牛磺酸对LPS诱导小鼠急性肺损伤的治疗效果
2020-04-07彭燕
彭燕
摘要:目的 評价牛磺酸对LPS诱导急性肺损伤小鼠的治疗作用。方法 将BALB/c小鼠随机分为正常对照组、LPS模型组、牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组,正常对照组小鼠经鼻吸入50 μl生理盐水,LPS模型组小鼠经鼻吸入8 mg/ml的LPS溶液50 μl,牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组分别经腹腔注射100、200、400 mg/kg牛磺酸,监测并比较5组小鼠肺功能、肺指数及髓过氧化物(MPO)酶活性。结果 ①LPS模型组呼气末期停顿(EEP)、最大呼气流量(PEF)、支气管收缩的程度(PENH)、吸气时间(TI)及呼气时间(TE)均高于正常对照组及牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组;牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组EEP、PEF、PENH、TI及TE均高于正常对照组,且依次降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。LPS模型组呼吸频率(RR)、呼吸松弛时间(RT)、每分钟呼气量(MV)、吸气末期停顿时间(EIP)、最大吸气流量(PIF)、潮气量(TV)及呼气量(EV)均低于正常对照组及牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组;牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组RR、RT、MV、EIP、PIF、TV及EV均低于正常对照组,且依次升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。②LPS模型组肺湿/干重比、MPO酶活性高于正常对照组及牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组;牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组肺湿/干重比、MPO酶活性高于正常对照组,且依次降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 牛磺酸对LPS诱导的小鼠急性肺损伤具有一定的保护作用,可减轻小鼠肺损伤,且其呼吸功能改善程度与剂量有一定联系。
关键词:急性肺损伤;牛磺酸;LPS;小鼠
中图分类号:R965 文献标识码:A DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-1959.2020.03.023
文章编号:1006-1959(2020)03-0079-03
Therapeutic Effect of Taurine on LPS-induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice
PENG Yan
(ICU of Tianjin TEDA Hospital,Tianjin 300457,China)
Abstract:Objective To evaluate the therapeutic effect of taurine on LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice. Methods BALB/c mice were randomly divided into normal control group, LPS model group, taurine low, medium and high dose groups. Normal control group mice inhaled 50 μl physiological saline,mice in the LPS model group inhaled 50 μl of 8 mg / ml LPS solution nasally, and the low, medium, and high dose groups of taurine were injected intraperitoneally with 100, 200, and 400 mg / kg taurine. Rat lung function, lung index, and myeloperoxidase (MPO) enzyme activity.Results ①The end-expiratory pause (EEP), the maximum expiratory flow (PEF), the degree of bronchoconstriction (PENH), the inspiratory time (TI) and the expiratory time (TE) in the LPS model group were higher than those in the normal control group and taurine. The low, medium, and high dose groups; the low, medium, and high dose taurine EEP, PEF, PENH, TI, and TE were all higher than the normal control group, and they decreased in order, the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). LPS model group breathing frequency (RR), breathing relaxation time (RT), expiratory volume per minute (MV), end of inhalation time (EIP), maximum inspiratory flow (PIF), tidal volume (TV) and exhalation amount (EV) is lower than the normal control group and low, medium and high dose of taurine; RR, RT, MV, EIP, PIF, TV and EV of the low, medium and high dose of taurine are lower than the normal control group, and increased in order, the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). ②The lung wet / dry weight ratio and MPO enzyme activity of the LPS model group were higher than those of the normal control group and low, medium, and high dose taurine; lung wet/dry weight ratio and MPO enzyme activity of the low, medium, and high dose taurine group was higher than the normal control group and decreased in order,the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).Conclusion Taurine has a certain protective effect on acute lung injury induced by LPS in mice, which can alleviate lung injury in mice, and its degree of improvement in respiratory function is related to the dose.
