Land Suitability Evaluation of Zanthoxylum schinifolium in Dry and Hot Valley of Jinsha River: A Case Study of Jiaopingdu Town of Luquan Yi and Miao Autonomous County, Yunnan Province
2020-04-10MeiqiSHAOZishengYANG
Meiqi SHAO, Zisheng YANG
Institute of Land & Resources and Sustainable Development, Yunnan University of Finance and Economics, Kunming 650221, China
Abstract According to the recent practice in Laopingzi Village, Jiaopingdu Town, Luquan Yi and Miao Autonomous County (Luquan County hereinafter) in dry and hot valley of Jinsha River, the development of Zanthoxylum schinifolium Sieb. et Zucc planting industry can help farmers gradually get rid of poverty and achieve a virtuous cycle of ecological environment. It is a sustainable poverty alleviation way. Based on the three aspects of soil properties, climatic conditions, and topographical conditions influencing the growth of Z. schinifolium, this paper selected eight evaluation factors to establish a suitability evaluation system for Z. schinifolium, used the analytic hierarchy process to determine the indicator, and determined the weight of the evaluation indicators. Besides, it calculated the comprehensive suitability index of land suitability of Z. schinifolium and evaluated the suitability of Z. schinifolium land in Jiaopingdu Town of Luquan County. The results showed that the suitable area for the cultivation of Z. schinifolium in Jiaopingdu Town reached 7 270.78 ha, accounting for 88.69 % of the study area; the area of unsuitable land was 922.07 ha, accounting for 11.31% of the study area. Among the suitable land areas, the high suitability area reached 562.99 ha, accounting for 7.79%; the moderate suitability area was 2 206.76 ha, accounting for 28.61%; the low suitability area was 4 599.03 ha, accounting for 63.6%. Based on the results of suitability evaluation, it came up with pertinent recommendations for the development of Z. schinifolium industry in Jiaopingdu Town.
Key words Zanthoxylum schinifolium Sieb. et Zucc, Planting industry, Land suitability evaluation, Dry and hot valley of Jinsha River, Luquan Yi and Miao Autonomous County (Luquan County)
1 Introduction
The dry and hot valley of Jinsha River is one of the concentrated distribution of poverty-stricken counties in China. Luquan Yi and Miao Autonomous County (Luquan County) is a state-level poverty county with a wide range of poverty and deep poverty. In recent years, Laopingzi Village of Jiaopingdu Town in Luquan County greatly developedZanthoxylumschinifoliumSieb. et Zucc planting industry, which helped farmers gradually get rid of poverty and achieve a virtuous cycle of ecological environment[1].Z.schinifoliumbelongs to shrubs, is thermophilic and likes light, both its growth and development need higher temperature, it is cold and drought resistant, but not waterlogging resistant.Z.schinifoliumhas excellent medicinal value. According to records ofCompendiumofMateriaMedicawritten by Li Shizhen,Z.schinifoliumhas functions of strengthening teeth, blackening hair, brightening eyes, increasing years, aging resistant, and enhancing mental health. Besides, the peel ofZ.schinifoliumcan be used as spices and flavors. So far, more than 60 kinds of seasonings have been developed by using the peel ofZ.schinifolium. Seeds ofZ.schinifoliumcan used to extract edible oil and industrial oil, used in food processing and light chemical industry. In addition,Z.schinifoliumleaves can be used not only to prevent diseases and insect pests, but also to make edible spices. The production areas ofZ.schinifoliumare mainly distributed in most provinces and regions north of Wuling and south of Liaoning. However, the increase in market demand has driven the rapid development of theZ.schinifoliumplantation. Jinyang of Sichuan and Youyang of Chongqing have also become the representative origin ofZ.schinifolium. Developing famous and excellent agricultural products according to local conditions is an important way to develop the rural economy and benefit farmers, as well as an effective measure for the prosperity and active agricultural product market[2]. There are many kinds of famous and excellent agricultural and livestock products in the region, but most of them lack scientific development. At present, under the urgency of developing commodity production, adjusting the agricultural industrial structure, and increasing farmers’ income, improving the quality of premium agricultural products and increasing their added value are one of the key links in the development of modern agriculture. The study of land suitability is an important precondition for providing a scientific basis for developing high-quality famous agricultural products according to local conditions[3]. In order to make more reasonable plan and use the land for the cultivation ofZ.schinifolium, coordinate the development of agricultural economy, improve the economic benefits ofZ.schinifoliumcultivation, and rational use of land resources in the region,with the aid of GIS spatial analysis technology, taking Luquan County as the study area, we investigated the ecological conditions of growth, selected a total of 8 evaluation indicators for the three criteria hierarchy factors of terrain, temperature, and soil. Using the analytic hierarchy process (AHP), we established an evaluation model for the growth suitability ofZ.schinifolium. Based on this, we came up with recommendations for optimizing the production layout ofZ.schinifolium.
