An Empirical Analysis on the Impact of Rural Financial Development on the Income Gap between Urban and Rural Residents in Heilongjiang Province
2020-04-10
College of Economics and Management, Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, Daqing 163319, China
Abstract The high-quality development of rural finance is an important support for rural revitalization. In recent years, it continuously expands the investment in rural finance in Heilongjiang Province, and optimizes the rural financial service system and mechanism. The overall income level and living conditions of rural residents have been significantly improved, but there still exists income gap between urban and rural residents. Therefore, based on analyzing and combing current situation and problems of rural financial development and urban-rural income gap in Heilongjiang Province, multiple linear regression model is used to study the impact of rural financial development on the income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province. The research results show that the scale of rural financial development in Heilongjiang Province will enlarge the income gap between urban and rural residents, while rural financial development efficiency and urbanization level reduce income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province. Based on the above conclusions, some policy suggestions to promote the equalization of urban and rural income in Heilongjiang Province are puts forward in this paper.
Key words Rural finance, Income gap between urban and rural areas, Development scale, Development efficiency
1 Introduction
In No.1 document of "central committee" of 2019, the focus of "agriculture, rural areas and farmers" work was promoting the development of rural finance. It was proposed getting through all links of finance servicing for "agriculture, rural areas and farmers", and encouraging financial institutions to increase medium and long-term credit support for rural revitalization and poverty alleviation, to gradually narrow the gap between urban and rural areas by optimizing services for agriculture, rural areas and farmers. Meanwhile, it gave guidance to promote the high-quality development of rural finance from different dimensions in policy. In recent years, Heilongjiang Province takes deepening the rural financial reform as the focus of the work of "agriculture, rural areas and farmers", and actively issues a series of policies and guidelines such as theOverallSchemeofComprehensiveSupportingReformExperimentofModernAgriculturein"TwoPlains"HeilongjiangProvinceand theInnovatingthePromotionPlanofRuralFinancialService. Moreover, the innovation and upgrading of rural finance in terms of organizational system, financial products, financing guarantee mode and supervision mechanism are vigorously impelled. In early 2019, rural financial service platform of Heilongjiang Province was officially launched in all parts of the province. Rich achievements in rural financial development of Heilongjiang provide capital guarantee for the continuous increase of grain output, agricultural output value and regional GDP in the province. But under the background of dual structure of urban and rural economy in China, the distribution of social resources tends to urban areas, and urban-rural economic development is still not coordinated. As a core index of measuring agricultural economic development level, the income development level of rural residents still lags behind the average income development level of urban residents, making income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province continuously increase. As the core of economic development, financial development will also cause fluctuations in urban and rural income distribution. Therefore, based on the current situation of income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province, the impact of rural financial development level on the income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang is studied. Moreover, some suggestions are put forward to reduce the income gap between urban and rural residents and realize the coordinated development of urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang Province.
2 Research background
Foreign scholars mainly studied the impact of financial development on the change of urban-rural income gap from the scale and level of financial development and government intervention. Kuznets curve thought there was an "inverted U-shaped" relationship between the degree of financial development and the income gap between urban and rural areas, and the relationship was called Kuznets effect. Some scholars thought financial development would narrow the gap between urban and rural areas. On the basis of Kuznets research, Clarke introduced Gini coefficient, bank assets and GDP for regression analysis, and studied the impact of financial development level on urban-rural income gap in 91 countries. It was found that financial development can narrow the income gap between urban and rural areas by optimizing income distribution[1]. But the researches by some scholars showed that financial development would expand the income gap between urban and rural areas in some cases. Burgessetal. studied the effect of government intervention on the income gap between urban and rural areas in rural financial development. It was found that it was conducive to narrowing the income gap between urban and rural areas when government made preferential subsidy policy and encouraged financial institutions to increase the number of rural business branches. But in the areas with high credit risk, credit business faced high moral hazard, causing that it was difficult to meet the capital demand of these areas, and the income gap between urban and rural areas continued to expand[2]. After Sehrawatetal. used ARDL model to analyze the relationship between financial development level and urban-rural income gap in India, they pointed out that the improvement of the financial development level has widened the income gap between urban and rural areas[3]. By analyzing statistical data of 121 countries in 31 years, Haan found that the improvement of financial development level would not only affect financial liberalization, but also enlarge the income gap between urban and rural areas[4].
The researches of domestic scholars mainly focused on the causes of urban-rural income gap and the impact mechanism of rural financial development on the change of urban-rural income gap. For the causes of urban-rural income gap, Wu Fuxiangetal. thought that the opportunity difference, capital share difference and labor quality difference of urban and rural residents were the important factors that caused the income gap between urban and rural areas[5-6]. Long Haiming divided China into three regional plates: the east, the middle and the west, and studied the influence of difference in policy, economy, urbanization, finance and human capital on the income gap between urban and rural areas. The results showed that economic development and urbanization level had positive effects on the income gap between urban and rural areas, and the influence degree was the maximum[7]. For the impact mechanism of rural financial development on urban-rural income gap, Hu Zongyi used spatial econometric model to analyze the impacts of formal and informal rural financial institutions on the income gap between urban and rural areas respectively. It was found that their development can narrow the income gap between urban and rural areas, but the impact of informal rural financial institutions was more significant, and it was because that informal rural financial institutions were more in line with the actual local financial needs[8]. Zhang Hongyan introduced rural financial development scale and efficiency and other evaluation indexes, and used VAR model to study the impact of rural financial development on the income gap between urban and rural areas. The results showed that rural financial development would widen the income gap, and it was related to serious outflow of rural funds[9]. Zhou Zejiong analyzed the mechanism of financial development affecting the income gap between urban and rural areas, and pointed out that threshold effect and disequilibrium effect were directly proportional to the income gap between urban and rural areas, while the effect of poverty reduction and trickle-down effect were inversely proportional to it[10]. Yan Ruizeng studied the influence of the unbalanced development of urban and rural finance on the income gap of residents, and thought that the difference between urban and rural areas in the level of financial development would widen the income gap between urban and rural residents. In short term, the influence of financial structure difference on income gap was more obvious; in the long run, the difference in financial efficiency had a greater impact on the income gap, and the level of non-agricultural industrial structure would have a strong negative effect on the income gap between urban and rural residents in the long run[11].
