MEBT/MEBO对糖尿病大鼠创面组织中ULK1表达的影响
2020-03-05麻华胆郑爱甜刘贤彬吴标良
麻华胆 郑爱甜 刘贤彬 李 政 王 琳 曾 娜 吴标良
作者单位:533000 广西 百色,右江民族医学院研究生学院2017级内科学专业(麻华胆,刘贤彬),研究生学院2016级内科学专业(郑爱甜),研究生学院2018级内科学专业(李政,王琳,曾娜);533000 广西 百色,右江民族医学院附属医院内分泌科(吴标良)
目前,皮肤再生医疗技术(moist exposed burn therapy/moist exposed burn ointment,MEBT/MEBO)被广泛应用于糖尿病足的治疗并取得了显著的临床疗效,且部分研究发现,其加快创面修复的作用与Smad3、TGF-β1、ERK1/2、p38、MAPKK6等蛋白分子的高度表达密切相关[1-2],但具体作用机制尚未完全明了。研究显示,自噬在创面愈合的炎症反应、血管形成、组织再生中具有重要作用,且丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶-失调51样激酶1(uncoordinated 51like kinase-1,ULK1)是重要的自噬相关蛋白,在自噬的起始过程中发挥着关键作用[3-4],故笔者于本研究中观察了MEBT/MEBO对糖尿病大鼠创面组织中ULK1表达的影响,并分析了其可能的作用机制,现报告如下。
1 实验材料
1.1 实验动物
SPF级3月龄Wistar雄性大鼠90只,体重230~260 g,由长沙市天勤生物技术有限公司提供,饲养环境清洁,室温(25.0±3.0)℃,自由进食进水。该实验经右江民族医学院动物伦理委员会批准,符合动物实验的伦理学要求。
1.2 主要试剂
链脲佐菌素(streptozotocin,STZ):北京华越洋生物科技有限公司生产;水合氯醛:成都市科龙化工试剂厂生产;湿润烧伤膏(moist exposed burn ointment,MEBO):汕头市美宝制药有限公司生产;Anti-ULK1-Antibody:Abcam公司生产;辣根过氧化物酶标记山羊抗兔IgG(100μL)、β-actin抗体(100μL):北京中杉金桥生物技术有限公司生产;ULK1、β-actin引物:上海捷瑞生物工程有限公司合成。
2 方法
2.1 实验分组与模型制备
大鼠于适应性喂养1周后随机分为对照组、模型组和MEBO组,每组30只。对照组大鼠正常进食进水,腹腔注射7%水合氯醛0.5 mL/100 g麻醉,并于背部备皮处理后切除面积约2.5 cm×2.5 cm的全层皮肤。模型组及MEBO组大鼠于高脂饮食4周并禁食16 h后腹腔注射STZ 45 mg/kg,1周后大鼠出现多饮、多尿、体重下降等糖尿病症状且空腹血糖≥16.0 mmol/L代表糖尿病大鼠模型建立成功,造模成功后1周,腹腔注射7%水合氯醛0.5 mL/100 g麻醉,并于背部备皮处理后切除面积约2.5 cm×2.5 cm的全层皮肤[5]。
2.2 创面处理及血糖管理
对照组及模型组大鼠创面于0.02%呋喃西林抑菌溶液清洗后依次覆盖2层生理盐水纱布及2层消毒干纱布包扎固定,MEBO组大鼠创面于0.02%呋喃西林抑菌溶液清洗后覆盖2层MEBO药纱及2层消毒干纱布包扎固定,每天换药2次。
模型组及MEBO组大鼠根据血糖水平予以长效胰岛素皮下注射,每天2次,每次4~8 IU/kg[6],将血糖控制在16.0 mmol/L左右。
2.3 标本采集与处理
分别于创面建立第1、11、18天,每组随机选取10只大鼠,于7%水合氯醛0.5 mL/100 g腹腔注射麻醉后切取创面组织标本,并将其均分为2份后分别放入去核糖核酸酶冻存管中,置于-80℃环境内冷冻保存。
2.4 记录创面面积并计算创面愈合率
分别于创面建立第1、11、18天,每组随机选取10只大鼠,将刻度尺置于大鼠创面边缘后用数码相机拍照,并采用Image J图像分析软件对未愈合创面面积进行测量,计算创面愈合率。创面愈合率= (原始创面面积-未愈合创面面积)/原始创面面积×100%。
2.5 Western blotting法检测ULK1蛋白表达水平
取冻存创面组织标本进行液氮研磨后放入EP管中,加组织裂解液充分裂解,提取总蛋白,并采用紫外分光光度计测定总蛋白浓度,绘制蛋白浓度标准曲线。将提取的蛋白上样水煮变性后置于-20℃环境中保存备用。制作SDS-PAGE凝胶,并注入等体积蛋白上样电泳、转膜、封闭后,置于4℃环境中孵育一抗过夜;一抗孵育后,PBST洗膜3次,然后加入二抗,室温下孵育60 min;二抗孵育后,PBST洗膜3次,并曝光显影;最后用Image J图像分析软件检测蛋白条带灰度值。
2.6 qRT-PCR技术检测ULK1 mRNA表达水平
取冻存创面组织标本置于灭菌研钵内,加入液氮,反复研磨至粉末状后转移至EP管中,按照TAKARA试剂盒说明书提取总RNA,并用紫外分光光度计测定其浓度及A260/A280比值,将A260/A280比值在1.8~2.1范围内的总RNA作为反转录模板,按照反转录试剂盒说明书反转录合成cDNA,然后以cDNA为模板进行PCR扩增及检测,结果使用公式F=2-△△Ct计算。其中,引物序列为F:5'-CTCACGGACCAG GCAGACATTG-3',R:5'-GCAGCAGTCTCAGCA CCATCAG-3'。
2.7 统计学处理
采用SPSS 17.0统计软件对所得数据进行统计学分析,其中正态分布数据以均数±标准差表示,非正态分布数据以中位数和四分位数间距表示,两样本间比较采用t检验,多样本间比较采用单因素方差分析,均以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
3 结果
3.1 3组大鼠创面愈合情况及创面愈合率对比