Key words:Acute lung injury;Taurine;LPS;Mice
急性肺损伤(acute lung injury,ALI)是以急性炎症和组织损伤为特征,影响肺部正常气体交换,逐渐导致呼吸功能衰竭的急性呼吸综合征[1]。欧美联席会议在1994年将该综合征重新命名为急性呼吸窘迫综合征(acute respiratory distress syndrome,ARDS)[2],是监护室患者病死率高的重要原因[3],因而ALI/ARDS被认为是临床常见危重症。由LPS所导致的脓毒症是引起ARDS的重要常见病因,大量研究表明,LPS引起ARDS的机制与自由基的产生、脂质过氧化和炎症反应有重要关系[4,5]。牛磺酸(taurine)大量存在于哺乳动物体内,能够维持机体的免疫功能,调节全身多个系统、器官[6]。在牛磺酸的作用下,内皮细胞的凋亡及由脂多糖、肿瘤坏死因子刺激的氧化应激状态明显减轻,牛磺酸还可以降低中性粒细胞介导的内皮细胞的坏死,可用于急性肺损伤的治疗。基于此,本研究建立LPS诱导急性肺损伤小鼠动物模型,旨在观察牛磺酸对急性肺损伤的治疗作用。
1材料与方法
1.1材料与仪器 雄性BALB/c小鼠共50只,体重20~24 g,购自天津医科大学实验动物中心,许可证編号:SYXK(津)2013-0001。脂多糖(LPS)和牛磺酸均购自Sigma-Aldrich;髓过氧化物酶活性检测试剂盒购自Genmed Scientifics Inc;清醒动物肺功能监测系统购自EMKA Technologies。
1.2方法 将BALB/c小鼠按照随机数字表法分为正常对照组、LPS模型组、牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组。LPS模型组及牛磺酸治疗组小鼠经鼻吸入8 mg/ml的LPS溶液50 μl,正常对照组小鼠经鼻吸入同体积的生理盐水。实验开始0.5 h和12 h,牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组分别腹腔注射100、200、400 mg/kg牛磺酸。实验开始24 h后,对全部BALB/c小鼠进行肺功能监测,取血及肺组织。
1.3观察指标 比较各组小鼠肺功能、肺指数及髓过氧化物(MPO)酶活性。①肺功能:实验开始24 h后,监测各组小鼠在清醒无束缚状态下的肺呼吸情况,包括吸气时间(TI)、呼气时间(TE)、最大吸气流量(PIF)、最大呼气流量(PEF)、潮气量(TV)、呼气量(EV)、呼吸松弛时间(RT)、每分钟呼气量(MV)、呼吸频率(RR)、吸气末期停顿(EIP)、呼气末期停顿(EEP)及支气管收缩的程度(PENH)。②肺指数测定:取小鼠的肺脏,洗净,记录湿重;100℃干燥至恒重,称干重,计算肺的湿干重比。③MPO酶活性测定:采用髓过氧化物酶活性测定试剂盒测定肺组织中MPO酶的活性,具体步骤严格参考试剂盒说明书进行。
1.4统计学方法 选用SPSS 20.0软件处理实验数据,计量资料以(x±s)表示,两组间比较采用独立样本t检验,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析;采用Pearson 相关性分析牛磺酸剂量与呼吸功能的相关性。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2结果
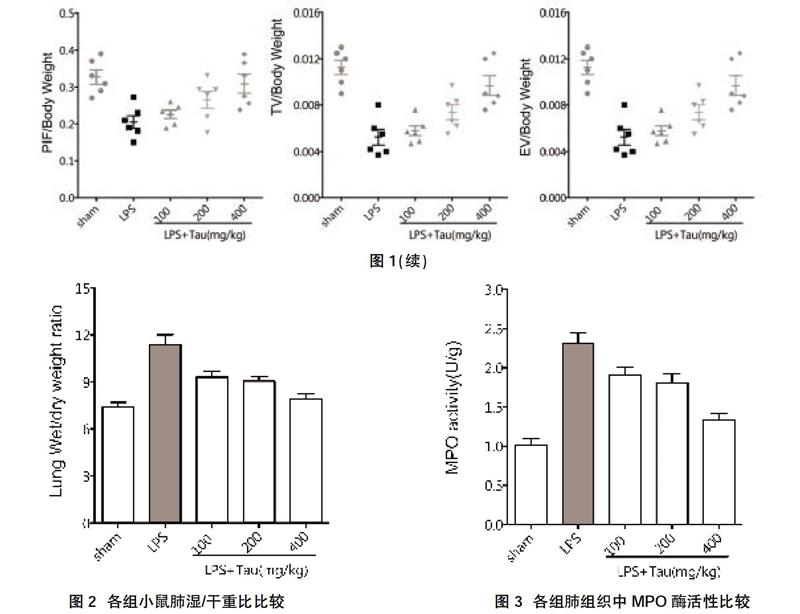
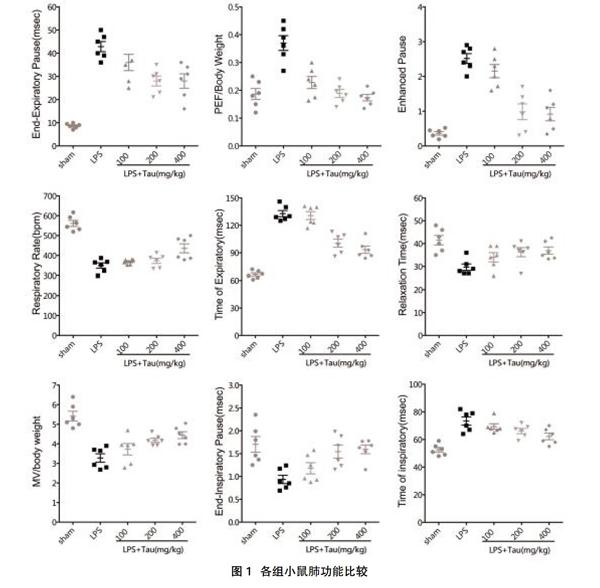
2.1各组小鼠肺功能比较 LPS模型组EEP、PEF、PENH、TI及TE均高于正常对照组及牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组;同时牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组EEP、PEF、PENH、TI及TE均高于正常对照组,且依次降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。LPS模型组RR、RT、MV、EIP、PIF、TV及EV均低于正常对照组及牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组;同时牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组RR、RT、MV、EIP、PIF、TV及EV均低于正常对照组,且依次升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),见图1。