2 Overview of the study area and data source
2.1 Overview of the study areaLuquan Yi and Miao Autonomous County (102°14′3″ E-102°56′8″ E, 25°24′39″ N -26°22′2″ N) is located in the northern part of Kunming City, Yunnan Province. Luquan County is located in the middle of the Hengduan Mountains and the Dianchi fault depression zone with strong north-south cuts. The geological structure is complex; the height difference in the territory is large, the terrain is high in the northeast and the southwest is low, and it descends gradually from northeast to southwest in a stepwise manner. The county has a total area of 4 249 km2, of which mountainous areas account for 98.4%. The county has an average elevation of 1 750.5 m and belongs to a subtropical monsoon climate zone. It is dry in winter and spring, rainy in summer, distinct in dry and wet, and has three-dimensional climatic characteristics. The annual average temperature is 13.5 ℃, and the annual average rainfall is 946.7 mm[4]. Jiaopingdu Town is located in the northwest of Luquan County, 108 km from Luquan County. The geographical coordinates are 102°27′ E and 26° 07′ N. It borders Malutang Township in the east, Sayingpan Town in the south, Tanglang Township in the west, Jinsha River in the north, and Huili County in Sichuan Province across the river. High mountains and ridges, cliffs are on both banks. It is one of the main ferries between Yunnan and Sichuan, and also north gate of Kunming City. The town’s land area is 254.6 km2, the highest altitude is 3 211 m, and the lowest altitude is 890 m. The annual average temperature is 12.7 ℃ and the annual average rainfall is 1 142.6 mm.
2.2 Determination of evaluation rangeAccording to the actual situation and land use characteristics of Jiaopingdu Town, we evaluated the suitability of the land in Jiaopingdu Town except for construction land, cultivated land and forest land. Using ArcGIS software, we extracted vector data for the survey of land use change in Jiaopingdu Town in 2016, and selected the parcels except Jiaopingdu Town for construction land, cultivated land, and forest land. According to statistics, the total area we evaluated was 8 152.85 ha, accounting for 32.56% of the total land area of Jiaopingdu Town.
3 Evaluation units and evaluation factors
3.1 Dividing evaluation unitsThe land evaluation unit is the "objective carrier" of the natural and social attributes of land, and is the basic unit of suitability evaluation. The evaluation unit used in this paper is the land map (parcel) in the vector data of the Land Use Change Survey (2016) as the evaluation unit.
3.2 Selecting evaluation factorsOne of the most critical research links in land suitability evaluation is the rational selection and determination of factors[5]. In selecting the evaluation factors, an index system should be constructed according to local conditions, and the evaluation indicators should be selected to reflect the comprehensiveness, representativeness, and dominance of the land quality, the relative independence, stability, regional differences of the evaluation factors, and the availability of data[6]. Based on the analysis of relevant data, consultation with local technicians, and field surveys, we took an overall consideration of the impact of various factors on the cultivation ofZ.schinifolium, and selected indicators including effective soil layer thickness, texture, annual precipitation, ≥10 ℃, altitude, slope, organic matter, and soil pH as indicators for establishing a hierarchical model.