3 The current situation for development level of rural finance and the income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province
3.1 Development level of rural finance in Heilongjiang ProvinceRural financial institutions in Heilongjiang Province mainly include policy financial institutions, commercial banks, rural cooperative financial institutions and new rural financial institutions. As the main body of rural cooperative financial institutions, rural commercial banks and rural credit cooperatives become the main force to develop financial services in the form of agricultural credit to agricultural production and operation entities with the advantages of large number of business branches and wide service coverage area. By the end of 2018, the balance of domestic and foreign currency deposits of banking financial institutions in Heilongjiang Province was 2 548.66 billion yuan, which increased by 7.1% year on year, and it continued to operate at high level. The balance of domestic and foreign currency loans of banking financial institutions was 2 032.6 billion yuan, which increased by 4.4% year on year; there were 85.91 billion yuan of new loans, in which RMB loan balance was 2 015.63 billion yuan, up 4.9% year on year. As a pilot province of mortgage loan for the right to operate the contracted land and the right to housing property of farmers (hereinafter referred to as "the two rights"), Heilongjiang Province continuously improved management mechanism of mortgage loans of the "two rights". By the end of 2018, the balance of mortgage loans of "two rights" in pilot counties (cities and districts) had reached 22.91 billion yuan.
3.2 The current situation of income gap between urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang ProvinceWith the continuous development of economy and society in Heilongjiang Province, the per capita income of urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province continues to rise. As shown in Table 1, the per capita disposable income of urban residents increased from 12 566 yuan in 2009 to 29 191 yuan in 2018, which increased by 2.32 times; the per capita net income of rural residents increased from 5 207 to 13 804 yuan, which increased by 2.65 times. Seen from growth velocity, the per capita disposable income of urban and rural residents increased steadily, but growth velocity for per capita disposable income of urban residents was higher than that for per capita disposable income of rural residents.
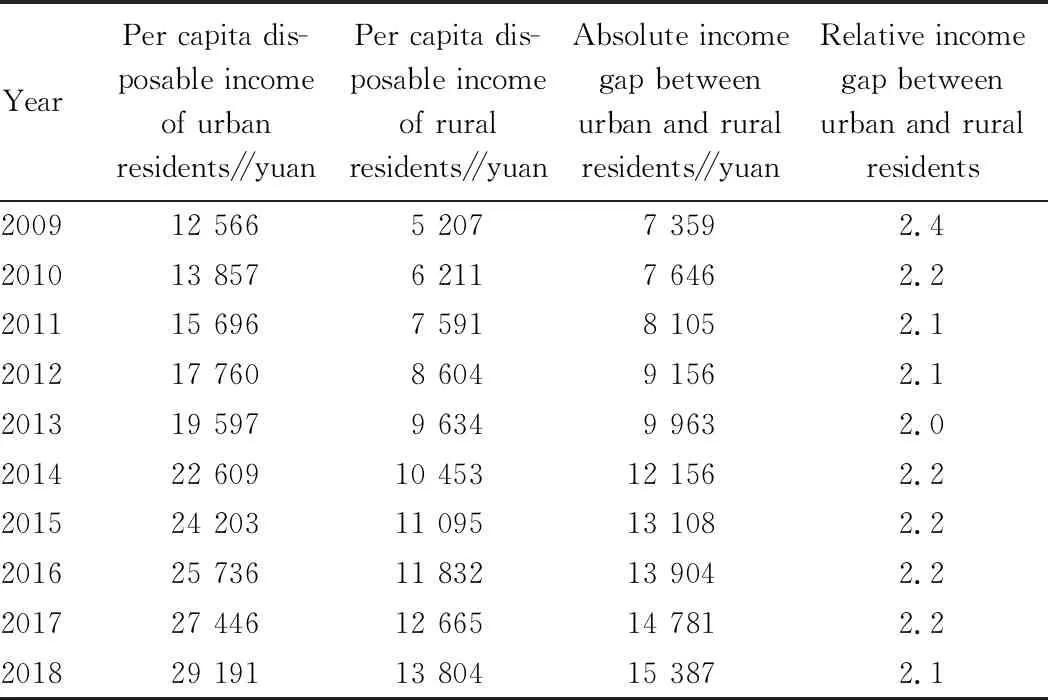
Table 1 Income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province
Table 2 showed income gap between urban and rural residents in China. By comparison of per capita disposable income of rural residents between Heilongjiang Province and the whole country (Fig.1), it was found that the growth trend and range of per capita disposable income of rural residents in Heilongjiang Province and the whole country were basically the same, and the gap between the per capita disposable income of rural residents in Heilongjiang Province and the national average level has been widening since 2015.
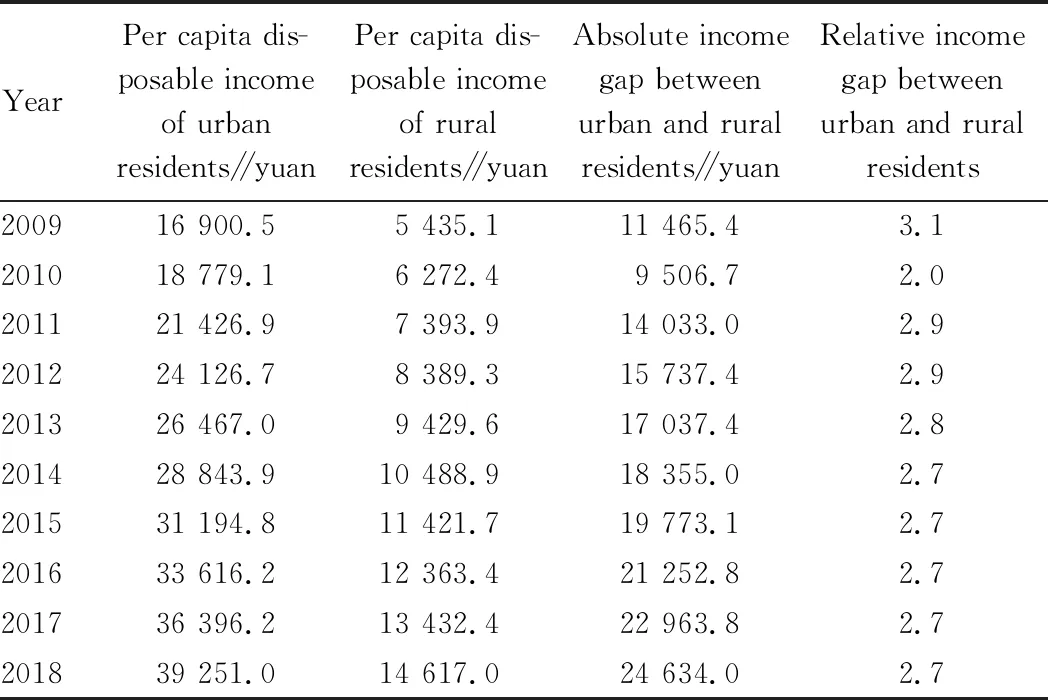
Table 2 Income gap between urban and rural residents in China
By comparison of per capita disposable income of urban residents in Heilongjiang Province and the whole country (Fig.2), it was found that the per capita disposable income of urban residents in the province and the whole country showed a steady growth trend during 2009-2018, but per capita disposable income of urban residents in Heilongjiang Province was still at lower level when compared with average level of whole country. In recent 5 years, growth velocity for per capita disposable income of urban residents in the whole country gradually accelerated, and the gap between Heilongjiang Province and the whole country gradually enlarged. It was related to economic structure in Heilongjiang Province. The increase of the proportion of the first industry would lead to the decrease of the proportion of the second and third industries, while the second and third industries mainly concentrated in urban area. So, the growth rate of per capita disposable income of urban residents was reduced. Therefore, when valuing agricultural development, it should stimulate the development vitality of the second and third industries, and further drive the economic development of the first industry. It should take financial reform as an opportunity, and sufficiently use favorable conditions such as Internet platform and RMB internationalization. By adjusting economic structure, and optimizing economic proportion of various industries in Heilongjiang Province, it could realize coordinated development and narrow the gap with other regions of China.
