以健康理念出发:戴尔医学区景观设计
2019-12-03Sasaki事务所
Sasaki事务所
戴尔医学院及附属教学医院戴尔塞顿医疗中心地处奧斯汀中部德州大学奥斯汀分校校园。占地逾6.5 hm2的医学区是市内最大的医疗卫生开发区的一部分,不仅为医学院全院师生及访客提供服务,更在校园景观中创造出一片新风貌,立下全新的生态绩效标准。
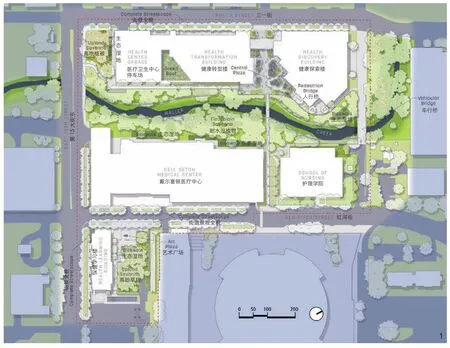
1 医学区第一期工程实施着重在现有的路网和沃勒溪走廊The key organizing elements of the phase 1 medical district plan are the existing street grid and the Waller Creek corridor
戴尔医学区的景观设计过程是Sasaki及顾问团队过去2年规划工作的延续,项目团队先后在2012—2014年为大学制定了校园总体规划、医学区总体规划以及德州大学奥斯汀分校景观总体规划与设计导则。与之前的总体规划项目一样,戴尔医学区的景观设计同样以多元包容、覆盖广泛的工作进程为方针。这样一来,景观开发和维护人员以及项目团队之间早已确立的合作关系得以延续,为项目带来最大裨益。
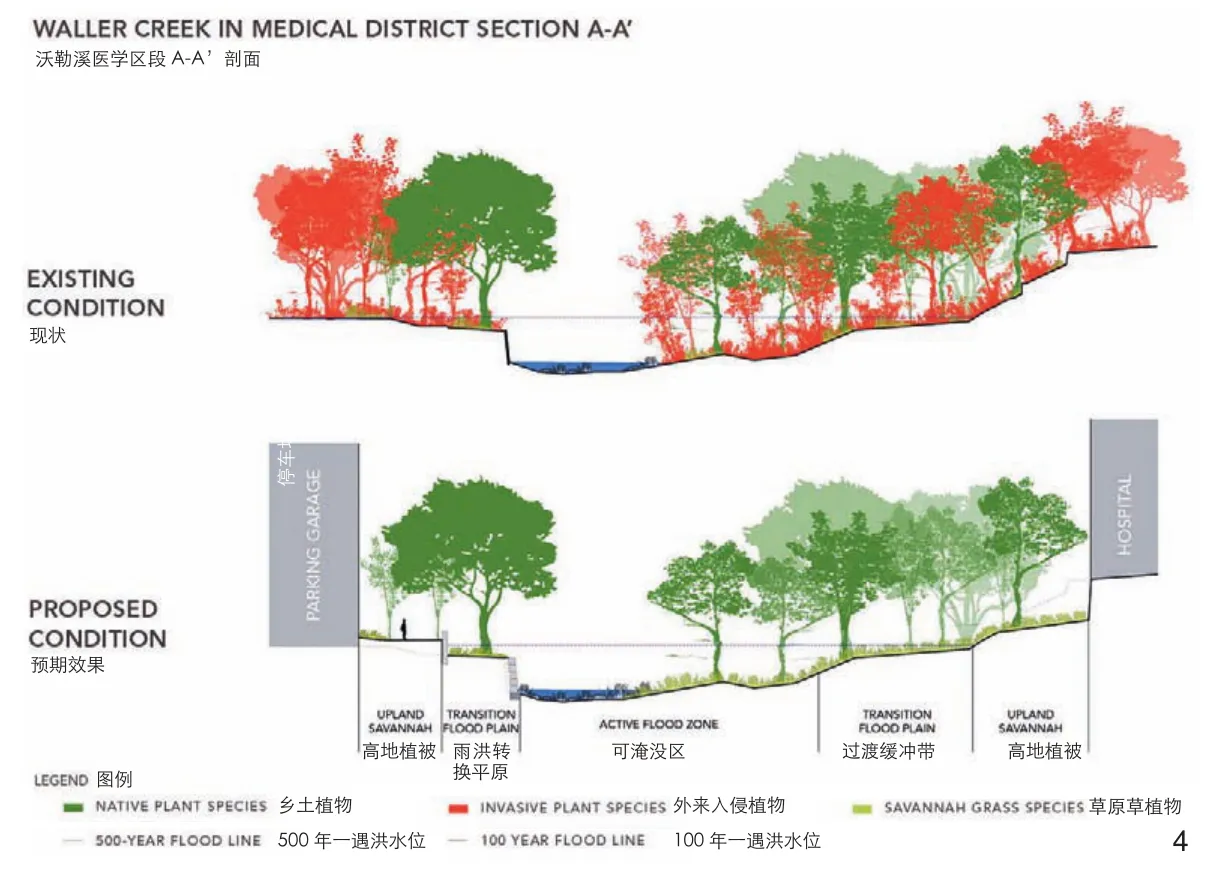
2012—2014年期间制定的总体规划方案皆以德州大学独有的历史文脉出发,在深度和广度上对校园未来的拓展和优化进程奠定框架。以医疗卫生为焦点的校区成功落实,充分反映了总体规划的全面愿景—即打造一个融会贯通、满足医疗卫生用途的区域,复兴沃勒溪(Waller Creek)走廊,以及加强区域与奥斯汀市的连接。曾被荒废的沃勒溪重新被视为校区的重要资产和开放空间,发挥关键的连接作用。恢复沃勒溪的医学区段是将其纳入广域校园景观的首要一步,这对景观的视觉美感和实际功能都是必不可少的举措。
在历时一年半的沃勒溪复兴过程中,多种措施得到实施,其中包括在附近的自然保护区种植一个参照植物群落,移除外来入侵植物,稳固河岸,以及恢复原生河岸和高地植被的多样性。团队实际开展的工作涵盖建造雨水花园,并在重要区域进行土壤修复。这些工作一旦确立到位,校园的大多数景观区域将无须依赖人工灌溉。
街道景观和广场区的设计除了鼓励人际互动,更将校园与周边城市环境联系起来。医学区的景观规划旨在强化生态系统服务,成为一个具有抗灾力且易于维护的景观典范。雨水花园、透水铺装、雨水回收设备和绿色屋顶等多种融合雨水管理功能的基地设施,更让访客有机会认识和探索本地气候和水文环境。