3.2.1Terrain conditions. Terrain conditions are factors that must be considered for suitability analysis. Terrain will directly affect the growth of crops and the quality of land. In this study, we selected slope and altitude as evaluation factors. Slope is the steepness of the unit and is a quantitative indication of the steepness of the ground. Slope affects soil erosion and soil surface fluctuations in an area, so it is an important factor for proper analysis of cultivated land.Z.schinifoliumis generally planted on hilly slopes below 25°. The height is related to the water absorption and heat absorption ofZ.schinifolium, and the distribution will be different at different heights, which will then affectZ.schinifoliumand make it different in distribution.Z.schinifoliumis common in plains to sparse forests, shrubs or rocks with the altitude near 800 m. It is more suitable for altitudes of 800-2 200 m.
3.2.2Soil traits. Soil properties are important factors reflecting land quality. In this study, organic matter, texture, soil pH, and soil layer thickness were extracted as factors suitable for cultivated land suitability based on soil data. Based on these factors, the suitability of green pepper plants in Jiaopingdu Town was comprehensively analyzed. The soil depth directly affects the water content and organic matter content of the soil.Z.schinifoliumbelongs a shallow-rooted tree species. The root system ofZ.schinifoliumis mainly distributed in the soil layer about 60 cm from the ground. Under normal circumstances, the depth of the soil layer can meet the growth needs ofZ.schinifolium. The deeper the soil layer, the higher the yield ofZ.schinifolium. Soil texture refers to the relative proportion of the content of soil particles at various levels in the soil and the properties of the soil sandy stickiness.The ratio of the content of the three levels of sand, powder, and clay in the soil is also an important factor influencing a series of physical and chemical properties of the soil. The soil texture affects the physical and mechanical properties of the soil, and affects the ability of the soil to store water and retain nutrients. Different soil textures have different soil nutrient content and different effects on crop growth.Z.schinifoliumis suitable for soil, and especially likes deep, fertile and moist sandy loam. Soil organic matter content is an important indicator of soil fertility, it is closely related to soil water and fertilizer retention capacity. In general, under the same or similar conditions, the content of organic matter is positively related to the potential of soil production within a certain content range. The content of organic matter is also an important factor that determines the growth ofZ.schinifolium. Soil pH value affects soil structure, nutrient status, biological type and biological activity, and also affects the growth and development ofZ.schinifolium.Z.schinifoliumcan be planted in the soil with pH of 6.5-8.0, but the best range is 7.0-7.5.
3.2.3Climatic conditions. Climate is the most important factor affecting agricultural production. The quality of the climate environment can directly affect crop yields and the development of the local planting industry. In this study, we selected two indicators of annual precipitation and accumulated temperature ≥10 ℃ as evaluation factors.Z.schinifoliumis a relatively drought-resistant tree species, it can normally grow and fruit at annual precipitation of more than 400 mm, and the optimum rainfall is 500-800 mm. Accumulated temperature is an important factor affecting crop yield and quality.Z.schinifoliumis a tree species that likes light. When the annual average temperature is 10-14 ℃ and ≥0 ℃, and the annual accumulated temperature is 3 000-3 500 ℃, the growth and development are good, the fruit is normal, the color and taste are good, and the yield is high.
3.3 Establishment of hierarchy modelAccording to the characteristics of the selected indicators, we divided the evaluation factors into three criterion hierarchies, in which the target hierarchy (hierarchy A) is the suitability ofZ.schinifolium; the criterion hierarchy (hierarchy B) is terrain conditions, soil properties, and climatic conditions; the indicator hierarchy (hierarchy C) is slope, altitude, organic matter, soil pH, annual precipitation, ≥10 ℃, texture, and effective soil layer thickness. The structural relationships are shown in Table 1. Through consulting relevant data and combining with the actual situation of Jiaopingdu Town of Luquan County, we used the APH method to determine the indicator weight.