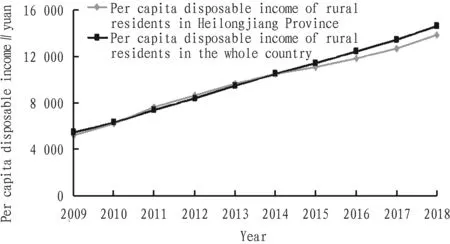
Fig.1 Per capita disposable income of rural residents in Heilongjiang Province and the whole country
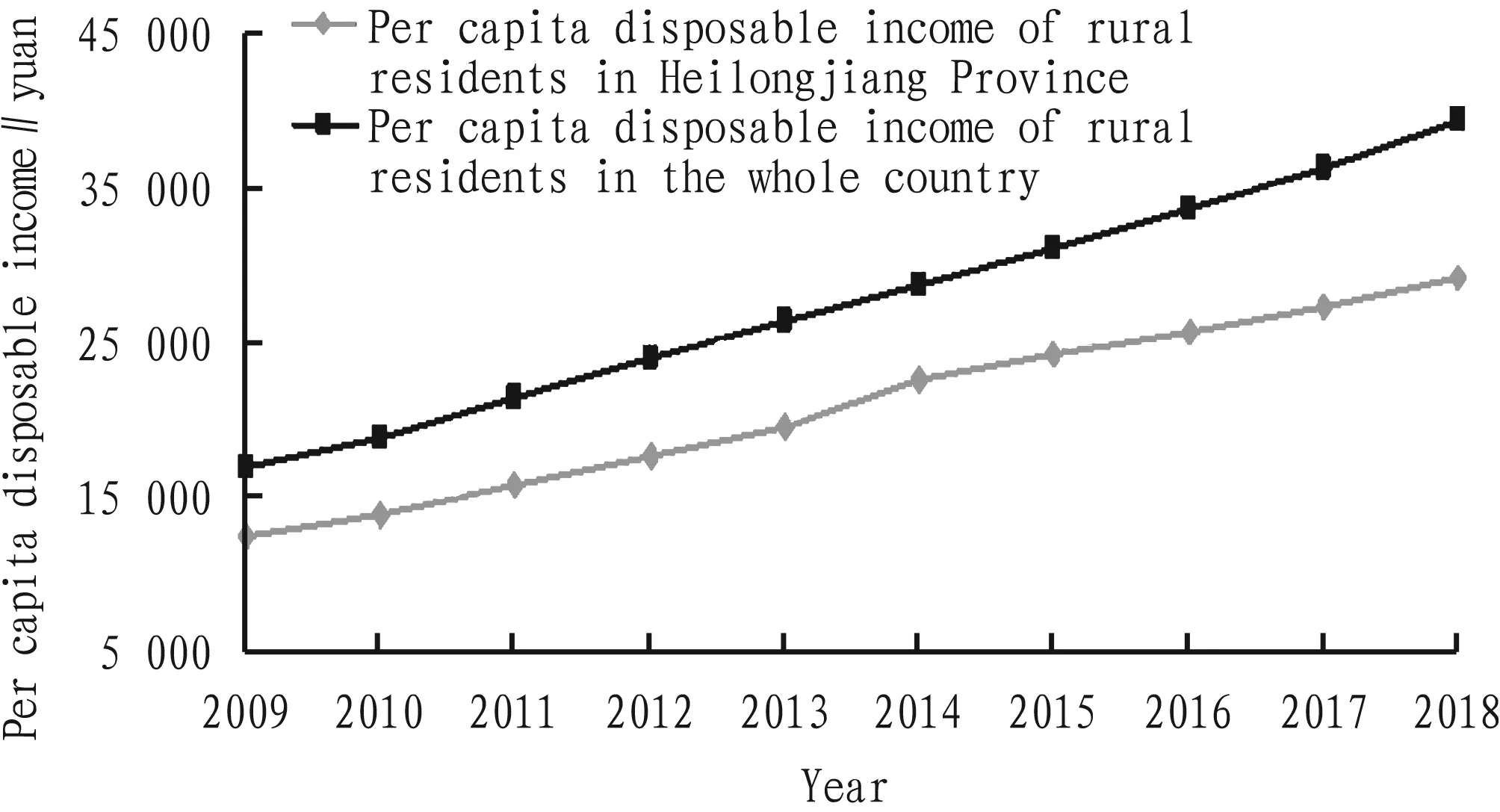
Fig.2 Per capita disposable income of urban residents in Heilongjiang Province and the whole country
The income gap between urban and rural areas can directly reflect the difference of economic development level between urban and rural areas, and evaluate the efficiency of urban and rural financial development. As shown in Fig.3, the absolute income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province was on the rise, with basic stable growth, and annual average increase extent was 802.8 yuan. It showed that although there was favorable situation of rural economic development, and the government has issued a series of preferential policies to support the development of "agriculture, rural areas and farmers", the increase in per capita net income of rural residents was still lower than that of urban areas. With the rapid development of urban and rural economy, the absolute income gap between urban and rural residents was gradually widening. On the one hand, it was because that the infrastructure and financial environment in urban areas were relatively good, and the capital investment of urban residents can obtain higher income. On the other hand, the financial reform in rural areas of Heilongjiang Province was still in its infancy, and there was still a large gap in the construction of financial system and the level of financial services in urban areas, making that the absolute income gap between urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang Province was expanding.