2.2各组小鼠肺湿/干重比、MPO酶活性比较 LPS模型组肺湿/干重比、MPO酶活性高于正常对照组及牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组;牛磺酸低、中、高剂量组肺湿/干重比、MPO酶活性高于正常对照组,且依次降低,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见图2、图3。
3讨论
牛磺酸可以明显减轻内皮细胞的凋亡及由脂多糖、肿瘤坏死因子刺激下的氧化应激状态,并可以降低中性粒细胞介导的内皮细胞坏死[5]。本实验采用LPS诱导急性肺损伤小鼠模型,考察了牛磺酸对小鼠呼吸功能保护作用及对肺损伤的治疗作用。实验结果显示,与正常对照组相比LPS模型组的各项呼吸功能均有受损,但牛磺酸组小鼠的呼气末期停顿时间、单位体重的最大呼气流量、支气管收缩的程度和呼吸频率等呼吸功能指标优于LPS模型组,呼吸功能改善程度与牛磺酸使用剂量密切相关,而且牛磺酸组小鼠的肺湿/干重比低于LPS模型组,提示牛磺酸对LPS诱导的小鼠急性肺损伤具有治疗作用,能够改善肺水肿程度。
髓过氧化物酶又称过氧化物,是由中性粒细胞、单核细胞或巨噬细胞等炎性细胞分泌的含血红素辅基的血红素蛋白酶,也是中性粒细胞的功能标识和激活标志,其活性变化反映着嗜中性多形核细胞的功能和活性状态[6]。本研究结果显示,吸入400 μg的脂多糖24 h后,实验小鼠发生明显的肺水肿,肺组织中MPO酶活性提高,但给予牛磺酸治疗后能够缓解小鼠肺水肿状况,降低肺组织中MPO酶活性,提示牛磺酸有可能通过抗氧化作用调节细胞内钙离子浓度,进而对急性肺损伤发挥一定的保护作用。
综上所述,牛磺酸对LPS诱导的小鼠急性肺损伤具有一定的肺脏保护作用,可减轻小鼠肺损伤,且其对呼吸功能的改善程度与应用剂量密切相关。
参考文献:
[1]Rubenfeld GD,Caldwell E,Peabody E,et al.Incidence and outcomes of acute lung injury[J].The New England Journal of Medicine,2005,353(16):1685-1693.
[2]Guillamat - Prats R,Puig F,Camprubi - Rimbias M,et al.Intratracheal instillation of alveolar type H cells enhances recovery from acute lung injury in rats[J].J Heart Lung Transplant,2017, 37(6):782-791.
[3]Mdca J,Jor 0,Holub M,et al.Past and present ARDS mortality rates:a systematic review[J].Respirat Care,2017,62(1):113-122.
[4]Zhu JB,Xu S,Li J,et al.Farnesoid X receptor agonist obeticholic acid inhibits renal inflammation and oxidative stress during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury[J]. Eur J Pharmacol,2018(838):60-68.
[5]An X,Shang F.RA-XII exerts anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory activities on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute renal injury by suppressing NF-κB and MAPKs regulated by HO-1/Nrf2 pathway[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2017:S0006291X17325317.
[6]林海洋,何涛,张剑辉.辛伐他汀对脓毒症早期大鼠血脂代谢及肝脏氧化应激的影响[J].广东医学,2017,38(21):3243-3246.
收稿日期:2019-11-21;修回日期:2019-12-13
编辑/钱洪飞