为在校园社区提倡身心健康的价值,项目其中一项措施是接收13株从美术学院主校区移栽过来的老橡树。对历史悠久的主校区而言,橡树极具标志意义。橡树优美形态及其带来的许多生态价值使这种树木备受喜爱,广阔的树荫更在奧斯汀的气候环境中发挥作用。移栽后的橡树把美术校区浓厚的历史氛围延伸到簇新的医疗卫生校区,高耸林立的橡树群体,为现代化的建筑增添丝丝绿意和平衡观感。
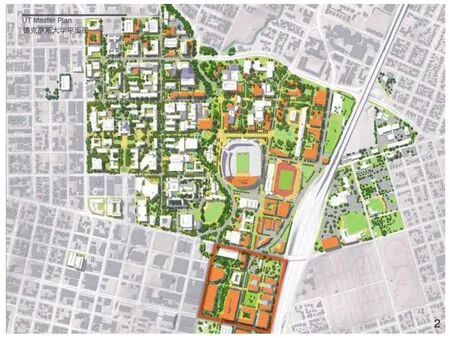
2 戴尔医学院位于占地面积178 hm2(440英亩)的德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校的南端,是学校重点发展的区域之一。当前,德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校的本科生人数为40 500人The Dell Medical Campus is located on the south edge of the 178 hm2 (440 acres) University of Texas at Austin campus.The medical campus is one of the major growth areas of the campus.Today, the undergraduate enrollment at UT Austin is 40,500
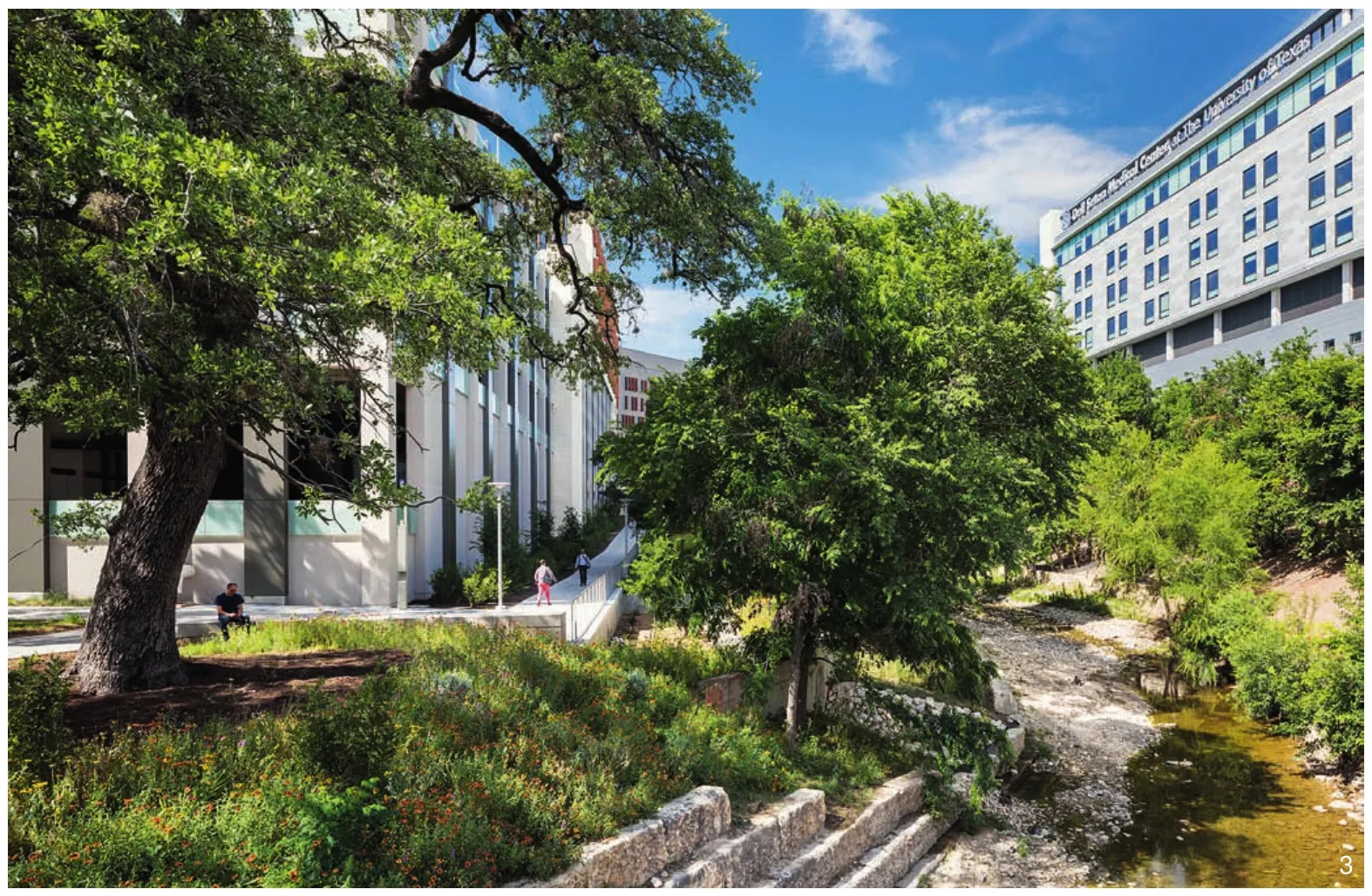

3 白天的德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校医学院UT Austin Dell Medical Campus during the day
4 建设前的沃勒溪走廊是一个被人遗忘并且未被开发的自然资产。走廊上曾经遍布的入侵植物现已被移除,为本土滨水植物群落提供了发展空间Prior to development, the Waller Creek corridor was a forgotten and unexploited natural asset.The corridor was overgrown with invasive vegetation which was removed to encourage a native riparian savanna plant community