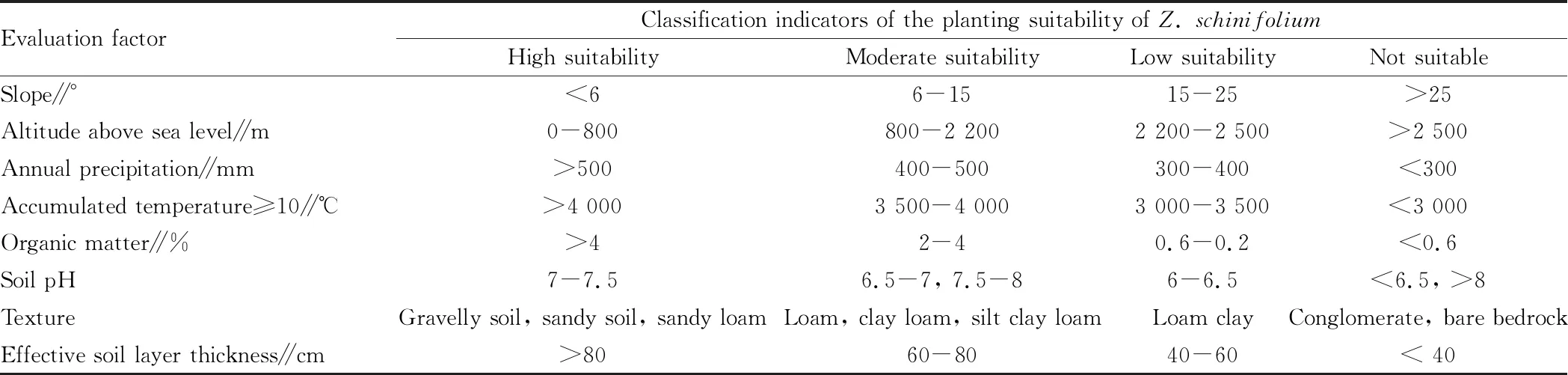
Table 1 Evaluation factors and classification indicators of the planting suitability of Zanthoxylum schinifolium
4 Determination method of indicator weight
Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is a method originally developed by Prof. Thomas L. Saaty in the 1970s[7]. It divides the various factors in complex problems into related hierarchies, making it a multi-target, multi-criteria decision-making method. It is an effective method combining quantitative analysis and qualitative analysis[8]. The AHP divides the influencing factors of the problem into ordered and interconnected multi-hierarchy models according to the hierarchies, and qualitatively and quantitatively analyzes the relative weights of each group of factors. Besides, it can introduce expert evaluation methods can be introduced, to obtain a judgment matrix composed of the weight values of each factor, and solve the maximum value of the eigenvalue of the matrix and its corresponding eigenvector to obtain the weight value of each factor in all hierarchies[9]. The operation steps of the analytic hierarchy process are as follows. (i) Establishing a hierarchical structure model. According to the needs ofZ.schinifoliumplanting, we divided into the model into target, criterion and indicator hierarchies. (ii) Establishing judgment matrix. The factors in the same hierarchy were compared in pairs to form a judgment matrix. The value ofaijcan be obtained from Table 2 to represent the relative weight values between different factors.
(1)

Table 2 Scale
(iii) Consistency test.
(2)
Comparing the consistency indicatorCIand the average consistency indicatorRIto obtain the consistency ratioCR, the average consistency indicatorRIwas 0, 0, 0.58, 0.90, 1.12, 1, 24, 1.32, 1.41, 1.45, respectively, when the matrix order was 1 to 9.
(3)
Only when the consistency ratioRI<0.10, the judgment matrix is feasible, otherwise the judgment matrix A will be adjusted to meet the conditions according to the value ofCR. We calculated with the aid of spssau program, and obtained the final indicator weight after performing consistency test (Table 3). From the AHP results, it can be seen that the degree of influence of each evaluation factor on the suitability of peppercorn production in Jiaopingdu Town is (from high to low): slope, altitude, annual precipitation, ≥10 ℃, organic matter, soil pH, texture, and effective soil layer thickness.