治疗第1天,3组大鼠创面均晦暗、淤血、水肿,无肉芽组织形成。治疗第11天,对照组大鼠创面干燥,可见大片鲜红色肉芽组织形成;模型组大鼠创面仍严重水肿、污秽模糊,无肉芽组织形成;MEBO组大鼠创面轻微水肿,可见散在粉红色颗粒状肉芽组织形成。治疗第18天,对照组大鼠创面完全愈合,愈后皮肤可见点状瘢痕增生;模型组大鼠创面轻微水肿,可见散在粉红色颗粒状肉芽组织形成;MEBO组大鼠创面干燥,可见大片鲜红色肉芽组织形成(图1)。

图1 3组大鼠创面愈合情况典型图Fig.1 Typical pictures of wound healing in the three groups
治疗第11天,3组大鼠创面愈合率对比,对照组>MEBO组>模型组,组间两两对比,P均<0.01,差异具有统计学意义;治疗第18天,3组大鼠创面愈合率对比,对照组>MEBO组>模型组,组间两两对比,P均<0.01,差异具有统计学意义。治疗第18天,3组大鼠创面愈合率均明显高于治疗第11天,各组组内对比,P均<0.01,差异具有统计学意义(表1)。
3.2 3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平对比
Western blotting检测结果显示,治疗第1、11、18天,对照组、MEBO组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平呈先升高后降低的趋势,模型组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平呈逐渐升高的趋势,各时间点组内两两对比,P均<0.01,差异具有统计学意义。治疗第1天,3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平对比,对照组>MEBO组=模型组,对照组与MEBO组及对照组与模型组对比,P均<0.05,差异具有统计学意义,而MEBO组与模型组对比,P>0.05,差异无统计学意义;治疗第11天,3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平对比,对照组>MEBO组>模型组,组间两两对比,P均<0.05,差异具有统计学意义;治疗第18天,3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平对比,对照组=MEBO组<模型组,对照组与模型组及MEBO组与模型组对比,P均<0.05,差异具有统计学意义,而对照组与MEBO组对比,P>0.05,差异无统计学意义(图2,表2)。
表1 3组大鼠创面愈合率对比Table 1 Comparison of wound healing rate among the three groups

表1 3组大鼠创面愈合率对比Table 1 Comparison of wound healing rate among the three groups
注:3组大鼠创面愈合率组间对比,其中与对照组对比,a P<0.01,差异具有统计学意义;与模型组对比,b P<0.01,差异具有统计学意义Note:The wound healing rate was compared between each two of the three groups,of which the comparison with the control group showed statistically significant differences(a P<0.01);and the comparison with the model group also showed statistically significant differences(b P<0.01)
组别Group鼠数(只)Number of rats(n)第11天Day 11第18天Day 18 t值t value P值P value对照组Control group 10 0.81±0.10 1.00±0.00 6.20 0.000模型组Model group 10 0.54±0.07a 0.79±0.01a 10.78 0.000 MEBO组MEBO group 10 0.63±0.05ab 0.86±0.04ab 12.01 0.000 F值F value 33.440 200.340 - -P值P value 0.000 0.000 - -
3.3 3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1 mRNA表达水平对比
qRT-PCR检测结果显示,β-actin及ULK1基因溶解曲线均呈单峰型,且溶解温度均处于87~90℃之间(图3);β-actin及ULK1基因扩增曲线均呈S型,线性期、指数增长期、线性增长期、平台期显示明显,复孔Ct值大致相当(图4)。
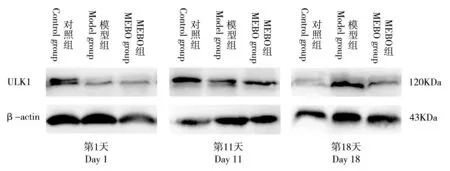
图2 Western blotting法检测3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平条带图Fig.2 Histogram of ULK1 protein expression levels in wound tissues of the three groups tested by Western blotting
表2 3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平对比Table 2 Comparison of ULK1 protein expression levels in wound tissues of the three groups

表2 3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平对比Table 2 Comparison of ULK1 protein expression levels in wound tissues of the three groups