5 夜幕中的德克萨斯大学奥斯汀分校医学院UT Austin Dell Medical Campus at night

6 步行走廊两侧种植了爱德华玆高原以及黑土草原生物区的本土植物Pedestrian corridors are flanked with savanna vegetation native to the Edward’s Plateau and Blackland Prairie bioregions
获得SITES金级认证的戴尔医学区景观设计方案,将德州大学奥斯汀分校的可持续场地开发标准推上新层次。凭借新设计的景观元素,基地尽享以下各种实际好处:减少用水量、改善雨水质量、减少土壤侵蚀、提升栖息地价值以及提高景观韧性。全新打造的开放空间使校园变得惬意舒适,以人为本,与周边社区和环境紧密相连,充分反映项目的设计愿景。人类与环境作为同一个功能体系在新校园相互协作,一起构建更健康、更美满的未来。
(编辑/遆羽静)
项目名称:戴尔医学区景观设计
项目位置:美国德州奧斯汀市
业主名称:德克萨斯州大学奥斯汀分校
现况:2017年秋季完成
规模:逾6.5 hm2(16.2英亩)
服务范围:景观建筑
图片来源:图1~3、6~7、9~13来自Sasaki事务所;图4~5来自Albert Vecerka;图8来自戴尔医学院
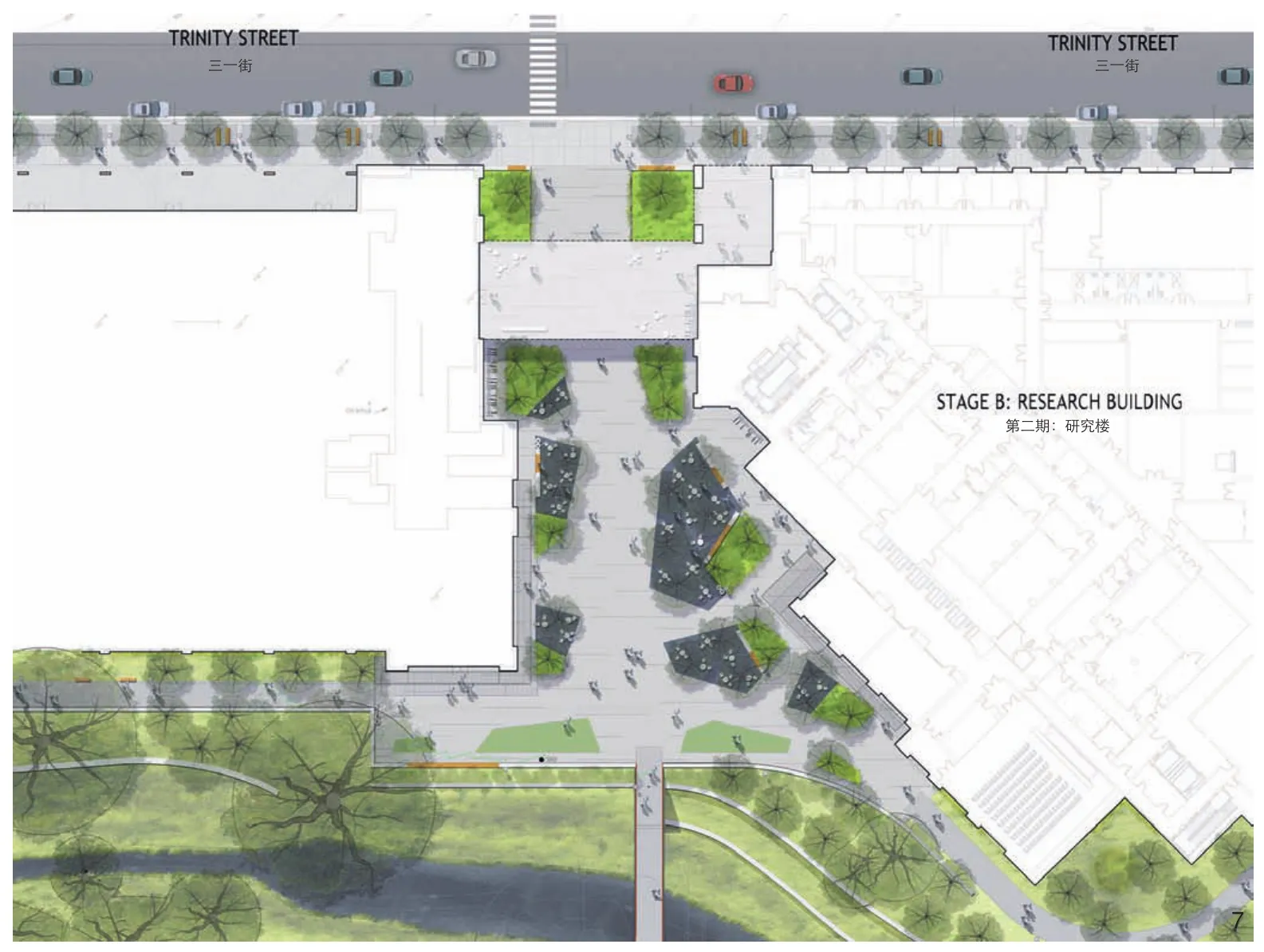
7 两个广场都被用于社交集会,其中一个广场位于临床楼与研究楼之间,连接了三一街与红河街Two plaza spaces serve as social gathering spaces.One plaza is located between the clinical and research facilities and connects Trinity street to Red River Street
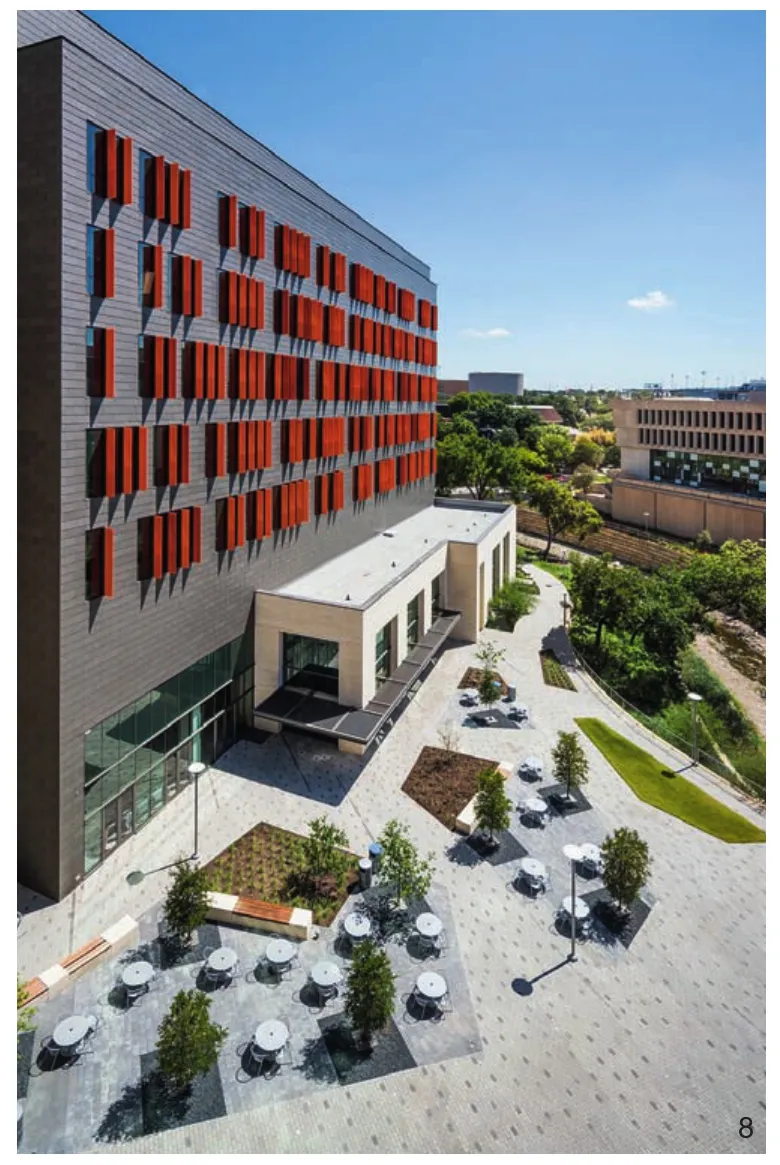

8 这些树栽植于广场下的土壤中,广阔的树冠为第17街广场的休息空间提供了荫蔽。该广场的铺装使用了面板支撑机构Sitting areas at the 17th Street Plaza will be shaded by native canopy trees.The trees are planted in soil below the palza level.The plaza paving is supported by a deck support system
