time and hospital duration were recorded for each patient in this study.
3.2 Criteria of clinical efficacy
Cured: Physical signs and symptoms such as distending pain and distressing feeling disappeared, the patient could spontaneously urinate smoothly, and the ultrasound examination suggested the residual urine volume was <50 mL.
Improved: Physical signs and symptoms such as distending pain and distressing feeling improved significantly, the patient could spontaneously urinate,while the ultrasound examination suggested the residual urine volume was 50-100 mL.
Invalid: The patient could not spontaneously urinate,or the residual urine volume was >100 mL.
3.3 Results
3.3.1 Comparison of effective rate
The total effective rate was 96.0% in the observation group versus 88.0% in the control group. The difference between the two groups was statistically significant(P<0.05), (Table 2).
3.3.2 Comparison of main symptom scores
There were no significant differences in the component scores of difficulty voiding urine, lower abdominal distending pain, soreness and weakness of low back and knees, and lassitude between the two groups before treatment (all P>0.05), indicating that the two groups were comparable. After treatment, the component scores of difficulty voiding urine, lower abdominal distending pain, soreness and weakness of low back and knees, and lassitude in both groups decreased, and the intra-group differences were statistically significant (all P<0.05), and these scores in the observation group were lower than those in the control group (all P<0.05), (Table 3).

Table 2. Comparison of clinical efficacy between the two groups (case)

Table 3. Comparison of main symptom scores between the two groups (x ±s, point)
3.3.3 Comparison of residual urine volume
There was no significant difference in residual urine volume between the two groups before treatment(P>0.05), indicating that the two groups were comparable. After treatment, the residual urine volume of both groups decreased (both P<0.05), and the between-group comparison suggested that the residual urine volume in the observation group was significantly less than that in the control group (P<0.05), (Table 4).

Table 4. Comparison of residual urine volume between the two groups (x ±s, mL)
3.3.4 Comparison of catheter indwelling time and inpatient time
After treatment, the inpatient duration and the catheter indwelling time in the observation group were significantly shorter than those in the control group(both P<0.05), (Table 5).

