Characteristics of Changes in Energy Consumption of Rural Residential Buildings from the Perspective of Province and Recommendations
2019-12-17
College of City Construction, Jiangxi Normal University, Nanchang 330022, China
Abstract In the context of the new period, the living standards and comfort demands of rural residents are increasing, which promotes the continuous growth of the total energy consumption of rural residential buildings. In this study, it estimated the total energy consumption of rural residential buildings in 30 provinces (or cities) in China from 2004 to 2016. Through the division of climate regions of the residential buildings, this paper analyzed the characteristics of changes in the energy structure of residential buildings and the trend of energy consumption from the perspective of the province. Then based on the people’s livelihood and from the perspective of development, it came up with some pertinent strategies and recommendations for energy saving and emission reduction in rural residential buildings.
Key words Rural residential buildings, Energy structure, Energy consumption of buildings, Dynamic changes
1 Introduction
At 2018 G20 Buenos Aires summit, China reaffirmed its commitment to the climate goal in theAccorddeParis(ParisAgreement), and energy conservation and emission reduction in the construction industry is an important part of achieving this commitment. According to some related reports, compared with the reference scenario, the 2050 remodeling energy scenario has a reduction potential of 74% in the construction industry, which is 1.5 times the industrial emission reduction potential, and the largest among the three major energy consumption sectors, contributing about 50% to the energy savings in the peak carbon emissions[1]. At the present stage, the energy consumption of urban residential buildings in China has received close attention and effectively controlled, while that of the rural residential buildings has grown rapidly with the improvement of rural economic level and lacks sufficient attention and effective solutions. According to the data ofChinaStatisticalYearbook, by 2016, the total number of rural population and the total construction area of new residential buildings in China was stable with slight decline in the past five years, but the total energy consumption and per capita energy consumption indicators showed an increasing trend, and the electricity consumption soared from 750.8 billion kW·h in 2013 to 923.8 billion kW·h in 2016[2]. In the past, the low energy consumption of rural residential buildings was at the expense of comfort. However, the present demands of rural residents’ living comfort have been increasing with the improvement of living standards. In 2000-2016, compared with the overall stability of unit area energy consumption and carbon emissions of urban residential buildings, the unit area energy consumption and carbon emissions of rural residential buildings showed an increasing trend, especially the rapid increase in electricity consumption per unit area[3]. This not only indicates that energy consumption of rural residential buildings has a large room for improvement, and it is also a new growth point for future social building energy consumption, which also means that it is particularly important to control the energy consumption of rural residential buildings.
2 Division of climate regions of buildings in China
Due to the regional climate, there are differences in the demand and mode of heating and cooling of rural residents in China. Such differences lead to large differences in energy consumption of residential buildings, especially the maintenance type energy consumption is significantly different. Besides, at the present stage, the energy conservation design and renovation work of buildings in China is also mainly concentrated on the northern heating areas, energy conservation in regions with hot summer and cold winter and other regions is relatively slow. In view of such situation, based on the climate zoning standards for buildings in China and the scope of the administrative areas under its jurisdiction, we divided 30 provinces (or cities) into four regions (as listed in Table 1), so as to conduct a detailed analysis of the energy consumption of rural residential buildings in China under climate differences, so as to come up with pertinent and effective countermeasures and recommendations.
3 Dynamic change characteristics of energy consumption of rural residential buildings from the perspective of province
3.1 Change characteristics of energy structure of rural residential buildingsThe energy consumption of rural residential buildings is mainly reflected in the direct energy consumption of users of residential buildings. The energy structure of rural residents has undergone tremendous changes with the development of social economy. According to the statistical data of the terminal energy consumption generated by the residents’ living consumption in theChinaEnergyStatisticalYearbook, combined with the characteristics of people’s use of the residential buildings, taking the energy consumption of coal, kerosene, natural gas, gas, liquefied petroleum gas, heat, other kinds of energy, and electricity as basis, we assessed the total energy consumption of rural residential buildings.