注:3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平组间对比,其中与对照组对比,a P<0.05,差异具有统计学意义;与模型组对比,b P<0.01,差异具有统计学意义。各时间点创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平组内对比,其中与第1天对比,c P<0.05,差异具有统计学意义;与第11天对比,d P<0.01,差异具有统计学意义Note:The expression levels of ULK1 protein in wound tissues of the three groups were compared in pairs,of which the comparisons with the control group and with the model group both showed statistically significant differences(respectively a P<0.05 and b P<0.01).The expression level of ULK1 protein in wound tissues at each of the three time points was compared within each of the three groups,of which the comparisons with that on day 1 and day 11 also showed statistically significant differences(respectively c P<0.05 and d P<0.01)
组别Group鼠数(只)Number of rats(n)第1天Day 1第11天Day 11第18天Day 18 F值F value P值P value对照组Control group 10 0.36±0.04 0.58±0.12c 0.19±0.04cd 63.10 0.000模型组Model group 10 0.15±0.03a 0.34±0.07ac 0.43±0.07acd 58.18 0.000 MEBO组MEBO group 10 0.16±0.03a 0.48±0.11abc 0.23±0.05bcd 56.16 0.000 F值F value 108.370 13.520 61.270 - -P值P value 0.000 0.000 0.000 - -

图3 β-actin/ULK1基因溶解曲线;图4 β-actin/ULK1基因扩增曲线Fig.3 The gene dissolution curve ofβ-actin/ULK1; Fig.4 The gene amplification curve of β-actin/ULK1
治疗第1、11、18天,模型组、MEBO组大鼠创面组织中ULK1 mRNA表达水平呈逐渐升高的趋势,各时间点组内两两对比,P均<0.01,差异具有统计学意义,而对照组大鼠创面组织中ULK1 mRNA表达水平无任何变化。治疗第1天,3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1 mRNA表达水平对比,对照组>MEBO组=模型组,对照组与MEBO组及对照组与模型组对比,P均<0.01,差异具有统计学意义,而MEBO组与模型组对比,P>0.05,差异无统计学意义;治疗第11天,3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1 mRNA表达水平对比,对照组>MEBO组>模型组,组间两两对比,P均<0.01,差异具有统计学意义;治疗第18天,3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1 mRNA表达水平对比,对照组=MEBO组<模型组,对照组与模型组及MEBO组与模型组对比,P均<0.01,差异具有统计学意义,而对照组与MEBO组对比,P>0.05,差异无统计学意义(表3)。
表3 3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1 mRNA表达水平对比Table 3 Comparison of ULK1 mRNA expression levels in wound tissues of the three groups

表3 3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1 mRNA表达水平对比Table 3 Comparison of ULK1 mRNA expression levels in wound tissues of the three groups
注:3组大鼠创面组织中ULK1 mRNA表达水平组间对比,其中与对照组对比,a P<0.01,差异具有统计学意义;与模型组对比,b P<0.01,差异具有统计学意义。各时间点创面组织中ULK1 mRNA表达水平组内对比,其中与第1天对比,c P<0.01,差异具有统计学意义;与第11天对比,d P<0.01,差异具有统计学意义Note:The expression levels of ULK1 mRNA in wound tissues of three groups were compared in pairs,of which the comparisons with the control group and with the model group showed statistically significant differences(respectively a P<0.01 and b P<0.01).The expression level of ULK1 protein in wound tissues at each of the three time points was compared within each of the three groups,of which the comparisons with that on day 1 and day 11 also showed statistically significant differences(respectively c P<0.01 and d P<0.01)