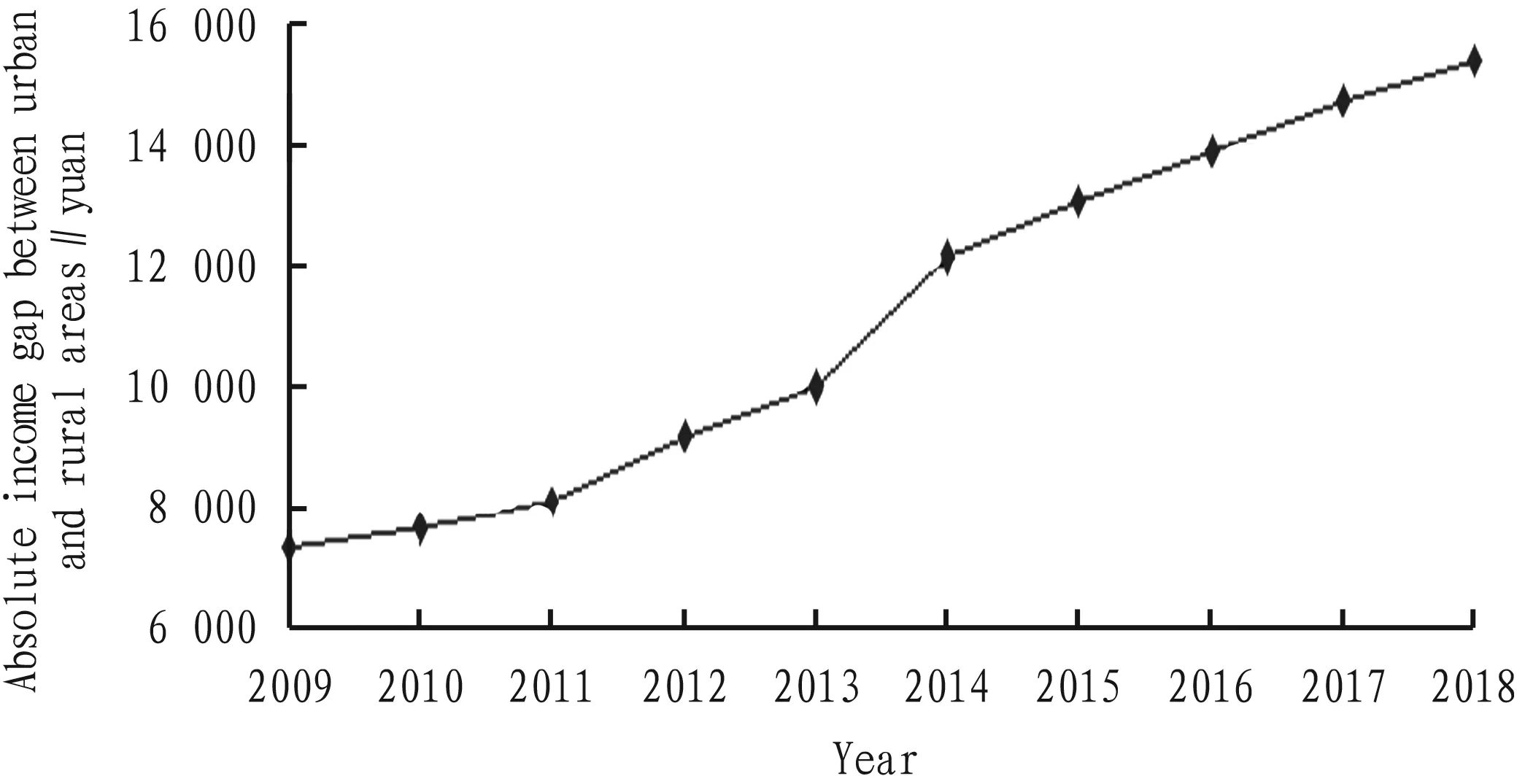
Fig.3 Absolute income gap between urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang Province
As shown in Fig.4, the relative income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province has generally maintained a steady and declining trend in the past ten years, which was basically same as change trend of national average level. During 2009-2011, per capita disposable income level had a obvious decline trend. Major causes were that both the real and virtual economy in cities and towns were severely damaged after the outbreak of the financial crisis in 2008, and the impact of financial crisis on the income of urban residents was far greater than that in rural areas. Additionally, food supply was tight in other provinces, and the price of grain sales went up, which increased farmers’ income. Under common effect of these factors, the relative income gap between urban and rural areas has decreased significantly. After the external environment’s impact was weakened, the change range of the relative income gap between urban and rural areas also tended to be flat. Relative income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province was far lower than national average level. It was because that agricultural development level in Heilongjiang Province was significantly higher than other provinces, and the central government and Heilongjiang Province have actively introduced preferential policies to promote the development of agriculture, rural areas and farmers, increased subsidies for agricultural infrastructure construction, and encouraged agricultural science and technology innovation. It made that the agricultural development of Heilongjiang Province had a strong advantage in the whole country, and it increased farmers’ income and reduced the relative income gap between urban and rural areas. But the phenomenon that the relative income gap between urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang Province is far lower than the national average level does not necessarily continue. Internationally, when the per capita GDP is around 900 dollars, the relative income gap between urban and rural areas remains around 1.7. But the relative income gap between urban and rural areas was all more than 2.0 in Heilongjiang Province during 2009-2018. According to the change rate of the relative income gap between urban and rural residents in the past decade, it will take more than ten years to reach the target value of 1.7. Additionally, the per capita disposable income of urban residents in Heilongjiang has been far below the national average, while the per capita disposable income level of rural residents is basically consistent with the national average level. It illustrates that good economic structure and development mode could not sufficiently explain the phenomenon that the relative income gap between urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang is better than the national level, and this is the numerical superiority brought by the lag of urban economic development.