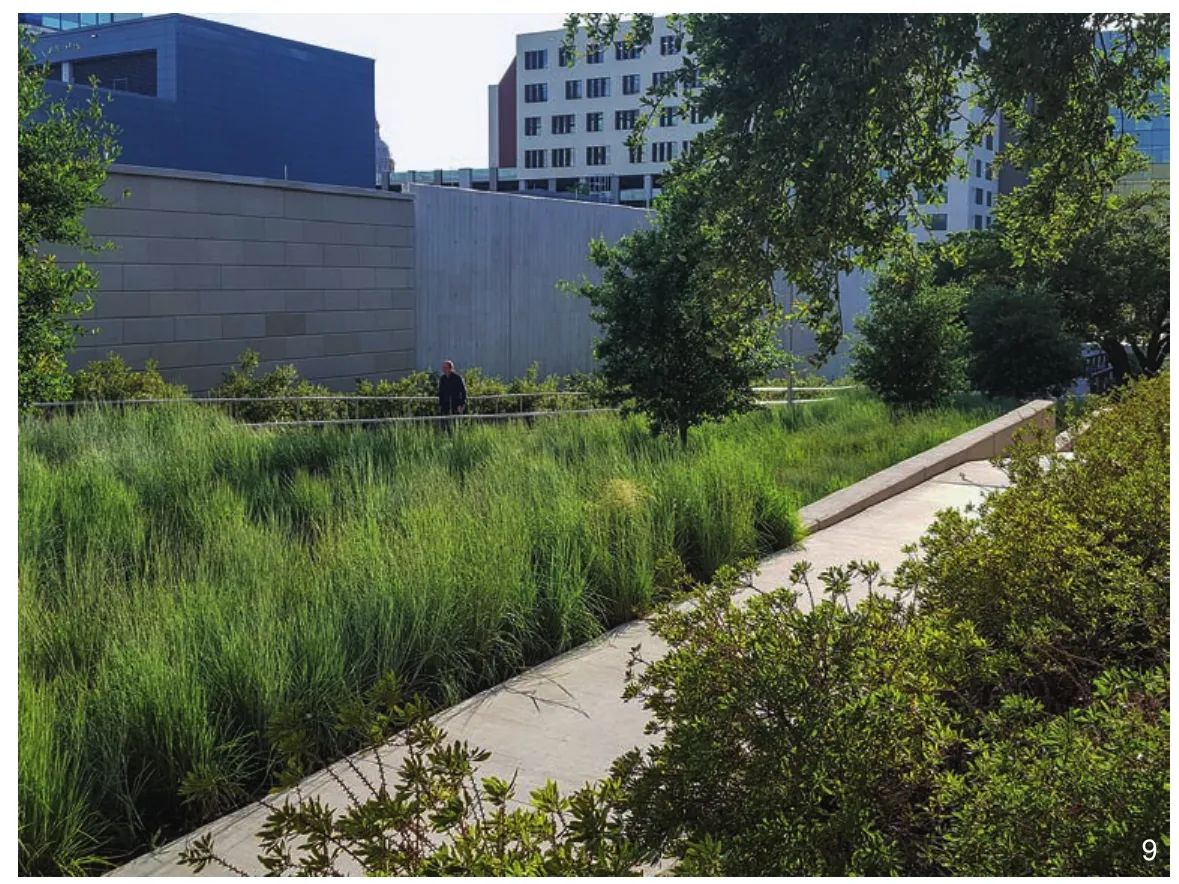

9 人行走廊两侧种植了爱德华兹高原和黑土草原生物区的稀树草原乡土植被。这张照片呈现出了种植着北美小须芒草的第17街步行走廊Pedestrian corridors are flanked with savanna vegetation native to the Edward’s Plateau and Blackland Prairie bioregions.This view shows the 17th Street pedestrian corridor planted with Little Bluestem (Schizacharium scoparium)

10 所有来自该基地的雨水都经由生态湿地净化后再进入溪流系统All of the storm water from the development is treated in vegetated bioswales (foreground) that cleanse storm water before it enters the creek system
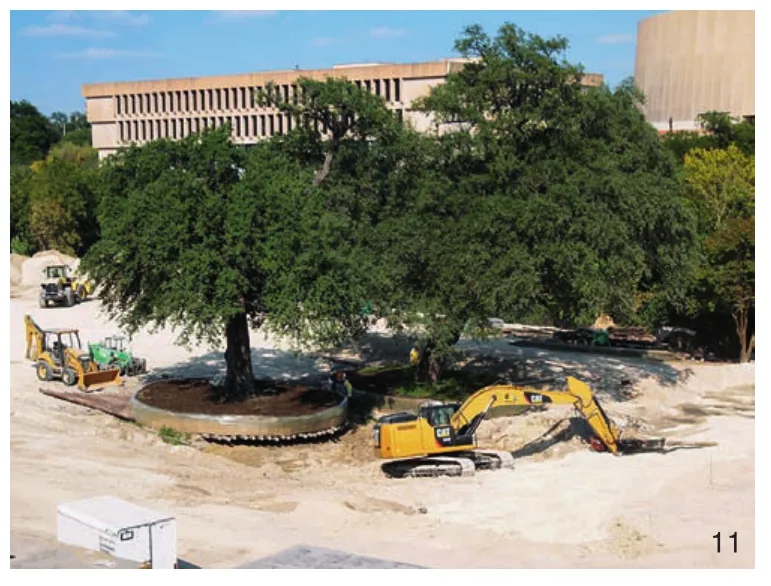

11 建设前,13棵老橡树被移植。 这些树的胸径在45.72~60.96 cm (18~24英寸)之间Prior to construction, 13 mature Live Oak trees were identified for transplanting.The trees averaged 45.72~60.96 cm(18~24 inches) in trunk diameter
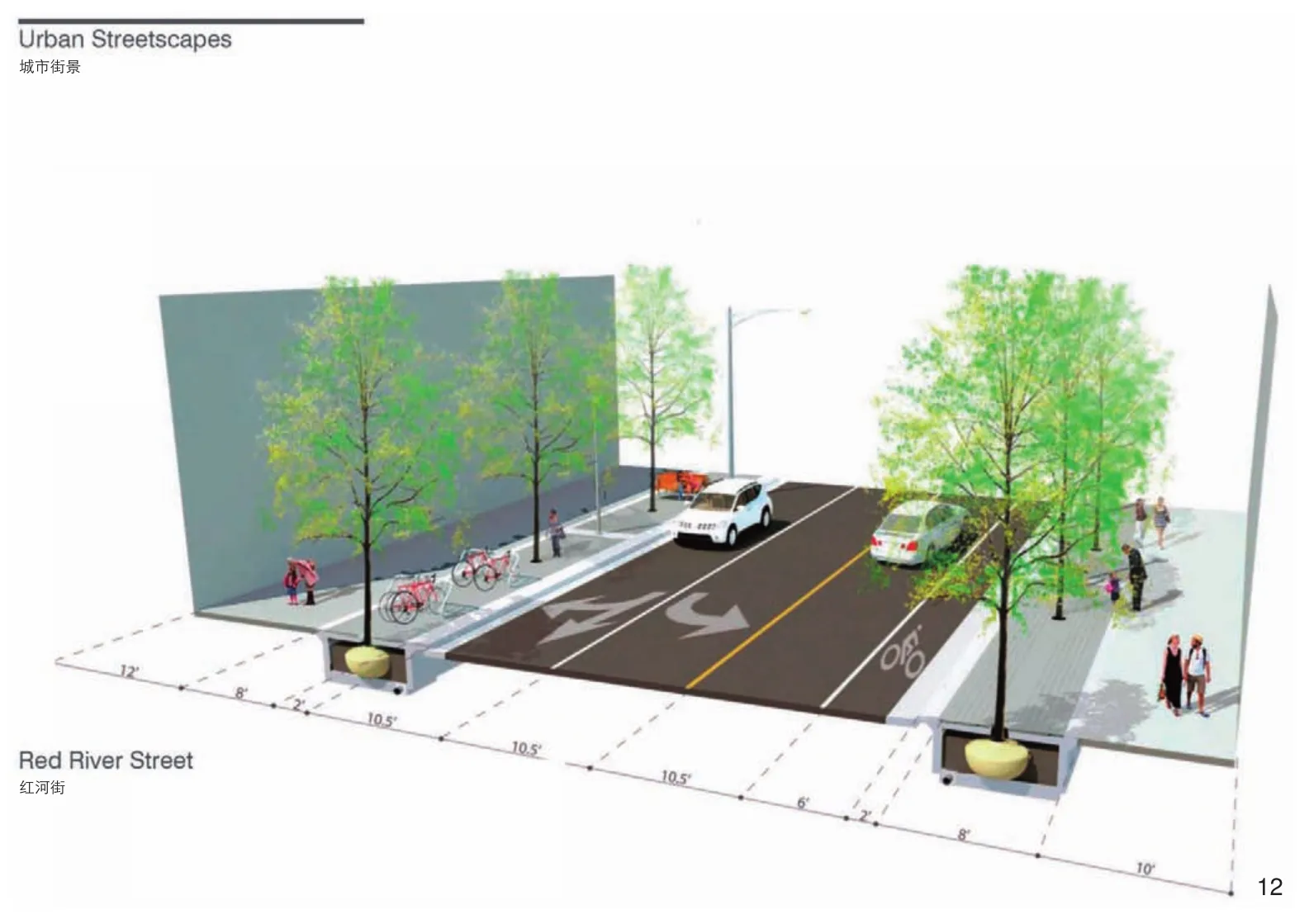
12 在广场和道路铺装区的树都种植于被木板路面系统保护着的土壤之中Plaza and street trees in paved areas are planted in soils protected by a plank pavement system