组别Group鼠数(只)Number of rats(n)第1天Day 1第11天Day 11第18天Day 18 F值F value P值P value对照组Control group 10 1.00±0.00 1.00±0.00 1.00±0.00 - -模型组Model group 10 0.16±0.02a 0.37±0.08ac 1.82±0.14acd 957.48 0.000 MEBO组MEBO group 10 0.15±0.02a 0.68±0.08abc 0.98±0.17bcd 151.60 0.000 F值F value 9948.760 228.460 148.650 - -P值P value 0.000 0.000 0.000 - -
4 讨论
众多研究表明,细胞自噬在创面修复中具有双重作用,既可降解受损细胞器[7],促进角质形成细胞迁移[8-9],保护内皮祖细胞,促进新生血管形成[10-11],又可通过抑制成纤维细胞的迁移、减少胶原蛋白的合成而延迟创面愈合[12-14]。且部分研究证实,缺血缺氧,氨基酸、ATP及生长因子缺乏等可抑制雷帕霉素靶蛋白C1(mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1,mTORC1)的活性,进一步激活ULK1而诱发细胞自噬[15]。笔者考虑,目前被广泛应用于难愈性创面治疗的MEBT/MEBO促进创面愈合的作用机制可能也与ULK1诱发的细胞自噬有关,遂于本研究中观察了MEBT/MEBO对糖尿病大鼠创面组织中ULK1表达的影响。
结果显示, (1)治疗第11、18天,对照组大鼠创面愈合率显著高于模型组与MEBO组,而MEBO组大鼠创面愈合率又显著高于模型组,可见相比于非糖尿病大鼠,糖尿病大鼠创面愈合明显延迟,而MEBO可有效促进糖尿病大鼠创面的愈合,这可能与高糖状态下蛋白质合成障碍、糖基化终末产物积聚、免疫功能受损等导致创面愈合延迟,而MEBT/MEBO可激活创面组织中血管内皮生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子等多种生长因子,促进新生血管形成,加速创面愈合有关。 (2)治疗第1、11、18天,对照组、MEBO组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平呈先升高后降低的趋势,推测可能与创面修复早期机体尚处于高度应激状态,创面缺血缺氧、合成生长因子不足,进一步促进了ULK1的高表达而强烈刺激细胞自噬的发生,后期随着创面新生血管的形成,缺血缺氧得到改善,对ULK1的激活作用减轻,细胞自噬功能亦随之降低有关。而模型组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白表达水平呈逐渐升高的趋势,可能与其创面愈合延迟,刺激作用持续增强有关[16-18]。(3)治疗第1、11天,MEBO组与模型组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白及ULK1 mRNA表达水平均明显低于对照组,推测糖尿病大鼠创面组织中细胞自噬功能受到抑制,其机制可能与高糖状态下具有调节基因表达功能的p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase,p38MAPK)下调,阻止了自噬相关蛋白基因的转录,进而引发了自噬抑制有关[19-20];治疗第11天,MEBO组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白及ULK1 mRNA表达水平明显高于模型组,推测MEBO可增强糖尿病大鼠创面组织的细胞自噬功能;治疗第18天,对照组与MEBO组大鼠创面组织中ULK1蛋白及ULK1 mRNA表达水平无明显差异,且显著低于模型组,推测可能与对照组大鼠创面完全愈合后细胞自噬功能回归正常,MEBO组大鼠创面接近愈合后对ULK1的激活作用减轻,加之糖尿病引发的自噬抑制,使得创面组织中ULK1的表达水平与对照组相当,而模型组大鼠创面尚未明显愈合,对ULK1的激活作用持续存在有关。
综上所述,MEBT/MEBO可有效促进糖尿病大鼠创面的愈合,诱导ULK1高表达,增强细胞自噬功能可能是其作用机制之一,有待通过观察多个自噬相关蛋白、利用多种实验方法等进一步证实。
At present,Moist Exposed Burn Therapy/Moist Exposed Burn Ointment(MEBT/MEBO)is widely used in the treatment of diabetic foot and significant clinical efficacy has been achieved.Some studies have found that MEBT/MEBO’s role in accelerating wound repair is closely related with the high expression of protein molecules like Smad3,TGF-β1,ERK1/2,p38 and MAPKK6[1-2],but the specific mechanism of action remains unclear.Given autophagy plays an important role in inflammatory response,angiogenesis,and