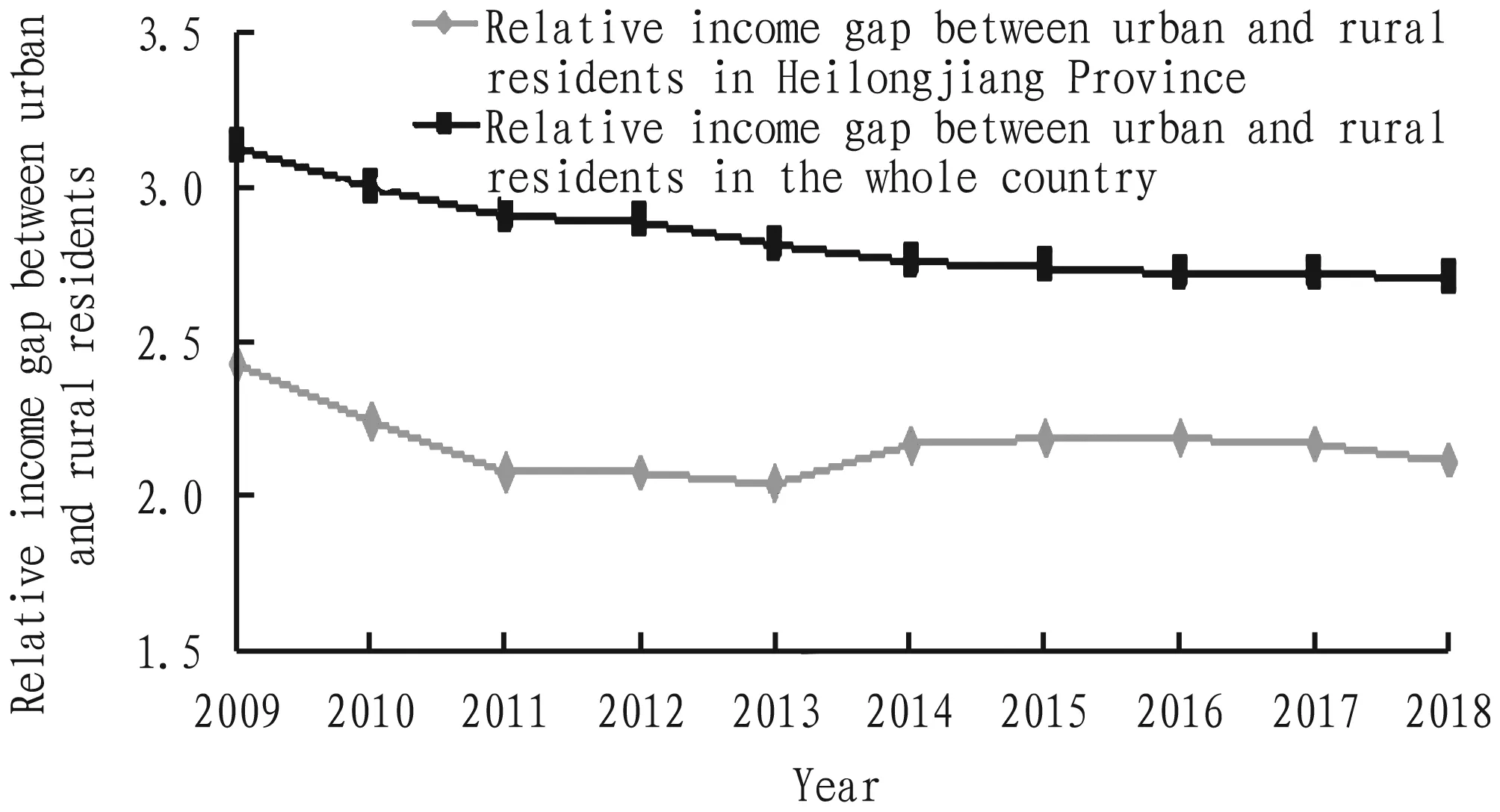
Fig.4 Comparison of the relative income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province and China
4 Index selection and model construction
4.1 Index selectionIn this paper, the income gap between urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang Province is taken as a dependent variable, and the development scale and efficiency of rural finance and urbanization level are taken as independent variables. The specific selection of indicators is as follows.
4.1.1Income gap between urban and rural areas (Y). Considering accuracy and representativeness of index selection, relative income ratio of urban and rural residents is used to show the income gap between urban and rural areas, namely ratio of per capita disposable income of urban residents to per capita disposable income of rural residents. The larger the numerical value is, the larger the income gap between urban and rural areas is. On the contrary, the smaller the numerical value is, the smaller the income gap between urban and rural areas is. The formula is as below:
Y=Per capita disposable income of urban residents/Per capita disposable income of rural residents.
4.1.2Development scale of rural finance(X1). Goldsmith thought that the change of financial stock in a certain region during a certain period of financial development can be expressed by financial assets and GDP of the region. The change of financial stock can be determined by the ratio of financial assets to GDP in the region. Rural financial assets in Heilongjiang Province are mainly loans, and stocks, bonds and other financial products account for a very small proportion, which are negligible. In this paper, the balance of rural loans could be selected as the index to measure financial assets. Due to the inability to obtain accurate statistics of the gross national product of Heilongjiang Province, the gross output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery in Heilongjiang Province is chosen to replace the gross national product of rural areas in Heilongjiang Province. Therefore, development scale of rural finance(X1) could be expressed as below:
X1=Balance of rural loans/Gross output value of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery.
4.1.3Development efficiency of rural finance (X2). It indicates the proportion of the idle funds of the rural residents absorbed by the rural financial institutions in the form of loans to the agricultural production and operation entities with capital needs. Existing research results indicate that the efficiency of financial development is calculated by the ratio of loans to reserves in rural areas under the economic system with public ownership as the main body. Therefore, development efficiency of rural finance (X2) could be expressed by the ratio of loan balance to deposit balance in rural areas of Heilongjiang Province, namely:
X2=Rural loan balance/Rural deposit balance.
4.1.4Urbanization level(X3). Urbanization is the process of rural population migrating from rural areas to urban areas. With the flow of a large number of labor, the city has absorbed the rural surplus labor, and agricultural productivity is improved, and farmers’ income is increased. Urbanization level is an important influence factor of income gap between urban and rural areas, and can be shown as below:
X3=Urban population/Total population in Heilongjiang Province.