Table 1 Division of regions and descriptions
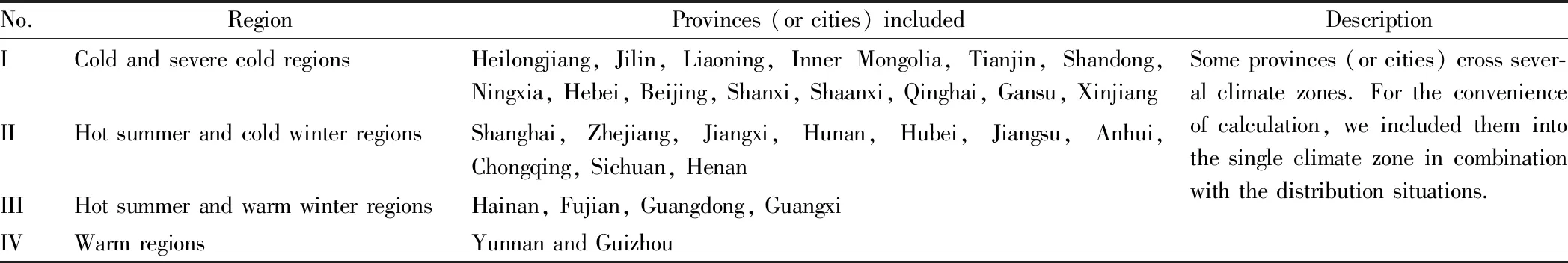
No.RegionProvinces(orcities)includedDescriptionIColdandseverecoldregionsHeilongjiang,Jilin,Liaoning,InnerMongolia,Tianjin,Shandong,Ningxia,Hebei,Beijing,Shanxi,Shaanxi,Qinghai,Gansu,XinjiangIIHotsummerandcoldwinterregionsShanghai,Zhejiang,Jiangxi,Hunan,Hubei,Jiangsu,Anhui,Chongqing,Sichuan,HenanIIIHotsummerandwarmwinterregionsHainan,Fujian,Guangdong,GuangxiIVWarmregionsYunnanandGuizhouSomeprovinces(orcities)crosssever-alclimatezones.Fortheconvenienceofcalculation,weincludedthemintothesingleclimatezoneincombinationwiththedistributionsituations.
According to the data of various energy consumption in the rural residential buildings in 2004-2016 and the trend of coal and electricity consumption in various climate regions (shown in Fig.1 and Fig.2), the rural energy structure takes on the following characteristics. (i) Coal is still the main source of energy consumption in rural residential buildings. Its changes have shown periodic characteristics in the past 13 years, including a sharp increase in 2004-2005, a sharp decline in 2006-2008, and a gradual recovery in 2009-2012, then a short time decline in 2013-2014, and later it began to grow again. The main reason is that the trend of change in each region was consistent in 2004-2007, while the trend in Region I in 2008-2016 was completely opposite to that in Region II. (ii) Electricity consumption is showing a rising trend. The national average annual growth rate of electricity was as high as 11.5%, which is the fastest growth of all energy consumption, not only becomes the second largest source of energy consumption in rural areas, but also is the key reason for the energy consumption growth. From a regional perspective, power consumption in the regions I to regions IV was increasing year by year, with growth rate of 10.1%, 12.4%, 11.1%, and 16.8%, respectively. The region IV obtained the fastest growth rate, but compared with other regions, the consumption is too small. In contrast, region II is not only one of the main sources of energy consumption of rural residential buildings in China, but its power consumption is also the highest in the four regions, and its growth rate is only second to that of region IV. Therefore, at the present stage, the energy consumption of rural residential buildings in region II should receive close attention.