tissue regeneration in wound healing,and serine/threonine protein kinase-uncoordinated 51 like kinase-1(ULK1)is an important autophagy-related protein[3-4],this study,with the purpose of further exploring the mechanism of action of MEBT/MEBO in diabetes-associated wounds,made an investigation on the effect of MEBT/MEBOon the expression of ULK1 in wound tissues of diabetic rats and the possible mechanism of action.The details are reported as follows:
1.Experimental material
1.1.Experimental animals
Experimental animals are 90 SPF-class Wistar male rats of 3 months old,weighing 230-260 g,provided by Changsha Tianqin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.,and are raised in clean environment at room temperature(25.0±3.0)℃with free access to food and water.The experiment has been approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities and met the ethical requirements of animal experiments.
1.2.Main reagents
Streptozotocin(STZ):produced by Beijing Huayueyang Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.;Chloral hydrate:produced by Chengdu Kelong Chemical Reagent Factory;Moist exposed burn ointment(MEBO):manufactured by Shantou MEBO Pharmaceutical Co.,Ltd.;Anti-ULK1-Antibody:produced by Abcam;HRP-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG(100μL),β-actin antibody(100μL):produced by Beijing Zhongshan Jinqiao Biotechnology Co.,Ltd.;ULK1,β-actin primer:synthesized by Shanghai Jierui Biological Engineering Co.,Ltd.
2.Methods
2.1.Grouping and establishment of animal models
The 90 rats were randomly divided into a control group,a model group and MEBO group after one week of adaptive feeding,with 30 rats in each group.The rats in the control group had free access to food and water,and were anesthetized with intraperitoneal injection of 7%chloral hydrate(0.5 mL/100 g),and then full-thickness skin resection of about 2.5 cm×2.5 cm in size were performed on the well-prepared back skin.The rats in the model group and MEBO group were given a high-fat diet for 4 weeks and then fasted for 16 hours before the intraperitoneal injection of STZ 45 mg/kg.One week later,the rats developed such symptoms as polydipsia,diuresis,weight loss and other diabetic symptoms,and their fasting blood glucose was≥16.0 mmol/L,indicating the successful establishment of diabetic rat model.One week after the model establishment,intraperitoneal injection of 7%chloral hydrate(0.5 mL/100 g)was given for anesthetization,followed by full-thickness skin resection of about 2.5 cm×2.5 cm in size on well-prepared back skin[5].