Table 5. Comparison of catheter indwelling time and inpatient time between the two groups (x ±s, d)
4 Discussion
In Chinese medicine, urinary retention falls under the category of Long Bi (dribbling and retention of urine).Chinese medicine holds that Long Bi (dribbling and retention of urine) actually represents two diseases:unsmooth urination, dripping, short and scanty, with slow onset of disease is considered as Long (dribbling of urine); urinary stoppage, with acute onset of disease is considered as Bi (retention of urine). Long (dribbling of urine) is milder than Bi (retention of urine), and patients with urinary retention after cervical cancer surgery mostly belong to Long (dribbling of urine), since they can urinate a little but urine in the bladder is not fully emptied, and the residual urine is too much. Although there are differences between the two concepts, they both refer to difficulty in urination, therefore, they are generally designated as Long Bi (dribbling and retention of urine)[16]. The etiology and pathogenesis are bladder fails to transform qi. The function of bladder mainly depends on the normal operation of three Jiao (triple energizer), spleen and kidney. Due to the wide range of radical hysterectomy for cervical cancer, the trauma is large, and the bladder collaterals are easily damaged,which leads to the meridian qi obstruction of bladder,the blockage of qi and blood, the failure of bladder qi transformation, and the blockage of water passages.Additionally, the primordial qi is seriously damaged after the operation, qi and blood are insufficient, and vital qi is deficient with spontaneous sweating, organs and meridian qi are injured. Therefore, the rise of pathogenic qi, the deficiency of vital qi, the insufficiency of kidney qi, and the dysfunction of bladder are the pathogenesis of this disease. It is deficiency complicated with excess, and dominated by deficiency. The deficiency is mainly the deficiency of spleen and kidney.The insufficiency of kidney yang impairs qi transformation of the bladder and causes difficulty in urination. The deficiency of spleen and stomach qi inhibits qi transformation of the bladder. The excess includes dysfunction of bladder caused by static blood obstruction and stagnation after pelvic surgery, and waterways blockage caused by stagnation of liver qi due to bad mood during long-time indwelling catheterization. Therefore, the principles of treatment are invigorating spleen for replenishing qi and warmly invigorating kidney yang, so as to promote qi transformation of the bladder, conveyance and dispersion of liver qi, and the harmonizing of three Jiao(triple energizer), and thus the urination can be smooth.
Intradermal needle therapy belongs to category of shallow puncturing method. The theory of shallow puncturing method is laid in Huang Di Nei Jing (Yellow Emperor’s Classic of Internal Medicine), which is based on the meridian and collateral theory and theory of acupoints, and is a specific application to stimulate twelve cutaneous regions. The twelve cutaneous regions are located in the outermost layer of the human body, connected with meridian qi and blood, and are the external defense barrier of the body. Shallow needling can regulate the defensive qi to protect the muscle surface against exogenous pathogens. The intradermal needle therapy belongs to embedding therapy in the Chinese medicine. It is a special small-sized needle with the advantages of small needle and painless feeling. It can pierce into intradermal or subcutaneous layer and fixed on the acupoint area to produce continuous effect of acupuncture. This therapy applies the ‘static for retention’ treatment method in acupuncture theory. It mainly works on related diseases of Zang-fu organs with a mild and continuing stimulation to the skin via meridians, so as to prevent and treat diseases[17-20]. Due to the short and small size,the intradermal needle would not reach the deep layer tissues, nor damage the Zang-fu organs, great vessels and nerve trunk. The therapy is safe and reliable[21].Meanwhile, not reaching the nerves makes the pain much slighter, and the treatment more acceptable[22].
Following the principle of treatment based on syndrome differentiation, we selected Qihai (CV 6),Guanyuan (CV 4), Zhongji (CV 3), Yinlingquan (SP 9),Zusanli (ST 36) and Sanyinjiao (SP 6) in this study. Qihai(CV 6) was beneficial for replenishing kidney, securing essence and activating yang. Guanyuan (CV 4) is the crossing point of the Conception Vessel and Three Yin Meridians of Foot, with the effect of warming kidney and activating yang, promoting bladder qi transformation to open the water passage. It is one of the basic acupoints to treat the urinary system diseases.Zhongji (CV 3) is the Front-Mu point of the bladder, with the effect of unblocking stagnation and resolving masses. It is the key acupoint to treat bladder diseases.Studies had shown that acupuncture at Zhongji (CV 3)could reduce intravesical pressure, increase bladder pressure, and excite detrusor muscle to promote its normal contraction[23-24]. Sanyinjiao (SP 6) is the crossing point of the Liver Meridian, Spleen Meridian and Kidney Meridian. It can regulate the meridian qi and blood of the Three Yin Meridians of Foot, invigorate the spleen and benefit qi, and disperse stagnated liver qi and replenish kidney. Yinlingquan (SP 9) is the He-Sea point of the Spleen Meridian. It can regulate fluid metabolism of the whole body, with the effect of invigorating spleen for eliminating dampness and diuresis. Zusanli (ST 36) is the He-Sea point of the Stomach Meridian, with the effect of invigorating qi and blood, and it is an important tonifying point. The combination of the above acupoints made the effect of tonifying kidney and benefiting qi, and helped the bladder qi transformation, improving the micturition.
In this study, there were no statistically significant differences between the two groups in the symptom scores of difficulty voiding urine, lower abdominal distending pain, soreness and weakness of low back and knees, and lassitude, and the residual urine volume before treatment. After treatment, the above symptom scores and residual urine volume in both groups decreased significantly, and the scores and residual urine volume in the observation group were significantly lower than those in the control group,indicating that the intradermal needle therapy can significantly improve the symptom scores and residual urine volume of urinary retention after the cervical cancer surgery. The inpatient duration and catheter indwelling time in the observation group were obviously shorter than those in the control group, and the differences were statistically significant, indicating that the intradermal needle therapy could reduce the inpatient duration and catheter indwelling time for the patients with urinary retention after cervical cancer surgery, thus reducing the financial burden to a certain extent and improving the quality of life. Regarding clinical efficacy of the two groups, the total effective rate of the observation group was superior to that of the control group, and the difference was statistically significant, indicating that intradermal needle therapy combined with basic nursing produced more significant efficacy than basic nursing alone. In summary,intradermal needle therapy can relieve symptoms of urinary retention after cervical cancer surgery, with advantages of easy-to-operate and stable efficacy and safety.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants.
Received: 15 July 2019/Accepted: 15 August 2019
杂志排行
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science的其它文章
- Effects of electroacupuncture on the behaviors and expressions of hippocampal neurotransmitters and Bax/Bcl-2 proteins in rat models of anxiety disorder
- Effect of An-pressing manipulation on post-stroke muscle spasticity in rats and its mechanism study
- Regulatory effects of moxibustion on ubiquitin and NLRP3 proteins in colon of ulcerative colitis rats
- Clinical observation of deep electroacupuncture at Baliao points for female stress urinary incontinence
- Clinical observation on prevention of chemotherapy infection in gastric cancer by moxa-stick moxibustion plus rhG-CSF and its effect on immune function
- Clinical observation of acupuncture plus repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in the treatment of post-stroke insomnia