4.2 Data sourceThe used statistical data in this paper are mainly from website of State Statistics Bureau and Heilongjiang Statistics Bureau and statistical yearbooks of Heilongjiang Province and China, containing theChinaStatisticalYearbook(2009-2018),StatisticalYearbookofHeilongjiangProvince(2009-2018),RuralStatisticalYearbookofChina(2009-2018),FinancialYearbookofChina(2009-2018),FinancialYearbookofHeilongjiang(2009-2018),FinancialOperationReportofHeilongjiangProvince(2009-2018),StatisticsBulletinofNationalEconomicandSocialDevelopment(2009-2018) andStatisticsBulletinofNationalEconomicandSocialDevelopmentinHeilongjiangProvince(2009-2018).
4.3 Model buildingIn the existing researches on the impact of rural financial development on income gap between urban and rural areas, VAR model is generally established. Via cointegration test, Granger causality test and pulse effect analysis, the relationship between rural financial development and income gap between urban and rural areas is determined. But considering that the selected statistical data (2009-2018) are limited, and the gray scale is large, and data distribution law is not obvious, it is easy to make the measurement results insignificant by using VAR model and violate the actual law of economic operation, and it is difficult to obtain scientific demonstration results. Therefore, development scale of rural finance in Heilongjiang (X1), development efficiency of rural finance (X2) and urbanization level(X3)are taken as independent variables, and income gap between urban and rural residents(Y)is taken as dependent variable to construct multiple linear regression model.
wherejshows the order of time during 2009 and 2018, andXijshows the numerical value of thei-th variable in thej-th year. For example,X23shows numerical value of development efficiency of rural finance in Heilongjiang Province in 2011.β0is constant term, andεis random error term.
5 An empirical analysis on the impact of rural financial development on the income gap between urban and rural residents in Heilongjiang Province
Empirical analysis includes two parts: parameter estimation and model test. The data for development scale of rural finance in Heilongjiang Province are shown as Table 3, and the data for income gap between urban and rural residents and development situation of rural finance in Heilongjiang Province are shown as Table 4.
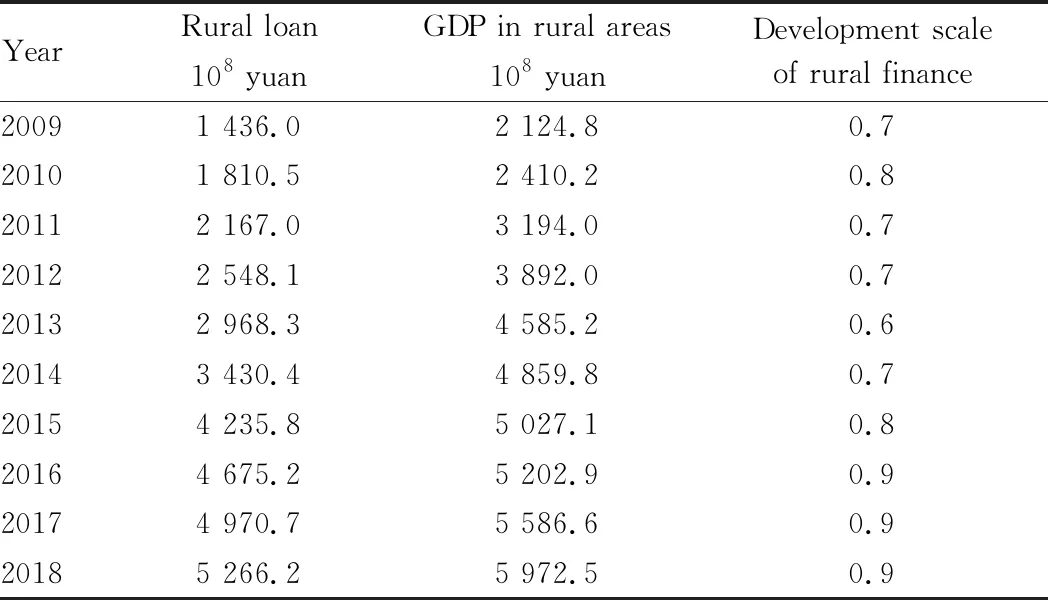
Table 3 Development scale of rural finance in Heilongjiang Province
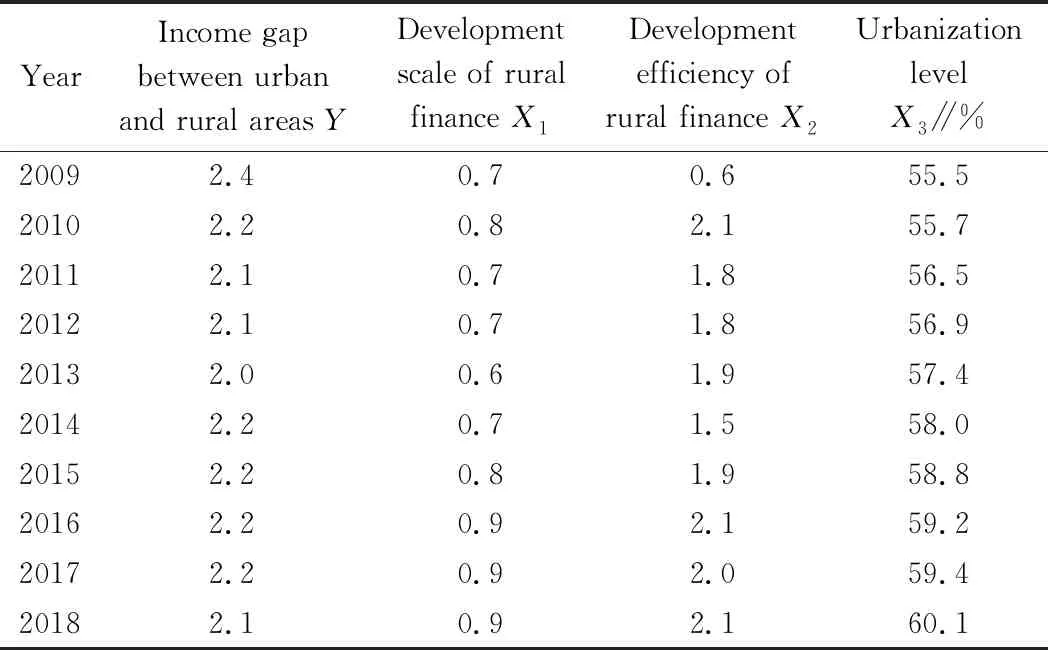

Table 4 Income gap between urban and rural areas and rural financial development in Heilongjiang Province
5.1 Parameter estimationIn multiple linear regression analysis, to guarantee that the dependent variables satisfy the using conditions of multiple linear regression model, the normal distribution test of income gap between urban and rural areas (Y) in Heilongjiang Province is conducted firstly. Due to fewer sample data in this study, Shapiro-Wilk method is used for normal distribution test, and test results are shown as Table 5.