2.2.Management of wound and blood glucose
The wounds of rats in the control group and model group were washed with 0.02%nitrofurazone antibacterial solution and covered with 2 layers of saline gauze and 2 layers of sterilized dry gauze for fixation.After the wound cleansing with 0.02% nitrofurazone antibacterial solution,the wounds in the MEBO group were covered with 2 layers of MEBO-impregnated gauze and 2 layers of sterilized dry gauze for fixation.Dressing change was performed twice a day.
Rats in the model group and MEBO group were given subcutaneous injection of long-acting insulin,twice a day and 4-8 IU/kg per time[6],according to the daily blood glucose levels of rats to maintain their blood glucose at about 16.0 mmol/L.
2.3.Specimen collection and processing
On day 1,11 and 18 of wound establishment,10 rats in each group were randomly selected to take the specimens of wound tissues after the intraperitoneal injection of 7%chloral hydrate0.5 mL/100 g.The collected specimens were divided into two equal parts to be put into cryogenic vials(without ribonuclease)for cryopreservation at-80℃.
2.4.Recording wound area and calculating wound healing rate
On day 1,11 and 18 of wound establishment,select 10 rats in each group randomly,put a calibrated scale on the wound edge to take photographs with a digital camera,use Image Janalysis software to measure unhealed wound area and calculate the wound healing rate.Wound healing rate= (original wound area-unhealed wound area)/original wound area×100%.
2.5.Measurement of ULK1 protein expression with Western blotting method
The cryopreserved wound tissue specimens were put in an EP tube after being ground with liquid nitrogen,add the tissue lysate for fully lysis to extract the total protein,use the ultraviolet spectrophotometer to detect its concentration,and then draw the concentration standard curve of the total protein.The extracted protein loading was boiled for denaturation and then stored in an environment of-20℃for later use.Make SDS-PAGE gel and add into an equal volume of protein loading for electrophoresis,transfer and blocking,and then place in an environment of 4℃to incubate the primary antibody overnight.After the primary antibody incubation,wash the membrane 3 times with PBST,and then add into the secondary antibody for incubation at room temperature for 60 min.After the secondary antibody incubation,washed the membrane again 3 times with PBST and then exposed to light for development,and finally,use the Image J analysis software to test the gray value of the protein bands.
2.6.Measurement of ULK1 mRNA expression with qRT-PCR
Put the frozen tissue specimens in a sterile mortar,add into liquid nitrogen,repeatedly grind them into powder,and then transfer the powder to an EP tube.Total RNA was extracted according to the TAKARA instructions and its concentration and A260/A280 ratio was measured with UV spectrophotometer.The total RNA with A260/A280 ratio at the range of 1.8 to 2.1 was taken as a reverse transcription template.The cDNA was synthesized with reverse transcription according to the instructions on the reverse transcription kit,then PCR amplification and detection were performed using cDNA as a template.The result was converted using the formula F=2-△△Ct,in which,primer sequences were F:5'-CTCACGGACCAGGCAGACAT TG-3',R:5'-GCAGCAGTCTCAGCACCATCAG-3'.
2.7.Statistical analysis
The SPSS17.0 software was adopted to analyze the study data,in which the normal distribution data was expressed as mean±standard deviation,and the non-normal distribution data was expressed as median and interquartile range.t test was used for comparison between two samples,and one-way ANOVA was used for comparison among multiple samples.P<0.05 was considered as statistically significant.