Fig.1 Curves for changes of coal consumption of climate regions in 2004-2016
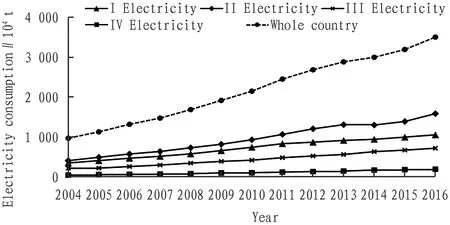
Fig.2 Curves for changes of electricity consumption of climate regions in 2004-2016
3.2 Change trend of the total energy consumption of rural residential buildingsFrom the total energy consumption indicator, from 2004 to 2016, the total energy consumption of rural residential buildings increased year by year, from 67 490 500 t of standard coal in 2004 to 1 172 215 t of standard coal in 2016 (as listed in Table 2), and the average annual growth rate was up to 4.9%. Regions I, II, and III also showed a rising trend, and the average annual growth rate was 4.4%, 5.9%, and 9.5%, respectively. By contrast, region IV showed the fluctuation trend of first decline then rising, the average annual growth rate was only 1%, mainly because the coal consumption fell sharply in 2008 and then gradually recovered, accompanied by rapid growth in energy consumption such as electricity. From the perspective of regional power consumption, in 2016, the proportion of region I was 42.3%, that of region II was 38.1%, that of region III was 11.3%, and that of region IV was 8.3%. Regions I and II were the main sources of energy consumption for rural residential buildings, and the total energy consumption in two region was also getting closer, and the growth rate of region II was faster. Therefore, the energy consumption of rural residential buildings would continue to grow for a certain period of time, and the growth of energy consumption of rural residential buildings in the hot summer and cold winter regions will have a huge hindrance to the future energy conservation and emission reduction of rural residential buildings.
Table 2 Total energy consumption of rural residential buildings in 2004-2016(unit: 104t of standard coal)

YearWholecountryRegionIRegionIIRegionIIIRegionIV20046756.183005.622314.46472.17963.9420057636.313200.382812.29623.76999.8720067694.593186.012928.61639.03940.9420077881.873312.162991.67666.71911.3220088045.713293.413377.23759.17615.9020098650.683630.593564.40801.89653.8020108842.433751.133567.04846.41677.8520119574.953859.103944.311030.79740.76201210115.633981.964177.491070.97885.22201310070.564445.163798.991014.52811.90201410414.004427.353988.921111.53886.21201511152.684720.654289.461247.04895.53201611841.915012.984509.441340.06979.43
Note: the total energy consumption in the table is the standard value, and the coefficient for converting to standard coal is selected fromChinaEnergyStatisticalYearbook.
4 Countermeasures and recommendations for energy conservation and emission reduction of rural residential buildings
Energy conservation renovation of rural residential buildings can not only improve the thermal condition of houses, improve the thermal efficiency of building energy systems, save energy, but also regulate the air temperature and humidity of houses, and improve the living environment of rural residents[4]. In the context of new urbanization, energy conservation renovation of rural residential buildings is dominated by the natural environment, combined with local climatic conditions and climate division design energy conservation regulations, comprehensive considerations should be taken in economic conditions, resource conservation,etc., to select more pertinent and feasible solutions[5].
4.1 Enhancing the energy conservation awareness and changing energy use behaviorEnergy conservation awareness has a direct impact on energy conservation behavior, and users’ improvement in knowledge, initiative, and values play a key role in achieving carbon emission reduction in buildings[6]. It is recommended to rely on the strength of the local government and third-party energy conservation and environmental protection organizations to actively promote energy conservation ideas, basic knowledge and energy conservation renovation policies in rural areas through the use of new media and Internet to enhance residents’ awareness of energy conservation, values and their perception of energy conservation issues. In addition, it is recommended to demonstrate to local residents the difference in energy consumption between the energy-efficient buildings and non-energy-saving buildings under the same conditions and the corresponding monetary value. Through the quantitative material analysis, it is able to reflect the differences and transform the concept of materialism of the residents, thus affecting their consumption behavior and guide residents to save energy. Furthermore, it is recommended to explore the potential of energy conservation from the user’s point of view, and achieve a certain energy conservation effect through spontaneous energy conservation in consciousness behavior, which is not only favorable for improving the actual effect that can be achieved by the established energy conservation technology, but also favorable for reducing the economic cost. Under the development of new urbanization and urban-rural integration, it is recommended to take advantage of radiation of small towns, to coordinate the promotion of energy conservation renovation of rural residential buildings, and dispatch relevant personnel to carry out innovative energy conservation publicity work in rural areas to raise awareness of energy conservation among rural residents. In this way, it can lay a preliminary foundation for the rural residential energy conservation renovation work, and can effectively alleviate the pressure on the energy conservation and emission reduction work of the rural economic level.