Table 5 Normality test
Seen from test results,Pvalue is 0.095, which is more than 0.05. Therefore, income gap between urban and rural areas (Y) in Heilongjiang Province obeys the normal distribution and satisfies the using conditions of multiple linear regression model, which could be used for multiple linear regression analysis.
Statistical data of rural financial development and income gap between urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang during 2009-2018 are inputted into SPSS software for multiple linear regression analysis, and results are shown as Table 6.
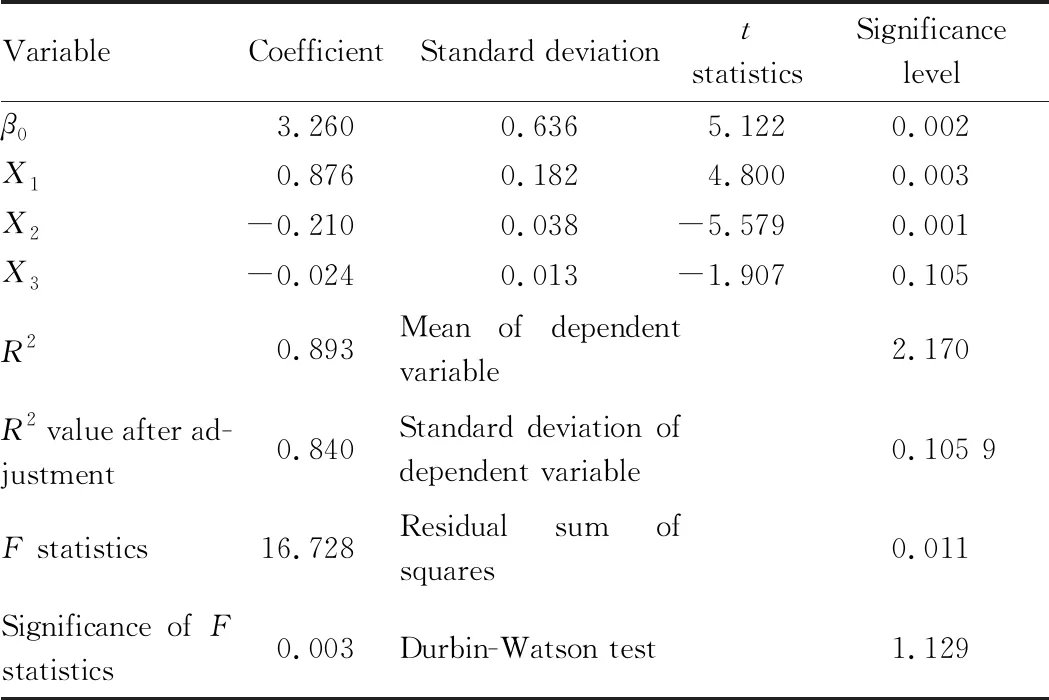
Table 6 Results of multiple linear regression analysis
By sorting out data of multivariate linear regression analysis, parameter estimation results could be obtained as below:
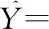
(0.636)(0.876)(-0.21)(-0.024)
t=(5.122)(4.800)(-5.579)(-1.907)
5.2 Test of model results
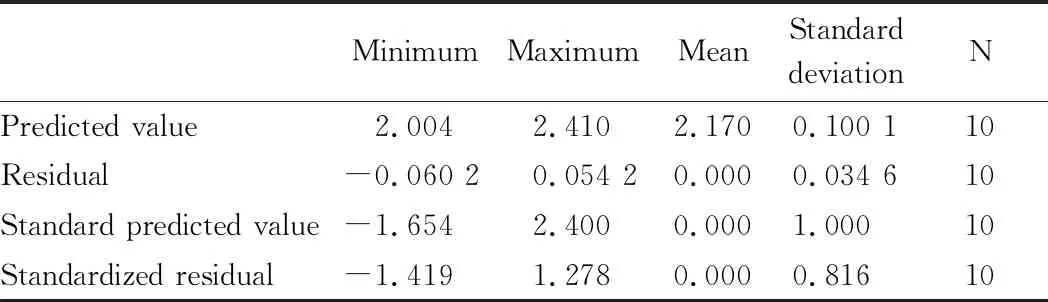
Table 7 Residual statistics
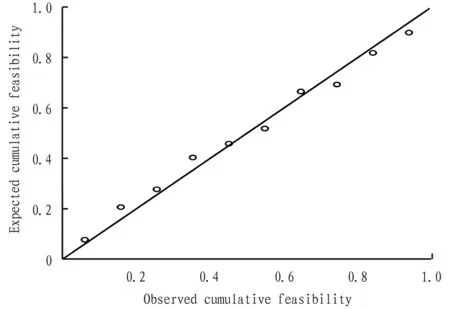
Fig.5 Scatter plot
In multiple linear regression model, the residuals and standardized residuals should obey the normal distribution, but standardized residuals are usually checked in practice. When coordinates of standardized residuals are within the range of (-2,2), the results of the model agree with the hypothesis. On the contrary, it refuses to participate in fitting of regression line. Seen from Table 5 and Fig.5, coordinates of all standardized residuals are in the range of (-2,2). It illustrates that the analysis results of regression model conform to relevant assumptions.
5.2.2Ftest.Ftest is used to test the significance level of regression equation fitting, and judge if the impact of rural financial development on income gap between urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang Province is significant. WhenFvalue is larger, it illustrates that regression effect is better. Seen from Table 7,F=16.728. In hypothesis H0:β1=β2=β3=0, the given significance level isα=0.05. Freedom degree ofFdistribution is (k-1,n-k)=(2,7), in whichkis number of independent variables, andnis number of samples. Seen fromFdistribution table, when degree of freedom is (2, 7), critical value isFα(2, 7)=4.1, andF=16.728>4.1. So it rejects H0hypothesis, and illustrates that the development situation of rural finance has a significant impact on the income gap between urban and rural areas.