3.Results
3.1.Comparison of wound healing and wound healing rate among the three groups
On day 1 of treatment,the wounds in the three groups were all dark in color,with blood congestion and edema but without granulation tissues.On day 11 of treatment,the wounds in the control group were dry,and large pieces of bright red granulation tissue were formed.In the model group,the wounds still had severe edema with much foul secretion,and no granulation tissues were found.In the MEBO group,the wounds were only mildly edematous,and scattered pink granulation tissues could be observed.On day 18 of treatment,the wounds in the control group healed completely,and dotted scar hyperplasia could be observed on the healed skin surface;in the model group,mild edema was observed on the wound surface and dotted pink granular granulation tissues were observable;and in the MEBO group,the wound surface was dry,and large pieces of bright red fresh granulation tissues were formed(Fig.1).
The wound healing rate was compared among the three groups and the results respectively showed as control group>MEBO group>model group,and control group>MEBO group>model group,and the pairwise comparisons of wound healing rate among the three groups respectively on day 11 and 18 of treatment all showed statistically significant differences(P<0.01).On day 18 of treatment,the wound healing rates in the three groups were all markedly higher than their respective levels on day 11 of treatment,and the comparison of wound healing rate at the two time points within each of the three groups all showed statistically significant differences(P<0.01)(Table 1).
3.2.Comparison of ULK1 expression levels in wound tissues of the three groups
The results of Western blotting showed that the expression levels of ULK1 protein in wound tissues of the control group and MEBO group presented a tendency of increase firstly followed by decrease on day 1,11 and 18 day of treatment,while the expression level of ULK1 protein in wound tissues of the model group were increased gradually as the treatment progressed.The expression level of ULK1 protein at the three different time points was compared in pairs within each of the three groups,and the results all showed statistically significant differences(P<0.01).On day 1,the expression levels of ULK1 protein in wound tissues of the three groups were compared:control group>MEBO group=model group,and the comparisons between the control group and MEBO group,and between the control group and the model group showed statistically significant differences(both P<0.05),while the comparison between MEBO group and the model group,showed no statistically significant difference(P>0.05).On day 11 of treatment,the expression levels of ULK1 protein in wound tissues of the three groups were compared:control group>MEBO group>model group,and the comparisons between each two of three groups all showed statistically significant differences(P<0.05).On day 18 of treatment,the expression level of ULK1 protein in wound tissues of the three groups was compared:control group=MEBOgroup<model group,and the comparisons between the control group and model group,and between MEBO group and model group showed statistically significant differences(P<0.05)while the comparison between the control group and MEBOgroup showed no statistically significant difference(P>0.05)(Fig.2,Table 2).
3.3.Comparison of ULK1 mRNA expression levels in wound tissues of the three groups
The results of qRT-PCR detection showed that gene dissolution curves of theβ-actin and ULK1 were unimodal ones and dissolution temperature(Tm)was between 87 and 90℃ (Fig.3).The gene amplification curves ofβ-actin and ULK1 were S-type,and the linear phase,exponential growth phase,linear growth phase and plateau phase were clear-cut.Ct values of duplicated wells were approximately equal(Fig.4).
On day 1,11 and 18 of treatment,the expression level of ULK1 mRNA in wound tissues of the model group and MEBO group gradually increased as the treatment progressed,and the pairwise comparisons at the three different time points within each of the two groups all showed statistically significant differences(P<0.01),while no change was observed in the expression level of ULK1 mRNA in wound tissues of the control group.On day 1 of treatment,the expression levels of ULK1 mRNA in wound tissues of the three groups were compared:control group>MEBO group=model group,and the comparisons between the control group and MEBO group,and between the control group and the model group both showed statistically significant differences(P<0.01),while the comparison between the MEBO group and model group showed no statistically significant difference(P>0.05).On day 11 of treatment,the expression levels of ULK1 mRNA in wound tissues of the three groups were compared:control group>MEBO group>model group,and the pairwise comparisons among the three groups all showed statistically significant differences(P<0.01).On day 18 of treatment,the expression levels of ULK1 mRNA in wound tissues of the three groups were compared:control group=MEBO group<model group,and the comparisons between the control group and the model group,and between the MEBOgroup and the model group both showed statistically significant differences(P<0.01),while the comparison between the control group and MEBO group showed no statistically significant difference(P>0.05)(Table 3).