4.2 Optimizing the energy structure and raising the utilization efficiencyThe energy consumption of rural residential buildings is mainly generated from the direct living energy consumption of rural residents. At the present stage, coal still maintains the largest proportion of rural residents’ energy consumption, while the consumption level of energy such as electricity is also increasing year by year. Although the proportion of coal consumption is declining, the use of clean energy is still very less. Therefore, it is recommended to actively promote the application and expansion of new energy-related technologies in rural areas by combining the geographical advantages of each region and following the principle of suitability. Taking the improvement of economic and technological level as the driving force, through the continuous adjustment of the energy structure of rural residential buildings, it is expected to achieve the goal of optimizing the energy consumption of rural residential buildings through optimizing the energy structure. On the basis of raising the awareness of rural residents’ ecological consumption, it is recommended to comprehensively take advantage of the renewable energy including wind, water, solar energy and geothermal energy, and properly treat domestic pollutants with certain physical methods to reduce energy consumption in rural residential buildings and promote energy conservation and emission reduction of rural residential buildings, and accordingly improve the living environment.
4.3 Attaching importance to energy conservation renovation and stimulating energy conservation powerUnder the background of the prevailing non-energy-saving buildings in rural areas and increasing energy consumption and carbon emissions, the energy conservation of rural residential buildings should implement the strategy of "attaching importance to the existing building renovation and taking into account new construction", select suitable methods and adopt special energy-saving design and the energy-saving technology to transform the enclosure structure of new and old buildings, thereby improving the energy conservation effect and solving the outstanding problems of excessively high consumption in winter or summer. The energy conservation renovation of existing residential buildings has strong public welfare nature and the investment is huge, while the privatization of property rights of rural residential buildings also determine that the main body of energy conservation renovation in the future should be farmers.
Farmers will care more about the economic costs at the same time of considering energy-saving measures. On the basis of paying attention to the economic and high efficiency of energy conservation transformation, the government’s policy and economic guidance have stimulated the enthusiasm of villagers for energy conservation renovation, which is the only way for energy conservation of rural residential buildings to constantly advance. In summary, the design and transformation of energy conservation of rural residential buildings should follow the guiding principle of "government guidance, social participation, market operation", attach importance to the guidance of village and town governments, proceed from the economic and efficiency, build ownership as the main body, broaden the channels for capital investment, and highlight key points, consider both old and new, research and development, apply and transform new technologies, and establish livable transformation program that can realize sustainable development and promote urban construction.
5 Conclusions
Under the background of the new period, the income of rural residents needs to be further increased and the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy will certainly promote the income level of rural residents. At the same time, rural residents have an increasing demand for living comfort, which further promotes the gradual increase of the power consumption of rural residential buildings. At present, China has entered the stage of control of the total carbon emissions, so the energy consumption in the construction industry will be a key field for realizing this objective. Therefore, in order to promote green rural revitalization and accelerate the realization of carbon emission reduction, it is imperative to implement energy conservation of rural residential buildings.
杂志排行
Asian Agricultural Research的其它文章
- Application Effects of Stabilized Fertilizer with Reduced Amount and Frequency on Rice
- Contents of Heavy Metals in Typical Aquatic Products from a Market in Binzhou
- Analysis of the Land Use Structure in Alpine Valley Area of Jinsha River: Taking Xueshan Township, Luquan County, Yunnan Province as an Example
- Assessment on Ecological Capital of Small Towns: A Case Study of Baita Town, Weifang
- Yield Gap Analysis of Wheat in Rice-wheat Rotation Regions of Anhui Province, China
- Effects of Different Storage Temperatures on Shelf Life and Quality of Strawberry Fruit after Hot Water Treatment