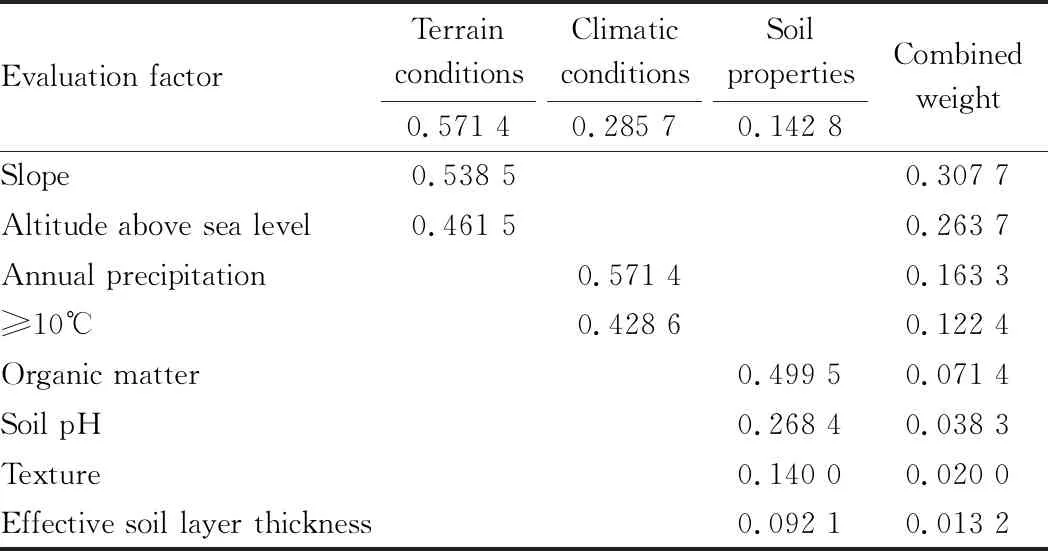
Table 3 Combined weight of each evaluation factor
5 Determination method of suitability level
5.1 Establishing evaluation modelAfter calculating the impact factor data and the weights of each factor with the aid of GIS technology, we used the respective weight values to perform weighted superposition to obtain the final suitability data. The formula is as follows:
(4)
whereCis the sum of suitability,Cidenotes the score of thei-th impact factor, andWidenotes the weight of thei-th impact factor, that is, the contribution rate of this indicator to the size of the restriction on the development ofZ.schinifolium, andnis the total number of impact factors .
5.2 Dividing suitability levels ofZ.schinifoliumIn the ArcGIS software system, with the help of its spatial analysis and mapping functions, we conducted calculation according to formula (4), and plotted to obtain the map of suitability evaluation ofZ.schinifoliumplanting in Jiaopingdu Town, the levels of suitability can be divided into four according to the comprehensive score, that is, high, moderate, low, and unsuitable (Fig.1). Using the grid computing tool of ArcGIS software, we substituted the processed 8 suitability evaluation indicator data and corresponding weight values into the weighted index and model to calculate the final suitability distribution map ofZ.schinifoliumin Jiaopingdu Town (Fig.1). According to statistics, we obtained a table showing the area and proportion of suitability forZ.schinifoliumplanting in village committees of Jiaopingdu Town (Table 4).