4.Discussion
Many studies have shown that autophagy plays a dual role in wound repair:on the one hand,it can degrade damaged organelles[7],promote keratinocyte migration[8-9],protect endothelial progenitor cells,and promote neovascularization[10-11];on the other hand,it can delay wound healing by inhibiting fibroblast migration and reducing collagen synthesis[12-14].Some studies have confirmed that ischemia,hypoxia,amino acid,ATPand growth factor deficiency can inhibit the activity of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1(mTORC1)and activate ULK1,thus inducing autophagy[15].In this study the authors supposed that the mechanism of action of MEBT/MEBO,which is widely used in the treatment of refractory wounds,may be related to ULK1-induced autophagy,and thus the effect of MEBT/MEBO on the expression level of ULK1 in wound tissue of diabetic rats was observed.
The results showed:(1)on day 11 and 18 of treatment,the wound healing rate in the control group was significantly higher than that in the model group and the MEBO group,and the wound healing rate in the MEBOgroup was significantly higher than that in the model group,from which it can be concluded that the wound healing of diabetic rats was much slower as compared with non-diabetic rats,and MEBOcan effectively promote the wound healing of diabetic rats.Under high glucose condition,protein synthesis slows down,glycosylation end products accumulate,immune function is impaired,etc.,leading to delayed wound healing.MEBT/MEBOcan activate various growth factors such as vascular endothelial growth factor(VEGF)and fibroblast growth factor(FGF)in wound tissues to promote neovascularization,thus accelerating wound healing.(2)On day 1,11 and 18 of treatment,the expression levels of ULK1 protein in wound tissues of the control group and MEBO group increased firstly followed by decrease as the treatment progressed.The reason might be that at the early stage of wound repair,the body is still at a state of high stress,and growth factors are insufficiently synthesized due to wound ischemia and hypoxia,which will further promote the high expression of ULK1,thus strongly stimulating the occurrence of autophagy.While at the later stage,with the formation of new blood vessels in the wound,the condition of ischemia and hypoxia will improve,as a result of which ULK1 could not be as strongly activated as before,and thus the autophagy function of cells will reduce.In contrast,the expression level of ULK1 protein in wound tissues of the model group gradually increased as the treatment progressed,which probably attributed to the delayed wound healing and the accumulated stimulation[16-18].(3)On day 1 and 11 of treatment,the expression levels of ULK1 protein and ULK1 mRNA in wound tissues of MEBO group and model group were significantly lower than that in the control group,from which it was speculated that the autophagy function of the wound tissues in diabetic rats was inhibited.The mechanism might be that the down-regulation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase(p38 MAPK)-with the function of regulating gene expression under the high glucose condition,prevented the transcription of autophagy-associated protein genes,thus inhibiting autophagy[19-20].On day 11 of treatment,the expression levels of ULK1 protein and ULK1 mRNA in wound tissues of MEBO group were significantly higher than that in the model group,from which it is presumably held that MEBO can enhance the autophagy function of wound tissues in diabetic rats.On day 18 of treatment,no significant difference was observed in the expression levels of ULK1 protein and ULK1 mRNA between the control group and the MEBO group,and the levels were significantly lower than that in the model group.The reason may be that when the wounds in the control group were completely healed,the autophagy function of cells returned to normal level,when the wounds in the MEBO group were basically healed,the activation of ULK1 was lessened,in addition to the inhibition of autophagy induced by diabetes itself,resulting in the equivalent expression level of ULK1 between the control group and MEBO group.However,in the model group,since the wounds did not heal well,the activation of ULK1 still went on.In summary,MEBT/MEBO can effectively promote the wound healing of diabetic rats,of which one possible mechanism of action might be that it can induce the high expression of ULK1 and enhance autophagy function,but it still needs further confirmation by observing multiple autophagy-related proteins and adopting different study methods.
(收稿日期:2019-07-13)