The Dell Medical School and its teaching hospital, Dell Seton Medical Center, are part of a vibrant health district that is one of Austin’s largest development projects.The 6.5 hm2(16.2 acres)development is located in central Austin on the University of Texas campus—serving the faculty,staff, students and visitors of the Dell Medical School and setting a new image and ecological performance standard for the UT Austin landscape.
The design process for the Dell Medical District landscape was a seamless extension of two previous years of planning by Sasaki and the consultant team.The team had already developed the 2012 Campus Master Plan, the 2013 Medical District Master Plan, and the 2014 UT Austin Campus Landscape Master Plan and Design Guidelines.The development of the Dell Medical District landscape plan employed the same broad-based,inclusive process that characterized the preceding master plans, furthering established collaborations with those responsible for the development and maintenance of the campus landscape.
The 2012—2014 University master plans established a framework for campus growth and improvement unique in the campus’s history in scope and depth.The successful implementation of the Health Campus realized the master plan’s comprehensive vision for a coherent district of health-related uses, the reclamation of the Waller Creek corridor, and the strengthening of connections to the City of Austin.
Once neglected, Waller Creek is now celebrated as a campus asset and important connective open space.Reclaiming the medical district segment of the creek is a first step towards reintegration of this important visual and functional landscape feature into the larger campus.
Restoration of Waller Creek was an 18-month long process that included establishing a reference plant community at a nearby Nature Conservancy preserve, the removal of invasive species, stream bank stabilization and the re-vegetation of diverse native riparian and upland communities.The work involved the creation of rain gardens and the remediation of soils for significant areas.Once established, most areas of the campus landscape will not require irrigation.
Streetscapes and plaza areas encourage social engagement and connect the campus to its surrounding urban environment.The Medical District landscape plan is designed to enhance ecosystem services and to be a model for a resilient and affordable-to-maintain landscape.Stormwater management features were designed as site amenities to connect visitors to the local climate and hydrology—through a combination of rain gardens, pervious pavers, rainwater harvesting, and a green roof.
The University’s commitment to the health and well-being of the campus community drove the project to undertake the relocation of 13 mature Live Oak trees.Live Oaks are emblematic features of the historic Beaux Arts main campus, beloved for their beauty and the many ecosystem benefits they provide, including welcome shade in the Austin climate.The transplanted Oaks extend the best aspects of the historic campus to the new Health Campus district.The majestic trees confer instant grace on developed areas, offsetting the presence of large heath care facilities.