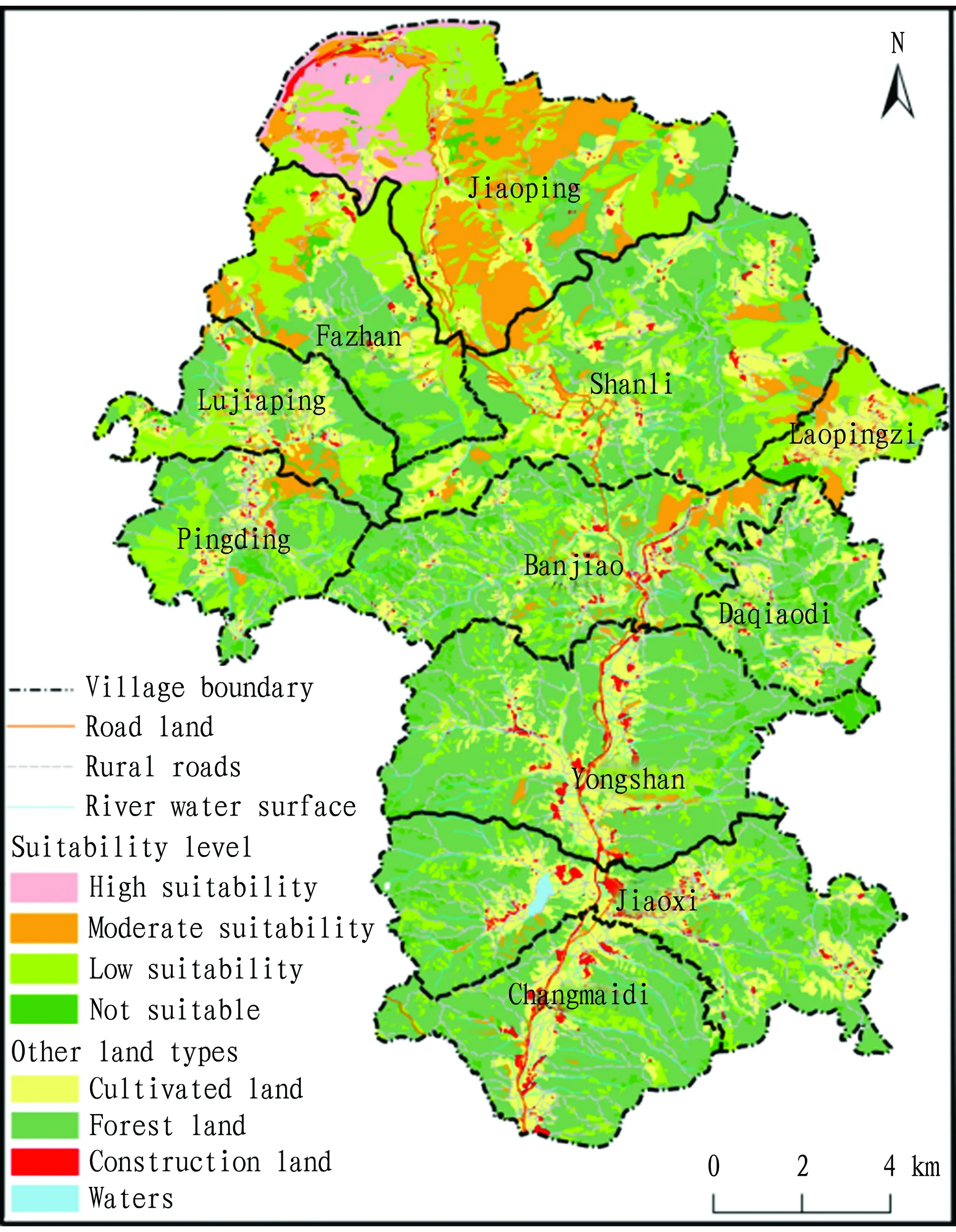
Fig.1 Evaluation map for suitability of Z. schinifolium in Jiaopingdu Town
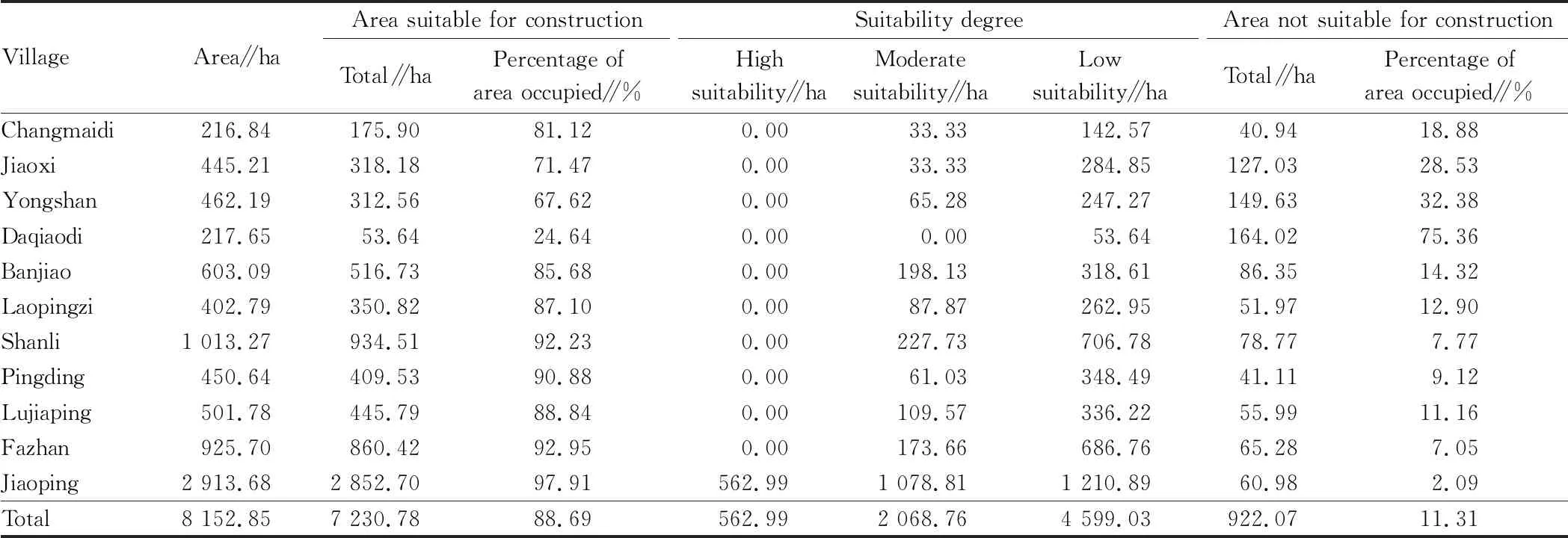
Table 4 Area of planting suitability of Z. schinifolium in Jiaopingdu Town
6 Result analysis and recommendations
6.1 Evaluation result analysisAccording to the evaluation results, the suitability of Jiaopingdu Town for plantingZ.schinifoliumis very high, only 11.31% land (922.07 ha) is not suitable for plantingZ.schinifolium, and 7 230.78 ha (about 88.69%) is suitable for plantingZ.schinifolium. There is a large difference in the proportion of areas that are suitable for construction and not suitable for construction in each village committee. Judging from the area of suitable construction, Jiaoping Village is the largest in the town, with an area of 97.91%, accounting for 34.99% of the total area. The village committee most suitable for plantingZ.schinifoliumin the town is Jiaoping Village, and the more suitable areas for plantingZ.schinifoliumare Shanli Village, Jiaoxi Village, Pingding Village, Yongshan Village, Banjiao Village, and Fazhan Village. Village not suitable for plantingZ.schinifoliumare Changmaidi Village and Daqiaodi Village.
In Jiaopingdu Town, the highly suitable area for growingZ.schinifoliumis Jiaoping Village in the north, where the altitude is about 1 200 m, there is sufficient sunshine and abundant heat, the annual average temperature is about 28 ℃ and the annual rainfall is about 500 mm, the soil is red soil, with a small slope and gentle terrain, which is very suitable for plantingZ.schinifolium. The villages suitable for plantingZ.schinifoliumin Jiaopingdu Town are Shanli Village, Lujiaping Village, Banjiao Village, and Fazhan Village in the northwest and northeast, where there are sufficient light and suitable heat, the annual average temperature is about 22 ℃, the soil is mainly red