5.3 Results and discussionsSeen from measurement analysis results, the development of rural finance in Heilongjiang Province has a certain impact on the income gap between urban and rural areas, but the influence size and direction of each index are different. Multiple linear regression results are as below:
5.3.1Development scale of rural finance generating positive impact on income gap between urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang Province, with larger influence degree. According to the general law of financial market, in the formation process of rural financial market, the financial institutions firstly entering the market can obtain all market shares, and the financial institutions which enter the market later need to seize the limited market share through competition with the financial institutions entering the market in advance. When the income of financial market is equal to the cost of financial institutions, the balance is reached. If scale continues to enlarge and exceed balance point, rural financial development will be affected, further causing that the income of rural residents is reduced, and the income gap between urban and rural areas is widened. But regression analysis results in this paper is obtained on the basis of statistics of rural financial development during 2009-2018. During the period, the scale of rural finance has not exceed the balance point. Therefore, above rule could not explain that the scale of rural financial development in Heilongjiang Province has expanded the income gap between urban and rural areas. Real cause for the phenomenon is that the capital outflow widely exists in rural financial market at present. Taking rural credit cooperatives as an example, the loan balance of rural credit cooperatives was only half of the savings deposit balance by the end of 2018, and capital flows to the second and third industries with high investment returns due to the influence of profit-seeking characteristics of financial institutions, and flows from rural areas to urban areas, which enlarges threshold effect and disequilibrium effect of financial development, further increasing rural income gap.
5.3.2Development efficiency of rural finance and urbanization level generating negative impact on income gap between urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang Province. The improvement of rural financial efficiency meets the needs of local agricultural production and operation entities for capital and financial services, and it can promote farmers to better carry out agricultural production and operation activities by strengthening financial support, thereby improving the overall income level of farmers. When farmers who obtain more income carry out simple reproduction and expand reproduction, the proportion of farmers’ own funds in total investment will be expanded, further driving economic growth in rural areas, improving the overall income level of rural areas, and narrowing the income gap between urban and rural areas. The mechanism of urbanization narrowing the income gap between urban and rural areas in Heilongjiang Province is that urbanization can promote the transfer of rural surplus labor to urban areas, expand the area of cultivated land per capita, and increase the marginal productivity of agriculture, and the income of agricultural production and operation entities has been improved. The rural labor force employed in cities and towns can get higher labor remuneration, and part of the remuneration will flow back to the countryside in the form of remittance, which narrows the gap between urban and rural areas. Additionally, urbanization has expanded the supply of labor market in urban areas, and reduced the wages of urban labor, which also reduced the income gap between urban and rural areas to some extent.
6 Policy suggestions
6.1 Strengthening rural financial supervisionThe government should make preferential policies according to the development of rural finance in Heilongjiang Province, guide rural financial service institutions to lower the threshold for credit access, and encourage rural financial service institutions to improve their ability to absorb deposits. It should clear service objects of new rural financial institutions, strictly supervise the loan scale of new financial institutions, and standardize the use of funds, making that new rural financial institutions achieve healthy and sound development and better provide financial support for agricultural production and operation entities. For private financial behaviors, the government should promulgate policies and regulations, and standardize the transaction process, capital source and interest rate of private finance. When standardizing the private financial market, it should provide legal guarantee for the transaction subjects of private finance.
6.2 Improving the financial service systemAccording to the characteristics of agricultural weakness, Heilongjiang Province should actively construct agricultural production risk guarantee mechanism and credit default guarantee mechanism, and establish special fund for agricultural credit risk compensation. When the main body of agricultural production and operation defaults on credit caused by natural disasters and market volatility, the special fund will compensate the financial institutions’ capital loss and farmers’ property loss by means of cash, discount interest, tax preference, etc., to promote the development of agricultural credit business in rural areas. It should vigorously support credit guarantee institutions. To the qualified guarantee subject, the government can build a specialized credit guarantee institution by supporting or encouraging the qualified guarantee subjects to jointly establish guarantee companies. Meanwhile, for the characteristics of the simplification of rural financial business, diversified financial service products should be promoted in rural areas, to realize rational allocation of financial resources and construct diversified rural financial system.
6.3 Curbing the outflow of rural fundsIn recent years, the second and third industries in Heilongjiang Province are developing rapidly, and large amount of financial resources flow into industry and service industry, and the proportion of loans to the second and third industries is increasing, making imbalance of financial resources allocation. The continuous loss of rural financial resources limits the capital supply in rural areas. Therefore, government should construct the return mechanism of rural capital by means of re-lending, making the outflowed rural funds return to agricultural production, and enhance fund supply in rural areas. Supervision departments should study setting a fixed proportion of agricultural-related loans in rural financial service institutions. When the deposits of financial institutions reach a certain scale, it is necessary to issue agricultural-related loans at the prescribed proportion to ensure the financial support for agricultural production.
6.4 Accelerating the cultivation of village banksVillage bank is a financial institution that serves the countryside professionally,
and the development of rural banks in Heilongjiang Province is still in its infancy. The government should give some tax preference to village banks to reduce their tax burdens in the early stage of operation. It should make standard supervisory system, and guarantee the opportunity of fair competition between village banks and other financial institutions in the field of rural finance. Village banks should strengthen their own construction, broaden their business scope, develop Internet finance, promote innovative financial products and services to agricultural production and operation entities with the help of network platform, and cultivate the financial management concept of farmers. Branches and business outlets should be actively set up to expand the coverage of financial services.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Empirical Research on E-commerce to Increase the Scale of Agricultural Products Trade: Taking Guangxi Hezhou Zhengfeng Modern Agriculture Co., Ltd. as an Example
- Current Status and Development Countermeasures of Forest Land Resources in Southern Cixi City
- Optimization of Acetic Acid Fermentation Process of Apple Cider Vinegar
- Organic Carbon: A New Concept for Development of Modern Fertilizers and Plant Nutrition Theory
- Research on the Problem Investigation and Standardized Improvement Paths of Farmers’ Cooperatives
- A Preliminary Study on the Rational Utilization of Land Resources in the Poverty-Stricken Mountainous Areas in the Upper Reaches of the Yangtze River: A Case Study of Xueshan Township