The Dell Medical District landscape sets a new standard for sustainable site development on the UT Austin campus, achieving SITES Gold Certification.The reduction of water consumption, improved stormwater quality,reduced soil erosion, increased habitat value, and enhanced landscape resilience are tangible benefits of the new landscape.The overall design vision is expressed in the new open, inviting, and peoplecentered campus, connected to its environment and community.On the new campus, people and the environment work together as a functioning system, focused on improving health.
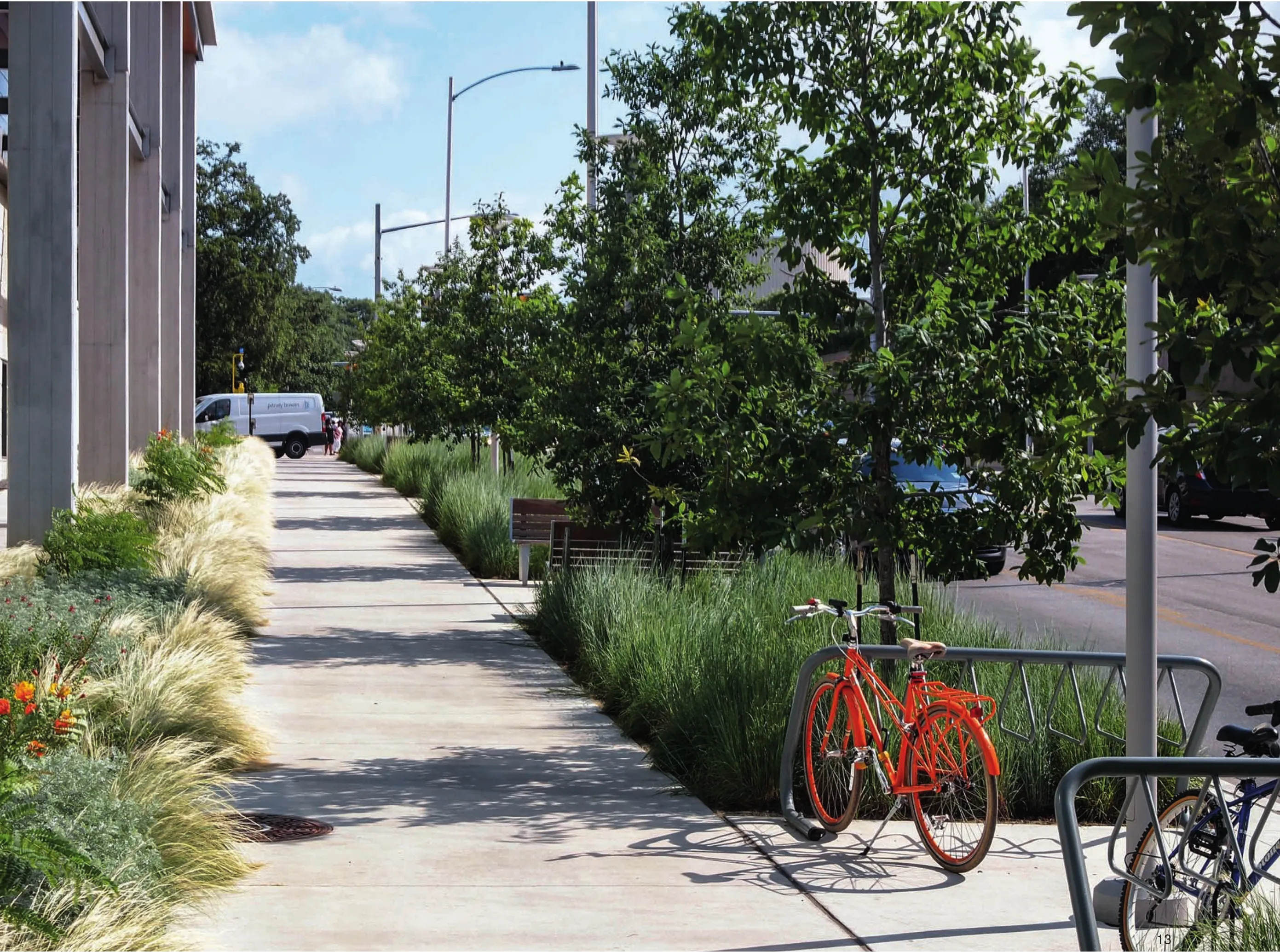

13 街道景观的塑造中使用了一些本土的橡树(Quercus polymorpha与 Quercus muhlenbergii)以及北美小须芒草(Schizacharium scoparium)Streetscapes are defined with plantings of native oak trees (Quercus polymorpha and Quercus muhlenbergii) and little bluestem prairie grass (Schizacharium scoparium)