and yellow which is more suitable for plantingZ.schinifolium. The villages with low suitability for plantingZ.schinifoliumin Jiaopingdu Town are Laopingzi Village, Pingding Village, Yongshan Village, and Jiaoxi Village, where the annual average temperature is about 18 ℃, and the rainfall is about 800 mm, but the terrain is steep and the slope is large, which restricts the growth ofZ.schinifoliumto a certain extent, and the planting degree is low. The areas that are not suitable for plantingZ.schinifoliumare mainly distributed in the east and south, mainly in Daqiaodi Village and Changmaidi Village where there are relatively more restrictive factors, large slopes, and altitudes above 2 200 m, especially the annual average temperature of Daqiaiodi Village is about 13 ℃, the altitude is too high, and the temperature is low, it is not suitable for plantingZ.schinifolium. Jiaopingdu Town, located in the mountainous area of Yunnan, has high altitude. The northern area of Jiaopingdu Town is more suitable for the growth ofZ.schinifolium. It has high irrigation conditions, good ground conditions, and small slopes, and has excellent agricultural production conditions. From the analysis results of GIS, it can be seen that in the Jiaopingdu Town, there is still a large area suitable for plantingZ.schinifoliumapart from Laopingzi Village, which currently plants moreZ.schinifolium, and the suitable area accounts for 88.69%. Therefore, in accordance with the rules of nature, economics and scientific development, in accordance with the requirements of "high yield, high quality, high efficiency, ecology, and safety", and following the principle of market orientation, farmers’ willingness and priority of benefits, the suitable area for plantingZ.schinifoliumis above 7 230.78 ha, it is recommended to implement the yield and income increase plan and expand theZ.schinifoliumplanting area.
6.2 Recommendations for development ofZ.schinifoliumindustry(i) In view of significant climate and regional differences in Jiaopingdu Town, it is recommended to start from the actuality and characteristics of each village and implement classified guidance, so as to adapt to local conditions and villages, and develop in succession to form a scale advantage. The key to the scale advantage ofZ.schinifoliumindustry is to seize the most advantageous area for the development ofZ.schinifoliumin Jiaoping Village, develop large-scale cultivation, and reduce production costs. It is recommended to adopt the intensive, large-scale, and institutionalized production model. (ii)Z.schinifoliumnot only can be used as a condiment, but also has great medicinal value, and has great development potential and economic value. It is suggested that local science and technology departments should increase the research and development, management, and protection of varieties ofZ.schinifolium, carry out comprehensive utilization and deep processing of resources, deepen the research and development ofZ.schinifoliumproducts, and broaden the reasonable development and utilization of resources and product markets[10]. Local enterprises should bring into full play to their regional advantages and continuously explore the potential use value ofZ.schinifolium, so that the market demand forZ.schinifoliumwill greatly increase. If farmers increase the quantity and quality ofZ.schinifoliumresources simultaneously, there will be more and better new products. A complete industrial chain will be formed, to gradually realize the good social and economic benefits of plantingZ.schinifolium. (iii) Building independent brands with local characteristics[11]. Brand is the main way to market competition. It is recommended to pay attention to brand awareness. Special attention should be paid to the JiaopingduZ.schinifoliumbrand, ensuring the establishment ofZ.schinifoliumgarden, pruning ofZ.schinifolium, soil and water and fertilizer management, comprehensive control of pests and diseases inZ.schinifoliumgarden, post-harvest classification ofZ.schinifolium, dried fruit, product packaging, storage and transportation standardize operations at every step. It is recommended to strengthen scientific and technological support, actively develop and expand the rural e-commerce service platform, break through the traditional marketing model, realize the organic integration of traditional marketing and online marketing, open up large channels for product production bases and markets through e-commerce platforms, expand sales channels, and help registered poor households to get rid of poverty[12]. It is recommended to establish a brand effect to increase promotion efforts and form a one-stop quality traceability mechanism and system for "production, supply, and marketing" of products to ensure the characteristics and healthy development of green industries.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Empirical Research on E-commerce to Increase the Scale of Agricultural Products Trade: Taking Guangxi Hezhou Zhengfeng Modern Agriculture Co., Ltd. as an Example
- Current Status and Development Countermeasures of Forest Land Resources in Southern Cixi City
- Optimization of Acetic Acid Fermentation Process of Apple Cider Vinegar
- Organic Carbon: A New Concept for Development of Modern Fertilizers and Plant Nutrition Theory
- An Empirical Analysis on the Impact of Rural Financial Development on the Income Gap between Urban and Rural Residents in Heilongjiang Province
- Research on the Problem Investigation and Standardized Improvement Paths of Farmers’ Cooperatives
